The Ultimate Guide For UPSC CSE
“Where Aspirations Meet Achievements”
We believe in Relevancy, so instead of focusing on why you should join us etc. etc. This brochure will include one-stop solution for all your queries regarding the UPSC CSE exam.
- The Ultimate Guide For UPSC CSE
- "Where Aspirations Meet Achievements"
- Opportunities through UPSC Exam
- CIVIL SERVICES EXAMINATION
- STAGES OF EXAMINATION
- PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
- MAIN EXAMINATON
- INTERVIEW
- ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA
- SYLLABUS
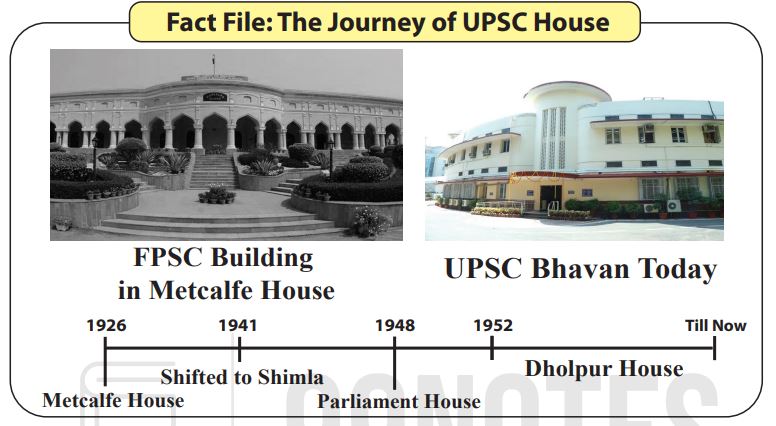
- Prelims GS Cut-Off
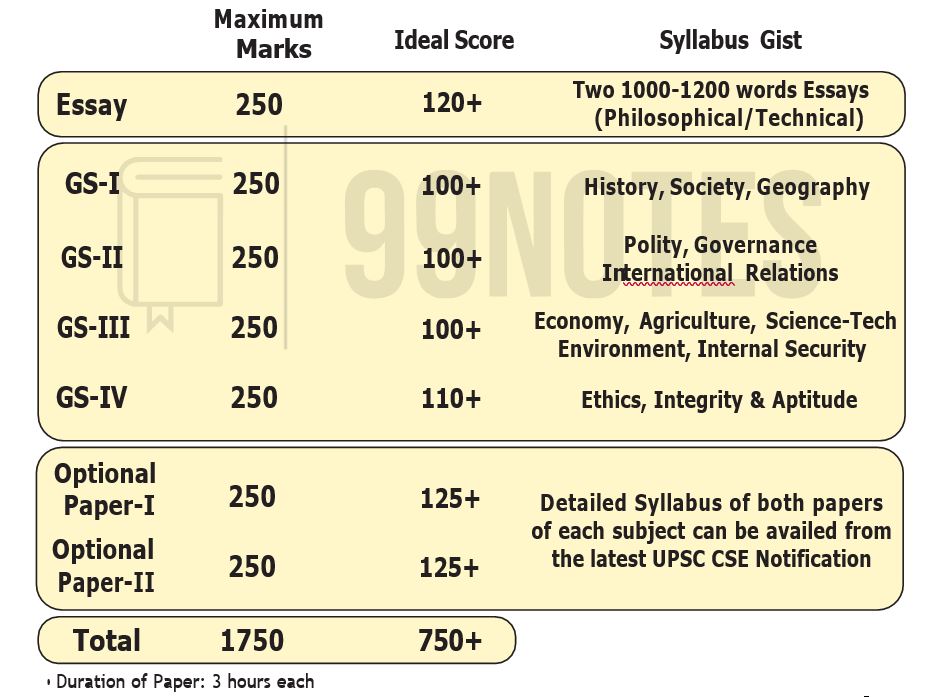
- Syllabus of Language Papers
- Essay Paper ( PAPER-1 )
- General Studies – I (Paper II)
- General Studies – II (Paper III)
- General Studies – III (Paper IV)
- General Studies – IV (Paper V)
- Importance of the Optional Subjects
- Factors considered for selecting Optional Subjects.
- Checklist to select the Optional Subject
- BOOKLIST FOR UPSC CSE
- Polity&Governance
- IndianEconomy
- Indian History
- Art Culture
- Environment
- Science & Tech
- Geography
- Indian & Society
- International Relations
- Internal Security
- Ethics
- Books For CSAT
- How 99Notes covers the study Material
- Subject-wise courses
- Tips for UPSC
Opportunities through UPSC Exam
Since before the Indian Independence, the Civil services Exam conducted by UPSC has been the main mode through which India’s highest-ranking administrators have been selected.
| General Management Services | Specialized Services | Technical Services | ||
| Group A | All India Services | Indian Administrative Service (IAS) | Indian Police Service (IPS) | Indian Foreign Service (IFS) |
| Central Services | IFoS, IRS, IIS, IRTS, IRAS, IA&AS etc. | Railway EngineeringServices, CPWD, CGHS | ||
| Group B | CentralServices | CSS, RBSS, DANICS | CSCS | CSCS |
| Group C & Group D | Exists in all functional and general management areas | |||
The Union and State Services can be classified into Group A, B C and D categories, with the Group A Services generally carrying higher ranks and responsibilities. Though each of these groups has a different channel for recruitment, there is provision for promotion from Group C to Group B and from Group B to Group A.
Group A and B officers are recruited by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). Therefore, the UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE) isthe only channel through which the highest-ranking officers in the Union and the State government are selected. This makes the UPSC CSE the most sought-after examination in India.
CIVIL SERVICES EXAMINATION
About Examination
The Civil Services Exam (CSE) is conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) annually to select candidates for various civil services positions in the Indian government. The exam is conducted in three stages: the preliminary exam, the mains exam, and the interview
candidates
apply
each year
Approx.
4,00,000
candidates attempt
STAGE 1
Approx.
15,000
attempt Mains
STAGE 2
Approx.
3,000
are selected
for Interview
STAGE 3
1,100
are
fInally selected
The preliminary exam consists of two objective-type papers, General Studies and Civil Service Aptitude Test (CSAT), which assess the candidates’ knowledge and skills. The mains exam is a written exam consisting of nine papers, including two qualifying papers in Indian languages and English, and seven papers on various subjects such as history, geography, polity, economics, and ethics. Candidates who qualify the mains exam are called for an interview, which assesses their personality, communication skills, and knowledge of current affairs. The final selection is based on the candidate’s performance in the mains exam and the interview.
STAGES OF EXAMINATION
Preliminary Examination
PAPER 1 :- GENERAL STUDIES
PAPER 2 :- CSAT
Main Examination
WRITTEN PART :- ( 1750 MARKS )
INTERVIEW :- ( 275 MARKS )
ESSAY
FOUR GS PAPERS
TWO OPTIONAL PAPERS
QUALIFIFYING LANGUAGES
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
The Preliminary Examination is the compulsory Qualifying stage, the marks of which do not count in the final merit. It consists of two papers. Paper 1 is the General Studies Paper, and Paper 2 is the Civil Services Aptitude Test (CSAT) paper.
The CSAT paper is qualifying in nature. However, securing the minimum 33% score (i.e. 67 marks) in it has become increasingly challenging in recent years.The cutoff marks of the GS Paper decide the qualification for the Main Examination. As shown in the table below, these cutoff marks have remained in the 90-100 range in recent years. However, it can vary depending on the number of seats offered by UPSC and the difficulty of the paper.
| Subjects | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Polity &Governance | 11 | 15 | 18 | 12 | 16 |
| Environment | 9 | 11 | 15 | 14 | 19 |
| Geography | 11 | 14 | 9 | 11 | 8 |
| Science & Tech | 9 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 9 |
| Economy | 11 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 14 |
| History | 22 | 17 | 17 | 14 | 18 |
| Current Affairs | 27 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 16 |
| Cut-off | 98 | 98 | 92.51 | 87.54 | 92 (expected) |
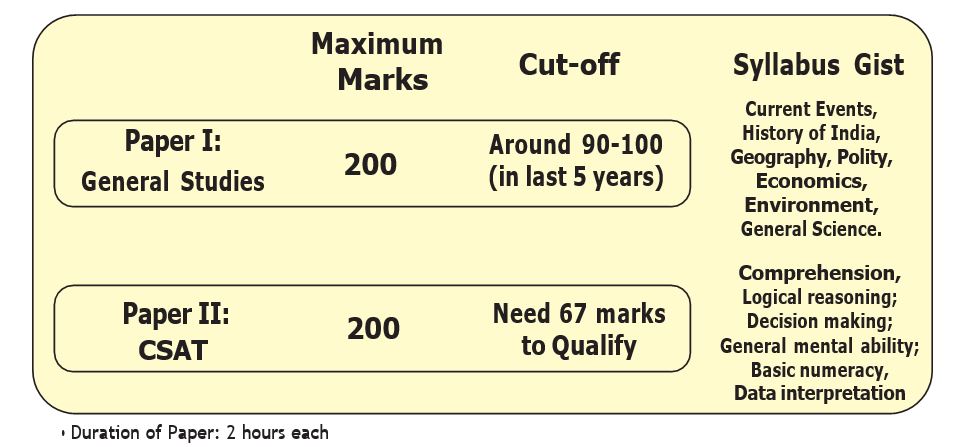
MAIN EXAMINATON
The UPSC Civil Services Exam (CSE) mains test is the second step of the selection process after the preliminary exam. The mains exam is a written test consisting of nine exams, two of which are qualifying in character and the remaining seven are used to determine merit.
The two qualifying papers are as follows:
Indian Language Paper A (300 marks) English – Paper B (300 marks)
The seven papers considered for the merit rating are as follows:
The mains papers last five to seven days. The marks gained in these seven examinations are combined together to produce a candidate’s ultimate CSE rank. A person who can achieve the ideal scores, as mentioned above, can generally qualify for the Interview. The cutoff for the Interview has remained in the range of 720-750 marks out of 1750 in the last few years.
Language Papers
The candidates must obtain a minimum qualifying score in English (Paper-A) and the Indian Language (Paper-B) examinations in order to qualify for the interview. The candidate can choose any one language of the eighth schedule as the Indian Language. In the UPSC-2023 Notification, the qualifying marks for both language papers have been fixed at 25%, i.e. 75 marks.’ Although, it is not mandatory for the candidates from Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Sikkim to attempt the Indian Language Paper
Optional Papers
The optional papers consist of two 250-marks papers. A candidate hasto choose one Optional subject from the following list of 25 academic subjects and 16 Literature subjects.
1. Agriculture
2. Animal Husbandry and Veternary Science
3. Anthropology
4. Botany
5. Chemistry
6. Civil Engineering
7. Commerce and Accountancy
8. Economics
9. Electrical Engineering
10. Geography
11. Geology
12. History
13. Law
14. Management
15. Mechanical Engineering
16. Mathematics
17. Medical Science
18. Philosophy
19. Physics
20. Political Science and International
Relations (PSIR)
21. Psychology
22. Public Administration
23. Sociology
24. Statistics
25. Zoology
Literature Optional Subjects
Candidates select optional papers based on their interests, specialty and past successes.
INTERVIEW
ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA
1. Nationality
The candidate must be either: Citizen of India, person of Indian origin who has migrated from Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka, East African countries of Kenya, Uganda, the United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Malawi,Zaire, Ethiopia, or Vietnam with the intention of permanently settling in India.
2. Age Limit
The candidate must have attained the age of 21 years and must not have attained the age of 32 years on 1st August of the year in which he/she is appearing for the exam. This means that the candidate must have been born not earlier
than August 2, 1989, and not later than August 1, 2000
Upper Age limit relaxation for candidates belonging to certain categories
a) SC/ST candidates: 5 years
b) OBC candidates: 3 years
c) Residents of J&K between 1st Jan 1980 to 31st Dec 1989: 5 years
d) Defense Services Personnel disabled during war or opera�on
in a disturbed area and released as a consequence thereof:
3 years
e) Ex-servicemen who have rendered at least 5 years Military
Service, and have been released:
5 years
f) Persons with Benchmark Disabili�es (PwBD) 10 year
3. Educational Qualification
The candidate must possess a Bachelor’s degree from a recognized university or possess an equivalent qualification.
The candidates who are in their final year of graduation can also apply for the UPSC CSE exam, but they have to produce the proof of passing the Bachelor’s degree examination at the time of filling up the application for the UPSC CSE Main Exam.
4. Number of Attempts
| Category No. of Attempts | |
| General | 6 |
| OBC | 9 |
| PwBD belonging to General and OBC categories | 9 |
| SC/ST | Unlimited |
5. Physical Standards
Candidates must meet certain physical standards as prescribed by the UPSC. The physical standards include parameters such as height, chest measurement, and eye-sight, among others. These are different for different posts and services, and candidates are required to meet the specific physical standards for the post/service they are applying for.
SYLLABUS
Paper I-(200 marks), Duration: Two hours.
• Current events of National & international importance.
• History of India & Indian National movement
• Indian and World Geography.
• Indian Polity and Governance – Constitution, Political System, Rights Issues, etc.
• Economic & Social Development – sustainable Development, Poverty etc.
• General issues on Environmental ecology, bio-diversity and Climate change
General Science
Paper II-(200 marks), Duration: Two hours.
• Comprehension,
• Interpersonal skills including communication skills;
• Logical reasoning and analytical ability;
• Decision making and problem solving;
• General mental ability;
• Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.)
• Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data suffciency etc. – Class X level);
Important Note
1: Paper-II will be qualifying paper with minimum qualifying marks fixed at 33%.
2: All Questions would be Multiple Choice Questions – objective type.
3: It is mandatory to appear in both the papers of CS(P)E for evaluation, otherwise candidate will be disqualified.

Prelims GS Cut-Off
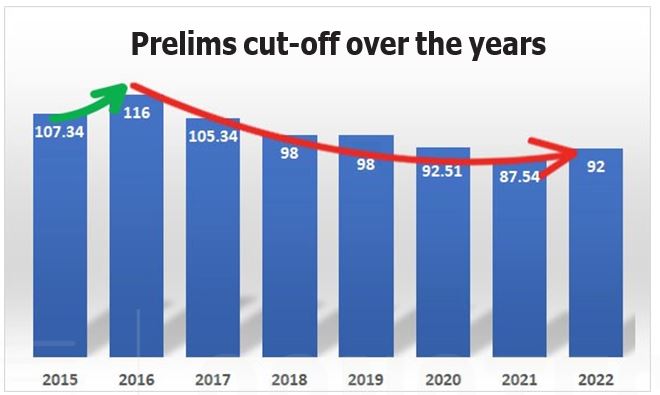
The Prelims cut-off keeps fluuctuating depending on the number of seats and the difficulty of the paper. In recent times, the questions have shifted towards the fine lines on the basic understanding of the concepts. Due to this, the difficulty of the
paper has increased, and therefore the cut-off has been falling despite the increase in competition, as illustrated below:
The main examination is intended to assess the overall intellectual traits and depth of understanding of candidates rather than merely the range of their information and memory.
The nature & standard of questions in the GS papers (Paper II to V) will be such that a well-educated person will be able to answer them without any specialized study. The questions will be such as to test a candidate’s:
• General awareness of variety of subjects, which will have relevance for a career in Civil Services.
• The questions are likely to test the candidate’s basic understanding of all relevant issues, and
• Ability to analyse, and take a view on confliicting socio-economical goals, objectives and demands.
• Type of Answers: The candidates must give relevant, meaningful and sucfficinct(brief) answers.
The scope of the syllabus for optional subject papers (Paper VI & VII) for the examination is broadly of the honours degree level i.e. a level higher than the bachelors’ degree and lower than masters’ degree. In case of engineering, medical science and law, the level corresponds to the bachelors’ degree.
Syllabus of Language Papers
Qualifying papers on Indian Languages & English: Aim is to test candidates’ ability to read & understand serious discursive prose, and to express his ideas clearly and correctly, in English & Indian language concerned.
Syllabus of English Language
i. Comprehension of given passages.
ii. Precis Writing.
iii. Usage & vocabulary.
iv. Short Essays.
Syllabus of Indian language paper:
i. Comprehension of given passages.
ii. Precis writing
iii. Usage and Vocabulary
iv. Short Essays
v. Translation from English to Indian Language & Vice-versa.
The papers on Indian Languages & English will be of Matriculation or equivalent standard and will be qualifying in natures only. The marks obtained in these papers will not be counted for ranking.
The candidates will have to answer the English and Indian languages papers in English & the respective Indian language(except where translation is involved).
Essay Paper ( PAPER-1 )
• Candidates may be required to write essays on multiple topics. These topics can be philosophical as well as Technical.
• They will be expected to keep closely to the subject of the essay to arrange their ideas in orderly fashion, and to write concisely.
• Credit will be given for effective and exact expression

General Studies – I (Paper II)
Indian Heritage & Culture, History and Geography of the World and Society
1. Indian Culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, literature & Architecture from ancient to modern times.
2. Modern Indian history from about the middle of the 18th century until the present -significant events, personalities, issues.
3. The Freedom Struggle – its various stages and important contributors/contributions from different parts of the country.
4. Post-Independence consolidation and reorganization within the country.
5. History of the world will include events from 18th century such as industrial revoluton, world wars, redrawal of national boundaries, colonization, decolonization,
6. Political philosophies like communism, capitalism, socialism etc. – their forms and effect on the society.
7. Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
8. Role of women and women’s organization,
9. Population and associated issues.
10.Poverty and developmental issues,
11.Urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
12.Effects of globalization on Indian society.
13.Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism and Secularism
14.Salient features of world’s physical geography.
15.Distribution of Key natural resources across the world (including South Asia & Indian sub-continent);
• factors responsible for location of primary, secondary and ternary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India).
16.Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic
activity, Cyclone etc.,
• geographical features and their location changes in critical geographical
features (including water-bodies & ice caps) and in flora and fauna and
the effects of such changes
General Studies – II (Paper III)
Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice & International Relations
1. Indian constitution – historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
2. Functions & responsibilities of the Union & the States,
i. Issues & challenges pertaining to the federal structure,
ii. Devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
3. Separation of powers b/w various organs dispute redressal mechanisms & institutions.
4. Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries.
5. Parliament and State legislatures—structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
6. Structure, Organization & Functioning of Executive & Judiciary – M/o & D/o the govt.;
7. Pressure groups & formal/informal associations and their role in the polity.
8. Salient features of Representation of People’s Act.
9. Appointment to various constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various constitutional bodies.
10.Statutory, regulatory and various Quasi-Judicial bodies.
11.Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre
and States and the performance of these schemes;
12.Mechanisms, laws, insitututions and Bodies constuted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
13.Issues relati ng to the development and management of social sector/services relating to Health, Education, resources.
14.Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
15.Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design & implementation.
16.Development processes and the development industry – the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders.
17.Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance – applications, models, successes, limitations and potential;
18.citizens charter, transparency & accountability and instutional and other measures.
19.Role of Civil Services in a democracy.
20.India and its neighbourhood – relations.
21.Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India &/or affecting India’s interests.
22.Effect of policies and policies of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
General Studies – III (Paper IV)
Technology, Economic Development, Bio-diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management.
- Indian Economy and issues relating to
- planning.
- mobilization of resources.
- growth.
- development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from
- Government Budgeting.
- Major crops – cropping patterns in the various parts of the country, – different types of irrigation and irrigation systems
- storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce and issues and related constraints; e-technology in the aid of farmers.
- Issues related to Direct & indirect farm subsidies & MSP;
- PDS – objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security;
- Technology missions; Economies of Animal –
- Food processing and related industries in India – scope and significance, location , upstream & downstream requirements, supply chain
- Land reforms in
- Effects of liberalization on the economy,
- Changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railway
- Investment
- Science & Technology: development & their applications & effects in everyday
- Achievements of Indian S&T; indigenization of technology and developing new
- Awareness in the fields of IT, space, computers, robotics, nano- technology,
- Bio-technology and issues relating to Intellectual property Rights(IPR).
16. Conservations, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
- Disaster and disaster management.
- Linkages b/w development & spread of extremism.
- Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal Security.
- Challenges to internal security through communication networks, role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cyber security; money-laundering and its preservations.
- Security challenges and their management in border areas – linkages of
- organized crime with terrorism.
General Studies – IV (Paper V)
Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
The paper will include questions to test the candidates’ attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity, probity in public life and his problem-solving approach to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with the society. Questions may utilize the case study approach to determine these aspects. The following broad areas will be covered:
- Ethics and Human interface:
- Essence, determinants and consequences of Ethics in human actions;
- Dimensions of ethics;
- Ethics – in private & public
- Human values – lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators;
- Roles of family, society and educational institutions in inculcating
- Attitude: content, structure, function;
- Its influence and relation with thought and
- Moral and political attitudes;
- Social influence and
- Aptitude and foundational values for Civil services, integrity, impartiality and non-partisanship, objectivity, dedication to public service, empathy, tolerance and compassion towards the weaker
- Emotional intelligence – concepts, and their utilities and application in administration and
- Contributions of moral thinkers & Philosophers from India &
- Public/Civil service values in Ethics & Public administration: Status & problems;
- Ethical concerns and dilemmas in government and private
- Laws, rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance;
- Accountability and ethical governance;
- Strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance;
- Ethical issues in international relations and funding;
- Corporate
- Probity in Governance:
- Concept of public service;
- Philosophical basis of governance and probity;
- Information sharing & transparency in government, Right to information,
- Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s Charter,
- Work Culture, Quality of Service delivery,
- Utilization of public funds, Challenges of
- Case studies on above issues.
Importance of the Optional Subjects
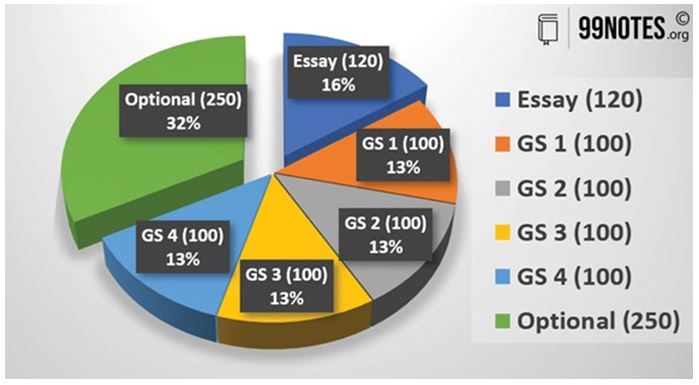
The Mains part of the UPSC CSE decides the actual rank of a candidate and therefore is the most significant aspect of the examination. Even after clearing UPSC CSE Prelims multiple times, candidates find it difficult to secure a rank. The selection of optional subjects plays a critical role in this aspect.
Out of 1750 marks in the written papers of the UPSC Main examination, only 500 marks are allotted to the Optional subject. However, when it comes to analysing the final scorecards, we find that candidates fetch over 33% of their scores from the optional subject itself.
Anything around 40% marks in the GS subjects is a good score, but anything less than 50% in the optional is not good enough. Thus, we can comfortably say that optional subjects can often be a rank-deciding factor in this examination.
Factors considered for selecting Optional Subjects.
- Candidate must have an Aptitude for the subject. A candidate must not get stuck with a subject which doesn’t suit them. Going through the syllabus gives a rough idea about the nature of the subject, and therefore, this must be the first step before choosing an optional
- Length of the syllabus: For many, a few optional subjects are too lengthy to cover, which makes it difficult for the student to both complete the syllabus as well as revise it on
- Availability of Study material and a peer group also plays a vital role in the If a candidate chooses an unpopular Optional subject, there is a high chance that they have to prepare the whole subject solitarily without a peer group or support from a teacher.
- Overlap of the syllabus with General Studies is another factor to be For example, the syllabus of Political Science and International Relations (PSIR) covers the syllabus of GS 2 completely.
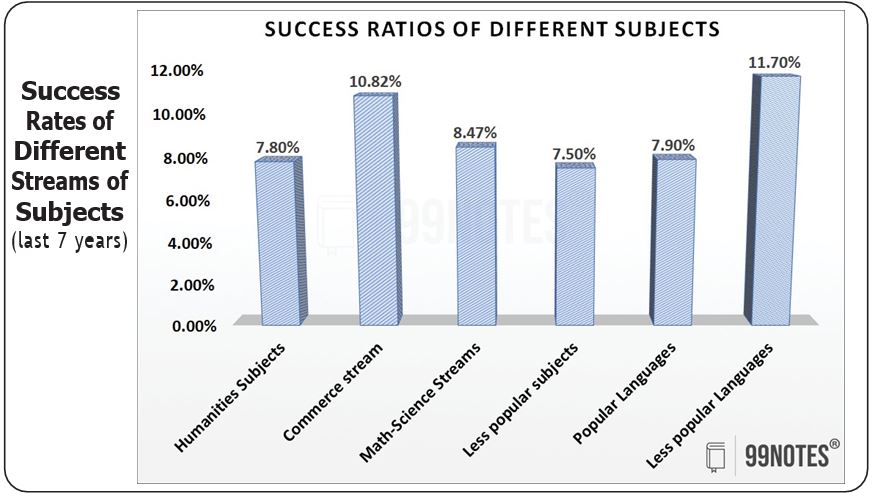
- Historic Success Rates: Every year, around 7.5% of all who write the Mains examination are recommended by UPSC for selection. However, many optional subjects are not able to achieve a success rate of even 7% for many
- Commentary by the previous toppers is also essential to grasp the nuances of a Although there can be more than one strategy to approach a subject, the solutions experienced candidates give to various challenges in a subject cannot be ignored. Nevertheless, candidates must always be mindful that the nature of the sub- ject might change in 3-4 years.
Checklist to select the Optional Subject
Generally, technical and professional subjects have higher rates of success. However, they are difficult to follow and have minimum overlap with the Gener- al Studies papers.
It is necessary that a candidate remains confident and motivated enough to pursue the study of the optional subject during preparation. Thus, choosing optional should be done with patience and after giving enough thought.
A candidate can follow the following steps before making a choice:
Step 1: Analyse the syllabus and check what you know already. You can also check the previous year’s papers to check the difficulty level of the subject.
Step 2: Check the reviews by the previous toppers.
Step 3: Search for the study material and peer groups (if you like to study in groups).
Step 4: If you think you would need to join a coaching class, search for classes and take their demo lectures.
Once all the above factors are considered, a candidate is well-equipped to make a choice. If some degree of confusion still persists, you might consult a mentor who has either attempted the UPSC CSE exam in previous years or has taught such candidates. But in any case, never go against your gut feeling.
BOOKLIST FOR UPSC CSE

Polity
&
Governance
NCERT Class XI – for understanding Political Theory
Indian Polity by Laxmikanth covers a large portion of the syllabus comprehensively.
Constitution of India by DD BASU; (important for mains perspective, and can be skipped if Laxmkanth suits you)
2nd ARC reports – It is a set of 15 reports, out of which:
5th report is important for police reforms,
10th report for overall reforms in civil services in recruitments as well as e-governance.
12th report for citizen-centric governance
All this should be complemented with regular news updates on the issues mentioned in the syllabus, as UPSC often asks conceptional questions based on current
Either The Hindu or Indian Express should suffice your
PRS Legislative research, PIB website and Vikaspedia are other useful sources to cover governmen;

Indian
Economy
Macroeconomics – NCERT Class XII;
• Indian Economic Development – NCERT Class XI;
• Economic Survey Summary of at least the past three
years;
• Budget Summary of at least the past three years;
• Websites like Arthapedia could work well for
understanding basic concepts;
• The Hindu/Indian Express/Yojana magazine;

Indian History
Ancient India
Old NCERT by RS Sharma;
• Tamil Nadu class 11,12NCERT;
• Note: Ancient India is important for understanding
Indian Heritage and culture
Medieval India
Only selective reading of Old NCERT by Satish
Note: Medieval history is too vast and much less Therefore, there is no need to dive deep into it.
Modern India
India’s Struggle for Independence by Bipan Chandra;
A brief history of Modern India- Spectrum Publications;
From Plassey To Partition and After by Sekhar Bandyopadhyay; (Only from the perspective of the main – and can be skipped if other books suit you)

Art Culture
An Introduc�on to Indian Art – Class XI NCERT;
• Centre for Cultural Resource and Training (CCRT)
booklet.
• Indian Art and Culture by Ni�n Singhania – this book itself
is the gist of NCERT and CCRT books. However, it is s�ll
advisable to first read the NCERTs.

Environment
Biology chapter no 14,15,16 from class 12 NCERT;
• Chemistry chapter no 14 from class 11 NCERT;
• Fundamentals of Physical Geography XI NCERT chapter
no 15,16;
• India: Physical Environment XI NCERT chapter no 5,7;
• Can refer to magazines like Down to Earth and Science
Reporter.

Science & Tech
General Science books – IX and X standard;
• The updates in the fields of Science in India can be noted
from The Hindu/Indian Express/Science Reporter.

Geography
Fundamentals of Physical Geography XI NCERT;
India: Physical Environment XI NCERT;
Fundamentals of Human Geography XII NCERT;
India: People and Economy XII NCERT;
Certificate Physical and Human Geography: GC Leong;
Geography of India – Majid Hussain; World Geography- by Majid Hussain; and Physical Geography by Savinder Singh can be seen from the perspective of the main, but it is advisable to stick to NCERTs and GC
World Atlas;

Indian & Society
Biology chapter no 14,15,16 from class 12 NCERT;
• Chemistry chapter no 14 from class 11 NCERT;
• Fundamentals of Physical Geography XI NCERT chapter
no 15,16;
• India: Physical Environment XI NCERT chapter no 5,7;
• Can refer to magazines like Down to Earth and Science
Reporter.

International Relations
Books like India’s foreign policy by Rajiv Sikri and Pax
Indica by Shashi Tharoor can be useful in making basic
understanding but are not necessary.
• The Hindu/Indian Express/The Diplomats are useful in
understanding the current issues

Internal Security
• The 8th report and 5th report of the 2nd ARC are useful in
understanding basic concepts in security.
• The Hindu/Indian Express.

Ethics
• Lexicon for Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude is a standard book
for reading ethics.
• Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude for Civil Services
Examination by Subba Rao and P.N. Roy Chaudhary.
Books For CSAT
• Verbal & Non-Verbal Reasoning by RS Agarwal;
• Logical Reasoning by RS Agarwal.
How 99Notes covers the study Material
1. Master Notes by 99Notes: Covers all the resources mentioned above and continuously updates them based on current developments.
2. Practising Questions: Alongside the content, we provide the database of PYQs and an ample number of Model ques�onsto cover each concept. All the material is uploaded to the website and can be browsed by anyone remotely with login credentials.
3. Current Affairs: 99Notes covers basic reports, Economic surveys, Budget, and Magazines (Science Reporter, Yojana etc.) in its current affairs
section.
4. Unique AI generated questions based on rigorous analysis of the previous trends.
Remember that success in the UPSC exam is not just about getting a job; it’s about becoming a part of the civil service community and working towards a better future for our country. Keep this in mind, stay focused, and keep moving forward.
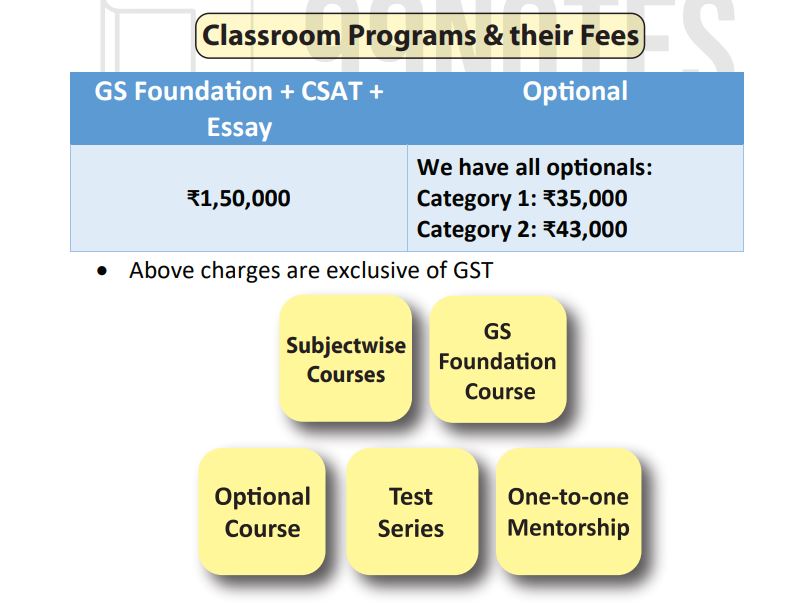
Subject-wise courses
Introducing the most unique and innovative coaching technique for UPSC CSE aspirants – our Subject-wise coaching program! We understand that every student has their own strengths and weaknesses, and therefore, requires customized guidance to achieve their dream of becoming a civil servant.
At our coaching institute, we offer you the flexibility to choose which subject you
need guidance in. Whether it’s polity, geography, history or any other subject, our esteemed teachers are here to mentor you and provide you with the best guidance at the lowest cost.
Our Subject-wise coaching program is the first of its kind in the history of UPSC CSE coaching, and we take pride in being pioneers in this approach. We firmly believe that this unique coaching methodology will help you achieve success in the most effecient and effective way possible.
So, don’t let anything hold you back from achieving your dream. Enroll in our Subject-wise coaching program today and let our expert teachers guide you towards success in UPSC CSE.
Program Summary
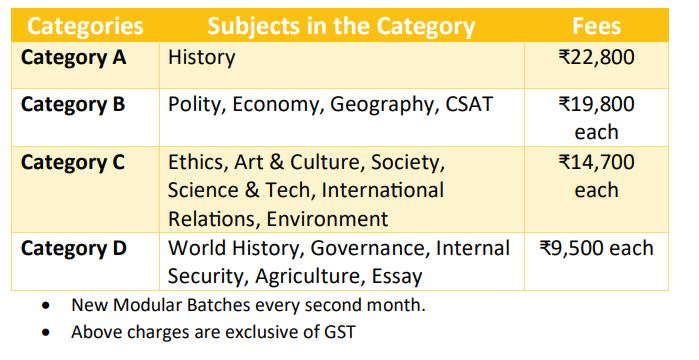
All subjects shall be organized into four categories of modules based on the time period taken to complete each subject holistically. These are:
Tips for UPSC
Based on the experiences of Successful aspirants turned bureaucrats and more importantly Battle-Hardened Veterans of UPSC CSE community.
Here are some tips every aspirant should know before kick-starting preparation:
