Amid high tensions with Israel, Iran’s missile programme comes into focus
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
| ● Iran’s missile programme, long seen as a key element of its defence, faced scrutiny after a largely unsuccessful April 2024 assault on Israel.
● Despite launching hundreds of projectiles, many failed or were intercepted, raising questions about their reliability as effective military tools, especially amid escalating tensions with Israel. |
Iran’s Missile Programme: Key Points:
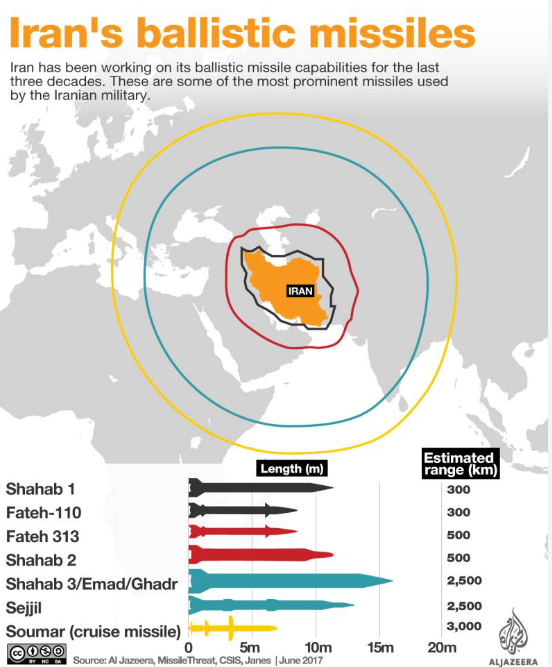
- Origins: Iran’s missile programme began in the 1980s during the Iran-Iraq War. Over time, it has become a core element of the country’s defence strategy.
- Capabilities: Iran possesses a range of missile types, including short-, medium-, and long-range ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and drones. Key missile classes include Shahab, Sejjil, and Ghadr missiles.
- Ballistic Missiles: Iran’s long-range missiles, like the Shahab-3, can reach up to 2,000 km, putting Israel and U.S. bases in the Gulf within range. The missiles’ accuracy, however, remains questionable.
- Missile Production: The country claims to produce its missiles domestically, though some reports suggest outside technological support from countries like North Korea.
- April 2024 Attack: Iran launched 120 ballistic missiles, 30 cruise missiles, and 170 drones at Israel. Many failed to reach targets, raising concerns about missile reliability.
- Strategic Importance: Iran’s missile programme is seen as a deterrent to regional rivals like Israel and Saudi Arabia. It serves as a key tool in asymmetric warfare, where Iran cannot match conventional military power.
- Proxy Use: Iran’s missiles have been used by regional proxies like Hezbollah in Lebanon and the Houthis in Yemen.
