Global Sea Ice Cover Hits Record Low, Triggering Climate Change Concerns
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained – Page No. – 17)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Climate Change |
| Context |
| ●Global sea ice cover hit a new record low, with combined Arctic and Antarctic sea ice extent dropping to 15.76 million sq km between February 8-13, 2025. |
Analysis of the news:
Record Low in Global Sea Ice Cover

- This surpasses the previous record low of 15.93 million sq km observed in early 2023, as per data from the US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
- Sea ice, distinct from icebergs and glaciers, plays a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate by reflecting solar radiation and insulating ocean heat.
Current Trends in Sea Ice Decline
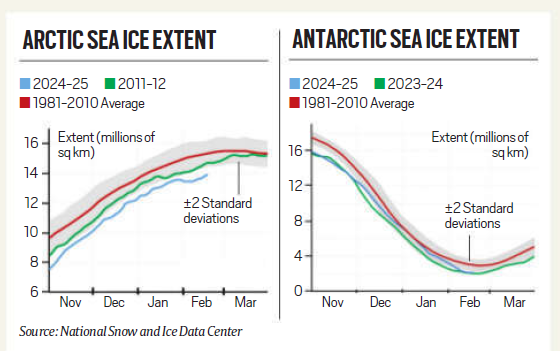
Arctic Sea Ice:
- Arctic sea ice has reached its lowest recorded extent for this time of year. Since the late 1970s, an average of 77,800 sq km of Arctic sea ice has been lost annually.
- Notably, between 1981 and 2010, Arctic sea ice shrank at a rate of 12.2% per decade each September, the month it typically reaches its minimum extent.
Antarctic Sea Ice:
- The Antarctic region, after witnessing year-on-year increases until 2015, experienced a dramatic loss of two million sq km of sea ice between 2014 and 2017.
- Although there was some recovery in 2018, sea ice levels again plummeted in 2023, falling two million sq km below average.
- Despite a slight improvement in 2024, levels remained 1.55 million sq km below the 1981-2010 average.
Key Drivers Behind the Dip
Arctic Factors:
- Delayed Freezing: Warm ocean waters around Hudson Bay delayed freezing.
- Storm Activity: Storms in the Barents and Bering Seas further fragmented fragile ice.
- Rising Temperatures: Elevated air temperatures, especially around Svalbard, exacerbated melting.
Antarctic Factors:
- Warm Air and Oceans: Higher air and sea temperatures during the southern hemisphere summer intensified ice melt.
- Ice-Breaking Winds: The thinner, more mobile Antarctic ice was vulnerable to winds that fragmented ice sheets.
- Ocean Warming: Persistent ocean warming provided a long-term backdrop for ice loss, affecting ice shelves and accelerating melt rates.
Implications of Declining Sea Ice
Accelerated Global Warming:
- Reduced sea ice exposes more ocean surface, increasing solar absorption and further warming the planet.
- Sea ice’s reflective surface (high albedo) is critical in maintaining cooler polar temperatures.
Polar Amplification:
- The polar regions are warming faster than the rest of the world.
- Loss of sea ice amplifies this effect, accelerating climate change impacts globally.
Disruption of Ocean Currents:
- Melting sea ice releases freshwater into oceans, reducing salinity and affecting the density-driven ocean circulation (thermohaline circulation).
- This slowdown can disrupt global climate patterns, threaten marine ecosystems, and destabilize polar ice shelves, raising the risk of further sea level rise.
Conclusion:
- The record-low sea ice extent serves as a stark warning of the accelerating impact of climate change.
- The intertwined dynamics of warming oceans, fragile ice systems, and disrupted global currents highlight the urgent need for global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the delicate balance of Earth’s polar ecosystems.
| Practice Question: Discuss the factors contributing to the recent record low in global sea ice cover and analyze its potential impact on global climate patterns and ocean circulation. (150 Words /10 marks) |
