12 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Is rising consumer credit cause for concern?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Rising Household Debt in India
- The Financial Stability Report (FSR) 2024 highlights the increasing stock of household debt in India.
- Household debt has risen from 36.6% of GDP in June 2021 to 41% in March 2024, and further to 42.9% in June 2024.
- While India’s household debt is lower than many emerging economies, its steady increase raises concerns.
Shifting Use of Borrowed Money
- Debt is generally taken to acquire assets, but household asset holdings have declined from 110.4% of GDP in June 2021 to 108.3% in March 2024.
- This suggests that more loans are being used for consumption rather than asset creation, which could indicate economic weaknesses.
Health of Borrowing and Borrowers
- Despite rising household debt, several factors indicate that the borrowing structure remains healthy.
- The rise in overall borrowing is due to an increase in the number of borrowers, rather than increased debt per borrower.
- The proportion of sub-prime borrowers (those with lower credit ratings) has declined, while prime and super-prime borrowers now hold nearly two-thirds of total household debt.
- Super-prime borrowers, who have the highest credit quality, are borrowing more but mainly for asset creation rather than consumption.
Impact of Consumer Borrowing on Credit Growth
- Since the pandemic, borrowing by individual consumers has been a key driver of credit growth.
- In response to this surge, regulatory measures were introduced in September 2023, slowing credit growth.
- The slowdown has led to a shift towards healthier borrowers, reducing risky lending.
Rising Consumption Loans and Income Inequality
- The share of loans taken for consumption has increased over time, with lower-income households borrowing mainly for daily expenses.
- Households earning less than ₹5 lakh per year mostly take unsecured loans (e.g., credit card debt) for consumption, while wealthier households borrow for housing.
- About 50% of loans taken by sub-prime borrowers are for consumption, whereas 64% of loans for super-prime borrowers are used for asset creation.
Rising Debt Stress for Lower-Income Groups
- Personal and credit card loan defaults increased in September 2024 compared to September 2023, signaling financial stress among lower-income borrowers.
- Many borrowers who have credit card or personal loan debt also have housing or vehicle loans.
- A default on one loan leads to all loans by the borrower being classified as non-performing loans (NPLs), increasing financial risks.
- If unsecured loans face growing defaults, it could create broader economic weaknesses.
Concerns About Household Debt and Economic Growth
- The increase in unsecured consumer loans could indicate that households are facing income insecurity post-pandemic.
- Alternatively, financial innovations like credit cards may be encouraging more borrowing.
- A higher share of consumption loans means fewer assets are being created, while household debt continues to rise.
Effects on Economic Growth and Multiplier Effect
- Lower-income households contribute more to economic growth because they spend a larger share of their income.
- However, if they are burdened with debt, a part of their income goes into loan repayments rather than consumption.
- This reduces the income multiplier, meaning that economic growth generated from the same level of investment is lower.
- When poorer households face high debt, policies like income tax cuts may not have the intended positive impact on economic growth.
Conclusion
- While the shift towards prime borrowers suggests a healthier loan portfolio, rising consumer debt remains a concern.
- Policymakers must monitor unsecured loans and rising consumption debt to prevent future economic instability.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of rising household debt in India, focusing on its impact on economic growth, financial stability, and income inequality. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. New, greener electrochemical process turns urine into plant fuel
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
A New Method to Extract Urea from Urine
- A new electrochemical process can extract urea from urine in solid form.
- This method converts urea into a crystalline compound called percarbamide.
- It helps in both wastewater treatment and resource recovery.
Importance of Urea in Agriculture
- Humans consume nitrogen from food and excrete it as urea in urine.
- Urea is nitrogen-rich and can serve as a natural fertilizer.
- Efficient extraction methods have been lacking, limiting its agricultural use.
The Potential of Pee-cycling
- An adult produces 450-680 liters of urine annually, containing essential nutrients.
- This amount of nutrients can grow wheat for a loaf of bread daily for a year.
- Extracting these nutrients can reduce waste and benefit agriculture.
The Scientific Process Behind Extraction
- Urea forms bonds with hydrogen peroxide, creating percarbamide, a stable solid.
- This solid releases oxygen steadily, making it useful in chemical reactions.
- Researchers used graphitic carbon catalysts to achieve nearly 100% purity in extraction.
Benefits and Future Applications
Researchers aim to expand this method to improve resource recycling.
The process enables slow nitrogen release for better crop growth.
It connects wastewater treatment with sustainable agriculture.
3. Proposed Income Tax Bill, 2025 Raises Privacy Concerns Over Digital Search and Seizure Powers
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 13)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Expanded Powers Over Digital Access
- While the existing Income-tax Act already allows tax authorities to search premises and seize electronic records, the new bill broadens this by authorizing officials to bypass access controls on digital environments.
- This includes social media accounts, email servers, cloud storage, and even encrypted communication platforms like WhatsApp.
- The bill explicitly allows the government to use password-breaking software or seek assistance from service providers to bypass login credentials.
Legal and Privacy Implications
- Privacy advocates argue that this change creates a legal loophole, as the existing Digital Personal Data Protection Act exempts tax authorities from privacy protections.
- Critics fear that the bill could lead to harassment, excessive government oversight, and misuse of personal data without proper legal safeguards.
- Legal experts point out that the bill represents a notable departure from the current Income-tax Act, which did not cover such extensive digital domains.
Expert and Stakeholder Reactions
- Legal and tax experts have voiced concern over the potential for misuse of power and lack of clarity on safeguards.
- The Internet Freedom Foundation (IFF) has urged the Select Committee of Parliament to incorporate the proportionality principle, ensuring that digital searches are conducted using the least invasive methods, as per the Supreme Court’s 2017 right to privacy judgment.
- Without clear protections, the bill risks facilitating unchecked surveillance and infringing on constitutional privacy rights.
Conclusion
- The proposed Income Tax Bill, 2025, significantly expands the government’s powers over digital search and seizure, raising critical privacy and legal concerns.
- Stakeholders have called for stronger safeguards to balance enforcement powers with individual privacy rights.
| Practice Question: Discuss the privacy concerns raised by the proposed Income-Tax Bill, 2025, regarding search and seizure powers in virtual digital spaces. How can a balance be maintained between the government’s investigative authority and citizens’ right to privacy? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 Introduced in Lok Sabha Amid Opposition Concerns Over Privacy and Rights
(Source – Indian Express, Section – In Parliament, Page – 08)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Objective and Scope
- The bill seeks to provide the Central Government with powers to regulate:
- Requirement of passports or other travel documents for entry and exit.
- Visa and registration requirements for foreigners.
- Oversight of foreigners’ activities through institutions like hospitals and universities.
- It aims to replace outdated pre-Constitution laws, including:
- Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920
- Registration of Foreigners Act, 1939
- Foreigners Act, 1946
- Immigration (Carriers’ Liability) Act, 2000
Government’s Justification
- Minister of State for Home Nityanand Rai argued that:
- The bill ensures national security and sovereignty.
- Reporting of foreign nationals by hospitals and medical institutions is already mandated under an existing order; the bill brings it under formal legislation.
- It will eliminate overlaps and contradictions in the existing legal framework.
Opposition’s Concerns
- Violation of Fundamental Rights – the bill violates multiple constitutional rights and lacks an appeal mechanism against immigration officer decisions.
- Impact on Talent Inflow – the bill might restrict the inflow of global talent in fields like academics and medical science.
- Superfluous Nature – Existing laws have so far regulated immigration effectively, making the bill redundant.
- Lack of Safeguards – Concerns about potential misuse of discretionary powers and the absence of a grievance redressal mechanism.
Potential Impact
- Positive Impact – Greater clarity and efficiency in handling immigration and foreigner registration issues.
- Negative Impact – Possible misuse of discretionary powers, affecting the rights of foreign nationals and Indian citizens interacting with them.
Conclusion
- The bill seeks to modernize and consolidate existing immigration laws but raises critical concerns over privacy, human rights, and administrative overreach.
- Addressing these issues through parliamentary scrutiny and incorporating safeguards will be key to ensuring a balanced and effective law.
| Practice Question: The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025, aims to streamline immigration and foreigner-related regulations in India. Discuss the key provisions of the bill, the concerns raised by the opposition, and its potential impact on constitutional rights and national security. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. SCHEME FOR TEXTILE INDUSTRY
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2110123 )
| Context |
|
PM MITRA Parks Scheme

- The scheme focuses on developing modern, large-scale, integrated industrial parks for the textile sector.
- Seven PM MITRA parks will be established in Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- These parks will provide world-class infrastructure, including plug-and-play facilities, with a financial outlay of ₹4,445 crore until 2027-28.
- The objective is to make India a global hub for textile manufacturing and exports.
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
- Encourages large-scale manufacturing in Man-Made Fibre (MMF) apparel and technical textiles.
- Aims to enhance India’s competitiveness in the global textile market.
National Technical Textiles Mission
- Focuses on research, innovation, market development, skill enhancement, and export promotion in technical textiles.
SAMARTH – Skilling Initiative
- Provides skill development programs for the textile sector.
- Aims to improve employment opportunities through demand-driven training.
Technology Upgradation and Sericulture Development
- ATUFS offers financial incentives for modernizing textile machinery.
- Silk Samagra-2 supports the sericulture value chain for better silk production.
Handloom and Handicraft Promotion
- National Handloom Development Programme and Raw Material Supply Scheme assist weavers with raw materials, upgraded looms, and concessional loans.
- National Handicrafts Development Programme and Comprehensive Handicrafts Cluster Development Scheme provide financial aid for artisan development, skill training, and marketing support.
Conclusion
- These initiatives aim to boost investment, improve infrastructure, and create employment opportunities in India’s textile sector.
| Practice Question: How does the PM MITRA Parks Scheme contribute to making India a global hub for textile manufacturing and exports? Explain its impact along with other government initiatives supporting the textile sector. (250 Words /15 marks) |
6. PM-DAKSH YOJANA
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
PM-DAKSH Scheme:

- PM-DAKSH Scheme is a Central Sector Scheme aimed at providing skill training to marginalized communities, including SCs, OBCs, EWSs, DNTs, and Safai Karamcharis, including waste pickers.
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It is implemented without state-wise fund allocation, as states have no role in its execution.
- Training is provided by empanelled institutes offering job-specific courses based on regional demand through the SIDH Portal of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
- The scheme focuses on wage and self-employment, ensuring certified trainees receive placement opportunities.
- Awareness campaigns are conducted through print and social media, as well as community outreach programs.
- Since its inception, over 1.87 lakh beneficiaries have been trained across various states and union territories.
7. Doubling Farmers Income
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2110414 )
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context |
|
Government Support for Agriculture in India
- Agriculture is a State Subject, but the Government of India supports states through policy measures, budgetary allocation, and various schemes to help farmers.
- The budget allocation for the Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) has increased from ₹21,933.50 crore in 2013-14 to ₹1,22,528.77 crore in 2024-25.
Major Schemes to Increase Farmers’ Income
The Government of India has launched several schemes to increase farmers’ income and provide financial security:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) – Provides ₹6,000 per year in three installments to landholding farmers for agricultural and domestic needs.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana (PM-KMY) – Offers pension benefits to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) – Provides crop insurance against losses due to natural calamities.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) – Helps farmers get affordable credit for farming activities.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) – Supports infrastructure development in the agriculture sector.
- Formation of 10,000 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) – Helps small farmers work together for better market access.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) – Promotes chemical-free farming to improve soil health and reduce costs.
- Other Schemes – Cover areas like agriculture mechanization, organic farming, irrigation, horticulture, oilseeds production, and digital agriculture.
PM-KISAN Scheme Achievements
- PM-KISAN is a Central Sector Scheme, implemented since December 1, 2018.
- As of March 5, 2025, over ₹3.68 lakh crore has been transferred to farmers’ accounts.
Promotion of Natural Farming
- The Union Cabinet approved the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) on November 25, 2024.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme with a budget of ₹2,481 crore (Government share: ₹1,584 crore, State share: ₹897 crore).
- Natural Farming is a chemical-free method using local livestock and diverse crop systems to improve soil health and climate resilience while reducing input costs.
| Practice Question: To what extent have government schemes and policy measures been effective in achieving the goal of doubling farmers’ income in India? (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Bharti to bring in Starlink’s satellite net services to India
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
What is Starlink?
- Starlink is a satellite-based internet service developed by SpaceX, a company founded by Elon Musk.
- It aims to provide high-speed, low-latency internet access globally, especially in remote and underserved areas.
- The network consists of thousands of small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO) to ensure fast and reliable connectivity.
- Users access the service through a Starlink dish and router, which connect to the satellites.
- It supports applications such as online streaming, gaming, video calls, and remote work.
- Starlink is expanding worldwide and requires government approvals before operating in specific countries.
| Other similar services: |
|
2. Nigeria moves to tame the largest cryptocurrency market in Africa
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Growing Crypto Adoption in Nigeria
- Nigeria is one of the largest cryptocurrency markets in the world.
- In 2023 and 2024, Nigeria ranked second globally in crypto adoption, following India.
Regulatory Efforts and Challenges
- Nigerian authorities are working to regulate the cryptocurrency market to provide legal clarity.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has granted initial approval to two cryptocurrency exchanges.
- The government is facing challenges due to widespread fraud and scams in the sector.
Future Regulatory Framework
- Nigeria’s parliament is discussing an investment and securities bill.
- If passed, the law will create a structured regulatory framework for digital currencies.
- The goal is to ensure investor protection and market stability.
3. Delhi Named World’s Most Polluted Capital for Sixth Consecutive Year
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 13)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
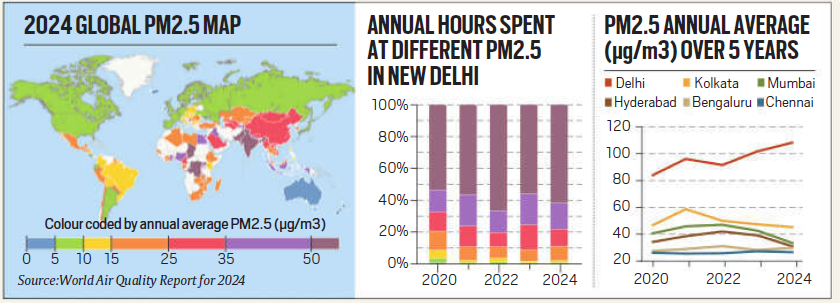
Global Air Quality Report Findings
- According to the World Air Quality Report 2024 by IQAir, Delhi has been ranked as the world’s most polluted national capital for the sixth consecutive year.
- Thirteen of the 20 most polluted cities are in India, with Byrnihat (Assam-Meghalaya border) recorded as the most polluted city globally with a PM2.5 concentration of 128.2 µg/m³.
- The report analyzed data from 40,000 air quality monitoring stations across 138 countries.
Global Pollution Status
In 2024, most of the global population breathed air exceeding the WHO’s PM2.5 safety limit of 5 µg/m³. Only 12 countries and regions, mainly in Latin America, the Caribbean, and Oceania, met the recommended limits. The five most polluted countries were:
- Chad – 91.8 µg/m³
- Bangladesh – 78 µg/m³
- Pakistan – 73.7 µg/m³
- Congo – 58.2 µg/m³
- India – 50.6 µg/m³

Pollution in India
- India’s average PM2.5 concentration in 2024 was 50.6 µg/m³, a 7% decline from 54.4 µg/m³ in 2023.
- Despite this, six Indian cities were among the 10 most polluted globally. Delhi recorded an annual average PM2.5 of 91.6 µg/m³, almost unchanged from 92.7 µg/m³ in 2023.
Causes of Pollution
The major contributors to India’s high PM2.5 levels include:
- Crop stubble burning – responsible for 60% of peak pollution levels.
- Vehicular emissions – particularly in urban areas.
- Industrial discharges – from manufacturing and processing units.
- Construction dust – from ongoing infrastructure projects.
Seasonal Pollution Patterns
- January – Poor air quality was reported in Delhi and Himachal Pradesh.
- November – Extreme pollution levels were recorded in Delhi, Punjab, Chandigarh, Haryana, and Himachal Pradesh, largely due to stubble burning.
Health Impact
High PM2.5 levels pose serious health risks, including:
- Respiratory problems
- Chronic kidney disease
- Cancer
- Stroke and heart attacks
check more – 11 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs

