How would a carbon market function?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation |
| Context |
| ● COP29 in Baku approved standards for establishing an international carbon market, emphasizing its potential to reduce global emissions.
● Carbon markets enable trading carbon credits to internalize environmental costs and curb pollution. ● However, challenges like governmental manipulation and corporate misuse persist. |
COP29 and Carbon Markets
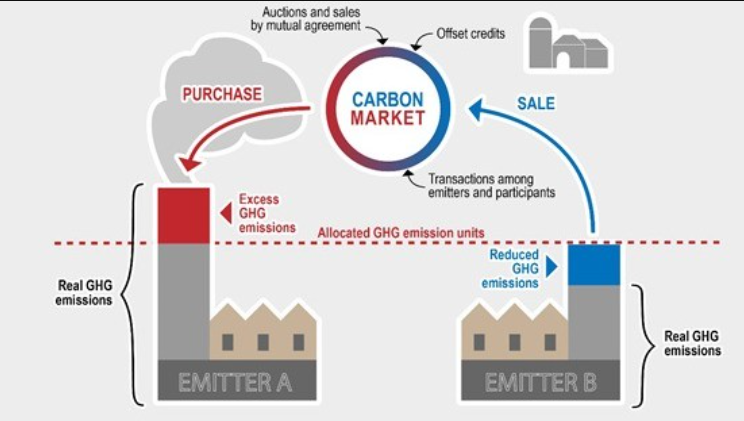
- COP29, held in Baku, Azerbaijan, has approved standards to establish an international carbon market, potentially operational by next year.
- This step highlights the role of carbon markets in curbing carbon emissions and addressing climate change challenges.
| What is a Carbon Market? |
| ● A carbon market allows buying and selling of rights to emit carbon dioxide.
● Governments issue carbon credits, each equivalent to 1,000 kilograms of carbon dioxide, to limit emissions. ● Entities without carbon credits are prohibited from emitting carbon. ● The market price for carbon credits is determined by supply and demand dynamics. ● Carbon offsets involve businesses purchasing credits from environmental organizations that commit to carbon reduction activities like tree planting. |
Benefits of Carbon Markets
- Carbon markets address the problem of externalities, where the environmental cost of economic activities is not internalized in market prices.
- They impose financial costs on firms for carbon emissions, encouraging them to reduce pollution.
- Standardized accounting frameworks and technological advancements have enhanced corporations’ ability to monitor emissions and report accurately.
- Voluntary reporting systems like the Carbon Disclosure Project are preferred by corporations, while they oppose government interventions.
- Firms advocate free trading of carbon credits, which they claim ensures efficient allocation of resources.
Challenges of Carbon Markets
- Governments may manipulate the supply of carbon credits, either oversupplying them to reduce prices or allowing firms to bypass regulations.
- Firms purchasing carbon offsets may engage in virtue signaling, with limited actual impact on reducing emissions.
- Critics question governments’ ability to determine the optimal supply of carbon credits, as political interests may lead to restrictive or overly lenient policies.
- Restrictive policies may hinder economic growth, while lax regulations may fail to achieve meaningful emission reductions.
The Way Forward
- The effectiveness of carbon markets depends on transparent governance, strict enforcement, and incentivized participation by firms and governments.
- Ensuring accountability in carbon offset mechanisms and maintaining optimal credit supply are critical for achieving environmental goals.
- Collaboration between governments, corporations, and international bodies is essential to balance economic growth and climate commitments.
| PYQ: Should the pursuit of carbon credit and the clean development mechanism set up under UNFCCC be maintained even though there has been a massive slide in the value of carbon credit? Discuss with respect to India’s energy needs for economic growth. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of carbon markets in mitigating climate change. Highlight the challenges associated with their implementation and suggest measures to enhance their effectiveness. (150 Words /10 marks) |
