22 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Centre plans to take caste count during Census
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|

Ongoing Discussions for Caste Enumeration in Census
- The Union government is actively discussing whether to include caste enumeration in the next Census.
- The demand for a caste census is being raised by various political parties, including those in the ruling alliance.
- No final decision has been made yet regarding caste data inclusion in the Census.
Historical Context and Previous Efforts
- India has not conducted a caste-wise population count, except for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST), since independence.
- A separate caste census was carried out in 2011 but was never published, and the data was found to be inaccurate.
- The 1931 Census recorded 4,147 castes, while the 2011 Socio-Economic and Caste Census (SECC) identified more than 46 lakh castes and sub-castes.
Challenges and Concerns
- Concerns about errors in caste data led the government to declare the 2011 caste enumeration unreliable.
- Political parties’ demands for a caste census have contributed to the delay of the Census.
Digital and Delayed Census
- The upcoming Census, scheduled originally for 2021, was delayed due to the pandemic and other factors.
- It will be India’s first digital Census, allowing respondents to fill the questionnaire online.
- The boundary freeze deadline for administrative divisions lapsed on June 30, 2024, after being extended multiple times.
Caste Census Initiatives in States
- Bihar completed and published its caste census in 2023.
- Other states like Karnataka also conducted caste censuses, but their reports remain unpublished.
| Benefits and Challenges associated with caste census: |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential benefits of including caste enumeration in the Census for policy formulation and social welfare programs. How could this data influence affirmative action and resource allocation in India? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. SC makes suo motu move to reform advocates’ bodies
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Issues Observed by the Supreme Court in Bar Bodies
- High Election Expenses: Candidates face significant costs during elections to Bar bodies, which can be prohibitive and influence the election process.
- Arbitrary Admission Criteria: The criteria for admissions to Bar associations and Bar Councils are perceived as inconsistent and lacking transparency.
- Poor Facilities: Many Bar bodies offer inadequate facilities, impacting the functioning and effectiveness of legal professionals.
- Criminal Antecedents: Concerns have been raised about individuals with criminal backgrounds being elected as office-bearers in Bar associations.
- Elitism Allegations: Complaints of elitism and exclusivity in Bar associations, as highlighted by a young lawyer’s allegation against the Madras Bar Association.
Way Forward
- Independent Arbitrator: Consider appointing an independent arbitrator to address and resolve disputes and issues within Bar bodies.
- Comprehensive Examination: Conduct a thorough examination of the various aspects affecting Bar bodies to identify and address systemic problems.
- Collating Suggestions: Gather recommendations from Bar associations, State Bar Councils, and other relevant bodies to formulate effective reforms.
- Improving Transparency: Enhance transparency in election processes and admission criteria to ensure fairness and inclusivity.
- Facility Upgrades: Invest in improving facilities offered by Bar bodies to support better functioning and services for legal professionals.
| What is a Bar Council? |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the issues identified by the Supreme Court in Bar bodies and propose measures to address these concerns and improve the functioning of Bar associations and Bar Councils. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. SC to examine need for environmental regulator
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Observations by the Supreme Court
- Need for Regulator: The Court is considering the establishment of a permanent environmental regulator similar to those in telecom and electricity sectors.
- Fragmented Regulation: Current environmental and climate regulators operate in isolation, leading to fragmented oversight.
- Government’s Mixed Response: The Union government expressed concerns that a new regulator might duplicate existing structures and layers of decision-making.
Need for Environmental Regulator
- Unified Oversight: Establishing a permanent environmental regulator would provide a cohesive body to oversee and integrate various environmental and climate-related functions.
- Enhanced Coordination: A central regulator could improve coordination among existing environmental authorities, reducing fragmentation and inefficiencies.
- Streamlined Monitoring: This would enable more effective enforcement of environmental standards, ensuring better compliance across sectors.
- Comprehensive Approach: A single regulator could address the comprehensive nature of environmental issues, combining expertise from different fields into a unified strategy.
- Reduced Duplication: By consolidating regulatory functions, a new body could minimise overlapping responsibilities and streamline decision-making processes.
- Improved Accountability: A dedicated regulator would enhance accountability and transparency in environmental governance, offering a clearer point of contact for addressing grievances and ensuring regulatory compliance.
| Practice Question: Evaluate the potential benefits and challenges of establishing a permanent environmental regulator in India. How could such a regulator impact the oversight of environmental and climate issues? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Africa can compliment India’s need for critical minerals needed for sectors like EVs: Union Minister Shri Piyush Goyal
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2047346 )
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
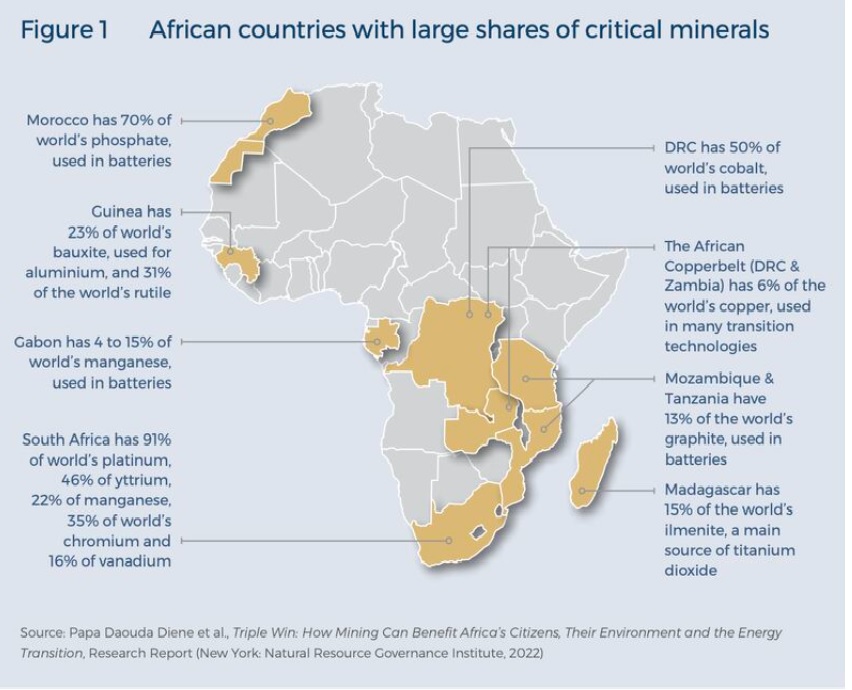
Africa’s Mineral Potential
- Africa is a major source of critical minerals crucial for various technological and industrial applications.
- The continent is rich in rare earth elements, lithium, cobalt, and other essential resources needed for electric vehicle batteries and renewable energy technologies.
- It also holds substantial deposits of gold, platinum, and diamonds, as well as industrial minerals like bauxite and phosphate.
- These resources are vital for supporting global tech advancements and industrial growth.
India-Africa Relations: A Collaborative Partnership
- Trade Expansion: The government has set a target to double trade between India and Africa within the next seven years, which can provide substantial economic advantages for both regions.
- Mineral Resources: Africa’s rich mineral deposits can meet India’s needs for critical materials used in electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies.
- Sustainable Mining: Joint efforts can lead to sustainable mining practices, enhancing environmental and economic outcomes.
- Technology Partnerships: Leveraging India’s Digital Public Infrastructure can drive technology adoption in Africa, fostering financial inclusion and digital development.
- Agricultural Collaboration: India can support Africa’s agricultural sector by facilitating the export of crops like oilseeds and pulses.
- MSME and Entrepreneurship: Strengthening MSME cooperation and fostering entrepreneurship can create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
- Financial Assistance: India has provided over US$12 billion in assistance to Africa through 196 Lines of Credit, supporting more than 42 countries.
- Cultural and Sports Exchanges: Enhancing collaboration in entertainment, sports, and cultural exchanges can strengthen mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Startup Ecosystems: Encouraging collaboration between startups in India and Africa can spur innovation and business growth.
- South-South Cooperation: Promoting partnerships aligns with broader goals for global cooperation and development.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of strengthening India-Africa relations in the context of mineral resources, technology partnerships, and economic cooperation. How can these collaborations contribute to sustainable development in both regions? (150 Words /10 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. 2023 Board Exams: State Boards See High Science Enrollment and Rising Failure Rates; Girls Outperform Boys
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 06)
| Context: |
| The analysis of the 2023 Class 12 board exams highlights significant trends in the choice of streams and pass/fail rates across various state and central boards in India. |
Analysis of News:
Stream Preferences:
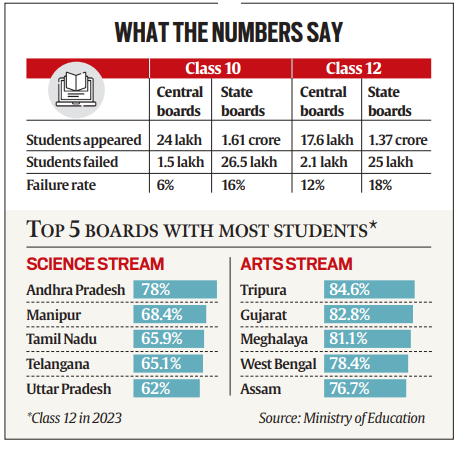
- Science Stream Dominance: Over 65% of students in Andhra Pradesh, Manipur, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana pursued science. Andhra Pradesh led with 78%.
- Arts Stream Preference: In Meghalaya, Tripura, West Bengal, and Nagaland, over 75% of students chose the Arts stream. Meghalaya had the highest Arts stream enrollment at 81.1%.
Failure Rates:
- State vs. Central Boards: The overall failure rate was higher in state boards (18%) compared to central boards (12%).
- Regional Disparities: Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra state boards had the highest number of failing students, contributing 53% of the total failures.
- Class 10 Results: 16% of students failed in state boards, and 6% in central boards. Andhra Pradesh had the highest number of failures in class 10.
Gender and Pass Rates:
- Girls had a slightly higher pass percentage (51%) compared to boys (49%).
- More girls were in the Arts stream, but there was a noticeable increase in the number of girls in the Science stream from 2022 to 2023.
Retention and Enrollment:
- Low retention and enrollment rates were noted, with around 33.5 lakh students not progressing from class 10 to class 11.
Standardization Efforts:
- The PARAKH body under NCERT is working on achieving equivalence across different school boards, as recommended by the National Education Policy 2020.
2. Malaysia Revises Orangutan Diplomacy: Shifts to Sponsorship for Conservation Amid Criticism
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 07)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Initial Proposal and Rationale
‘Orangutan Diplomacy’:
- Ghani originally proposed the idea in May 2023, inspired by China’s “panda diplomacy,” where pandas are sent as diplomatic gifts.
- The aim was to alleviate concerns about the environmental impact of Malaysia’s palm oil industry, which has been linked to deforestation and the loss of orangutan habitats.
Sustainability Efforts:
- Malaysia, the world’s second-largest palm oil producer, has faced significant pressure to make its industry more sustainable.
- Ghani emphasized that Malaysia should demonstrate its commitment to sustainable palm oil production and environmental conservation.
Criticism and Response
Backlash from Conservationists:
- The initial proposal received widespread criticism from wildlife conservationists, who deemed it hypocritical.
- Critics argued that instead of gifting orangutans, Malaysia should focus on protecting their natural habitats, which are threatened by palm oil production.
Comparison to China’s Panda Diplomacy:
- Experts highlighted the differences between Malaysia’s proposal and China’s panda diplomacy, noting that China has established protected areas and state-of-the-art facilities for pandas, which Malaysia lacks for orangutans.
Revised Conservation Approach
Conservation Programs:
- Under the revised plan, funds from the sponsorships will be used for orangutan conservation efforts within Malaysia, including monitoring their safety and condition through collaboration with experts.
- This shift aims to address the concerns raised by conservationists and ensure better protection for the endangered species.
3. Corporate Employment Growth Slows to 1.5% in FY24 Amid Post-Pandemic Adjustments
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 11)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Post-Pandemic Impact
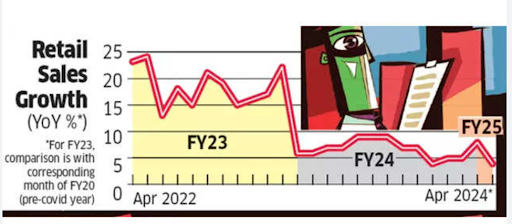
Post-Pandemic Effects:
- The surge in employment during FY23 was partly due to the post-pandemic recovery, where both voluntary and involuntary staff changes occurred.
- As businesses ramped up activities, there was a greater need for staff, which diminished in FY24.
Sector and Company Size Variations
Rationalization and Exclusions:
- The report highlights that the data mainly reflects larger to medium-sized companies, excluding micro and small enterprises.
- Some sectors underwent staff rationalization based on business prospects, contributing to the overall decline.
Mixed Outcomes Across Companies
Varied Employment Changes:
- Out of the 1,196 companies analyzed, 700 saw an increase in headcount, 121 remained unchanged, and 375 experienced a decline, indicating a mixed employment scenario at the micro level.
4. ICAR, Penn State team makes a tool small enough to edit plant genomes
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
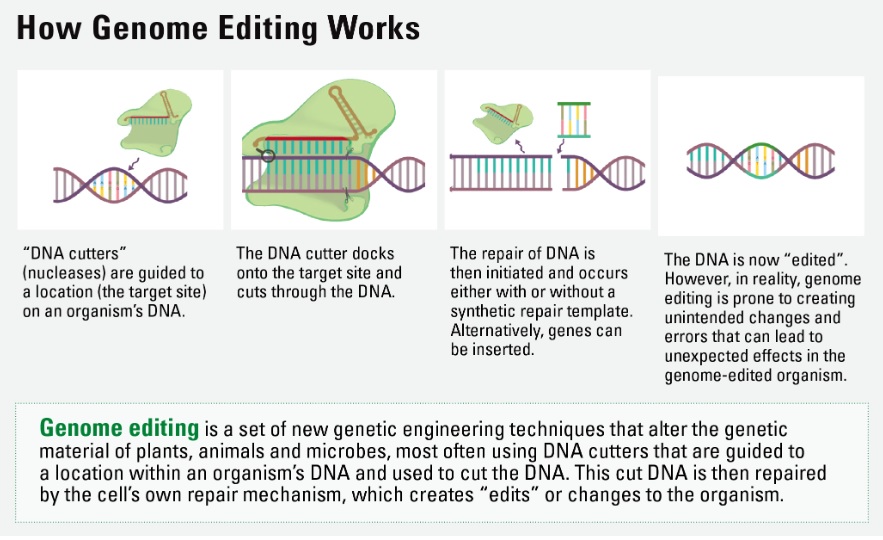
More information about gene-editing tool:
- Tool Name: TnpB-based genome editor
- Source: Derived from the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans.
- Size: Less than half the size of Cas9 and Cas12 proteins.
- Function: Targets specific DNA sequences and modifies them.
- Editing Efficiency: Achieved 33.58% efficiency in average plant genomes.
- Applications: Effective in both monocots (e.g., rice) and dicots (e.g., Arabidopsis).
- Improvements: Includes codon optimization and added regulatory elements for better performance.
- Capabilities: Supports base editing and transcription activation for precise gene modifications.
- Potential Uses: Enhances crop traits, improves resistance, and removes anti-nutrient factors.
5. Earth whistles when lightning strikes, and there’s a new melody
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Why does the Earth whistle when lightning strikes?
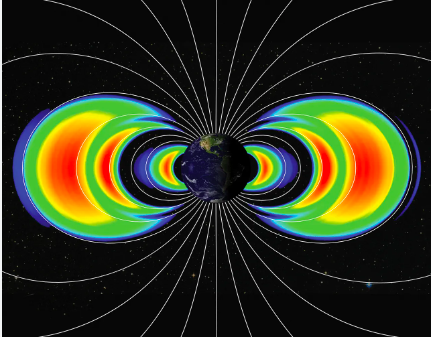
- Earth’s magnetosphere protects the planet by trapping charged particles from the Sun and cosmic radiation in the Van Allen radiation belts.
- Lightning strikes release electrical energy as electromagnetic waves, some of which are known as whistler waves.
- These waves travel along Earth’s magnetic field lines, moving between the northern and southern hemispheres.
- The frequencies of whistler waves are within the human hearing range (20–20,000 Hz) and can travel at speeds up to a tenth of the speed of light.
New Research:
- Recent research from the University of Alaska Fairbanks discovered a new type of whistler wave generated by lightning energy reflected from the ionosphere into the magnetosphere.
- This new wave mechanism suggests that more lightning energy may enter the magnetosphere than previously thought.
- The finding could impact calculations of lightning’s effects on the Van Allen belts and has implications for space exploration.
| Van Allen belts |
|