28 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Global Trade Tensions Escalate as US and India Respond to China’s Export Surge Amid Domestic Slowdown
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Rising Trade Tensions and Anti-Dumping Measures
- Countries, including India, are imposing anti-dumping and anti-subsidy measures to curb China’s export surge, fearing a repeat of manufacturing job losses seen after China’s entry into the WTO in the early 2000s.
- In 2024, India conducted over 30 anti-dumping investigations targeting Chinese products such as industrial machines and steel pipes, with Indian businesses accusing China of predatory pricing practices.
Historical Context: China’s WTO Entry and “China Shock”
- China’s accession to the WTO in the early 2000s, with expectations of political and economic reforms, led to the “China Shock”—the flooding of global markets with cheap Chinese goods.
- This disrupted global manufacturing, including in India, where imports from China surged significantly, hitting a record $100 billion in 2023-24 despite trade restrictions.
Domestic Slowdown Fueling Chinese Exports
- China’s export push is linked to its ongoing economic slowdown caused by a property crisis and weak domestic demand.
- This has led China to rely on global markets to absorb its excess industrial capacity, prompting concerns about a new wave of global economic disruptions, including in India, where imports from China rose nearly 60% between FY19 and FY24.
Impact on India’s Renewable Energy Sector
- China’s dominance in the global solar energy supply chain has resulted in India’s reliance on Chinese solar imports, which account for 80% of its solar cells and modules.
- China’s response to India’s anti-dumping investigations by restricting solar equipment exports threatens India’s ambitious target of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030.
Rising Chinese Steel and Electronics Imports
- India and Europe are witnessing a surge in Chinese steel imports, impacting domestic steel industries by driving down prices.
- India’s finished steel imports from China hit a seven-year high in 2024. Similarly, while India has made progress in mobile phone manufacturing, it remains heavily reliant on Chinese electronic components, with imports worth over $12 billion in FY24.
Conclusion: Growing Global Trade Tensions
- The increasing inflow of Chinese exports, coupled with heightened trade tensions and retaliatory measures like tariff hikes and anti-dumping probes, underscores the global economic disruptions triggered by China’s export strategy amid its domestic slowdown.
- India’s response to the situation reflects broader concerns about economic dependence on China in critical sectors like steel, solar, and electronics.
| What are the Challenges Hindering India’s Progress? |
|
Infrastructure Constraints: Despite ongoing improvement, India’s infrastructure, including power grids, logistics networks, and transportation systems, lags behind China’s, potentially hindering manufacturing competitiveness and attracting investment Skilled Workforce Shortage: While demographics offer a large working-age population, a significant portion lacks the specific skills (Skill India Report: Only 5% Indians formally skilled) required for high-value manufacturing, necessitating heavy investment in upskilling and vocational training. Lack of Desired Ease of Doing Business: While initiatives like Make in India aim to improve, India still ranks lower than China in global ease of doing business rankings, requiring further measures to simplify processes and reduce red tape. Lack of R&D Push: Despite advancements, India continues to trail in research and development capabilities, allocating only 0.6-0.7% of its GDP to R&D, in stark contrast to China’s 2.56% investment. |
| PYQ: ‘China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia’, In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbor. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Amid growing trade tensions and the resurgence of Chinese exports, countries like India and the US have responded with protective measures such as tariffs and anti-dumping duties. Discuss the implications of China’s export dominance on global trade relations and domestic industries in India. What steps can India take to reduce its dependence on Chinese imports in critical sectors like renewable energy and electronics? (150 words/10 m) |
2. Supreme Court Expresses Concern Over Karnataka Judge’s Comments, Highlights Challenges in Judicial Accountability
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Impeachment: A Challenging Process
- The Indian Constitution provides for the removal of judges of constitutional courts (Supreme Court and High Courts) only through impeachment.
- According to Article 124(4), impeachment requires a rigorous process, needing approval by both Houses of Parliament with a two-thirds majority.
- However, impeachment has rarely been successful, with only five instances of proceedings being initiated. The difficulty in achieving political consensus for impeachment has resulted in alternative methods of disciplining judges.
Judicial Intervention as an Alternative
- In the absence of impeachment, the judiciary has taken actions to discipline judges through judicial intervention.
- A notable example is the 2017 case of Justice C S Karnan, who was found guilty of contempt by the Supreme Court and sentenced to six months in prison.
- This approach, however, raises concerns about constitutional courts holding one another accountable.
Transfer as a Disciplinary Tool
- The Supreme Court exercises influence over High Court judges through the transfer policy, managed by the Collegium system.
- Transfers, though not transparent, are sometimes used as a mechanism to discipline judges.
- A prominent example is the 2010 case of Justice P D Dinakaran, who was transferred amid allegations of corruption.
- However, critics argue that this method may merely shift the problem without addressing the root issue.
Conclusion
- The Supreme Court’s rare rebuke of a High Court judge highlights the challenges in disciplining judges within India’s judiciary.
- While impeachment remains the only constitutional recourse, alternative measures such as judicial intervention and transfers have been employed to uphold accountability, though these methods have their limitations.
| What steps can be taken to enhance Judicial Accountability? |
|
First, Parliament can enact a law that mandates Judiciary to publish an annual report. This law should clearly outline the expected content of the report and establish a clear timeline for its publication. Second, In India, the Judicial Standards and Accountability Bill was floated in 2010, but eventually lapsed. A new Bill on setting judicial standards is necessary. A permanent disciplinary committee should be set up at the central level to deal with complaints against judges. This committee should recommend further course of action based on the seriousness of misconduct (e.g., setting up a judicial inquiry committee under the Judges Inquiry Act for major misconduct). Third, the SC should clarify the extent and scope of RTI applicability to the judiciary. This will help in avoiding divergence in RTI response across the states. Fourth, the judiciary can also be brought under the scope of Lokpal to enhance accountability as seen in countries like Sweden where judiciary comes under the scope of the ombudsman. Fifth, a regular performance evaluation system for judges should be established. There is a mechanism of evaluation at lower judicial level. There is no performance evaluation for higher judiciary. It is difficult to create such a system. Best practices from global experience can be suitable adapted as a first step. |
| PYQ: Critically examine the Supreme Court’s judgement on ‘National Judicial Appointments Commission Act, 2014’ with reference to appointment of judges of higher judiciary in India. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the constitutional safeguards provided to judges of constitutional courts in India. In light of recent events, analyze the limitations of the impeachment process as a mechanism to ensure judicial accountability. (250 words/15 m) |
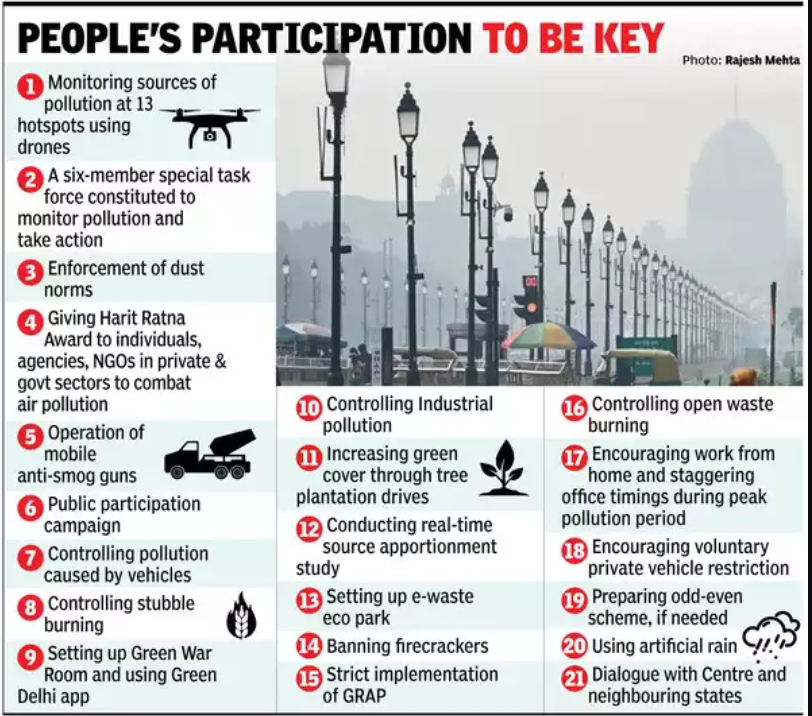
3. Delhi’s Air Quality Deteriorates as Winter Pollution Looms; Government Unveils 21-Point Action Plan
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 19)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environment Pollution and Degradation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Nature of the Problem
- Post-Monsoon Worsening: Air pollution worsens post-monsoon due to temperature inversion, where warm air traps cooler air, preventing the dispersion of pollutants like PM 2.5.
- Year-Round Issue: Air pollution remains a persistent problem, exacerbated during winter, but requires continuous efforts to address it throughout the year.
- Inequality in Exposure: Poorer communities suffer more from pollution, lacking resources like air purifiers or the means to relocate to less polluted areas.
Causes of Air Pollution
- Year-Round Contributors: Biomass burning, vehicular emissions, trash burning, and industrial activities are continuous sources of pollution.
- Seasonal Aggravators: Events like farm stubble burning and firecracker use during festivals further worsen air quality during this period.
- Meteorological Factors: Stagnant air and temperature inversion during the winter months trap pollutants close to the ground, intensifying the problem.
Superficial Solutions
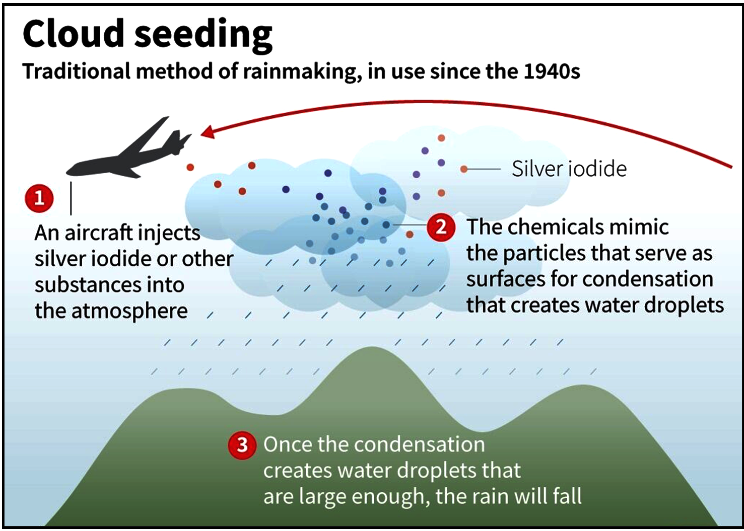
- Cloud Seeding: A method to induce rainfall by dispersing chemicals, cloud seeding is seen as a short-term solution with limited impact and environmental concerns, potentially leading to unintended consequences like depriving other regions of rainfall.
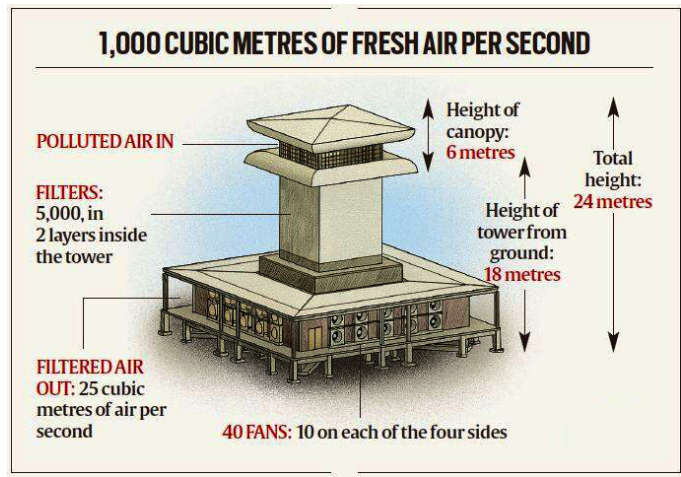
- Smog Towers: These large air purifiers have limited effectiveness, improving air quality only in the immediate vicinity, while their energy usage may contribute to emissions.
Concrete Solutions
- Coordinated Action: A multi-sectoral approach involving transport, industry, agriculture, and urban planning agencies is crucial for tackling pollution. Solutions must be implemented across city and state boundaries, with year-round policies.
- Capacity Building and Critical Thinking: Developing institutional frameworks, investing in research, and fostering collaboration among researchers, policymakers, regulators, and citizens are essential for long-term progress.
- Comprehensive Air Quality Monitoring: Expanding air quality monitoring beyond major cities to include rural and industrial areas can help identify pollution trends and enable targeted interventions.
Moving Beyond Quick Fixes
- Technological fixes like cloud seeding and smog towers serve more to demonstrate action rather than address root causes.
- Tackling air pollution requires sustained, science-based efforts and equitable policies, moving beyond quick fixes and vested interests.
| Government Initiatives to Control Delhi’s Pollution |
|
| PYQ: Describe the key points of the revised Global Air-Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve these revised standards? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
| Practice Question: Air pollution in India, particularly in regions like Delhi, is a persistent issue that intensifies during the winter months. Critically examine the effectiveness of current mitigation measures like cloud seeding and smog towers, and suggest long-term solutions that address the root causes of air pollution. (250 words/15 m) |
4. A journey across the Palk Strait
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
Palk Strait: Overview
- The Palk Strait is a narrow body of water between India and Sri Lanka.
- It connects the Bay of Bengal to the Gulf of Mannar.
- It is generally 40-85 kilometres wide, but it can be narrower in some areas.
- Major islands in the strait include Adam’s Bridge (Rama Setu).
- The region is characterised by shallow waters, making navigation challenging.
- It serves as a crucial fishing ground for local fishermen.
- The Palk Strait is known for its biodiversity, including coral reefs and marine species.
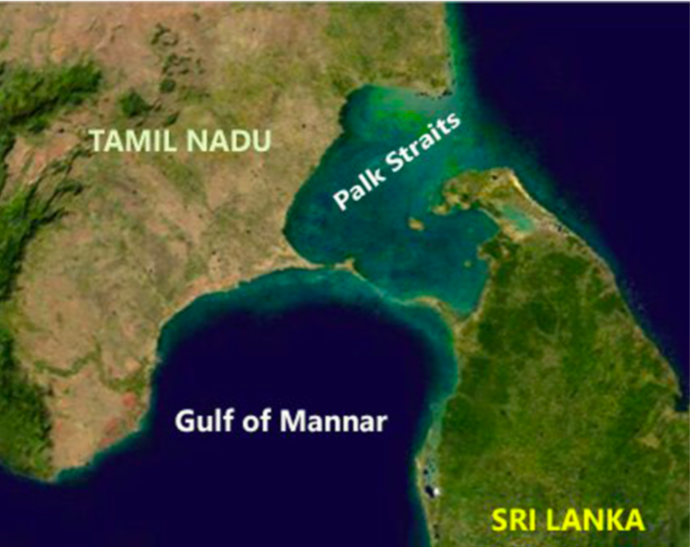
Significance in India-Sri Lanka Relations
- The Palk Strait is strategically significant for maritime security and trade routes.
- It facilitates bilateral trade and tourism between India and Sri Lanka.
- Disputes over fishing rights in the strait have caused tensions, affecting diplomatic relations.
- The area is vital for the livelihood of Tamil fishermen from both nations.
- Development of infrastructure projects, like ports, has implications for regional connectivity.
- The strait plays a role in humanitarian and environmental cooperation.
- Strengthening ties through joint initiatives in the strait can enhance regional stability.
- The Palk Strait is pivotal for maritime security and counter-terrorism efforts in the Indian Ocean.
| PYQ: In respect of India – Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2013) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the Palk Strait in shaping India-Sri Lanka relations, focusing on its strategic importance and economic implications. How can both nations enhance cooperation to address issues related to maritime security and fishing rights? (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. India and Uzbekistan Sign Bilateral Investment Treaty to Boost Investor Confidence
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 15)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Key Provisions of the BIT
- The treaty ensures protection for investors from both countries, offering assurances for fair and equitable treatment based on international precedents and practices.
- The agreement emphasizes non-discrimination and provides a minimum standard of treatment for investments in both nations.
Investor Confidence and Dispute Settlement
- The BIT is expected to boost investor confidence by providing mechanisms for fair treatment and access to an independent dispute settlement forum through arbitration.
- This will allow for the resolution of investment-related disputes in a transparent and neutral environment, further promoting cross-border investment flows between India and Uzbekistan.
2. CDSCO Flags 50 Common Medicines as Spurious or Substandard in Routine Quality Check
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
CDSCO and NSQ
- The CDSCO is the Central Drug Authority for discharging functions assigned to the central government under the Drugs and cosmetics Act, 1940.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- The CDSCO releases a monthly list of drugs that fail quality checks.
- Central and state regulators collect random samples of medicines from the market for testing.
- The list identifies drugs that are either spurious, of poor quality, or adulterated.
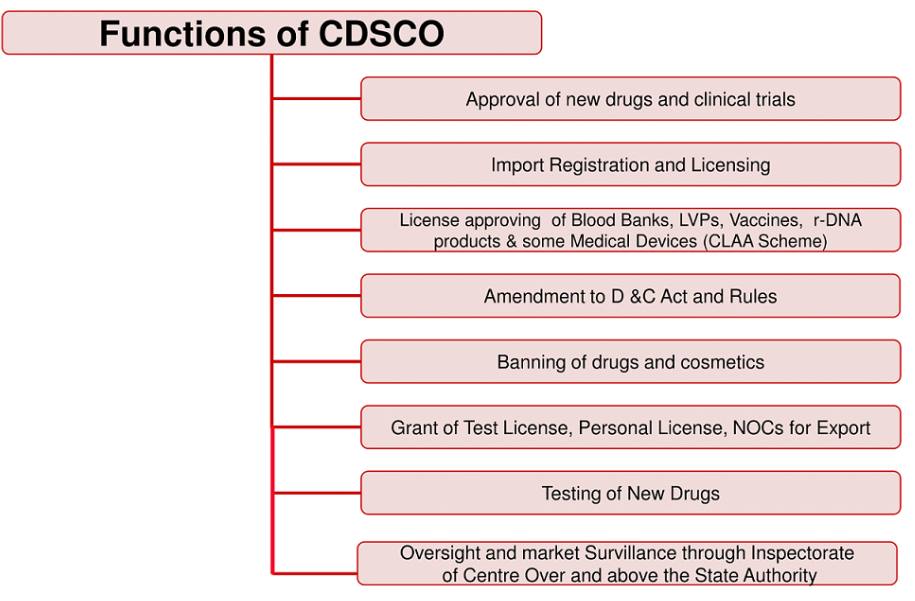
Reasons for Drug Failure
- Spurious Drugs: These are counterfeit products that falsely claim to be genuine brands. They may lack the active ingredient or be produced by fraudulent companies.
Example: Counterfeit telmisartan (for hypertension) and pantoprazole were found using Glenmark and Sun Pharma branding without being made by these companies.
- Poor Quality Drugs (NSQ): These drugs may contain the wrong formulation, fail to dissolve correctly, or have insufficient active ingredients.
Example: Metformin failed a dissolution test, meaning it wouldn’t function properly once ingested.
- Adulterated Drugs: These contain harmful contaminants or substances, potentially causing direct harm to consumers. Such drugs are usually recalled by the regulator or voluntarily by the manufacturer.
Purpose of Testing
The random sampling and public disclosure of NSQ drugs serve multiple purposes:
- Consumer Awareness: Informing the public about potentially unsafe medicines.
- Company Accountability: Encouraging manufacturers to improve quality.
- Regulatory Action: Giving regulators insight into which drugs need further scrutiny.
3. INDIAN OCEAN RIM ASSOCIATION SEMINAR
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2059304®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
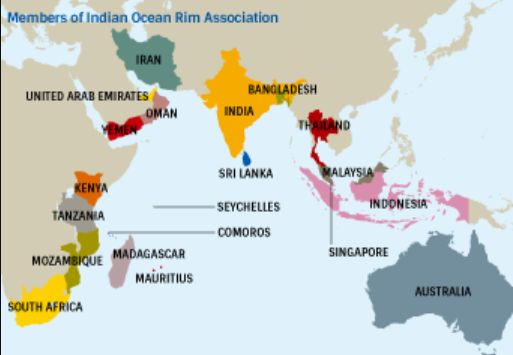
- IORA is a regional organisation comprising 23 member states along the Indian Ocean rim.
- Established in 1997, it aims to promote sustainable development and regional cooperation.
- It focuses on areas like maritime security, trade facilitation, disaster risk management, and blue economy.
- Member countries include India, Australia, Indonesia, South Africa, and several others from the Indian Ocean region.
- Observers include countries like China, the U.S., and the U.K.
- The IORA Secretariat is based in Mauritius.
- IORA fosters collaboration on economic growth, environmental protection, and maintaining maritime security in the Indian Ocean region.
- It also addresses challenges like illegal fishing, piracy, and climate change impacting coastal communities.
4. U.K. PM Starmer backs permanent seat in UN Security Council for India
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- During his address at the United Nations General Assembly, British Prime Minister Keir Starmer emphasised the need for reforms to make the global multilateral system more representative and responsive.
- The UK supports permanent membership for India, Africa, Brazil, Japan, and Germany on the UNSC.
- Starmer highlighted the importance of fairer representation and outcomes, stating that the UNSC must not remain “paralysed by politics.”
- He also proposed more seats for elected members to make the Security Council more effective.
- The UK’s approach will shift towards partnership rather than paternalism, offering British expertise while respecting equal collaboration.
5. Long-range rockets, futuristic ammunition on Army wish list
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
|
Long-range Rocket Development:
- The Indian Army is focused on extending the range of the Pinaka multi-barrel rocket launcher system.
- Efforts are underway to double the current range of Pinaka rockets and eventually increase it up to four times.
- Guided extended range (ER) Pinaka rockets are undergoing trials, which, if successful, will take the range to over 75 km.
- The high explosive pre-fragmented rockets for Pinaka are set to increase the range by 15%-20%.
- Trials of guided ER rockets have already been completed in high-altitude areas, with plains trials scheduled soon.
Futuristic Ammunition Development:
- Indian Army aims to indigenize and diversify the vendor base for 155mm artillery shells for resilient supply chains.
- A road map is in place to convert all artillery guns to the 155mm standard.
- Area denial munition (ADM) system, both anti-tank and anti-personnel, is under development.
- DRDO has successfully flight-tested the ADM rocket system, and further production partnerships have been identified.
- The development trials for Pralay ballistic missiles are nearing completion.
- Army trials are expected for Nirbhay cruise missiles next year.
| Pralay Ballistic Missiles And Nirbhay Cruise Missiles |
|
Pralay Ballistic Missiles Type: Quasi-ballistic surface-to-surface missile.
Nirbhay Cruise Missiles Type: Subsonic cruise missile.
|



