Income-tax Bill, 2025 Introduced
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained – Page No. – 19)
|
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
|
Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
A Move Towards Simplicity
-
The Income-tax Bill, 2025, introduced in Lok Sabha, aims to replace the six-decade-old Income-tax Act, 1961, by streamlining tax provisions, eliminating redundant sections, and introducing a more structured and comprehensible legal framework.
-
The bill focuses on clarity and ease of compliance for taxpayers, ensuring continuity without major structural changes in direct taxation.
Key Structural Changes: Shorter and More Organised
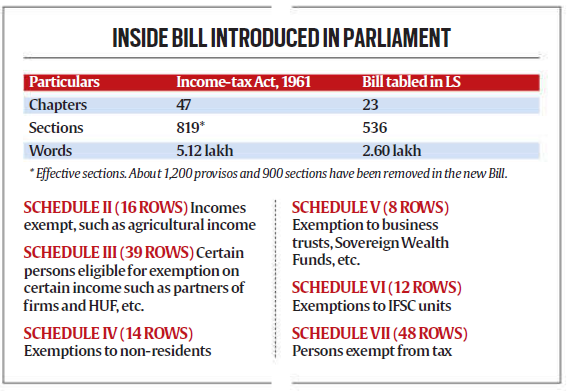
-
The new bill is 24% shorter than the current Act, with fewer chapters (23 vs. 47) and sections (536 vs. 819).
-
The complex numbering system used in the past has been eliminated, making navigation easier.
-
All tax-related deductions, exemptions, and TDS/TCS rates have been presented in tabular formats for better accessibility.
Shifting to ‘Tax Year’ from ‘Assessment Year’
-
A significant change is the replacement of the Assessment Year (AY) with the Tax Year, simplifying the process by aligning tax assessment with economic activity in the same financial year.
-
This eliminates confusion caused by tracking different periods for taxation.
Social Media and Crypto Regulation
-
The bill expands tax authorities’ access to digital assets and online spaces, including social media accounts, cloud servers, and online investments, enhancing scrutiny in surveys and searches.
-
Furthermore, cryptocurrencies have been formally classified as capital assets, reinforcing their taxability under capital gains.
Reforming Dispute Resolution
-
The bill introduces greater clarity in Dispute Resolution Panel (DRP) decisions by explicitly stating points of determination and reasoning, addressing past ambiguities that led to litigation.
Capital Gains and Deductions: Streamlining Exemptions
-
Outdated provisions such as Section 54E, which covered exemptions for capital gains before April 1992, have been removed.
-
The standard deduction, gratuity, and leave encashment provisions have been reorganized into a structured format for better comprehension.
Taxation Framework and Income Scope
-
While the income tax structure remains largely unchanged, the bill expands the definition of income to incorporate emerging sources.
-
Tax slabs for the new tax regime are clearly listed, but old tax regime slabs are not explicitly detailed, indicating a possible shift in focus towards the new structure.
The Road Ahead: Legislative Process and Implementation
-
The bill, following its Interim Budget 2024 announcement, is expected to undergo Parliamentary review before final approval.
-
Once passed, it will come into effect on April 1, 2026.
-
Despite its simplifications, tax experts note that compliance provisions remain largely unchanged, focusing primarily on reducing redundancy rather than introducing major policy shifts.
Conclusion: Towards a More Transparent Tax System
-
The Income-tax Bill, 2025, marks a major step toward simplification and transparency in India’s direct taxation system.
-
By reducing legal complexity, introducing structured formats, and eliminating obsolete provisions, the bill aims to enhance tax certainty, reduce litigation, and create a modernized and taxpayer-friendly framework.
|
Practice Question: Discuss the key features of the Income-tax Bill, 2025 and analyze its impact on India’s taxation system. How does it aim to simplify compliance and enhance tax transparency? (150 Words /10 marks) |

