19 November 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. 56th Tiger Reserve of the country notified in Chhattisgarh
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2074302®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
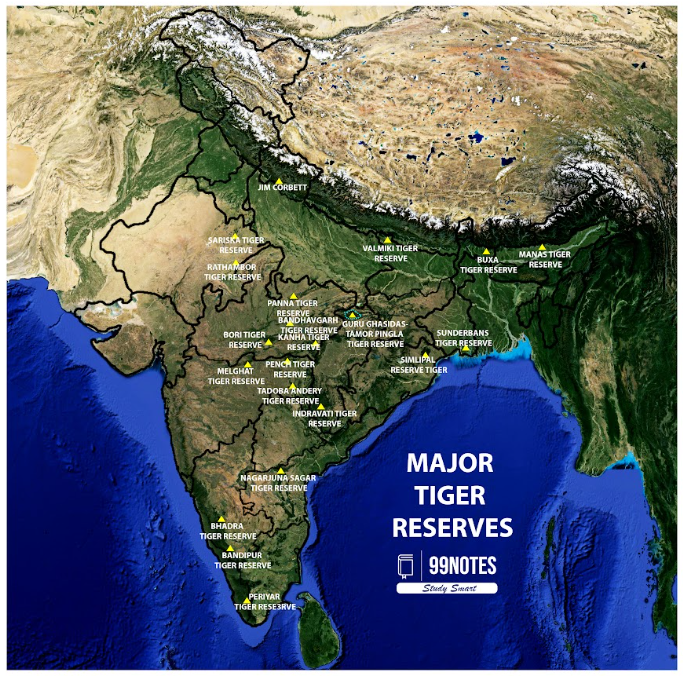
Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Chhattisgarh, covering Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, Korea, Surajpur, and Balrampur districts.
- Size: 2,829.38 sq.kms, making it the 3rd largest tiger reserve in India.
- Core Area: 2,049.2 sq.kms, including Guru Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Buffer Zone: 780.15 sq.kms.
- Connected Reserves: Part of a landscape complex with Sanjay Dubri Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh), and links to Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (West) and Palamau Tiger Reserve (East).
- Fauna: 753 species documented, including 230 bird species and 55 mammal species, with many threatened species.
| More About Tiger Reserves |
|
Definition: Tiger reserves are protected areas established for the conservation of tigers and their habitats. Management: Managed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) in India. Core and Buffer Zones: Core zones are strictly protected; buffer zones allow limited human activity. Legal Framework: Governed by the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, and the NTCA guidelines. Ecological Importance: They help maintain ecological balance by protecting various species and forest ecosystems. Tourism: Some reserves promote eco-tourism, supporting local economies while ensuring wildlife protection. Examples: Jim Corbett, Sundarbans, and Ranthambhore are prominent tiger reserves in India. |
| Practice Question: Tiger reserves play a crucial role in conservation efforts in India. Discuss their significance in biodiversity preservation, challenges faced in their management, and the role of the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA). (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. ‘One Day One Genome’ initiative to harness the microbial potential of India
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2074247®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|

‘One Day One Genome’ Initiative:
- Initiative: ‘One Day One Genome,’ launched on the foundation day of the Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC).
- Objective: To highlight India’s microbial diversity, focusing on unique bacterial species found across the country.
- Key Focus Areas: Environmental conservation, agriculture, and human health.
- Microbial Importance: Microorganisms play a crucial role in biogeochemical cycles, soil formation, degradation of organic waste, and pollution control. They also contribute to methane production and nutrient cycling in agriculture.
- Agricultural Role: Aid in nitrogen fixation, maintaining soil fertility, pest control, and plant stress responses.
- Health Contribution: Microorganisms are vital for digestion, immunity, and mental health, with non-pathogenic microbes protecting against infectious diseases.
- Genome Sequencing: Enables visualisation of microbial potential, identifying enzymes, antimicrobial resistance, and bioactive compounds.
- Public Access: Fully annotated bacterial genomes will be freely available, along with graphical summaries and genome assembly details.
- Impact: Promotes scientific research, innovation, and public awareness, benefiting the environment, agriculture, and human health.