Decoding India’s growth slowdown
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
| ● India’s real GDP growth rate for 2024-25 is forecasted to drop to 6.4% from 8.2% in 2023-24. |
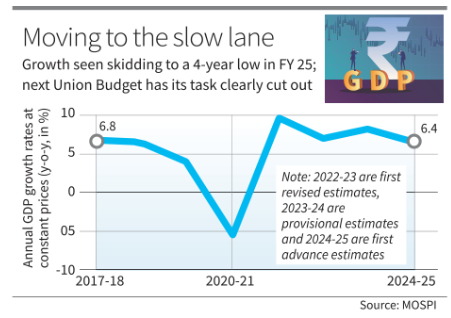 Decline in GDP Growth
Decline in GDP Growth
- This estimate is below the 6.5% to 7% range projected in the Economic Survey of July 2024.
- The nominal GDP growth rate, which accounts for inflation, is expected to be 9.7%, lower than the 10.5% projected in the Union Budget.
Discrepancies in Data Estimation
- Experts, including the IMF, have criticized the official GDP estimates, particularly the use of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) as a deflator.
- The IMF has suggested using the Producer Price Index (PPI) instead of WPI for more accurate GDP deflation.
- Data issues such as revisions to historical series and discrepancies between GDP by activity and expenditure complicate monitoring of India’s economy.
| What is GDP Deflation? |
| ● GDP deflation is the process of adjusting nominal GDP (which includes inflation) to real GDP by removing the effects of price changes over time.
● This is done using a deflator, typically the GDP deflator, which reflects changes in the prices of goods and services. ● It allows for a more accurate comparison of economic output across different periods by focusing on the actual growth in volume rather than price fluctuations. |
Impact of Volatility in WPI
- WPI has shown significant volatility over the years, which has caused discrepancies between the WPI and the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- For example, in 2023-24, the nominal GDP showed a deceleration, while real GDP growth indicated acceleration due to discrepancies in the GDP deflator, which misrepresents economic conditions.
| Wholesale Price Index (WPI) |
| ●The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) measures the average change in prices of goods at the wholesale level, before they reach consumers.
● It includes the prices of goods such as raw materials, intermediate goods, and finished products. ●WPI is used to track inflation trends in the economy, providing insights into price changes at an early stage of production. ●It is published by the Office of Economic Advisor (Ministry of Commerce and Industry). ● WPI does not include services or products purchased directly by consumers, unlike the Consumer Price Index (CPI). ●A high WPI indicates inflationary pressures in the economy. |
Private Investment Challenges
- Despite the Economic Survey highlighting the private sector’s slow response to tax cuts, the Union Budget projected a revival in private corporate investment to fund the ‘Prime Minister’s Package for Employment and Skilling.’
- However, the latest GDP estimates show a decline in real gross fixed capital formation from 9% in 2023-24 to 6.4% in 2024-25, signaling weak investment performance.
Investment and Consumption Trends
- During the UPA era, real private investment growth was over 10%, significantly higher than under the NDA regime, where private investment growth stagnated.
- Despite tax cuts in 2019, corporate investment has failed to drive substantial economic activity, highlighting the lack of a private investment-led recovery in the post-pandemic period.
Fiscal Strain and Budgetary Challenges
- Tax revenue growth is below target, with only 56% of the net tax revenue goal met by November 2024.
- Capital expenditure has been underutilized, with less than half of the projected ₹11.11 trillion capex spent by November.
- The government faces the dilemma of maintaining fiscal discipline while addressing the economic slowdown, requiring adjustments to revenue mobilization strategies, such as increasing taxation on wealth and profits.
Conclusion
- The ongoing economic slowdown is evident, affecting key sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
- To avoid worsening the fiscal situation, the government must reassess its revenue mobilization strategy and prioritize spending on capital and welfare.
| Practice Question: Examine the challenges in estimating India’s GDP growth, particularly focusing on the issues with the use of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) as a deflator. Discuss the implications of the declining private investment and fiscal constraints on the economy. (250 Words /15 marks) |
For more such UPSC related Current Affairs, Check Out –Union govt. yet to wake up from its slumber on Dam Safety Act, says SC
