Antimatter idea offers scientists clue to cracking cosmic mystery
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Antiparticles and Their Mysteries
- Antiparticles are counterparts to particles, with the same mass but opposite charge, theorized by Paul Dirac in 1928 and observed by Carl Anderson in 1932.
- For instance, the antielectron (positron) is the antiparticle of the electron and carries a positive charge.
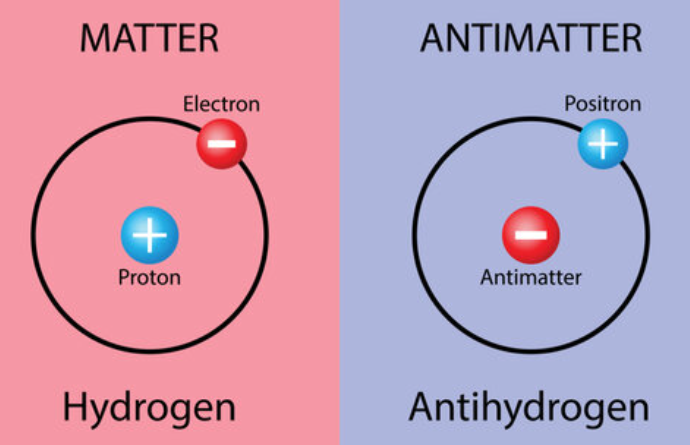
- They are a consequence of quantum mechanics and special relativity, traveling as if backward in time.
Scarcity of Antimatter in the Universe
- While antiparticles are present in cosmic rays and even generated by human bodies, antimatter is scarce in the observable universe.
- Matter dominates galaxies, with the early universe having a slight asymmetry: for every 1.7 billion proton-antiproton pairs, one extra proton existed.
- This asymmetry allowed matter to survive annihilation and form stars and planets.
Challenges in Explaining the Asymmetry
- The Standard Model of particle physics struggles to fully explain why matter dominates over antimatter.
- Any theory addressing this requires meeting the Sakharov conditions, which include CP symmetry violation, baryon number violation, and interactions out of thermal equilibrium.
| Sakharov Conditions: |
These three conditions explain how matter could dominate over antimatter after the Big Bang. |
Recent Progress
- A 2024 study showed that meson decays could satisfy CP symmetry violation in the Standard Model, involving hypothetical particles.
- The new mechanism suggests these particles were prominent in the early universe but rare today, aligning with quantum field theory.
Path Ahead
- This finding addresses one Sakharov condition but challenges remain for the others, advancing understanding of the universe’s matter-antimatter asymmetry.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of the Sakharov conditions in explaining matter-antimatter asymmetry in the universe. Highlight recent developments and their implications for the Standard Model of particle physics. (150 Words /10 marks) |
