16 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India’s Economic Shift: Service Sector Growth Outpaces Manufacturing, Limiting Job Creation in Low-Skill Industries
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
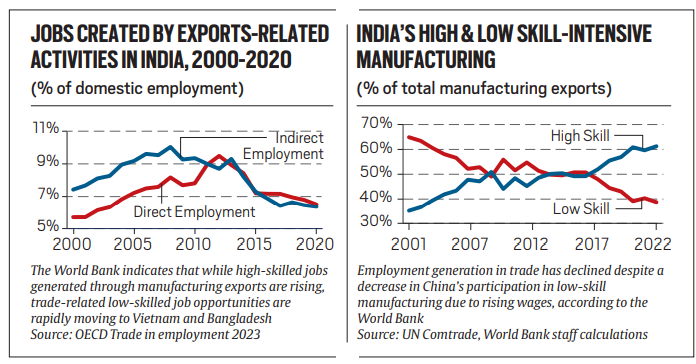
Decline in Labour-Intensive Jobs
- The shift to high-skill sectors has caused a reduction in low-skilled job creation. The World Bank reported that export-related jobs have decreased, with direct employment linked to exports falling from 9.5% in 2012 to 6.5% in 2020.
- This decline is largely due to the dominance of the services sector and high-skill manufacturing in India’s export portfolio, reducing opportunities for low-skilled workers.
India’s Missed Manufacturing Opportunity
- Despite China’s exit from low-skill manufacturing, India has been unable to capture this market, losing ground to countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam.
- Initiatives like the PM MITRA Textile Parks and Industrial Smart Cities aim to address these shortcomings but are yet to show significant results.
Rise of Global Capability Centres (GCCs)
- While manufacturing has slowed, India has emerged as a hub for Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in sectors like IT and software development.
- India is home to 1,600 GCCs, managing key functions for multinational companies.
- However, recent slumps in hiring by major IT firms like TCS and Infosys signal a slowdown in job creation even in the IT sector.
Declining Participation in Global Value Chains (GVCs)
- India’s low participation in Global Value Chains (GVCs) has been a barrier to job creation.
- Despite rapid economic growth, India’s trade in goods and services has declined, further limiting its role in international trade.
- High tariffs and complex procedures have hindered India’s competitiveness in global markets.
Conclusion
- India’s reliance on the services sector has limited job creation in low-skill industries.
- To address this, India needs structural reforms to boost manufacturing, improve GVC participation, and create jobs across all sectors.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of India’s economic shift from traditional manufacturing to a service-driven growth model, particularly focusing on the challenges in job creation for low-skilled workers and the declining participation in global value chains. Suggest measures to address these challenges. (250 words/15 m) |
2. India Faces ‘Food vs Cars’ Dilemma as Phosphoric Acid Diverted from Fertilizers to EV Batteries
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
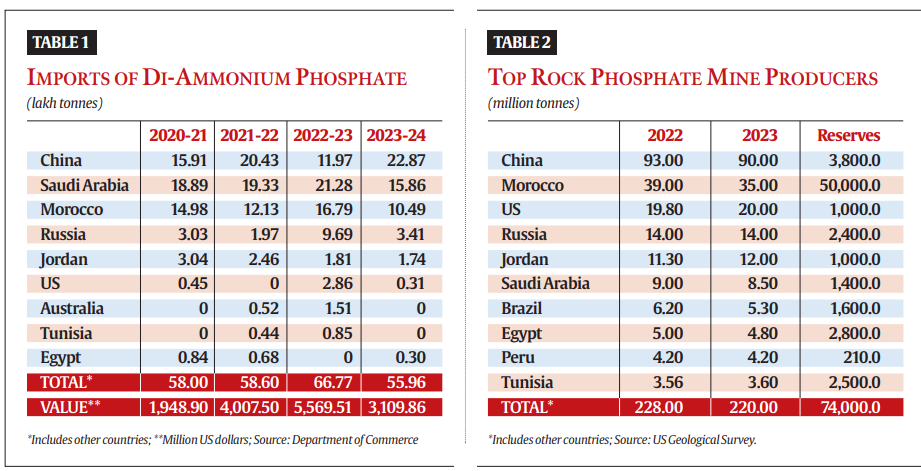
Impact on Agriculture and Fertilisers
- Dependency on Imports: India relies heavily on imports for DAP and its raw materials like phosphoric acid and rock phosphate from countries like China, Morocco, and Russia.
- Falling DAP Supply: The growing demand for LFP batteries in EVs, particularly in China, is reducing the availability of phosphoric acid for fertiliser production, which could impact Indian agriculture, especially during critical planting seasons like rabi and kharif.
Implications of Global Market Dynamics
- Shift to LFP Batteries: LFP batteries, which use iron phosphate instead of expensive and scarce minerals like cobalt, are gaining popularity, especially in China. This shift is expected to expand globally, reducing the availability of phosphoric acid for fertilisers.
- Risk of Supply Shortages: India’s dependence on foreign suppliers makes it vulnerable to global market changes, such as shifts towards battery production or geopolitical events affecting raw material supplies.
The Way Forward for India
- Diversification of Fertiliser Use: To reduce reliance on DAP, Indian farmers are turning to complex fertilisers with lower phosphorous content but higher nutrient efficiency. The government’s subsidy on DAP is also straining fertiliser companies.
- Securing Raw Material Supplies: India needs to secure more joint ventures and buy-back arrangements with phosphate-rich countries like Morocco to ensure a stable supply of phosphates for both fertiliser and industrial uses.
Conclusion
- The growing competition for phosphoric acid between agriculture (fertilisers) and the EV sector (batteries) poses a significant challenge for India.
- The country must adapt by diversifying fertiliser use and securing raw material supplies to mitigate the potential risks.
| Practice Question: In light of the increasing demand for lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) and the diversion of phosphoric acid from traditional fertilizers like di-ammonium phosphate (DAP), analyze the potential impacts on India’s agricultural sector and food security. (250 words/15 m) |
3. What are AM, FM, and signal modulation?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
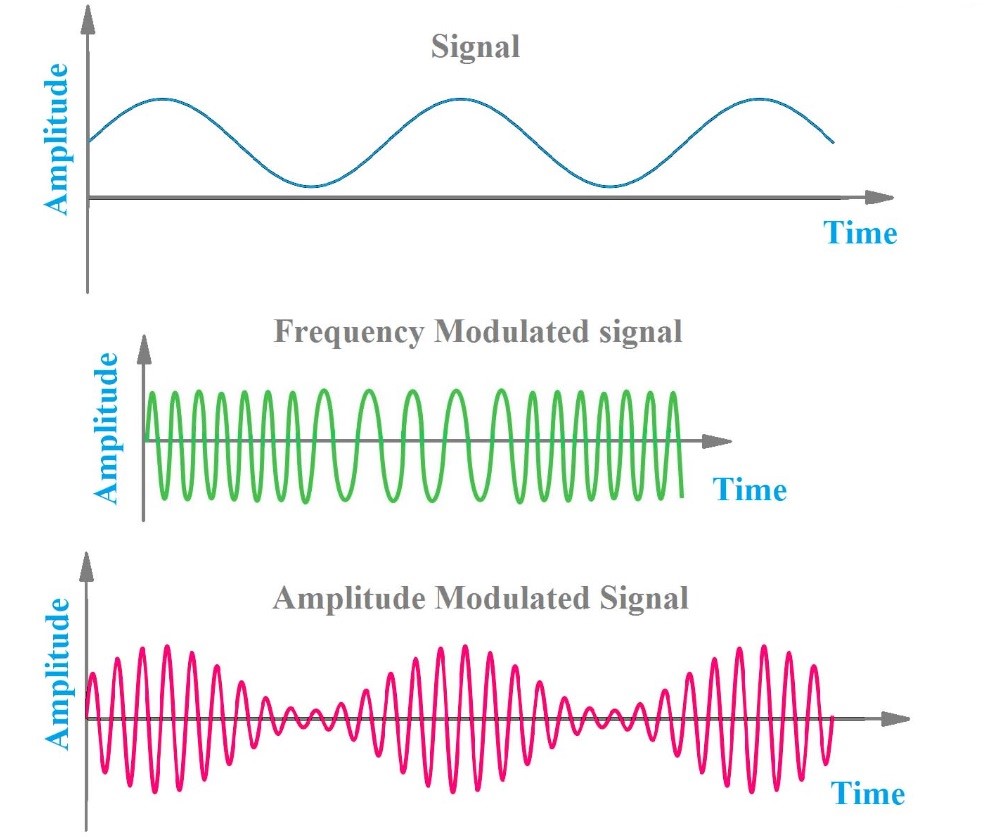
AM (Amplitude Modulation):
- In AM, information is encoded by varying the amplitude of a constant frequency carrier wave.
- The signal’s amplitude changes to represent different audio signals, with higher amplitudes corresponding to louder sounds.
- AM is used in AM radio broadcasts and is more susceptible to noise and interference.
FM (Frequency Modulation):
- FM involves encoding information by varying the frequency of a carrier wave.
- The frequency changes according to the amplitude of the input signal, resulting in different audio tones.
- FM provides better sound quality and is less prone to interference compared to AM. It is commonly used in FM radio broadcasts.
Signal Modulation:
- This is the technique used to encode information onto a carrier wave for transmission.
- There are several types of modulation, including AM and FM. Modulation simplifies the transmission of signals over long distances and through various media by altering key properties of the wave—amplitude for AM, and frequency for FM.
Amplitude Modulation (AM):
- In AM, the height (amplitude) of the wave changes to convey information. The frequency remains constant, but the strength of the signal varies.
Frequency Modulation (FM):
- FM adjusts the frequency of the carrier wave according to the information being transmitted. The amplitude remains constant, and changes in frequency carry the information.
Phase Modulation (PM):
- PM involves varying the phase of the carrier wave to encode information. It is often used in digital communication due to its resistance to signal amplitude variations and is less affected by interference.
Analog vs. Digital:
- Analog signals vary continuously, whereas digital signals are discrete. AM and FM are analog techniques, while PM is typically used for digital communication.
Advantages of Modulation:
- Modulation allows multiple signals to share the same channel without interference and enhances signal quality by minimising the effects of noise and static.
| Practice Question: Compare Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM) in terms of signal quality and interference resistance. What are the key advantages of using modulation techniques in communication systems? (150 Words /10 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. PM Modi Flags Off Six Vande Bharat Trains in Jharkhand, Lays Foundation for ₹660 Crore Railway Projects
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 06)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
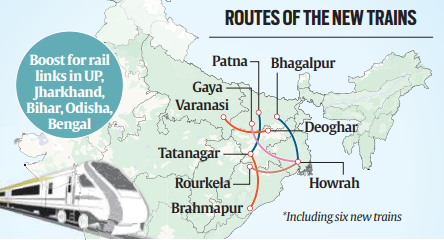
Enhanced Connectivity and Regional Impact
- The six Vande Bharat trains will connect major routes including Tatanagar-Patna, Bhagalpur-Dumka-Howrah, Brahmapur-Tatanagar, Gaya-Howrah, Deoghar-Varanasi, and Rourkela-Howrah, enhancing rail connectivity between Jharkhand and neighboring states like Bihar, Odisha, West Bengal, and Uttar Pradesh.
- This expansion is expected to strengthen the regional economy by benefiting businesses, professionals, and students.
Boost to Tourism and Cultural Activities
- Prime Minister Modi emphasized the cultural significance of the new trains, particularly the Varanasi-Deoghar route, which is expected to boost tourism by providing better access for pilgrims to visit religious sites such as Kashi and Baba Baidyanath.
- This, in turn, will create new job opportunities for the local youth in tourism-related sectors.
Infrastructure Development for Economic Growth
- Modi also highlighted the importance of modern railway infrastructure for the overall development of eastern India.
- The foundation stones laid for the Madhupur bypass line and a railway coach depot in Hazaribag will further improve travel efficiency, particularly reducing travel time between Giridih and Jasidih once completed.
2. Nipah death confirmed in Malappuram; 150 contacts asked to isolate themselves
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
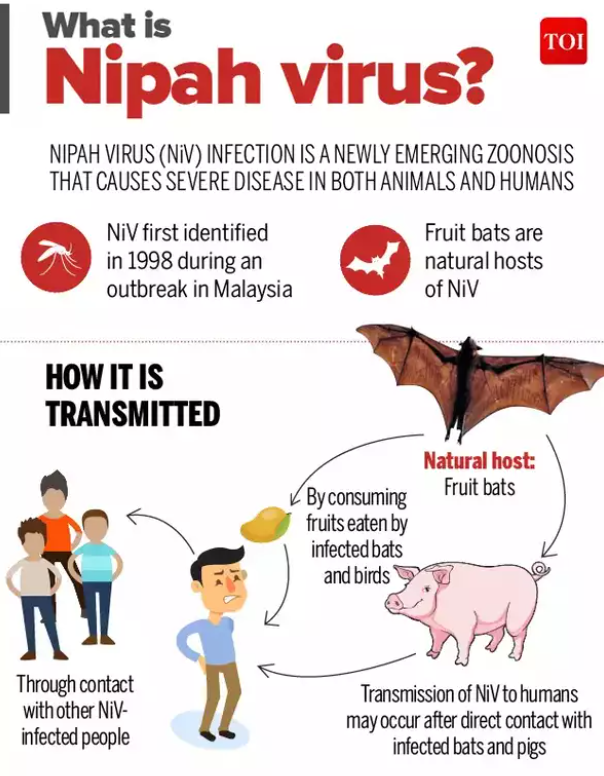
Nipah Virus (NiV):
- Zoonotic virus transmitted from animals (bats, pigs) to humans, or through contaminated food and human-to-human contact.
- Origins: First identified in Malaysia in 1998; associated with pig farming.
- Natural Host: Fruit bats (Pteropus species).
- Transmission: Direct contact with infected animals, consumption of contaminated fruits, or close contact with infected individuals.
- Symptoms: Fever, headache, respiratory issues, encephalitis (brain inflammation), and in severe cases, coma or death.
- Incubation Period: Typically 5-14 days, but can extend to 45 days.
- Fatality Rate: Between 40% to 75%, depending on outbreak management.
- No Specific Treatment: Only supportive care; antiviral research is ongoing.
- Prevention: Avoiding bat-contaminated food, practising good hygiene, and avoiding close contact with infected patients.
- Outbreaks: India (especially Kerala), Bangladesh, and Southeast Asia have faced multiple outbreaks.
3. India sends supplies to typhoon-hit Laos, Myanmar, Vietnam
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
| India launched Operation Sadbhav to aid Laos, Myanmar, and Vietnam hit by Typhoon Yagi.Committing $1 million to Vietnam and $100,000 to Laos, India deployed naval ships and IAF aircraft with relief supplies to assist flood-affected regions. |
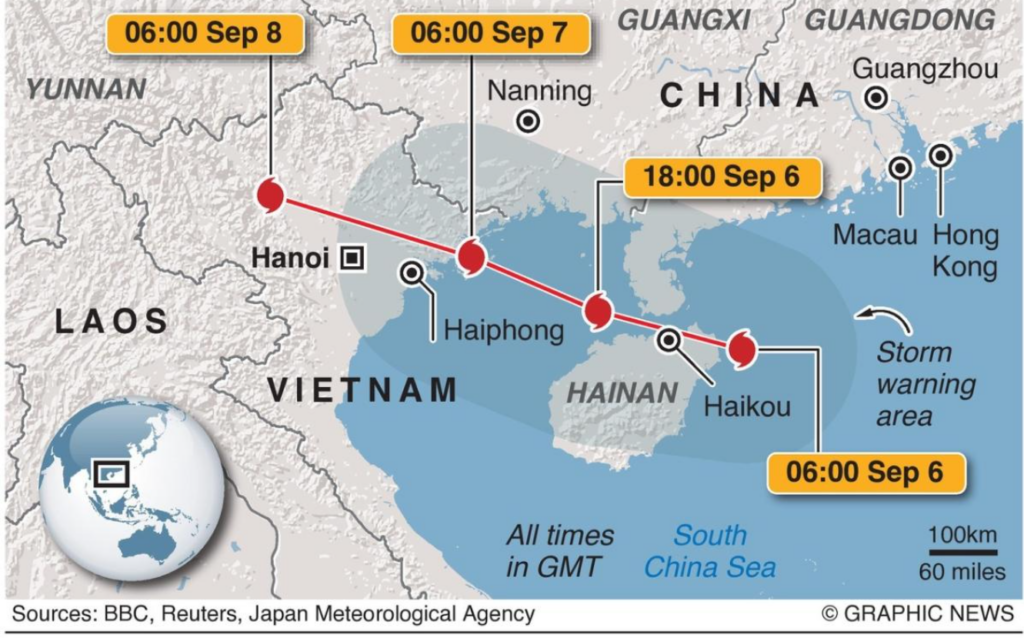
Typhoon Yagi:
- A tropical cyclone that originated in the Pacific Ocean.
- Formation: Developed as part of the northwest Pacific typhoon season.
- Affected Areas: Southeast Asian countries such as Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar are vulnerable to its impact.
- Impact: Caused heavy rainfall, severe flooding, and strong winds, leading to widespread damage in affected regions.
- Flooding: Resulted in significant damage to infrastructure, displacement of people, and loss of livelihoods.
- Humanitarian Assistance: Countries, including India, often launch relief operations to provide aid and support recovery efforts.
- Precautionary Measures: Evacuations and disaster preparedness help mitigate the typhoon’s impact on human life and property.
3. New research rescues the dodo’s reputation from confusion and myth
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Dodo Bird:
- The dodo was a flightless bird native to Mauritius.
- Closely related to pigeons and doves, it was known for its large size and inability to fly.
- The dodo became extinct in the late 17th century due to human activities and introduced species.
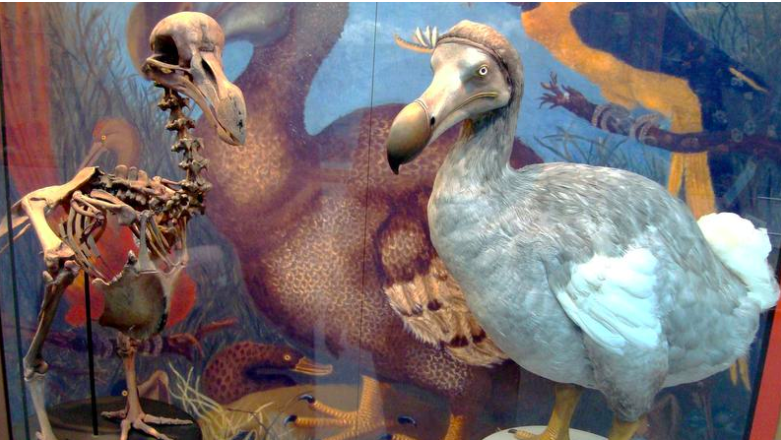

Extinction and New Research:
- Extinction caused by habitat destruction, predation by introduced animals (pigs, rats, goats), and overhunting.
- New research suggests dodos were not slow-witted but possibly swift runners.
- Studies reveal dodo’s taxonomy as part of the Columbidae family.
- Eyewitness accounts describe dodos as fast runners, challenging prior misconceptions.
- Current research aims to understand their extinction better and protect modern bird species.
4. DPIIT to launch BHASKAR: A Revolutionary Platform for India’s Startup Ecosystem
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2055243 )
| Context |
|
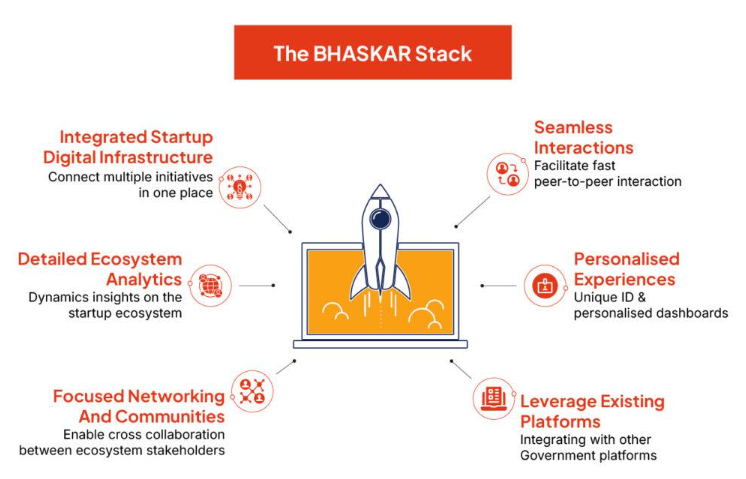
More About BHASKAR:
- Launched By: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Objective: Centralise and streamline collaboration within India’s startup ecosystem
- Target Stakeholders: Startups, investors, mentors, service providers, and government bodies
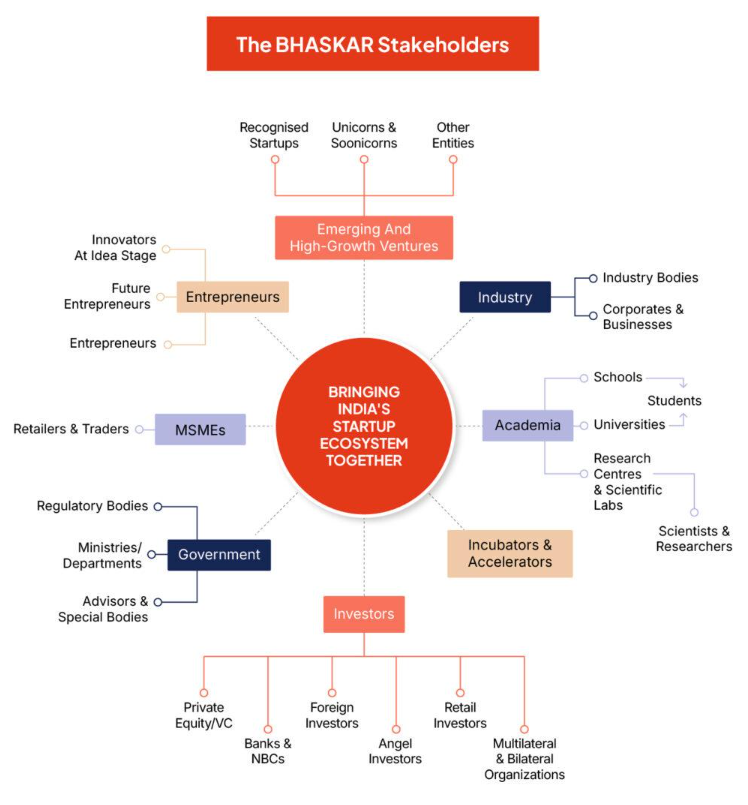
- Key Features:
- Networking and Collaboration: Facilitates seamless interaction across sectors
- Centralised Access: Provides startups with immediate access to tools and knowledge
- Personalised Identification: Unique BHASKAR IDs for each stakeholder
- Enhanced Discoverability: Powerful search features for locating resources and opportunities
- Impact: Supports India’s vision to be a global leader in innovation and entrepreneurship
- Launch Date: Scheduled for tomorrow
- Significance: Aims to create a more connected, efficient, and collaborative startup environment in India




