15 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India, U.S. to double bilateral trade by 2030
- 1. India, U.S. to double bilateral trade by 2030
- 2. Vice-President questions involvement of Chief Justice in executive appointments
- 3. Trump’s Reciprocal Tariffs: A Disruptive Shift in Global Trade Dynamics
- 4. India-US Energy & Nuclear Partnership
- 5. Conserving the Immortal Marks of Archaeological Sites
- Prelim Facts
- 1. Guardians of ‘green gold’
- 2. Bangladesh in talks with Musk for rollout of Starlink service
- 3. US-India COMPACT
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Trade Negotiations and Energy Cooperation
- India and the U.S. have agreed to negotiate the first part of a trade agreement by autumn 2025.
- India aims to increase energy purchases from the U.S. to address concerns about the trade deficit.
- The two countries have set a target to more than double bilateral trade to $500 billion by 2030 under ‘Mission 500’.
- India is expected to increase its energy imports from the U.S. from $15 billion to $25 billion in the near future.
- Both nations have agreed to collaborate on Small Modular (nuclear) Reactors to strengthen India’s energy security.
Border Issue with China
- The U.S. President has offered to assist India in managing its border tensions with China.
Defence Cooperation and Military Sales
- The U.S. is working towards providing India with F-35 stealth fighter jets in the future.
- A new decade-long framework for defence cooperation has been announced.
- India will procure six additional P-8I Maritime Patrol aircraft to improve surveillance in the Indian Ocean Region.
- The U.S. and India will reopen talks on a Reciprocal Defence Procurement (RDP) agreement to align their defence procurement systems.
- The U.S. will review its International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) to facilitate military technology transfers to India.
- The two sides announced the U.S.-India COMPACT (Catalysing Opportunities for Military Partnership, Accelerated Commerce & Technology) framework to strengthen cooperation in defence, commerce, and technology.
Technology and Indo-Pacific Security Cooperation
- A new initiative, the Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance, has been launched to enhance underwater domain awareness technologies in the Indo-Pacific.
- The U.S. and India will scale up joint production and partnerships in the Indo-Pacific region.
Conclusion
- The bilateral discussions covered a wide range of topics, including defence, trade, energy, and technology.
- Both countries are working towards strengthening economic ties while addressing security and geopolitical concerns.
- The agreements mark a significant step in deepening India-U.S. cooperation for the future.
| Practice Question: Evaluate the significance of India-U.S. cooperation in trade, defense, and energy for regional stability and global strategic balance. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Vice-President questions involvement of Chief Justice in executive appointments
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|
Arguments in Favour of the Chief Justice’s Role in CBI Director’s Appointment
- Ensures Judicial Oversight: The Chief Justice’s involvement prevents arbitrary executive decisions, ensuring fairness in key appointments.
- Checks and Balances: This maintains a balance of power between the executive and judiciary, preventing excessive government control over investigative agencies.
- Protects Investigative Independence: A judicial presence safeguards CBI from political influence, ensuring impartial investigations.
- Precedent-Based System: The practice was introduced following judicial intervention to uphold transparency and fairness.
- Democratic Safeguard: In a democracy, multi-institutional participation prevents any one branch from overpowering others.
Arguments Against the Chief Justice’s Role in CBI Director’s Appointment
- Separation of Powers: Judiciary’s involvement in executive decisions contradicts the principle of separation of powers.
- Judicial Overreach: It may lead to excessive judicial interference in administrative matters.
- Accountability Issues: The executive, not the judiciary, is directly accountable to the people for governance.
- Delays in Appointment Process: Legal complexities and judicial scrutiny can slow down the selection of crucial officers.
- Global Practices Differ: In most democracies, investigative agency appointments are handled solely by the executive or legislature.
| PYQ: Constitutionally guaranteed judicial independence is a prerequisite of democracy. Comment. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2023) |
| Practice Question: Examine the implications of judicial involvement in executive appointments, particularly in the selection of the CBI Director, on the principle of separation of powers. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Trump’s Reciprocal Tariffs: A Disruptive Shift in Global Trade Dynamics
(Source – Indian Express, Section – The Ideas Page – Page No. – 11)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Understanding Reciprocal Tariffs
- Reciprocal tariffs refer to a system where the US imposes the same level of import duties on foreign goods as the exporting country imposes on US goods.
- This challenges existing trade norms under the WTO, which have historically allowed developing countries to maintain higher tariff barriers for economic protection.
- If implemented, this approach could significantly disrupt global trade flows.
Impact on Free Trade and WTO Norms
- Since World War II, global trade policies have moved towards liberalization, promoting free trade as a mutually beneficial system.
- Under WTO agreements, developing countries like India enjoy “special and differential treatment” to protect their domestic industries.
- Trump’s reciprocal tariffs disregard these exemptions, threatening the carefully balanced international trade system.
Potential Challenges in Implementation
- Calculating reciprocal tariffs is complex, as it involves accounting for government subsidies, tax breaks, and other economic incentives provided to domestic industries.
- If the US factors in these elements while setting tariffs, developing nations like India—which support their industries through subsidies—could face severe tariff hikes, impacting their exports to the US.
Trump’s Motivation Behind the Move
- Trump’s tariff policy stems from his belief that trade deficits are unfair and harm the US economy.
- The US runs a significant trade deficit, particularly with China, and Trump views this as evidence of other nations exploiting American markets.
- By enforcing reciprocal tariffs, he aims to reduce this imbalance either by forcing countries to buy more US goods or compelling foreign businesses to establish manufacturing bases in the US.
Are Trade Deficits Always Harmful?
- While a trade deficit indicates that a country imports more than it exports, it is not necessarily harmful.
- It can reflect strong consumer demand and economic prosperity. In a globalized economy, trade deficits and surpluses are relative—India has a surplus with the US but runs a deficit with China.
- A balanced trade policy should focus on boosting domestic productivity rather than imposing restrictive tariffs.
Impact on India
- India has been directly mentioned in Trump’s tariff rhetoric.
- If reciprocal tariffs are imposed, India may have to increase imports of US goods—such as defense equipment and energy—to offset the trade imbalance.
- While this could lower the cost of American products for Indian consumers, it may also weaken the rupee due to increased dollar demand.
- Additionally, the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative could be impacted, as increased reliance on US imports may hinder domestic manufacturing growth.
- While cheaper American products may benefit Indian consumers, the long-term economic impact on India’s self-reliance strategy needs careful evaluation.
Geopolitical Considerations
- The US’s aggressive trade stance is not limited to China or India—it extends to allies like Canada and the EU.
- Trump’s dismissive attitude towards trade agreements and economic partnerships suggests that India should be cautious in expecting stable trade relations with the US.
- While India stands to gain from better trade access to US markets, over-reliance on American economic policies could create vulnerabilities in the long run.
Conclusion
- Trump’s reciprocal tariff policy represents a major shift in global trade dynamics, moving away from cooperative frameworks towards a more unilateral approach.
- While the short-term impact may be a reduction in trade deficits, the long-term effects could include trade disruptions, strained diplomatic relations, and economic instability for developing nations like India.
- Balancing trade with self-reliance will be crucial for India as it navigates this evolving landscape.
| Practice Question: Discuss the concept of reciprocal tariffs and analyze their potential impact on global trade, especially for developing countries like India. How should India respond to such trade policies? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. India-US Energy & Nuclear Partnership
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 14)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Civil Nuclear Collaboration & Legislative Challenges
- A crucial development is the commitment to fully implement the US-India 123 Civil Nuclear Agreement.
| India-US Nuclear Deal |
|
- However, India must amend its Atomic Energy Act, 1962, to allow private sector participation in nuclear power operations, and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010, to address liability concerns that have deterred foreign investors.
- The US seeks legislative assurances from India, but India’s political landscape could pose hurdles in passing these amendments.
‘810’ Roadblock & US Legislative Restrictions
- India is pressing the US for an exemption from the ‘810’ authorisation, which restricts American nuclear companies from manufacturing nuclear equipment or designing reactors outside the US.
- This exemption is critical for India’s plans to develop Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), as India aims to co-produce components and localize technology transfer.
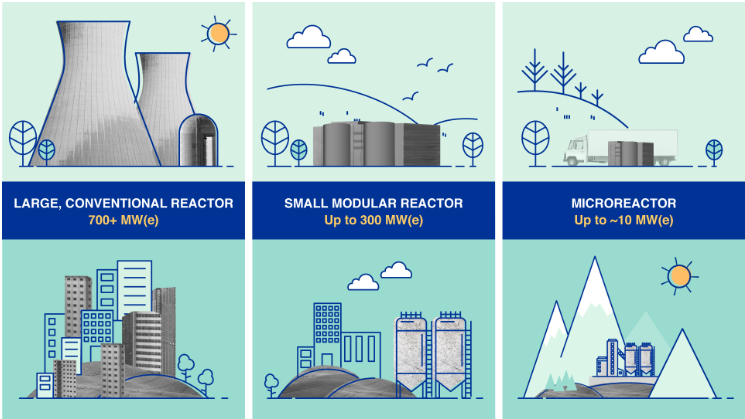
| What are Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)? |
Features:
|
Importance of SMRs for India
- SMRs, with capacities between 30MWe to 300MWe, are seen as the future of nuclear energy due to their cost-effectiveness and adaptability.
- India is positioning itself as a leader in SMR technology to support its clean energy transition and enhance global strategic influence.
- However, for this ambition to materialize, US legislative flexibility on ‘810’ will be crucial.
Conclusion
- While both nations recognize the potential of their nuclear partnership, successful collaboration will depend on legislative amendments in India, US policy adjustments on ‘810’ restrictions, and ensuring a commercially viable framework for foreign investors.
| Significance of the deal |
|
| PYQ: With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the India-US Energy Security Partnership in the context of civil nuclear cooperation. Analyze the legislative and regulatory challenges that need to be addressed for the successful implementation of the 123 Civil Nuclear Agreement. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Conserving the Immortal Marks of Archaeological Sites
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2103241 )
| Topic: GS1 – History – Architecture |
| Context |
|
India’s Rich Cultural Heritage
- India is home to some of the most iconic cultural and archaeological treasures in the world.
- These include intricately carved temples, historic ruins, and religious sites spread across the country.
Threats from Climate Change
- Climate change and extreme weather patterns are putting these historical sites at risk.
- Factors such as rising sea levels, heatwaves, forest fires, torrential rains, and strong winds are accelerating damage.
- Both movable and immovable heritage is deteriorating due to these environmental challenges.
- Urgent intervention is necessary to protect these cultural landmarks and preserve India’s cultural identity.
| Role of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) |
|
Increased Funding for Monument Protection
- The Government has significantly increased funding for monument conservation.
- In 2020-21, ₹260.90 crores were allocated, with an expenditure of ₹260.83 crores.
- By 2023-24, this amount increased to ₹443.53 crores, reflecting a 70% rise in funding.
- The Government has enacted strict legal measures to prevent the commercialization and urban encroachment of heritage sites.
- The National Conservation Policy, 2014, provides guidelines for maintaining and conserving monuments.

Measures to Protect Cultural Sites from Climate Change
- ASI regularly monitors cultural heritage sites to assess climate change impacts.
- Climate-resilient solutions, such as scientific treatments and preservation techniques, are being adopted.
- Automated Weather Stations (AWS) have been installed in collaboration with ISRO to track weather conditions affecting monuments.
- Air pollution monitoring is conducted at key sites to control the impact of pollutants on heritage structures.
- ASI coordinates with other government agencies to develop strategies for protecting historical sites.
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and ASI have formulated guidelines for risk assessment, preparedness, and recovery in case of disasters.

Conclusion
- Preserving India’s cultural heritage is a continuous process that requires coordinated efforts.
- ASI, in collaboration with other agencies, is actively working to monitor, protect, and conserve historical sites.
- By implementing environmental, legal, and security measures, the Government is ensuring that these historical treasures are safeguarded for future generations.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges posed by climate change and urbanization to India’s cultural heritage. What measures has the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) taken to address these threats? (250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelim Facts
1. Guardians of ‘green gold’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 9)
| Context |
|
Introduction
- Konda Veduru is a species of bamboo particularly found in the Godavari Valley of Andhra Pradesh.
- It is widely used by the Konda Reddi and Koya tribes for food, livelihood, and commercial purposes.
Why is it called green gold?
- Konda Veduru is called “green gold” due to its fast growth, high economic value, and multiple uses in construction, handicrafts, and paper production.
- Its eco-friendly nature and sustainability enhance its importance.
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in hill plains and forests, especially in the Godavari Valley.
- Covers over 53% of India’s total bamboo area (about 2.25 lakh hectares in Andhra Pradesh).
Culinary Significance
- A staple food of Konda Reddi tribes.
- Used in making Kommu Koora, a dish with bamboo shoots, cereals, and meat.
- Must be boiled before consumption to remove toxins.

Economic and Cultural Importance
- Used in tobacco curing and sold in tribal markets.
- A vital livelihood source for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
2. Bangladesh in talks with Musk for rollout of Starlink service
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
What is Starlink?
- Satellite Internet Service: Starlink is a satellite-based broadband internet service developed by SpaceX, the aerospace company founded by Elon Musk.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites: It uses a constellation of low Earth orbit satellites to provide high-speed internet access globally, especially in remote and underserved areas.
- High-Speed Connectivity: Starlink aims to deliver speeds of up to 250 Mbps, with low latency compared to traditional satellite internet.
- Global Coverage: It is designed to provide internet access in rural and geographically isolated locations where traditional broadband infrastructure is limited or unavailable.
- Growing Network: As of 2025, Starlink has deployed thousands of satellites and continues to expand its coverage worldwide.
- Affordable Access: While initially expensive, SpaceX is working to make Starlink more affordable for widespread adoption.
- Applications: It can support education, emergency response, businesses, and government services in remote regions.
3. US-India COMPACT
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Cover Page- Page No. – 01)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Strengthening Strategic Ties
- The launch of the US-India COMPACT (Catalyzing Opportunities for Military Partnership, Accelerated Commerce & Technology) for the 21st Century marks a significant step in deepening bilateral relations across multiple domains.
- This initiative reflects mutual trust and aims for transformative change, particularly in defence and high-tech sectors.
Strategic Defence Cooperation
- The agreement underscores India’s growing defence partnership with the US, particularly in countering China’s assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific.
- Key components include increased military sales, co-development, and technology transfers.
- Discussions on the F-35 stealth fighter jets and the Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance highlight the focus on future defence capabilities.
10-Year Defence Framework
- Both nations announced a new 10-year defence partnership framework, emphasizing interoperability, logistics, and joint manufacturing.
- Notable US-origin defence platforms integrated into India’s arsenal include C-130J Super Hercules, P-8I Poseidon, AH-64E Apache helicopters, and MQ-9B drones.
- Plans to co-produce Javelin Anti-Tank Missiles and Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicles in India further strengthen indigenous manufacturing.
Technology & Procurement Reforms
- India’s Major Defence Partner status and STA-1 designation facilitate access to advanced US military technology.
- To streamline defence trade, both nations plan to review arms transfer regulations (ITAR) and open negotiations for a Reciprocal Defence Procurement (RDP) agreement to align procurement processes and enhance bilateral defence supply chains.
Expanding Defence Technology Cooperation
- Recognizing India’s role in the Quad alliance, both nations pledged to accelerate cooperation in air defence, space, missile technology, and undersea systems.
- The US is also considering policy changes to release fifth-generation fighter jets and advanced maritime defence systems to India, strengthening its strategic deterrence capabilities.
check more – 14 February 2025 : Daily Current Affairs