Key Insights from the 2024 Panchayat Devolution Index
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Express Network- Page No. – 12)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
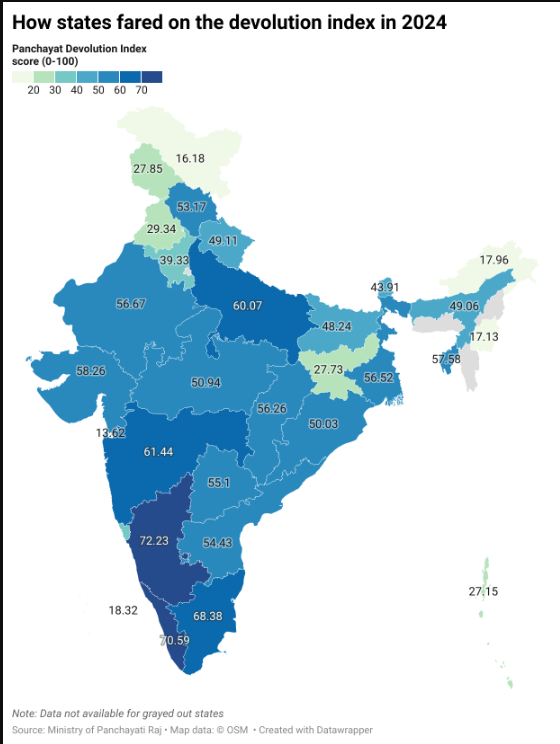
Top Performers and Improvements
- The 2024 Panchayat Devolution Index (PDI), developed by the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA), highlights Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu as the top performers in devolution of powers to panchayats.
- Uttar Pradesh and Bihar recorded the most significant improvements.
- The index, based on six parameters—framework, functions, finances, functionaries, capacity building, and accountability—shows a modest national average increase from 92 (2013-14) to 43.89 (2024).

- However, Manipur, Arunachal Pradesh, and Jharkhand rank lowest, with Manipur, Arunachal, and Haryana showing the biggest declines.
Representation and Inclusivity Challenges
- The representation of marginalized groups remains uneven.
- While Odisha leads with 51% women representation, Uttar Pradesh trails at 33.33% due to a lower reservation threshold.
- The national average for women representatives rose marginally to 44% in 2024. For marginalized communities, Punjab leads in SC representation (36.34%), Chhattisgarh in ST representation (41.04%), and Bihar in OBC representation (39.02%).
- However, disparities persist, with some states lagging in meeting reservation thresholds.
Infrastructure and Funding Constraints
- Inadequate infrastructure and inconsistent funding continue to hinder panchayats.
- Of the ₹47,018 crore allocated by states in 2023-24, only ₹10,761 crore was released by November 2023.
- Infrastructure gaps are stark, with only seven states and UTs reporting 100% pucca panchayat buildings, while Arunachal Pradesh (5%) and Odisha (12%) lag significantly.
- Digital connectivity also remains a challenge—while 14 states and UTs reported 100% internet access, Haryana reported zero and Arunachal just 1% internet access in panchayats.
Way Forward
For strengthening local governance, states must ensure:
- Timely fund releases and consistent financial support.
- Universal digital infrastructure and internet connectivity in panchayats.
- Enhanced capacity building and training programs for local representatives.
- Strict adherence to reservation policies for better gender and social inclusivity.
A balanced devolution of powers, coupled with adequate infrastructure and inclusive representation, is essential for empowering panchayats and realizing the vision of grassroots democracy in India.
| Practice Question: Despite constitutional provisions for decentralization, Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in India continue to face challenges related to devolution of powers, representation, and infrastructure. Critically examine these challenges in light of the 2024 Panchayat Devolution Index and suggest measures to strengthen grassroots governance. (150 Words /10 marks) |
check more – Understanding the Importance and Quality of Government Spending in India

