6 June 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. With bad news from Cassini, is dark matter’s main rival theory dead?
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
| Astrophysicists are grappling with the mystery of why galaxies rotate faster than predicted by Newton’s laws.This has led to debates between the existence of dark matter and alternative theories like Milgromian dynamics (MOND).Recent research challenges Milgromian dynamics (MOND), reinforcing the dark matter hypothesis. |
Introduction to Galactic Mysteries
- Galactic Rotation Anomaly: One of the biggest mysteries in astrophysics is the discrepancy in the rotational speeds of galaxies. Galaxies rotate much faster than predicted by Newton’s law of gravity when applied to their visible matter, even though these laws work well in the Solar System.
- Need for Additional Gravity: To prevent galaxies from flying apart, an additional source of gravity is required. This led to the proposal of dark matter, an invisible substance. However, dark matter has never been observed directly, and it does not fit within the Standard Model of particle physics.
Milgromian Dynamics (MOND)
- Alternative Theory – MOND: In 1982, an Israeli physicist proposed an alternative theory known as Milgromian dynamics or MOND. This theory suggests that Newton’s laws of gravity break down under very weak gravitational forces, such as those found at the edges of galaxies.
- Successes and Challenges: MOND has had some success in predicting galaxy rotation without requiring dark matter. However, many of these successes can also be explained with dark matter while preserving Newton’s laws.
Testing MOND
- Key Characteristics: MOND modifies gravity based on the level of acceleration rather than distance. Thus, MOND effects should be observable in various celestial objects, depending on their distance and the strength of gravitational forces.
- Application to Stars and Planets: While MOND effects are typically expected at several thousand light years from a galaxy, significant effects should appear at a tenth of a light year from individual stars. Weaker effects might even be detectable within the Solar System.
Cassini Mission and MOND
- Cassini’s Orbit and Testing MOND: The Cassini mission, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, provided an opportunity to test MOND. Saturn orbits the Sun at 10 astronomical units (AU). According to MOND, the galaxy’s gravity should cause Saturn’s orbit to deviate subtly from Newtonian predictions.
- Radio Pulse Timing: The timing of radio pulses between Earth and Cassini helped measure the Earth-Saturn distance and track Saturn’s orbit precisely. However, Cassini found no anomaly of the kind expected by MOND. Newtonian gravity worked well for Saturn.
Further Analysis and Studies
- Investigating Cassini Data: One of the researchers investigated whether adjusting galaxy mass calculations or considering surrounding galaxies’ gravitational effects could align MOND with Cassini data. However, the analysis showed that MOND could not fit the Cassini results, regardless of adjustments.
- Probability Analysis: Given the most likely assumptions and a wide range of uncertainties, the chance of MOND matching Cassini results was likened to flipping a coin heads up 59 times in a row. This probability is significantly higher than the “5 sigma” standard for scientific discoveries.
Additional Evidence Against MOND
- Wide Binary Stars: Another test involved wide binary stars, which MOND predicts should orbit each other 20% faster than expected by Newton’s laws. A detailed study showed that these predictions did not hold, with a probability equivalent to a coin landing heads up 190 times in a row.
- Outer Solar System Objects: MOND also fails to explain the energy distribution of comets from the distant outer Solar System. These comets exhibit a narrower energy distribution and less inclination than MOND predicts.
MOND on Different Scales
- Failure on Small and Large Scales: MOND is not consistent on scales smaller than a light year or larger than galaxies. It cannot explain the motions within galaxy clusters, where dark matter still provides a better fit. For example, the Coma Cluster requires more gravity than visible mass can provide, and MOND does not account for this in central regions.
Conclusion: The Role of Dark Matter
- Dark Matter’s Persistence: Despite MOND’s initial appeal, it fails to provide a viable alternative to dark matter. Newtonian gravity, supplemented with dark matter, remains the best explanation for many astronomical observations.
- Imperfections in Dark Matter Model: The standard dark matter model is not without its challenges, such as explaining the universe’s expansion rate and large cosmic structures. However, dark matter is still considered essential, though its nature may be different from current models.
- Future Directions: Future research may reveal new aspects of dark matter or modifications to gravity on very large scales. Nonetheless, as presently formulated, MOND cannot replace dark matter in explaining galactic phenomena. The dark side of the cosmos, therefore, continues to dominate our understanding of the universe.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of recent research challenging Milgromian dynamics (MOND) on our understanding of galaxy rotation and the existence of dark matter. (150 Words /10 marks) |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 9)
2. Global project ‘paints’ evidence of air pollution in India
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation |
| Context |
| Researchers and artists have teamed up for the “Air of the Anthropocene” project, which visualizes air pollution in India using digital light painting and low-cost sensors.Their work, published in Nature Communications, aims to raise awareness and spark discussions on the health impacts of air pollution. |
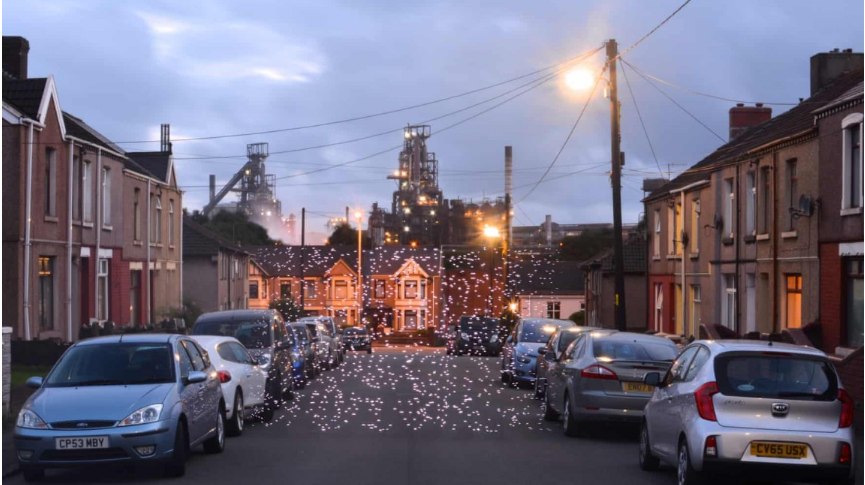

Heol-Yr-Orsedd by Tata Steel Works, Port Talbot, Wales – PM 2.5 20 – 30 micrograms per cubic metre
Introduction
- Researchers and artists have collaborated on an international project to visualise air pollution in India, highlighting the associated health risks.
- The project combines digital light painting with low-cost air pollution sensors, producing photographic evidence of pollution levels in various cities.
Project and Methodology
- The initiative, known as ‘Air of the Anthropocene,’ involves capturing photographs to stimulate discussions on air pollution.
- The findings were published in Nature Communications Earth & Environment.
- The project covered cities in three countries: India, Ethiopia, and the U.K., demonstrating the global nature of air pollution issues.
Findings in India
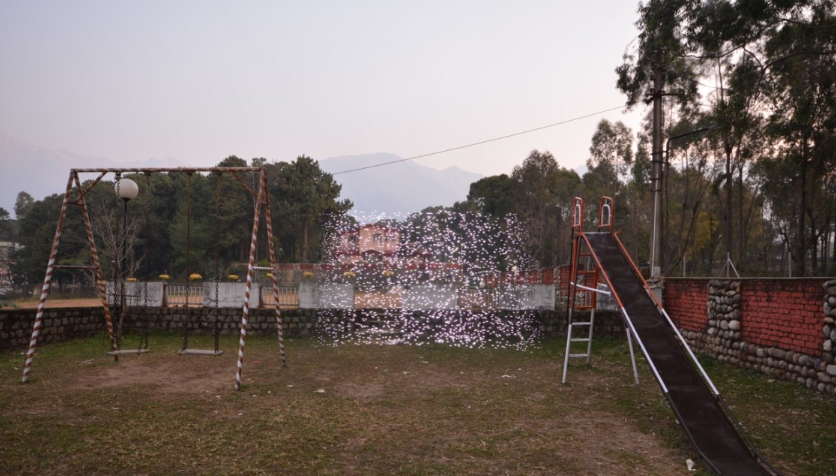

CSIR-IHBT Playground, Palampur, India – PM 2.5 30-40 micrograms per cubic metre
- Photographs were taken in two children’s playgrounds in India: one in urban Delhi and another in rural Palampur.
- The PM2.5 values in Palampur were at least 12.5 times lower than those in Delhi, indicating a stark contrast in air quality between urban and rural areas.
Significance of Light Painting
- The project uses light painting to create visual representations of air pollution, making the invisible visible.
- This method provides a simple and impactful way for people to compare air pollution in different contexts.
- The project aims to use art as a medium to foster discussions about the impacts of air pollution.
Health Impacts of PM2.5
- Particulate matter (PM) is a major air pollutant responsible for significant human morbidity and mortality.
- PM2.5 impacts physical health, causing diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and cancers.
Technology and Approach
- The project used low-cost air pollution sensors to measure PM concentrations in real-time.
- The sensors controlled a moving LED array, programmed to flash more rapidly as PM concentrations increased, providing a visual representation of pollution levels.
- The visual approach helps people without scientific backgrounds understand the severity of air pollution.
- By evoking emotional responses through powerful images, the project aims to raise awareness and prompt action against air pollution.
Exhibition and Impact
- The Air of the Anthropocene project has been exhibited in gallery shows in Los Angeles, Belfast, and Birmingham.
- These exhibitions aim to provoke discussions, share perspectives, and encourage actions to tackle air pollution.
Conclusion
- The collaboration between researchers and artists effectively highlights the health risks of air pollution through innovative visual methods.
- The project underscores the need for greater public awareness and action to manage and reduce air pollution levels globally.
| PYQ: Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata are the three mega cities of the country but the air pollution is much more serious problem in Delhi as compared to the other two. Why is this so? (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2015) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the innovative approaches being used to raise awareness about air pollution in India, such as the ‘Air of the Anthropocene’ project. How can these methods enhance public understanding and influence policy-making to address environmental health risks? (250 Words /15 marks) |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 9)
3. Telugu Desam Party’s Victory Spurs Renewed Push for Special Category Status for Andhra Pradesh
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context: |
| Telugu Desam Party (TDP) president N Chandrababu Naidu has emerged as a pivotal figure in national politics following his party’s success in securing 16 seats in the Lok Sabha election. This victory has positioned Naidu as a key ally for the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), which holds 240 seats, as his support is essential for the BJP’s parliamentary strength. In return, Naidu is likely to demand significant concessions, primarily the Special Category Status (SCS) for Andhra Pradesh (AP). |
Analysis of News:
What is Special Category Status (SCS)?
Origin and Purpose
- The Special Category Status (SCS) was introduced by the Fifth Finance Commission in 1969 to support states with historical economic or geographical disadvantages.
- The criteria for granting SCS included difficult terrain, low population density, significant tribal populations, border locations, and economic and infrastructural backwardness.
- This status was designed to assist these states in their development efforts by providing them with additional financial aid and incentives.
Discontinuation of SCS
- The 14th Finance Commission recommended the discontinuation of the SCS mechanism, proposing instead that the resource gaps of states be addressed by increasing the devolution of tax revenues from 32% to 42%.
- Despite this, 11 states, including the entire Northeast, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand, were granted SCS before the system was scrapped.
Why Does Andhra Pradesh Want SCS?
Historical Context
- When Andhra Pradesh was bifurcated in 2014 through the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) government had promised SCS to the residual state of Andhra Pradesh to compensate for the loss of revenue and developmental assets, particularly from Hyderabad, which became part of Telangana.
- This promise was seen as essential to address the financial disparities and developmental challenges faced by the new state.
Financial Disparities
- Post-bifurcation, Andhra Pradesh has struggled with financial deficits and increasing debt.
- Presentations by the AP government to NITI Aayog highlighted that the 14th Finance Commission’s estimated post-devolution revenue deficit for AP was significantly lower than the actual deficit. The state’s debt has risen sharply, illustrating the severe financial distress.
Economic Disadvantages
- The bifurcation resulted in AP inheriting a disproportionate share of the population, debt, and liabilities but only a fraction of the revenue-generating assets.
- This has led to a significant economic imbalance, with the state primarily relying on agrarian activities and lacking the economic buoyancy seen in Telangana, which retained Hyderabad and its associated economic benefits.
What Would Getting SCS Mean for Andhra Pradesh?
Financial and Economic Incentives
- Securing SCS would provide Andhra Pradesh with higher grants-in-aid from the central government.
- States with SCS receive significant financial benefits, including higher per capita grants and special industrial incentives such as income tax exemptions, custom duty waivers, reduced excise duty, and corporate tax exemptions.
- Additionally, the central government funds central schemes up to 90% in SCS states compared to 70% in non-SCS states.
Potential Benefits for Andhra Pradesh
- The AP government argues that SCS would spur rapid industrialization, creating employment opportunities and fostering overall development.
- The special incentives associated with SCS are seen as crucial for attracting investments, boosting the state’s economy, and addressing its developmental needs.
Challenges and Potential Compromises:
- Granting SCS to Andhra Pradesh alone could be challenging for the BJP, as other states like Bihar and Odisha have also demanded similar status. The 14th Finance Commission’s stance that SCS is a burden on central resources adds to the complexity.
- However, a potential compromise could involve granting SCS for a limited period or providing targeted financial assistance and development projects to meet Andhra Pradesh’s needs.
| What are the Concerns Related to Special Category Status? |
|
Resource Allocation: Granting SCS entails providing additional financial assistance to the state, which can strain the central government’s resources. Balancing the allocation of funds among various states becomes crucial, and granting SCS might lead to disparities or dissatisfaction among non-SCS states. Dependency on Central Assistance: States with SCS often become heavily reliant on central assistance. This could potentially discourage efforts toward self-sufficiency and independent economic growth strategies. Implementation Challenges: Even after the grant of SCS, there might be challenges in utilizing the funds effectively due to administrative inefficiencies, corruption, or lack of proper planning. Ensuring that the allocated funds are used for intended purposes is a significant challenge. |
| Practice Question: Examine the significance of Special Category Status (SCS) for Andhra Pradesh and discuss the challenges and potential benefits associated with its implementation. (250 words/15 m) |
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 02)
Prelims Facts
1. PMI signals services growth receded to a 5-month low in May
| Context |
| In May, India’s services sector experienced a slight slowdown due to competition, price pressures, and a heat wave, Despite this, international orders surged significantly, boosting confidence among firms.Hiring activity also rose to its highest level since August 2022, albeit input costs increased, particularly for labor and materials. |
What is Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI)?
- Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is an economic indicator used to gauge the health of a country’s manufacturing sector.
- It’s based on surveys of purchasing managers at private sector companies.
- PMI readings above 50 indicate expansion, while those below 50 signify contraction.
- Components of PMI typically include new orders, production, employment, supplier deliveries, and inventories.
- It provides insights into business conditions, including trends in output, employment, and inflation.
- PMI data is closely watched by investors, policymakers, and analysts for assessing economic activity and making informed decisions.
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
2. Health, Defence Ministries to set up Tele MANAS cell
| Context |
| The Ministries of Health and Family Welfare and Defence signed an MoU to collaborate on operating a Tele MANAS cell, an extension of the District Mental Health Programme.Tele MANAS offers 24/7 tele-mental health services via a toll-free number, 14416, across India. |
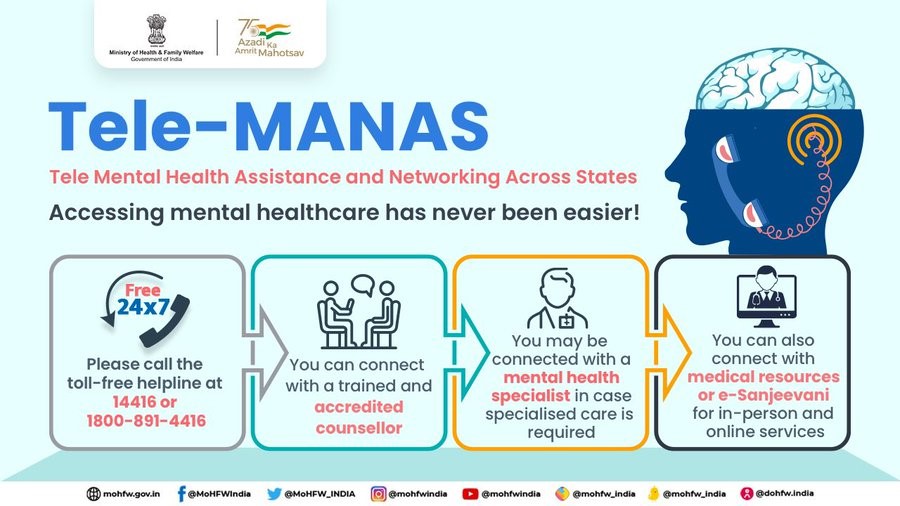
What is Tele MANAS Cell?
- Tele MANAS cell is an initiative facilitating tele-mental health services in India.
- It’s a digital extension of the District Mental Health Programme (DMHP).
- Operated jointly by the Ministries of Health and Family Welfare and Defence.
- Aims to provide comprehensive, integrated, and inclusive mental health support.
- Offers 24/7 services accessible via a toll-free number, 14416, in every State and Union Territory.
- Utilizes telecommunication technology to bridge gaps in mental health care accessibility and provide assistance remotely.
- Aims to address the growing mental health needs across the country efficiently.
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 8)
3. HRW says Israel used white phosphorous in Lebanon
| Context |
| Human Rights Watch accused Israel of using white phosphorus incendiary shells on residential buildings in southern Lebanon, potentially violating international law.Israel maintains it uses white phosphorus only as a smokescreen and denies targeting densely populated areas.Lebanon’s Health Ministry reports 173 people requiring medical care due to exposure. |
White phosphorus:
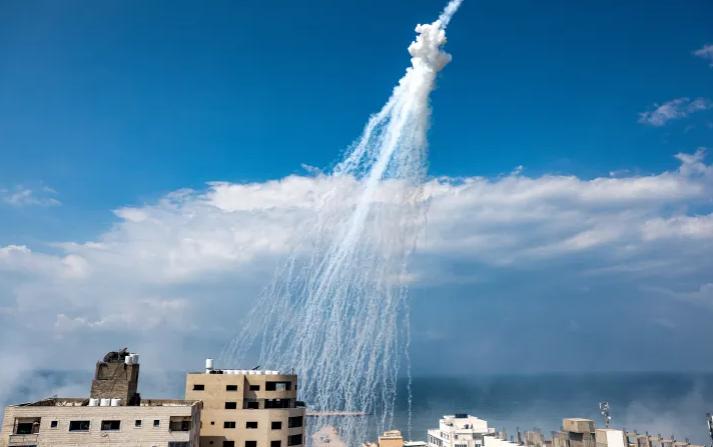

Artillery-delivered white phosphorus munition being airburst over Kfar Kila, a Lebanese border village with Israel.
- White phosphorus is a highly reactive chemical substance used in various military applications.
- It can create smoke screens, mark targets, and, controversially, as an incendiary weapon.
- Upon exposure to air, it ignites spontaneously, burning at extremely high temperatures.
- It can cause severe burns upon contact with human skin, often burning down to the bone.
- The use of white phosphorus as an incendiary weapon is highly contentious and regulated by international law.
- Accusations of its use in civilian areas raise concerns about potential harm to non-combatants.
- Its use has been reported in various conflicts, including the Lebanon-Israel conflict and the Iraq War.
- Despite its utility in warfare, its effects on civilians and the environment raise significant ethical and legal questions.
Human Rights Watch (HRW):
- Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organisation (NGO) advocating for human rights.
- It conducts research and advocacy on a wide range of human rights issues globally.
- Founded in 1978, it investigates and exposes human rights abuses by governments and non-state actors.
- HRW publishes reports documenting violations, conducts fact-finding missions, and engages in public campaigns.
- The organisation focuses on issues such as freedom of expression, women’s rights, refugee rights, and humanitarian law.
- It operates in over 90 countries, with offices and researchers worldwide.
- HRW often collaborates with local activists, lawyers, and victims to amplify their voices and push for accountability.
- The organisation’s work aims to hold perpetrators accountable, seek justice for victims, and promote human rights globally.
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)





