Kurukshetra Summary: December 2024.
1. Government Initiatives in Promoting Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Bridging the Skill Gap
- India faces a significant challenge in the form of a skill gap, particularly in rural areas, where a substantial portion of the workforce is unskilled or under-skilled for modern jobs.
- The government is actively addressing this issue through a range of skill development initiatives coordinated by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- These initiatives aim to:

Promoting Skill Development
- The MSDE is supported by several skill-centric organizations, including the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), which plays a vital role in:
- Providing certified skilling, upskilling, and reskilling courses.
- Delivering hands-on training and opportunities for international mobility.
- The NSDC collaborates with:
- Sector Skill Councils (SSCs).
- National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs).
- Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Other training partners to deliver a wide range of skill development programs across diverse sectors.
- The government’s efforts in promoting skill development extend to international collaborations, such as a recent agreement with Israel to provide skilled workers to address their workforce gap.
Fostering Entrepreneurship
- In addition to skill development, the government focuses on strengthening the entrepreneurial ecosystem by:
- Creating a vibrant and inclusive entrepreneurial environment.
- Supporting aspiring and existing entrepreneurs across rural and urban areas, as well as marginalized communities.
- Promoting women’s entrepreneurship through targeted initiatives, mentorship programs, and improved access to finance.
Key Government Initiatives
- Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN): Focuses on the upliftment of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups through skilling and entrepreneurship development programs implemented by NIESBUD and IIE in collaboration with TRIFED.
- Rashtriya Udyamita Vikas Pariyojana: Targets PM-SVANidhi beneficiaries, providing classroom training and mentoring support to enhance entrepreneurial skills.
- STRIVE Project: Aims to foster entrepreneurship among trainees and future trainers in ITIs and NSTIs through awareness programs, mentoring, and handholding support.
- SANKALP Scheme: Supports the development of entrepreneurs, including those from marginalized communities, through capacity building, mentoring, incubation support, and handholding.
- Entrepreneurship Development in Six Holy Cities: Promotes entrepreneurship and provides mentoring support to micro and small businesses in six temple towns.
- Capacity Building Programme for Fair Price Shop Owners: Equips Fair Price Shop (FPS) owners with skills to run their businesses effectively in line with modern retail practices.
- Establishing EDCs and ICs in Northeast Educational Institutions: Focuses on setting up Entrepreneurship Development Centres (EDCs) and Incubation Centres (ICs) in educational institutions across the Northeast region.
- Pradhan Mantri Dakshata Aur Kushalata Sampanna Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) Yojana: Provides skill development training to youth from Backward Classes, Scheduled Castes, and Safai Karamcharis.
- Solar Entrepreneurship Development: Develops skilled entrepreneurs capable of installing and maintaining solar PV systems under the PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
- Entrepreneurship-cum-Skill Development Programmes: Trains individuals in roles like traditional crafts and future-oriented skills such as LED light repair and solar PV installation.
- Promoting Entrepreneurship among Jail Inmates: Supports entrepreneurship development among jail inmates through capacity building, mentoring, handholding, and incubation support.
- Training of Trainers and ED Programme in Jan Shikshan Sansthans: Fosters entrepreneurial spirit through capacity building, incubation support, mentoring, and handholding in Jan Shikshan Sansthans (JSSs).
- SFURTI Programme: Focuses on the development and modernization of traditional industries in India through a cluster-based approach.
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programmes Supported by HUL: Collaborates with Hindustan Unilever Ltd (HUL) to organize entrepreneurship awareness programs for youth across India.
New Initiatives and Collaborations
- NITI Aayog’s Project SWAVALAMBINI: Aims to foster an entrepreneurial mindset among female students and provide resources for entrepreneurship.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan: Seeks to improve the socioeconomic conditions of tribal communities through skill development and entrepreneurship programs.
- Proposed MoU with the Ministry of Rural Development: Promotes skill development and entrepreneurship among Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and their members to enhance rural livelihoods.
Conclusion
- India’s skill gap is being addressed through comprehensive government initiatives focusing on skill development and entrepreneurship.
- These efforts empower individuals, promote economic growth, and enhance global workforce competitiveness.
- Collaboration with international and domestic partners strengthens these programs, creating sustainable livelihoods and driving inclusive development.
2. Skilling India: Empowering the Workforce
India’s Demographic Dividend
- India has one of the youngest populations globally, offering a unique opportunity to harness its demographic dividend.
- The government focuses on skill development, bridging the employability gap, and preparing the workforce for future needs.
Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme 2024
- Provides 12-month internships in India’s top 500 companies to bridge the gap between academic learning and industry requirements.
- Eligibility: Indian nationals aged 21–24, not employed full-time, and not in full-time education.
- Benefits:
- Monthly stipend of Rs. 5,000.
- One-time grant for incidentals.
- Insurance coverage and training cost reimbursement.
Other Recent Initiatives
- Swiggy Skills Initiative: Collaboration with Swiggy to provide skilling and employment opportunities for delivery partners.
- STRIVE Project: Focuses on entrepreneurship and mentoring in ITIs and NSTIs.
- PM-JANMAN Initiative: Targets skilling and uplifting vulnerable tribal groups.
- Capacity Building for Fair Price Shop Owners: Training 3,000 participants in entrepreneurship.
- SANKALP Scheme: Supports marginalized communities in entrepreneurship.
- Rashtriya Udyamita Vikas Pariyojana: Supports PM-SVANidhi beneficiaries with training and mentoring.
- Entrepreneurship Development among Jail Inmates: Supports entrepreneurship development among jail inmates.
- Bijnor Kaushal Mahotsav: Organized to create jobs for local youth.
- Women Empowerment Initiatives:
- Training in aspirational districts.
- MoU with Visa to upskill 20,000 youth in tourism.
- Skill India Centre at Rashtrapati Bhawan: Established for skilling in-house staff.
Key Programs under Skill India Mission
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Offers short-term skill training.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendras (PMKK): Standardizes quality training across India.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS): Targets non-literate and rural populations.
- Pradhan Mantri YUVA Yojana: Promotes entrepreneurship.
- Skill India Digital (SID): Introduces AI-driven tools for job matching and continuous learning.
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana: Supports traditional artisans by modernizing skills and integrating them into global markets.
Latest Achievements and Initiatives
- Revised Model Skill Loan Scheme:
- Loan amount increased from Rs. 1.5 lakh to Rs. 7.5 lakh for advanced-level skill courses.
- World Youth Skills Day Celebration: Marked the 10th anniversary of the Skill India Mission.
- Apprenticeship Training:
- 7.46 lakh apprentices undergoing training.
- 2.77 lakh engaged in the current financial year.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- Rs. 122.36 crore disbursed as apprentice stipends in the last four months.
Indian Institute of Skills (IIS)
- Designed to create an industry-ready workforce for Industry 4.0.
- Focuses on factory automation, digital manufacturing, AI, data analytics, and additive manufacturing.
- Offers short-term courses in collaboration with industry partners like Fanuc India and Taj Skyline.
Conclusion
- India’s demographic dividend presents an unparalleled opportunity to shape a skilled workforce.
- Government initiatives aim to bridge skill gaps, foster entrepreneurship, and prepare individuals for global and domestic industry demands.
3. Comprehensive Ecosystem for Rural Women Entrepreneurship
Untapped Potential of Rural Women
- Rural women possess entrepreneurial skills, resilience, and perseverance.
- Women’s contribution to GDP is low, underscoring the need to promote rural women’s entrepreneurship.
Challenges Faced by Women Entrepreneurs
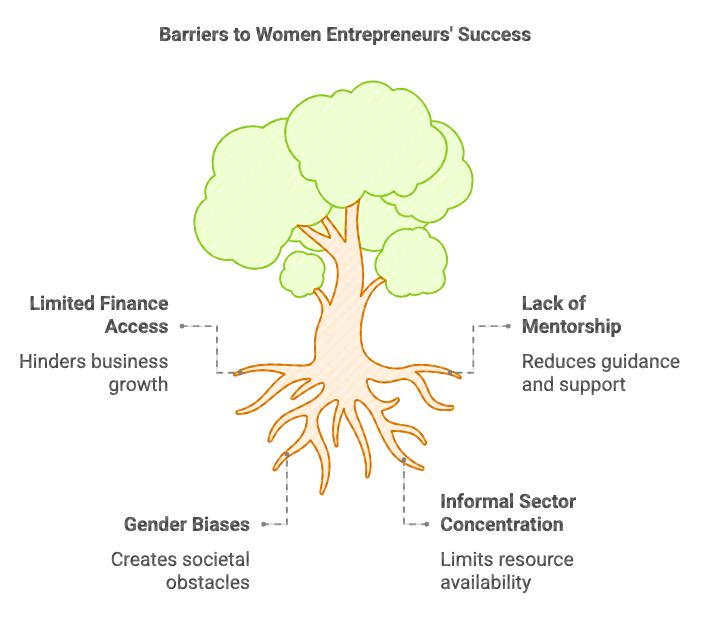
Government Schemes for Rural Women Entrepreneurship
- Skill Upgradation & Mahila Coir Yojana (MCY): Focuses on skill development for coir industry artisans with stipends and unit setup support.
- Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP): Helps SHG members establish non-farm enterprises to stimulate economic growth.
- Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): Empowers women in agriculture with enhanced productivity and resource access.
- Mahila Shakti Kendra (MSK): Offers skill development, employment assistance, and digital literacy for rural women.
- Women Enterprise Development Scheme (WED): Provides financial aid for North Eastern Region women entrepreneurs.
- Annapurna Yojana: Offers loans for women in the food service sector to meet working capital needs.
- Mudra Yojana Loans for Women Entrepreneurs: Provides micro-credit and special provisions for small women entrepreneurs.
- Start-Up India Initiative: Encourages startups with 46% of recognized startups having at least one woman director.
Addressing Loopholes in Existing Schemes
- Lack of awareness and promotion among beneficiaries.
- Overemphasis on financial and skill development support, neglecting market linkages and mentorship.
- Limited targeted schemes for rural women entrepreneurs.
- Neglect of sectors like services and the digital economy.
- Partial online access to schemes with unfriendly user interfaces.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Create comprehensive schemes covering entrepreneurship promotion, business support, market linkages, finance, and mentoring.
- Ensure a smooth user journey from registration to benefit availing.
- Enhance online access with improved user interfaces, multilingual content, and regional language support.
- Provide physical or assisted access for women with limited digital literacy.
- Collect gender-disaggregated data to monitor scheme performance by sector and region.
- Support formalization of women-owned informal enterprises by assisting with licenses and paperwork.
Conclusion
- Empowering rural women entrepreneurs is key to economic growth.
- Addressing existing scheme gaps and fostering inclusivity will unlock the untapped potential of women in driving sustainable development.
4. Building a Skilled Workforce in Rural India
Importance of Skilling in Rural India
- Skilling plays a crucial role in rural development by providing better job opportunities and reducing migration to urban areas.
- It fosters entrepreneurship among rural youth, enabling them to contribute to local economies.
- Targeted programs like DDU-GKY and RSETI have demonstrated encouraging results in enhancing rural livelihoods.
India’s Demographic Dividend
- India has a young population, with 65% under the age of 35, presenting a significant opportunity to harness its demographic dividend.
- Skilling is essential to prepare this young workforce for the demands of a modern economy.
- Despite improvements in employability, a large portion of the workforce still lacks critical skills.
Government Initiatives for Skilling
- Prime Minister’s Package for Skilling and Employment: This initiative aims to skill 20 lakh youth and upgrade 1,000 ITIs across the country.
- National Policy on Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (NPSDE): This policy focuses on bridging skill gaps, improving industry engagement, and expanding apprenticeship opportunities.
- Skill India Mission (SIM): This mission equips Indian youth with industry-relevant skills through schemes like PMKVY, JSS, NAPS, and CTS.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Since its inception, PMKVY has trained 1.42 crore individuals in various skill domains.
- Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS): This scheme provides vocational training through over 15,000 ITIs, with increasing participation of women.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS): JSS targets non-literates and marginalized groups, offering skill training to empower these communities.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS): NAPS supports over 32 lakh apprentices, promoting on-the-job training with increasing participation from women.
- Entrepreneurship Training: Institutions like NIESBUD and IIE have provided entrepreneurial training to numerous beneficiaries.
- Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH): SIDH facilitates access to skilling, credit, and employment through AI/ML integration.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY): This placement-linked program mandates a 70% minimum placement rate for trained candidates.
- Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETIs): RSETIs offer free skill training and credit assistance to rural youth for self-employment.
Partnering with Industry for Skilling
- The Skill India Mission collaborates with industries through NSDC-driven partnerships to support skill development, reskilling, and upskilling.
- The government aligns skilling programs with market demands by collaborating with industries and prioritizing future-ready job roles.
Skilling India at Global Standards
- India is expanding its global skilling footprint through initiatives like Skill India International Centers (SIICs).
- Partnerships with countries such as Australia, Germany, Japan, and the UK focus on aligning skilling with international standards.
- Migration and Mobility Agreements with several countries support skilling aligned with global demands.
Impact of Skill Development Initiatives
- These initiatives have contributed to reducing unemployment rates and increasing wages in rural areas.
- The focus on skilling has led to the growth of rural industries and created employment opportunities in the hinterlands.
Conclusion
- Skilling programs are crucial for rural development and the effective utilization of India’s demographic dividend.
- Continued investment and innovative strategies are needed to ensure long-term economic growth and inclusivity in rural areas.
5. Skilling the Youth through Technology
The Importance of Skilling in the Digital Age
- India faces the challenge of preparing its youth for a competitive, digital-first world.
- Skilling is crucial for improving job prospects, productivity, and adaptability in a rapidly changing global economy.
- Technology plays a vital role in skilling by providing scalability, accessibility, and customization.
Government Initiatives for Technology-Driven Skilling
- Digital India Campaign: Enhances digital literacy and infrastructure, creating the foundation for online skilling.
- Skill India Mission: Aligns vocational training programs with the demands of the 21st-century economy.
- Atal Innovation Mission: Introduces students to emerging technologies through Atal Tinkering Labs.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Focuses on short-term skilling programs that integrate digital tools.
Budget 2024-25 Initiatives
- The Union Budget 2024-25 outlines a strategy for education, employment, and skills development.
- It includes an internship program at leading companies to enhance employability.
- Increased funding has been allocated for the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme.
- The budget proposes the enhancement of 1,000 ITIs to align with modern skilling requirements.
Challenges and Way Forward
- The percentage of the formally skilled workforce in India remains low despite these initiatives.
- There is a pressing need for continuous learning and upskilling to meet evolving industry demands.
- Addressing the digital divide is crucial to ensure equitable access to skilling opportunities.
- India must focus on training programs that develop future-ready skills to harness its demographic dividend effectively.
Specific Courses for Technological Development
- Several courses can help students develop skills in emerging technologies, including:
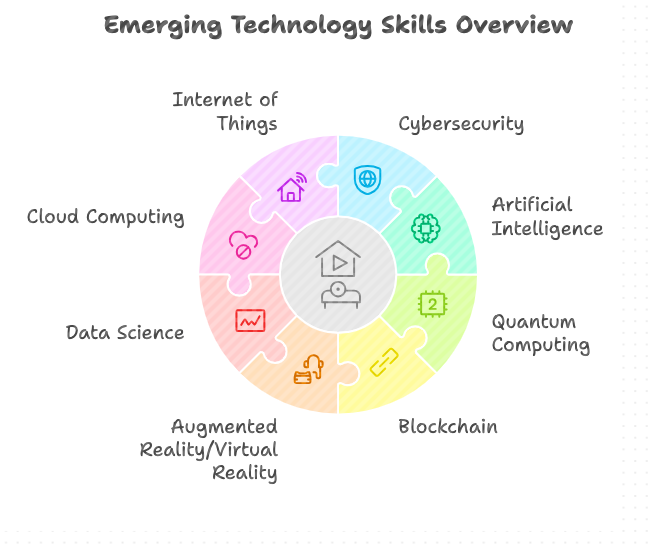
Conclusion
- Skilling youth through technology is essential for India’s future.
- Technology must be leveraged to provide accessible, scalable, and industry-aligned training programs.
- Collaboration among the government, commercial sector, and educational institutions is crucial to empower India’s youth in a rapidly changing global economy.
6. Skilled Farmers: Bright Future of Indian Agriculture
The Need for Skilled Farmers
- Despite India’s long history as an agricultural country, agriculture and farmers are often perceived as untrained and unskilled.
- The Green Revolution, while increasing production, also led to problems like soil degradation and groundwater depletion.
- To address these challenges and ensure food security, it is crucial to develop a skilled and business-oriented farming community.
Importance of Skill Development in Agriculture
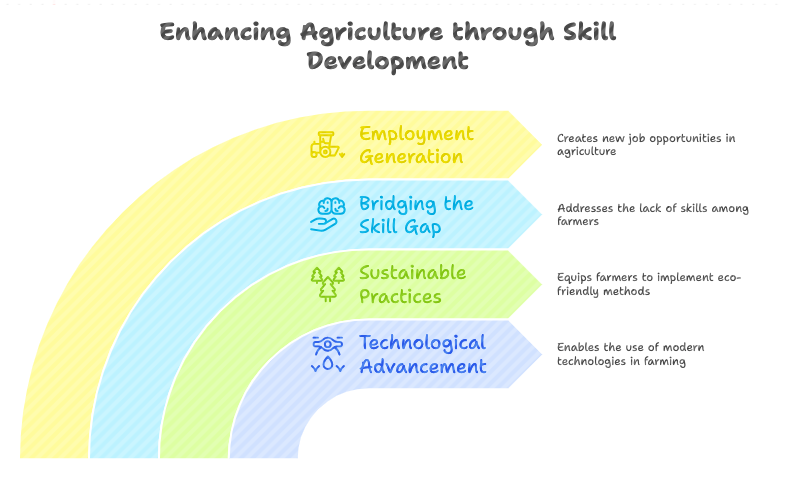
Government Programs for Skill Development in Agriculture
- Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): Empowers women farmers with skills and resources.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM): Focuses on livelihood enhancement and skill development for rural communities.
- PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprise (PMFME): Aims at formalizing and supporting small food processing units.
- Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SHAM): Encourages the use of agricultural mechanization through skill development.
- National Beekeeping and Honey Mission: Promotes beekeeping as an income-generating activity.
- Agricultural Technology Management Agency (ATMA): Promotes a farmer-friendly decentralized extension system.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Enhance farmers’ capacity through training in various agricultural aspects.
- National Skill Development Mission: Implements skill training courses for rural youth and farmers.
- Skill Training for Rural Youth (STRY): Upgrades rural youth’s knowledge in agriculture and allied sectors.
- Centers of Excellence (CoE): Provide training to farmers in various horticultural crops.
- Per Drop More Crop (PDMC): Organizes awareness and training programs for farmers on efficient irrigation practices.
- Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM): Develops skills for mechanization in agriculture.
- Drone Training for Women SHGs: Provides training on drone operation for agricultural purposes.
- Food Processing Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): Provides training to farmers and SHGs on food processing.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM): Provides training on various agricultural practices, including drone use, natural farming, and livestock management.
Collaboration between Government and Private Sector
- The private sector, through agri start-up companies, is also contributing to skill development in agriculture.
- Collaboration between the government and the private sector is crucial for effective skill development and ensuring the bright future of Indian agriculture.
Conclusion
- Developing skilled farmers is vital to address challenges like climate change and food security.
- Government and private sector collaboration ensures the growth of modern agriculture and promotes income generation through skill development.
7. Skill and Entrepreneurial Ecosystem in India
Skill and Entrepreneurship Development: Crucial for India
- Skill development and entrepreneurship are crucial for India to maximize its social and economic benefits.
- The Indian government emphasizes skill development and entrepreneurship through initiatives like “Skilled India”, “Make in India”, and “Start-up India”.
- The evolving job market and advancements in technology necessitate continuous skilling, reskilling, upskilling, and lifelong learning.
The Significance of Skill Development
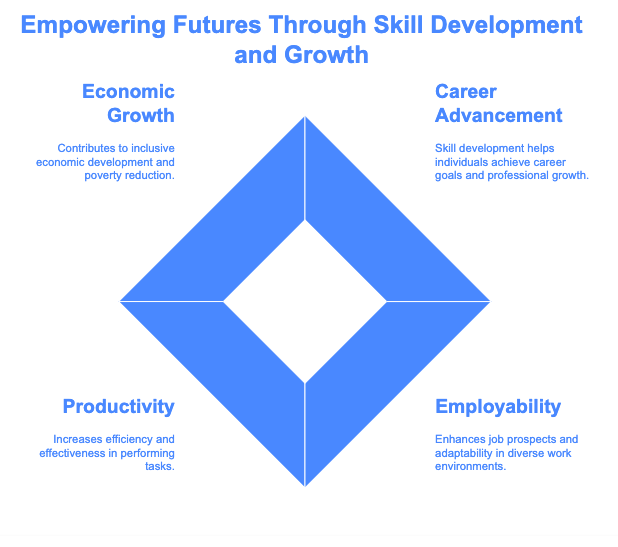
The Role of Entrepreneurship
Government Initiatives for Skill Development
- The Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) coordinates skill development efforts across India with the following objectives:
- Enabling individual economic gains and social mobility.
- Creating a learner-centric and demand-driven skills market.
- Facilitating aspirational employment and entrepreneurship generation.
- Improving overall productivity for enterprises.
- Catalyzing economic growth.
National Education Policy (NEP) 2020
- NEP 2020 emphasizes the integration of skill education programs into mainstream education, promoting a flexible and multidisciplinary approach.
- It aims to bridge the gap between education and employment by exposing students to a wide range of work opportunities and skill development courses.
Bridging the Skills Gap
- NEP 2020 aims to remove the societal stigma associated with skill education and provide multiple pathways for students to explore their interests and career options.
- Skill modules are introduced early in the school curriculum, and students can choose skill development courses aligned with industry standards.
- Various states have adopted innovative approaches to skill education, such as establishing incubation centers and integrating skill development into the curriculum.
Schemes of Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Provides free short-duration skill training programs and monetary rewards to encourage skill development. Over 1.48 crore people have been trained/oriented under this scheme.
- Skill India Mission: An umbrella scheme encompassing various skilling programs to empower youth with industry-relevant skills and improve productivity.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS): Provides vocational training and skill development to non-literates and school dropouts, with a focus on women and marginalized communities. Around 26.4 lakh people have been trained under this scheme.
- Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS): Provides long-term training through a network of ITIs to ensure a steady flow of skilled workers in different trades. Over 79.5 lakh people have been trained under this scheme.
- Advanced Vocational Training Scheme (AVTS): Offers short-term modular courses and tailor-made programs to meet specific industry requirements.
- Vocational Training Programme for Women: Focuses on providing skill training to women and creating employment opportunities for them.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme: Promotes apprenticeship training and increases the engagement of apprentices in industries. Approximately 30 lakh apprentices have been engaged in training.
- SANKALP (Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion): Improves short-term skill training qualitatively and quantitatively, strengthens institutions, and promotes market connectivity and inclusion.
- Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH): A unified platform for skilling, education, employment, and entrepreneurship, providing access to training programs, courses, and government services.
- PM VISHWAKARMA: Aims to upskill traditional artisans and provide them with credit support for business expansion.
- Skill Loan Scheme: Offers institutional credit to individuals for skill development courses aligned with the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF).
Entrepreneurship Development
- Startup India Programme: Launched to build a strong ecosystem for nurturing innovation and startups, driving economic growth, and generating employment opportunities.
- BHASKAR (Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry): A one-stop digital platform for connecting and collaborating with diverse stakeholders in the startup ecosystem.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Provides micro-credit and loans to micro-enterprises engaged in non-farm sectors, including activities allied to agriculture.
Conclusion
- India’s skilled workforce percentage is low, but initiatives like MSDE’s Vision 2025 present opportunities for skill development and entrepreneurship.
- Addressing challenges such as social acceptability, labor laws, and infrastructure is crucial to making India the Skill Capital of the World.


