How can design help a building be more climate-resilient?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment |
| Context |
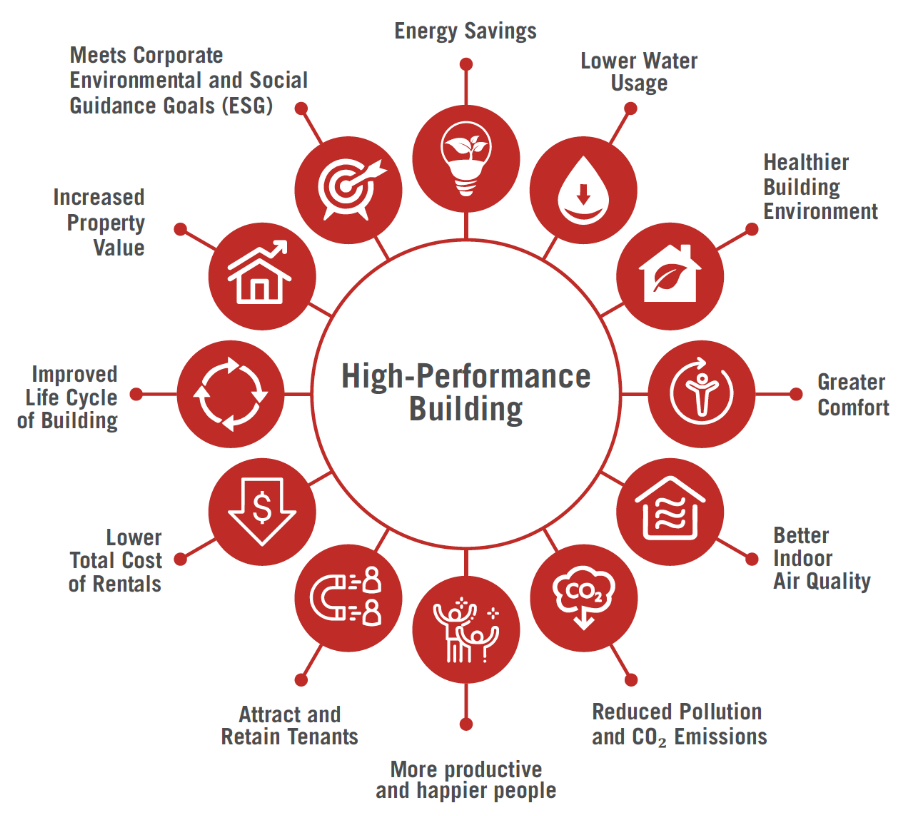
| ● High-performance buildings (HPBs) are key to sustainable construction, focusing on energy efficiency, climate resilience, and resource conservation.
● These buildings employ integrative design, sustainable materials, and advanced technologies to minimise environmental impact. ● HPBs are crucial in addressing global challenges such as climate change and urbanisation while improving operational efficiency. |
| What Are High-performance buildings (HPBs)? |
| ● High-performance buildings (HPBs) focus on sustainable construction with an emphasis on energy efficiency, climate resilience, and resource conservation.
● They utilise integrative design approaches and advanced technologies for energy-saving and environmental performance. ● HPBs are critical in mitigating climate change and addressing urbanisation challenges while enhancing operational efficiency. ● They are Designed to use less energy, conserve resources, and withstand unpredictable weather, HPBs play a key role in achieving sustainable living.
|
Sustainable Materials
- Focuses on materials that are durable, energy-efficient, and prioritise occupant health.
- Prefers materials with low embodied carbon (emissions produced during manufacturing) and high recycled content.
- Life-cycle assessments evaluate the environmental impact of materials and help select the most sustainable options.
- Low-emission interior materials improve indoor air quality by reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Energy Efficiency
- Buildings account for approximately 40% of global energy consumption.
- Passive design strategies use natural light, optimise building orientation, and take advantage of thermal mass to reduce heating, cooling, and lighting demands.
- Active design strategies include energy-efficient HVAC systems, lighting, appliances, and smart technologies (e.g., automated lighting control and occupancy sensors).
- HPBs aim for net-zero or net-positive energy performance by using renewable energy systems such as solar and wind.
Water Conservation
- HPBs address water scarcity through efficient fixtures, rainwater harvesting, and on-site wastewater treatment systems.
- Rainwater harvesting provides water for non-potable uses like irrigation and sanitation.
- On-site systems recycle greywater for irrigation and treat blackwater using biological systems like constructed wetlands.
- Advanced water management systems, such as aerobic membrane bioreactors, contribute to zero-discharge status.
Performance Monitoring
- Continuous performance monitoring ensures HPBs operate efficiently and meet design goals.
- Advanced systems track energy consumption, water use, and indoor environmental quality in real time.
- Real-time data helps identify inefficiencies and informs corrective actions, enhancing operational performance.
Climate Resilience
- HPBs are designed to withstand extreme weather events, including heatwaves and flash floods.
- Features like durable materials, diverse energy systems, and passive survivability ensure buildings remain habitable during power outages.
- Renewable energy systems and water management practices (e.g., rainwater harvesting) ensure sustainability during adverse weather conditions.
Conclusion
- HPBs set benchmarks for sustainability and resilience in modern construction.
- They provide environmental, economic, and social benefits, including reduced operational costs and improved real estate value.
- Widespread adoption of HPBs can lead to a more sustainable and resilient built environment.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of High-Performance Buildings (HPBs) in promoting sustainability in urban construction. Highlight the key strategies involved in their design, energy management, and climate resilience. (150 Words /10 marks) |