10 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India, UAE ink pact for civil nuclear cooperation
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
|
India-UAE Civil Nuclear Cooperation:
First-ever MoU for Nuclear Cooperation:
- India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) for civil nuclear cooperation.
- The agreement was made between Nuclear Power Corporation of India Ltd. (NPCIL) and the ENEC-led Barakah Nuclear Power Plant Operations and Maintenance.
- This is the first such agreement between the two nations and aligns with their commitment to “peaceful use of nuclear energy” as agreed during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s 2015 UAE visit.
Trilateral Cooperation Initiative:
- The MoU is a result of ongoing discussions between India and the UAE.
- On September 19, 2022, India, France, and the UAE established a trilateral cooperation format to enhance collaboration in energy sectors, including solar and nuclear energy.
Additional Agreements: In addition to the nuclear deal, India and the UAE signed several other agreements:
- Long-term LNG Supply: An MoU between Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) and Indian Oil Corporation Ltd.
- Production Concession Agreement: An agreement between ADNOC and India Strategic Petroleum Reserve Ltd. for Abu Dhabi Onshore Block 1.
- Food Parks Development: An MoU between the Government of Gujarat and Abu Dhabi Developmental Holding Company PJSC (ADQ).
Broader Diplomatic Context:
- The visit of the Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi also saw the signing of agreements coinciding with the first India-Gulf Cooperation Council meeting in Saudi Arabia.
- India and the UAE are members of the I2U2 grouping, which includes Israel and the United States.
| PYQ: In what ways would the ongoing US-Iran Nuclear Pact Controversy affect the national interest of India? How should India respond to this situation? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) for civil nuclear cooperation. What are its implications for India’s energy and strategic interests? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. On the challenges to road safety in India
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Overview and Key Findings of the Study
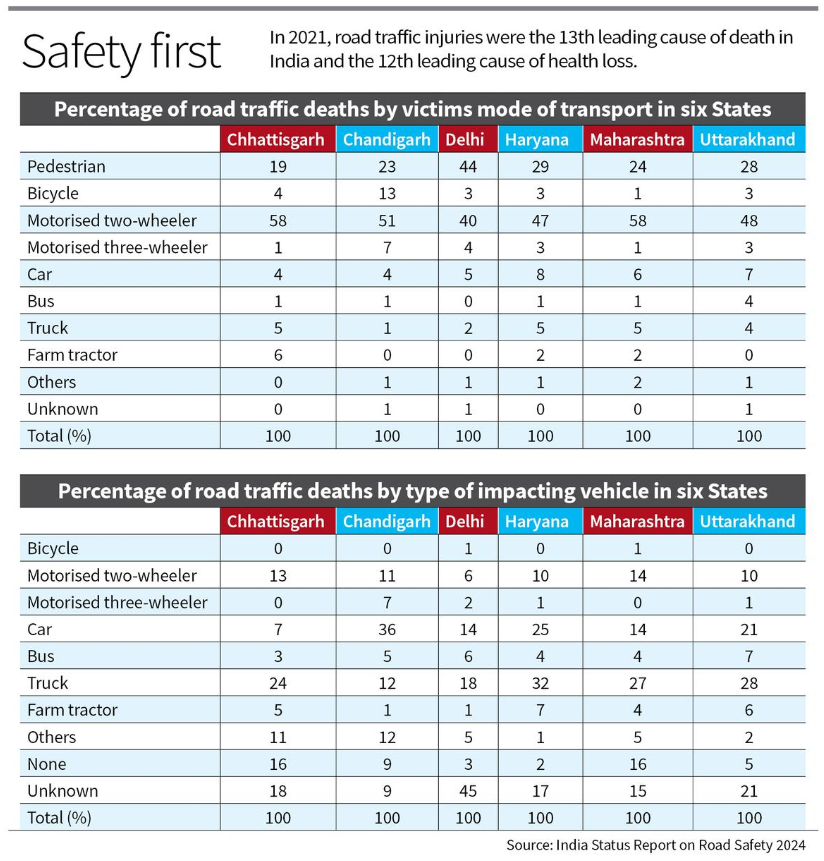
- Insufficient Progress: India is lagging in meeting international road safety goals.
- Data Analysis: Study used FIR data from six States and audits of road safety governance.
- High Fatality Rates: Motorcyclists are particularly vulnerable; truck crashes are frequent.
- Public Health Challenge: Road traffic injuries are a major health issue, with minimal progress in reducing fatalities.
- Disparities: Significant differences in road safety performance across States.
Global Comparison
- India vs. Developed Countries: In 2021, Indians were 600% more likely to die in road accidents compared to people in Sweden and other Scandinavian countries, up from 40% more likely in 1990.
Why is crash surveillance necessary?
- Crash surveillance is essential because it provides detailed, accurate data on road traffic incidents, which is critical for effective public policy and intervention.
- Without a national crash-level database, current statistics, derived from aggregated FIRs, are often inaccurate and inadequate for thorough analysis.
- This data gap hinders targeted road safety measures, effective program evaluation, and accurate understanding of risks, impeding progress in reducing road traffic fatalities.
Issue of Road Safety in India
- Data Limitations: No national crash-level database; reliance on aggregated FIRs and audits.
- Disparities: Per capita death rates vary widely among States.
- High Risk Groups: Pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists are the most affected.
- Helmet Usage: Low in rural areas; only seven States have over 50% helmet usage.
- State Variability: Some States lack basic safety measures and adequate trauma care facilities.
Recommendations
- Establish National Database: Create a national crash-level database to guide policy and interventions.
- Improve Data Accuracy: Address inaccuracies in existing road safety statistics through continuous monitoring.
- Increase Helmet Usage: Promote helmet use, especially in rural areas, through stricter enforcement and awareness.
- Audit and Upgrade Infrastructure: Ensure comprehensive audits of National and State Highways; improve safety features like traffic calming, markings, and signage.
- Tailored Strategies: Develop State-specific road safety strategies to address unique challenges.
- Enhance Trauma Care: Upgrade trauma care facilities to better handle road traffic injuries.
- Prioritise Interventions: Central and State governments should scale up road safety interventions and public access to data.
| Practice Question: Discuss the key findings of the “India Status Report on Road Safety 2024” and analyse the implications of the report’s recommendations for improving road safety in India. How does India’s road safety performance compare globally? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. India and US Forge New Semiconductor Partnership to Strengthen Global Supply Chain
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
|
Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
India-US Semiconductor Partnership
- Ahead of Prime Minister Modi’s expected visit to the US, Washington announced a new partnership with India to explore opportunities in the semiconductor supply chain.
- This collaboration will involve a comprehensive assessment of India’s current semiconductor ecosystem, regulatory framework, workforce, and infrastructure needs.
- This groundwork will pave the way for future joint initiatives to strengthen the sector.
Purpose and Scope of the Partnership
- The US Department of State will collaborate with the India Semiconductor Mission to enhance and diversify the global semiconductor ecosystem.
- The initial phase involves engaging Indian stakeholders like state governments, educational institutions, and private companies to identify areas of improvement.
- The partnership aims to create a resilient and secure global semiconductor value chain, addressing the demands of global digital transformation.
Alignment with the CHIPS Act
- This initiative aligns with the CHIPS Act of 2022, signed by US President Joe Biden, which seeks to boost domestic semiconductor manufacturing and research.
- The act also created the International Technology Security and Innovation (ITSI) Fund, with $500 million allocated to promote secure semiconductor supply chains and trusted telecom technologies in collaboration with global allies, including India.
Potential Impact
- The partnership underscores the strategic importance of semiconductors in manufacturing essential products such as vehicles and medical devices.
- By strengthening India’s semiconductor industry, both nations aim to benefit from a more robust supply chain, ensuring global competitiveness and security in the technology sector.
|
Where does India Stand in the Semiconductor Market? |
|
|
Practice Question: Analyze the significance of the new semiconductor partnership between India and the US. How might this collaboration impact both nations’ semiconductor industries and their broader technological strategies? (250 words/15 m) |
4. Supreme Court Directs Himachal Pradesh HC Collegium to Reconsider Judicial Elevation
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Procedure for Appointing High Court Judges
- The collegium system, established by the Second Judges Case (1993), involves the Chief Justice of India (CJI) and senior Supreme Court judges making recommendations for appointments.
- The government can delay appointments but cannot reject the collegium’s choices.
- For High Court appointments, the HC collegium consults the Chief Justice, senior HC judges, and relevant SC judges, following a Memorandum of Procedure (MoP).
Case Background: Himachal Pradesh HC
- In December 2022, the Himachal Pradesh HC collegium recommended Singh and Malhotra for elevation.
- However, after SC collegium reconsideration and the Law Minister’s request for fresh recommendations, the HC collegium recommended two other judicial officers in April 2024, leading Singh and Malhotra to challenge the decision.
Supreme Court’s Decision
- Maintainability: The SC ruled the case fell within its scope of review to assess whether “effective consultation” occurred following its January 4 resolution.
- Proper Procedure: The SC held that the HC Chief Justice acting alone did not meet the requirement of “collective consultation” with the senior-most HC judges. The collegium must act collectively in such matters.
|
Procedure to appoint judges of High Courts |
|
Constitutional Provision
Eligibility
Procedure
Controversy over the Word Consultation
Evolution of Collegium System First Judges Case (1982)
Second Judges Case (1993)
Third Judges Case (1998)
|
|
PYQ: Critically examine the Supreme Court’s judgement on ‘National Judicial Appointments Commission Act, 2014’ with reference to appointment of judges of higher judiciary in India. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
|
Practice Question: Discuss the role of the collegium system in the appointment of judges to the High Courts and the Supreme Court in India. In light of recent developments, critically evaluate the challenges and effectiveness of the collegium system in maintaining judicial independence and transparency. (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Professor, translator K. Chellappan passes away at 88
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
| Professor K. Chellappan, an acclaimed translator and scholar known for his Sahitya Akademi Award-winning Tamil translation of Gora and significant contributions to comparative literature, has passed away at 88. |
K. Chellappan, commonly known as K.C.:
- Awards: Sahitya Akademi Award for Tamil translation of Rabindranath Tagore’s Gora (2020)
- Academic Focus: Comparative studies; doctorate on “Shakespeare and Ilango as Tragedians”
- Contributions:
- Authored The World as a Stage: Shakespearean Transformations and other literary works.
- Translated M. Karunanidhi’s works, including Kuraloviyam and Thenpandi Singam.
- Supervised over 50 Ph.D. students.
- Teaching and Philosophy:
- Known for bridging English and Tamil literary worlds.
- Advocated translation as an act of cognition and creation.
- Believed in balancing fidelity to the original with creative liberties.
2. Two anti-submarine warfare vessels for the Indian Navy launched at Cochin Shipyard
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Vessels Launched: Two anti-submarine warfare shallow watercraft vessels, INS Malpe and INS Mulki, were launched at Cochin Shipyard.
- Specifications:
- Length: 78 metres
- Width: 11.36 metres
- Draught: 2.7 metres
- Maximum Speed: 25 knots
- Endurance: 1,800 nautical miles
- Displacement: 900 tonnes
- Design and Features:
- Designed to accommodate indigenously developed sonar for underwater surveillance.
- Equipped with light-weight torpedoes, anti-submarine warfare (ASW) rockets, and mines.
- Includes close-in weapon systems and stabilised remote-control guns.
- Installed propulsion power: 12 MW
- Purpose and Role:
- To replace the Abhay-class ASW corvettes.
- Intended for anti-submarine operations in coastal waters, low-intensity maritime operations, mine-laying, and search and rescue.
3. Why do rockets require helium?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
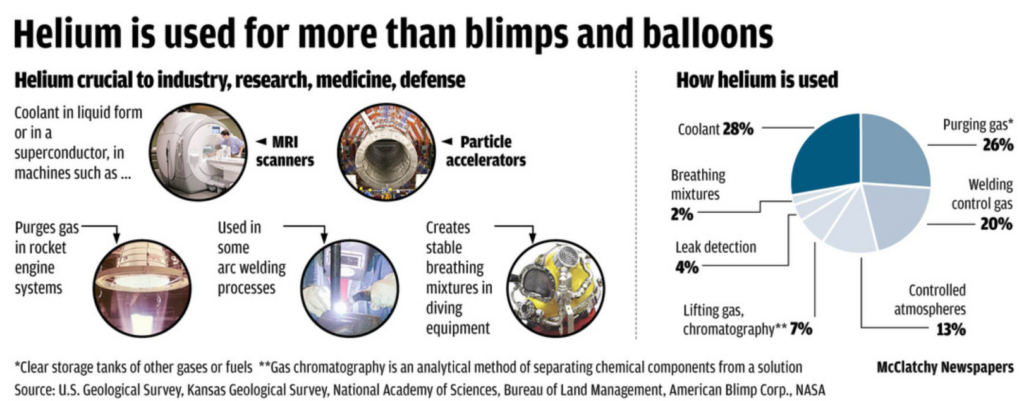
Importance of helium:
- Pressurisation: Helium is used to pressurise fuel tanks, ensuring that fuel flows smoothly to the rocket engines without interruption.
- Cooling Systems: Its low boiling point (-268.9°C) allows it to remain a gas in super-cold environments, aiding in cooling systems.
- Non-reactive: Being inert, helium safely interacts with the tanks’ residual contents without chemical reactions.
- Density: Helium’s low density helps it fill empty spaces in tanks as fuel is used, maintaining pressure.
- Leak Detection: Helium’s presence in trace amounts makes it easier to detect leaks in rocket systems.
- Alternative: While argon and nitrogen are alternatives, helium’s prevalence and properties make it a preferred choice.
| Boeing’s Starliner And SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn Mission |
|
Boeing’s Starliner Mission Objective: To validate the Starliner spacecraft’s ability to safely transport astronauts to and from the International Space Station (ISS) under NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Launch Date: Orbital Flight Test-3 (OFT-3) is planned for late 2024. Crew: Uncrewed for the OFT-3, with future missions intended to carry astronauts. Destination: Will dock with the ISS, allowing astronauts to conduct research and perform maintenance. Significance: Successful completion will enhance NASA’s ability to perform regular ISS missions and potentially support future missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn Mission Objective: To advance human spaceflight technology, perform scientific research, and test new technologies such as a commercial spacewalk suit and laser communication systems. Launch Date: Expected to launch in early 2025. Crew: A team of four, including Jared Isaacman and three US Air Force personnel. Destination: High Earth orbit, without docking at the ISS. Significance: Will test cutting-edge technology and contribute to research in fields like medicine and astrophysics, advancing commercial space exploration capabilities. |
4. Google’s Privacy Sandbox adoption costs burden small ad-tech firms
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
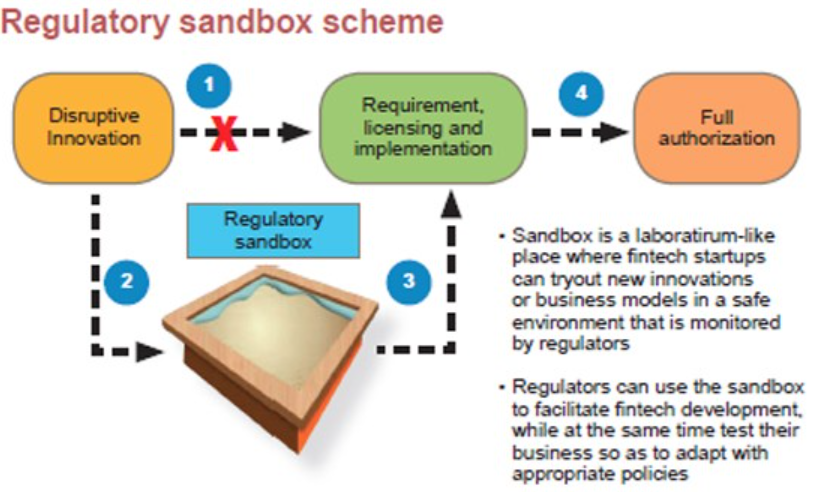
What is Google’s Privacy Sandbox?
- Google’s Privacy Sandbox is a set of technologies designed to replace third-party cookies and enhance user privacy on the web.
- It aims to anonymize data, implement stricter access controls, and enable ad targeting based on groups rather than individuals.
- The initiative seeks to improve privacy by reducing the ability to track and identify individual users while still allowing for effective digital advertising.
- Privacy Sandbox is being developed to address privacy concerns and regulatory pressures surrounding cookie-based tracking.
5. Five Successful Years of Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY)
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2053142 )
| Context |
|
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY):
- Launch Date: September 12, 2019
- Objective: Provides old-age pension to Small and Marginal Farmers (SMFs)
- Eligibility: Farmers with cultivable land holdings up to 2 hectares and listed in state/UT land records as of August 1, 2019
- Contribution: Monthly contributions range from Rs. 55 to Rs. 200, based on entry age, with matching contributions from the central government
- Pension: Fixed monthly pension of Rs. 3,000 starting at age 60
- Family Pension: Rs. 1,500 per month to the spouse if the subscriber dies, provided the spouse is not already a beneficiary
- Management: Fund managed by LIC, with registration through Common Service Centres (CSCs) and State Governments
- Current Enrollment: 23.38 lakh farmers as of August 6, 2024
- Key States: Bihar (3.4 lakh), Jharkhand (2.5 lakh), Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha with significant registrations

6. INDIA- USA JOINT MILITARY EXERCISE YUDH ABHYAS -2024 COMMENCES IN RAJASTHAN
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2053095 )
| Context |
|
Exercise YUDH ABHYAS-2024:
- Dates: September 9 to 22, 2024
- Location: Foreign Training Node, Mahajan Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan, India
- History: Held annually since 2004, alternating between India and the USA
- Participants: Indian Army’s RAJPUT Regiment (600 personnel) and US Army’s 1-24 Battalion, 11th Airborne Division (600 personnel)
- Objective: Enhance joint military capabilities for counter-terrorism operations in a semi-desert environment under Chapter VII of the UN Charter
- Focus Areas: Tactical drills, joint response to terrorism, joint planning, and combined field training exercises
- Outcomes: Improved interoperability, sharing of best practices, strengthened defence cooperation, and enhanced bilateral relations
7. Minister Pledges to Replace Sakthan Thampuran Statue, Honoring Historic Ruler’s Legacy in Thrissur
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News: 
Sakthan Thampuran: Ruler of Cochin Kingdom
- Sakthan Thampuran, born in 1751 as Rama Varma IX, ruled the Cochin kingdom from 1790 to 1805.
- Known for his powerful rule, he restructured the kingdom and fostered relations with both the Dutch and British during a time of regional conflict.
Strategic Diplomacy and Reforms
- Sakthan Thampuran played a key role in securing Cochin’s independence from Mysore and established a formal relationship with the British.
- He also abolished the institution of Yogiatirippads, taking control of temple management and ensuring administrative reforms.
Development of Thrissur and Introduction of Thrissur Pooram
- Sakthan Thampuran relocated the kingdom’s capital to Thrissur, laying the foundation for its modern infrastructure and encouraging religious and commercial growth.
- He is credited with starting the famous Thrissur Pooram festival in 1797, enhancing the cultural prominence of the city.
8. DRC Receives First Mpox Vaccine Amid Global Surge, Africa Faces Shortages
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
|
Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
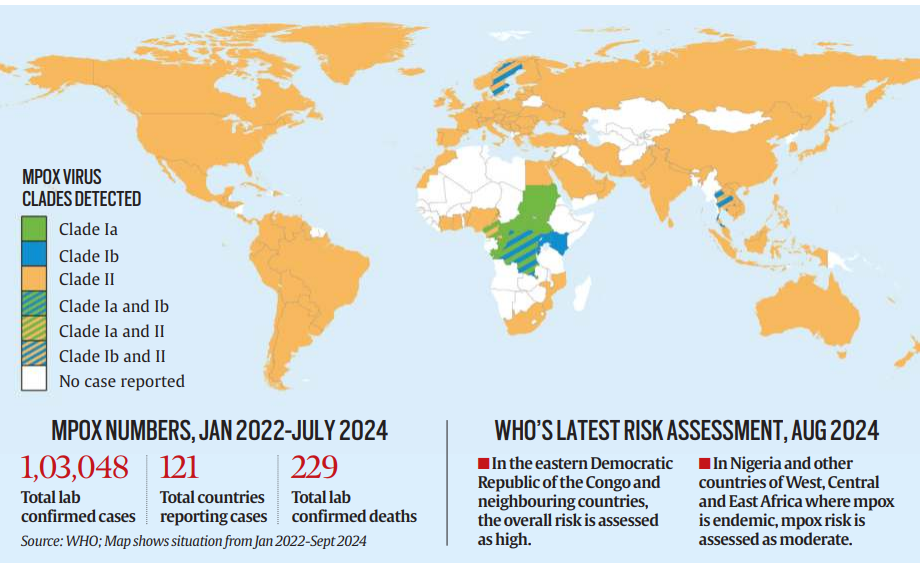
Vaccine Shortages in Africa
- Despite the increase in cases, Africa faces vaccine shortages. Only DRC and Nigeria have mpox vaccines, which has contributed to the rapid spread, prompting WHO to declare a global health emergency.
Spread and Variants of Mpox
- Mpox was first reported in humans in 1970, with two main clades: Clade I (deadlier) and Clade II.
- The newly spotlighted Clade Ib is spreading more rapidly, including through sexual activity, affecting more women and children. Scientists are still studying the transmission patterns.
Available Mpox Vaccines
Three mpox vaccines are currently available:
- Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA): Manufactured by Bavarian Nordic, approved by the FDA and EMA, and supplied to the DRC.
- LC16m8: Produced by Japan’s KM Biologics, approved only by Japan.
- ACAM2000: Made by Emergent BioSolutions, recently approved by the FDA.
New vaccines are being developed by BioNTech and Serum Institute of India (SII).
Africa’s Vaccine Access Challenges
- Vaccines are expensive ($50-$75 per dose), leading to reliance on donations and purchases by organizations like Gavi and UNICEF. Delays in WHO approvals for emergency use have hindered vaccine distribution.
Prevention and Vaccination Strategies
- Vaccination is recommended for high-risk populations, particularly during outbreaks.
- Post-exposure vaccination within four days is advised for those in contact with an infected person, and up to 14 days if symptoms have not yet developed.



