
Indian Constitution Free UPSC Notes Download

1. What is a Constitution?
Constitution is a document or set of documents that lays down basic set of rules for the establishment of a state and its governance and is legally enforceable. A modern state is virtually impossible to be run without such basic sets of rules that defines the powers, responsibilities and limits of the ruling class. Any political system works in a constitutional framework .

2. Evolution of Indian Constitution
Indian constitution was adopted on 26th January 1950 after almost three years of hard work by the Constituent Assembly of India. However, the constituent assembly itself did not make it completely fresh. It took the best of the principles and ideas of the world and the already existing Indian law to form the Indian Constitution.

3. The Crown Rule
The Crown Rule refers to the British Raj or Direct rule in India. It was the time when the British power in India shifted from the East India Company to the British Crown. The Crown’s control over the Indian subcontinent from 1858 to 1947. Since the Pitts India Act of 1784, the British parliament curtailed the power of the Company and eventually brought the Government in India under the British Crown. The whole process was completed with the Government of India Act 1858.

4. The Making of the Constitution
A Constitution is a set of rules, written or unwritten, acceptable to all the people living together in a country. It is the supreme legislation that governs how residents of a territory interact with one another and how they interact with the government.With the build-up of national consciousness among Indians and the decline of moderate elements in the Indian freedom struggle, the demand for the formation of a constitution for Indians by themselves became even louder.
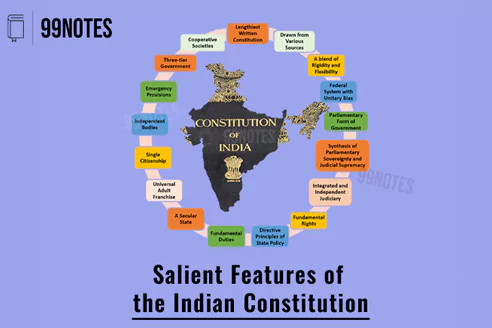
5. Salient Features of the Indian Constitution
The Indian Constitution is considered unique in its contents and spirit worldwide. It has the distinction of being most lengthy and detailed due to the vastness of the country and the unique socio-economic and political issues that it faces. The constitution reflects the legacy of the freedom struggle.

6. Sources of the Indian Constitution
The constitution makers of India wanted to accommodate universal values of democracy in the Indian Constitution; hence the constituent assembly adopted several provisions from the Constitution of other countries and adapted them to the needs of the country.

7. The preamble of the Indian Constitution
The Preamble of the Indian Constitution is a brief introductory statement that outlines the fundamental principles and objectives of the Constitution. Therefore, Eminent Jurist Nani Palkhiwala called Preamble as “Identity Card of the Constitution”.

8. Union and its Territory
Considering the vast diversity of this subcontinent, the framers of the Indian constitution created a federal Union structurally based on the Government of India Act 1935. It was a highly centralised structure; however, regional political forces have always worked towards reducing the centre’s grip over the states.

9. Citizenship
Citizenship can be defined as the legal status of membership in a political community. It is about the relationship between the state and its members and citizen-citizen relations.

10. Fundamental Rights
“Rights are claims of an individual necessary to ensure one’s happiness, without compromising the happiness of others.” The idea of rights as a claim to a life of freedom and dignity, irrespective of one’s caste, race, birth, class, gender, etc.,

11. Directive Principles of the State Policy (DPSPs)
Part IV (Articles 36 to 51) of the Constitution constitutes the Directive Principles of State Policy(DPSPs). The Constitution added these principles to bring about social and economic justice to the people. These directive principles embody the principles of a welfare state.

12. Fundamental Duties
The idea of fundamental duty refers to a sense of moral obligations and responsibilities that an individual should uphold as a member of society and a nation. It serves as a moral compass for individuals, guiding them to act responsibly, ethically and with consideration for the nation’s well-being.
13. Amendment of the Indian Constitution
The Constitution of a country is the fundamental law of the land. It has higher sanctity and more permanence than ordinary legislation. However, a democratic constitution has to be particularly responsive to the changing conditions. A government based on popular sovereignty cannot ignore the changing will of the people.

14. The Doctrine of Basic Structure
How comprehensively can Parliament amend the Constitution? Can it change the very nature of the Constitution? Can it rewrite the whole Constitution? These were the questions that our Supreme Court, the final interpreter of the Constitution, faced in the 1960s and 70s when, in just 10 years, more than 20 amendments were made.
15. Parliamentary System
In modern democracies, two kinds of relationships exist between the Legislature and the Executive; it can be defined by either the Parliamentary or the Presidential government system. The Parliamentary system involves a fusion of the Executive and Legislature, and the Executive is responsible to the Legislature for its acts and policies.
16. Federal System
ederalism is a governance mechanism in which the state’s sovereignty is distributed between different units, i.e. centre, state and local bodies. It is a vertical distribution of power, i.e. division of power between different layers of government. It seeks to define the relationship between the central government and regional governments.
17. Centre-State Relations
The distribution of power between the Centre and the States is known as the division of power. Division of power is different from the separation of powers: The former is about the distribution of powers between the Union and the states (vertical distribution of power), and the latter is about the separation of powers among three organs of government..
18. Inter-State Relations
In India, interstate relations are characterised by both conflict and collaboration. There are disputes among Indian states over sharing water and territorial boundaries. The disputes have resulted in violent clashes between states on several occasions; a recent example is violence that happened over the Assam-Meghalaya border dispute.

19. Reforms in Centre-State Relations
Despite the various provisions made in the Indian Constitution for the smooth functioning of the Indian Union, it has faced many practical challenges. Most of these challenges orbit around the demand for greater autonomy. In post-independent India, the need for planned development, national integration and maintenance of law and order led to a significant degree of centralisation of powers in the hands of the Centre.

20. Emergency Provisions
In Indian polity, Emergency refers to a situation where the Central executive exercises extraordinary powers given by the Constitution, to deal with a crisis caused by either internal or external factors that threaten the nation’s stability, unity and sovereignty. Emergency provisions are given in Articles 352 to 360 in Part XVIII of the Indian Constitution. The order to declare an emergency is passed by the President of India on the advice of the Central Council of Ministers.
- Indian Constitution Free UPSC Notes Download
- 1. What is a Constitution?
- 2. Evolution of Indian Constitution
- 3. The Crown Rule
- 4. The Making of the Constitution
- 5. Salient Features of the Indian Constitution
- 6. Sources of the Indian Constitution
- 7. The preamble of the Indian Constitution
- 8. Union and its Territory
- 9. Citizenship
- 10. Fundamental Rights
- 11. Directive Principles of the State Policy (DPSPs)
- 12. Fundamental Duties
- 13. Amendment of the Indian Constitution
- 14. The Doctrine of Basic Structure
- 15. Parliamentary System
- 16. Federal System
- 17. Centre-State Relations
- 18. Inter-State Relations
- 19. Reforms in Centre-State Relations
- 20. Emergency Provisions
- Other Related Links:
- Indian Constitution

Indian Constitution
Reading the Indian Constitution is an important topic for the UPSC Civil Services Exam (CSE) because it is one of the fundamental sources of law in India.
The Constitution of India lays down the framework for the government of the country and specifies the powers and duties of the various organs of the government. It also guarantees certain fundamental rights to the citizens of India and provides for the protection of these rights.
The UPSC CSE is a competitive examination that tests candidates on their knowledge of a wide range of topics, including Indian history, geography, economics, and current affairs. The Constitution of India is an important part of the exam syllabus and candidates are expected to have a good understanding of its provisions and how they are applied in practice.
In the UPSC CSE, questions on the Constitution of India is asked in the general studies paper as well as in the optional subjects. It is therefore important for candidates to have a thorough understanding of the Constitution and to be able to apply their knowledge to real-life situations.
It is not possible to provide a comprehensive overview of the Indian Constitution, as the Constitution is a complex and detailed document that consists of over 450 articles and 12 schedules. However, we can provide a general outline of the main features of the Constitution and its role in the governance of India.
The Constitution of India came into effect on January 26, 1950, and it is the supreme law of the land. It lays down the framework for the government of India and specifies the powers and duties of the various organs of the government, such as the Parliament, the President, the Vice President, the Prime Minister, and the Supreme Court.
The Constitution of India consists of a preamble and 22 parts, which are divided into articles. The preamble sets out the basic values and principles that guide the Constitution, such as justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity.
- The first part of the Constitution deals with the Union and its territory, and it includes provisions on the name and territory of India, the state and territory of the Union, and the capital of the Union.
- The second part of the Constitution deals with citizenship and includes provisions on the rights and duties of citizens, as well as the acquisition and termination of citizenship.
- The third part of the Constitution deals with the fundamental rights of citizens, which are guaranteed by the Constitution and cannot be infringed by the state. These rights include the right to equality, the right to freedom of speech and expression, the right to life and personal liberty, the right to education, and the right to freedom of religion, among others.
- The fourth part of the Constitution deals with the directive principles of state policy, which are guidelines for the government to follow in framing laws and policies. These principles are not enforceable by the courts, but they are considered to be fundamental in the governance of the country and are meant to guide the government in its actions.
- The fifth part of the Constitution deals with the executive, which consists of the President, the Vice President, and the Council of Ministers, headed by the Prime Minister. The President is the head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of the government.
- The sixth part of the Constitution deals with the legislature, which consists of the Parliament, which is made up of the President and two houses: the Council of States (Rajya Sabha) and the House of the People (Lok Sabha). The Parliament has the power to make laws for the entire country and to levy taxes.
- The seventh part of the Constitution deals with the judiciary, which consists of the Supreme Court and other courts. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land and has the power to interpret the Constitution and to ensure that the laws of the country are in conformity with it.
The remaining parts of the Constitution deal with various other matters, such as the finance, property, contracts, and suits of the Union and the states; the service and conduct of public servants; the Union and the states; and the amendment of the Constitution.
The Constitution of India also includes 12 schedules, which contain details on a variety of topics such as the distribution of powers between the Union and the states, the allocation of seats in the Parliament, and the procedure for the conduct of business in the Parliament.
In summary, the Constitution of India is a comprehensive document that lays down the framework for the governance of the country and guarantees certain fundamental rights to its citizens. It is an important topic for the UPSC CSE and candidates are expected to have a good understanding of its provisions and how they are applied in practice.
Here are some steps candidate can follow to prepare for the Indian Constitution topic for the UPSC Civil Services Exam (CSE):
- Familiarize yourself with the basic structure of the Constitution: You should have a good understanding of the different parts and articles of the Constitution and how they are organized. You should also be familiar with the preamble and the 12 schedules of the Constitution.
- Understand the main principles and values underlying the Constitution: The preamble of the Constitution sets out the basic values and principles that guide the Constitution, such as justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity. It is important to understand these principles and how they are reflected in the various provisions of the Constitution.
- Learn about the powers and functions of the different organs of the government: The Constitution divides the powers of the government between the Union (federal) and the states, and specifies the powers and functions of the various organs of the government, such as the Parliament, the President, the Vice President, the Prime Minister, and the Supreme Court.
- Understand the fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution: The Constitution guarantees certain fundamental rights to the citizens of India, such as the right to equality, the right to freedom of speech and expression, the right to life and personal liberty, the right to education, and the right to freedom of religion, among others. It is important to understand these rights and how they are protected by the Constitution.
- Learn about the directive principles of state policy: The Constitution also lays down certain directive principles of state policy, which are guidelines for the government to follow in framing laws and policies. It is important to understand these principles and how they are meant to guide the government in its actions.
- Understand the amendment process: The Constitution can be amended by the Parliament through a specified process. It is important to understand this process and to be aware of any recent amendments to the Constitution.
- Practice answering questions: To prepare for the exam, it is helpful to practice answering questions on the Constitution. You can find sample questions on the UPSC website or in practice books, and you can also ask your friends or teachers to give you questions to practice with.
- Seek help if needed: If you are having difficulty understanding any aspect of the Constitution, don’t hesitate to seek help from your teachers or mentors. It is important to have a thorough understanding of the Constitution to do well in the UPSC CSE.
