16 December 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. Public Sector Banks: A Resurgent Force
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2084546®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Introduction: Public Sector Banks’ Achievements
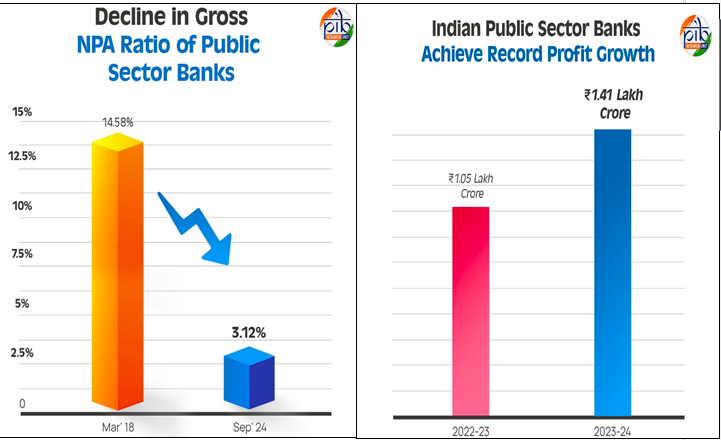
- Public Sector Banks (PSBs) in India achieved a record net profit of ₹1.41 lakh crore in FY 2023-24, marking their highest-ever aggregate profit.
- The sector saw a significant improvement in asset quality, with the Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio declining to 3.12% in September 2024.
- PSBs also recorded a net profit of ₹85,520.6 crore in the first half of 2024-25 and paid a total dividend of ₹61,964 crore over the past three years.
- These achievements reflect improved operational efficiency, stronger capital base, and better asset quality.
Decline in GNPA: Strengthening Resilience
- The GNPA ratio of PSBs dropped from a peak of 14.58% in March 2018 to 3.12% in September 2024.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) initiated the Asset Quality Review (AQR) in 2015, which helped in transparent recognition of NPAs and increased provisioning.
- To address banking stress, the Government introduced a comprehensive 4R’s strategy (Recognition, Resolution, Recapitalisation, and Reforms).
- The Capital to Risk (Weighted) Assets Ratio (CRAR) of PSBs rose by 3983 basis points to 15.43% in September 2024, indicating enhanced stability.
Expanding Financial Inclusion
- PSBs continue to drive financial inclusion, with 54 crore Jan Dhan accounts and 52 crore collateral-free loans under various schemes.
- The number of bank branches increased from 1,17,990 in March 2014 to 1,60,501 in September 2024, with most branches in rural and semi-urban areas.
- As of September 2024, the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme supported 7.71 crore accounts, with an outstanding loan of ₹9.88 lakh crore.
- MSME advances grew at a CAGR of 15% over the past 3 years, totaling ₹28.04 lakh crore in March 2024.
Strengthening PSBs through the EASE Framework
- The Enhanced Access & Service Excellence (EASE) framework promotes incremental reforms focusing on governance, risk management, technology, and data-driven banking.
- Key reforms have led to improved financial health and better banking services.
Conclusion: A Stronger Banking Sector
- PSBs have made significant progress in financial health and contributed to India’s economic growth.
- The decline in GNPA and improved CRAR reflect sound risk management.
- The EASE framework has facilitated reforms, and the focus on financial inclusion has expanded banking access. PSBs are now well-positioned to drive inclusive economic growth.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of Public Sector Banks (PSBs) in India’s economic growth, focusing on their financial performance, the decline in GNPA, and the impact of the EASE framework in strengthening the banking sector. (150 Words /10 marks) |


