Farm fire in China-US trade
(Source – Indian Express, Section –Explained, Page – 09)
|
Topic: GS3 – Economy |
|
Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
US Trade Actions
-
The U.S. imposed a 25% tariff on most Canadian and Mexican imports but exempted goods under USMCA, sparing 50% of Mexican and 38% of Canadian imports.
-
Canadian energy products and potash fertilizers from both nations face only a 10% tariff.
-
In contrast, China faces harsher trade measures, with tariffs escalating from 10% (Feb 4) to 20% (March 4), with no exclusions or pauses.
China’s Retaliation
-
China imposed 10-15% tariffs on U.S. agricultural products such as soybeans, wheat, corn, and meat.
-
In 2024, China’s total agricultural imports from the U.S. stood at $27.29 billion, with soybeans ($12.76 billion) being the largest component.
Shift in China’s Strategy
-
China aims to reduce dependence on U.S. agricultural imports and boost domestic production for food security.
-
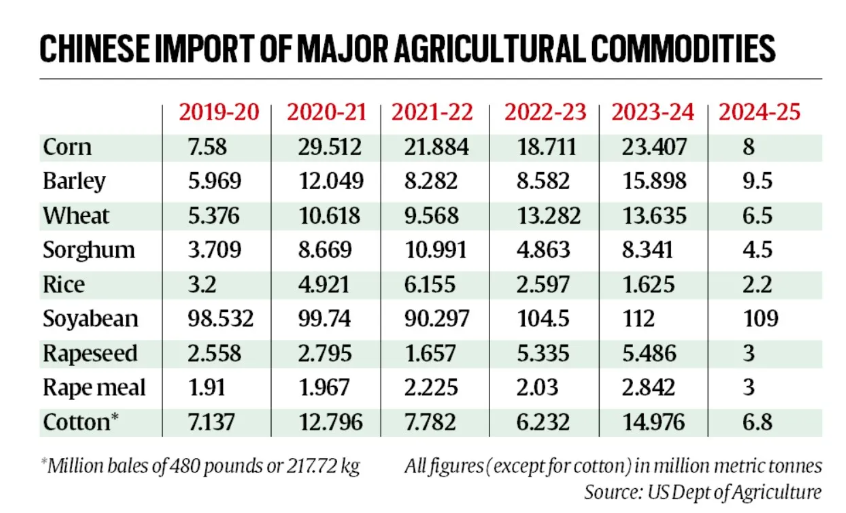
In 2023-24, China was the world’s largest importer of soybean, rapeseed, wheat, barley, sorghum, oats, and cotton.
-
COFCO and Sinograin, China’s state-owned firms, play a key role in securing food supply and reducing reliance on Western agri-commodity traders.
-
Following the 2008 food crisis and recent global disruptions, China ramped up strategic stockpiling through imports.
Emphasis on Self-Reliance
-
In April 2023, China’s Ministry of Agriculture projected an increase in domestic grain production from 694 MT to 767 MT by 2032, with imports reducing from 148 MT to 122 MT.
-
China is shifting towards Brazilian and Argentinian grain suppliers, reducing U.S. soybean market share from 30% (2017-18) to 22% (2023-24).
-
The U.S. share of China’s agricultural imports is declining, with China increasingly relying on alternative sources.
Future Implications
-
The U.S.-China trade war may escalate, impacting global trade dynamics.
-
There could be pressure on India to open its markets to U.S. agricultural products.
-
China’s push for agricultural self-sufficiency aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat strategy, highlighting a global shift towards food security.
|
Practice Question: The ongoing U.S.-China trade war has led to significant shifts in global agricultural trade and food security strategies. Discuss how China’s emphasis on self-reliance in agriculture could impact global trade dynamics and India’s agricultural sector. (250 words) |
