Agriculture and food management
Introduction
- Introduction
- Current Scenario
- Steps taken by the government in last few years:
- Allied sectors: Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries Catching Up In Recent Years
- Sahakar-Se-Samriddhi: From Cooperation to Prosperity
- Food Processing Sector- the Sunrise Sector
- Food security- Social & legal commitment to the People of the nation
- Conclusion
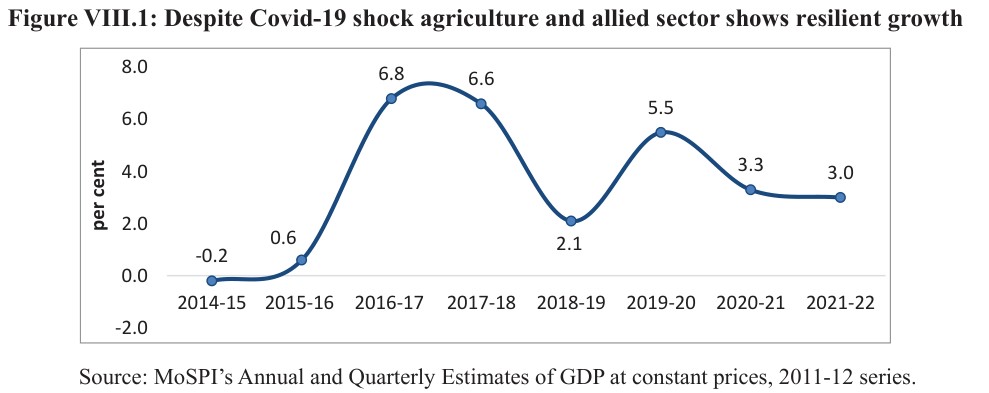
- With its firm forward linkages, agriculture and allied activities significantly contributed to the country’s overall growth and development by ensuring food security. But the performance has been buoyant over the past several years.
- To tackle the issue, the government intervened:
- to enhance credit availability,
- aggravate livestock and crop productivity,
- promote crop diversification,
- ensure certainty of returns to the farmers through price support,
- facilitate mechanisation and
- boost horticulture and organic farming through the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund.
Current Scenario
- The agriculture sector has thrived at an average annual growth rate of 6 %during the last six years.
- It grew by 0 %in 2021-22 compared to 3.3 %in 2020-21.
- The exports of agriculture and allied products grew by 18 % in 2022-21.
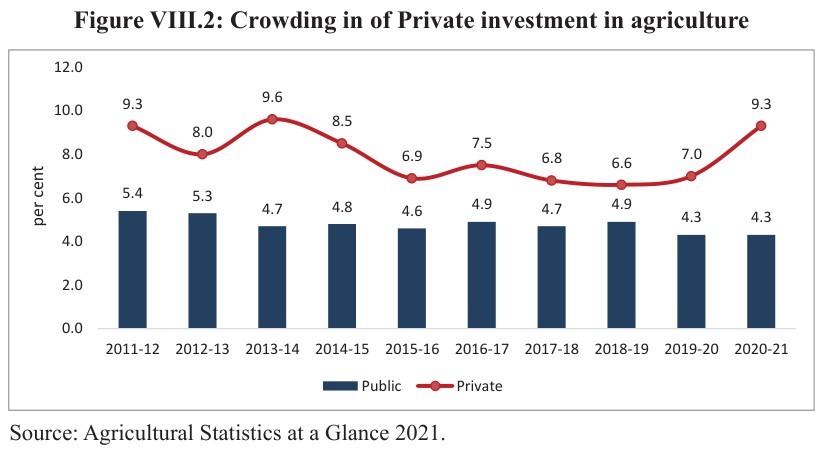
- This hour of buoyant performance could be ascribed to the measures taken by the GOI to promote farmer-producer organisations, improve productivity in agriculture and encourage crop diversification through the creation of the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund.
- Further, income support to farmers was given through the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN).
- While Indian agriculture has performed fair, the sector needs re-orientation in the backdrop of challenges like adverse impacts of climate change, sub-optimal farm mechanisation, fragmented landholdings, low productivity, disguised unemployment, rising input costs, etc.
Record Production of Foodgrains
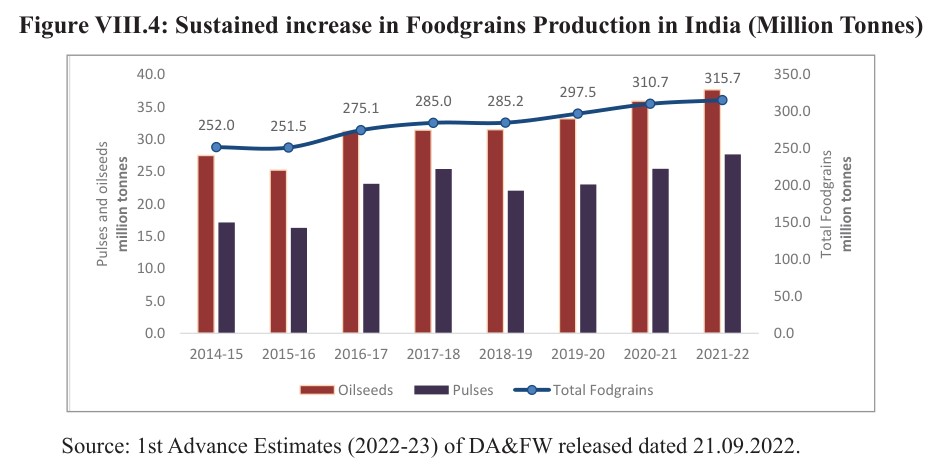
- As per Fourth Advance Estimate(2021-22), oil seeds and food grains production has been increasing year-on-year.
- Production of pulses has also been considerably upper than the average in the last 5 years.
- However, the variation in climate has been adversely impacting agriculture. For example, 2022 recorded an early heat wave during the wheat-harvesting which adversely affected its production. Furthermore, the year experienced a decline in the sown area for paddy cultivation in the Kharif season due to disrupted monsoon.
Steps taken by the government in last few years:
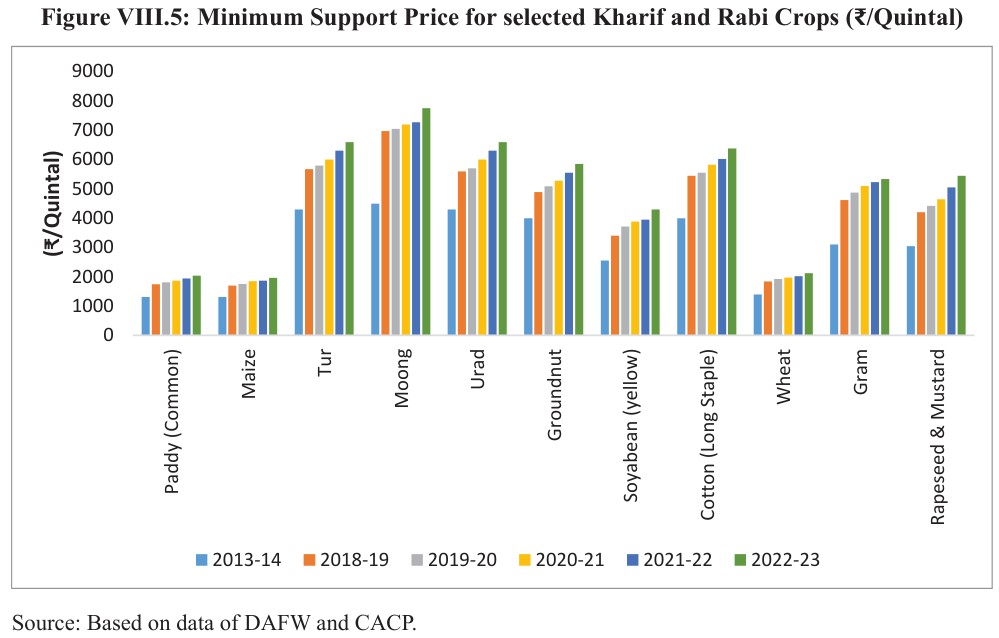
MSP to Ensure Returns Over the Cost of Production
- In the 2018-19 Union Budget, it was announced that farmers would be provided with an MSP of at least one and a half times the cost of production.
- Following it, the government had already increased the MSP for all 22 Rabi, Kharif and other commercial crops.
- Given nutritional requirements, changing dietary patterns, and achieving self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseed production, the government has fixed relatively higher MSPs for pulses and oilseeds.
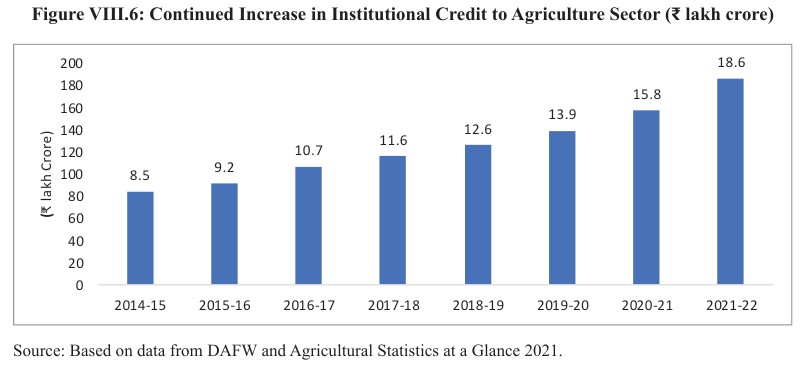
Enhanced Access to Agricultural Credit
- The government of India (GoI) wants to Ensure smooth credit availability at an inexpensive rate to farmers. Therefore, the Kisan Credit Card Scheme (KCC) for farmers was announced in 1998 to empower farmers to buy agricultural products and services on credit at the proper time.
- The GOI extended the KCC facility to fisheries and animal husbandry So now we can see a drastic increase in beneficiaries of KCC.
- To assure that the farmers pay a minimal interest rate to the banks, the GOI has introduced the Interest Subvention Scheme (ISS, also known as MISS) to provide short-term credit to farmers at subsidised interest rates.
Farm Mechanisation- Key to Improving Productivity
- Farm mechanisation helps increase productivity through the effective and efficient use of natural resources and other inputs, along with reducing the cost of cultivation and the glean.
- Farm mechanisation gets an immense boost Under the Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanisation (SMAM).
Chemical-Free India: Organic and Natural Farming
- India has around 44 lakh organic farmers (the highest in the world), and about 59 lakh hectares of area was brought under organic farming by 2021-22.
- Sikkim is the 1 st State in the world to become fully organic. Few other States, including Tripura and Uttarakhand, have set similar targets.
- The government has been promoting organic farming (since 2015)through 2 dedicated schemes, i.e., Mission Organic Value Chain Development for North Eastern Region (MOVCDNER) and Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY).
- In 2019-22 the Promotion of natural farming started with Bhartiya Prakratik Krishi Paddhati (BPKP, a sub-scheme of PKVY) to assist farmers in adopting traditional indigenous practices in all forms of ecological farming, including Zero-Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF).
Other Important Initiatives In agriculture
| International year of the Millets |
|
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) declared 2023 the International Year of Millets.
Significance of Millets: · Millets are Smart food (climate resilient ), it contains a high nutritional value and also aligns with several UN SDGs. · These are also important by their huge potential to create livelihood, increase farmers’ income and ensure food & nutritional security worldwide.
India and Millets: · India accounts for 80 %of Asia’s and 20 %of global millet production. · In India, millets are mainly a Kharif crop generally grown in rainfed conditions.
· In 2018 due to their immense nutritional value, the government notified Millets as Nutri-cereals. · Under the National Food Security Mission (NFSM), millets were also introduced to provide nutritional support. · India has more than 500 start-ups working in the millet value chains. The Indian Institute of Millets Research has incubated 250 start-ups under Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana – Remunerative Approaches for Agriculture and Allied Sectors Rejuvenation (RKVY-RAFTAAR). Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana – Remunerative Approaches for Agriculture and Allied Sectors Rejuvenation (RKVY-RAFTAAR).
|
Allied sectors: Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries Catching Up In Recent Years
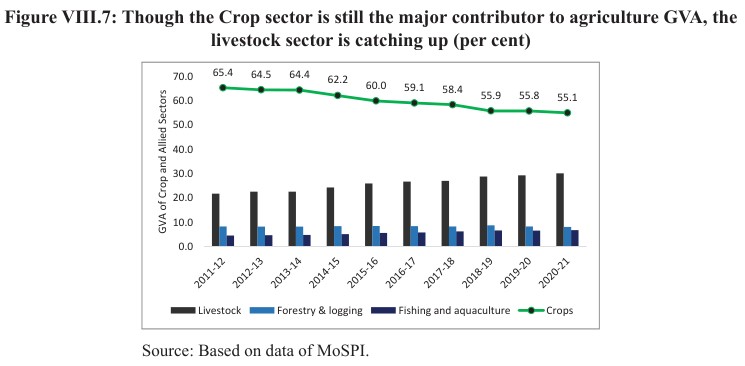
- The livestock sector progressed at a CAGR of 7.9 % during 2014-15 to 2020-21 (at constant prices), and its contribution to total agriculture GVA (at constant prices) has increased from 24.3 % in 2014-15 to 30.1 % in 2020-21.
- Accessing the importance of allied sectors, the Committee on Doubling Farmers’ Income considers fisheries, dairying, poultry, livestock and horticulture as high-growth engines and has recommended a focused policy for the allied sector.
- India ranks 1st in milk production in the world; it ranks 3rd in egg production and 8th in meat production in the world.
Important Initiatives In Allied Sectors

Sahakar-Se-Samriddhi: From Cooperation to Prosperity
- The cooperative societies provide livelihood opportunities and financial safety in rural India with a community-based approach.
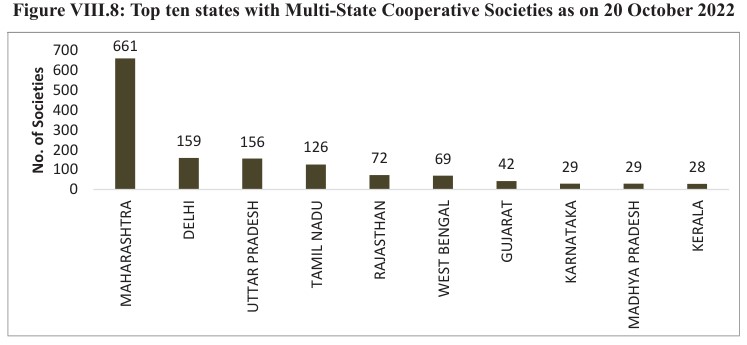
- Roughly 8.5 lakh registered cooperatives are presently available in the country.
- 98 % of villages are covered by Primary Agriculture Credit Societies (PACS).
- To realise the vision of “Sahakar-see-Samriddhi”, momentum was conferred to the growth of the cooperative sector. Currently, around 19 % of agriculture finance is done through cooperative societies.
- The Ministry of Cooperation was established in 2021 to focus more on the cooperative sector.
| New National Cooperation Policy |
|
Objective: To have a policy that unlocks the true potential of the Cooperation sector.
Stakeholders: A New National Cooperation Policy is being formulated involving the relevant stakeholders like experts of the cooperative sector, representatives from the union and various State level cooperative societies, Secretaries (Cooperation), Resident Commissioners from States/UTs, and Central Ministries/ Departments officers.
Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill, 2022: The government has also introduced the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill, 2022. The Bill was introduced to amend the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act 2002 to align with Part IXB of the Constitution and strengthen the country’s cooperative movement.
|
Food Processing Sector- the Sunrise Sector
- During the last 5 years, the food processing industry has been growing at an average annual growth rate of around3%.
- 2% of employees in the registered manufacturing sector are employed in the food processing sector, as per the latest Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) 2019-20.
- The value of agri-food exports(including processed foods) was about9 % of India’s total exports during 2021-22.
- The NITI Aayog Strategy for New India recognises the lack of adequate and efficient cold chain infrastructure as a critical supply-side bottleneck that leads to massive post-harvest losses.
- The Ministry of Food Processing Industries, through the component schemes of Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana (PMKSY), provide financial assistance for the inclusive growth and development of the food processing sector.
- The Ministry also launched the Prime Minister’s Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme to enhance the competitiveness of individual micro-enterprises in the unorganised segment and promote the formalisation of this sector by providing financial, technical and business support for upgradation/setting up of 2 lakh micro units in the country. The scheme adopts the One District One Product (ODOP) approach to reap the benefit of scale in procuring inputs, using shared services and marketing products.
- The Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Food Processing Industry (PLISFPI) enhanced the Sectors with high growth potential, like marine products, processed fruits & vegetables, and ‘Ready to Eat/ Ready to Cook’ products.
- To focus on transporting perishable food products, including horticulture, fishery, livestock and processed products, from the Hilly Areas, North-Eastern States and Tribal Areas, Krishi UDAN 2.0 version was launched in October 2021 as a six-month pilot project.
Krishi UDAN 2.0 |
|
· It is a convergence scheme of 8 ministries. · There is no specific budget allocation under the Krishi Udan scheme. Objective: · To increase the share of air carriage for the transportation of agri-produce, including horticulture, fishery, livestock and processed products. Components: · The Airports Authority of India provides a complete waiver of Landing, Parking, Terminal Navigational Landing Charges and Route Navigation Facility Charges for Indian freighters and P2C (Passenger-to-Cargo) aircraft. · The scheme covers around 25 airports in North Eastern, Hilly and Tribal regions and 28 airports in other areas.
|
Food security- Social & legal commitment to the People of the nation
- Food security is not only the ability to produce food but also the ability to access food.
- The GOI is currently driving the world’s most extensive food security programme( legislation-based), covering about 80 crores of India’s population under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013.
- To reduce the misery faced by the poor due to Covid-19, the government launched Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana.
- To further comfort the process of access to food, the government launched a technology-driven and citizen-centric scheme in 2019 called the One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC)
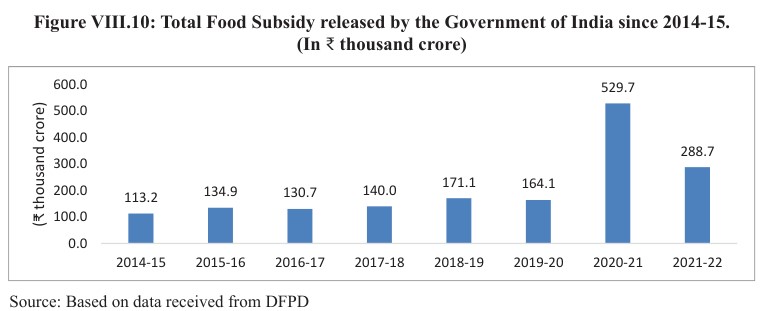
- Compared to the other years, the food subsidy bill was higher during 2020-21 and 2021-22.
Conclusion
The agriculture sector’s performance is crucial for growth and employment in the country. Investment in the industry must be incited by a timely, affordable, and inclusive approach to credit delivery. A well-developed food processing sector with exalted infrastructure like cold storage and better logistics is the need of the hour to reduce waste, improve value addition, improve value addition, ensure better farmers’ returns, promote employment, and increase export earnings.