India’s Bioeconomy Surges to $165 Billion
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 16)
|
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
|
Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Current Value and Growth Projections
-
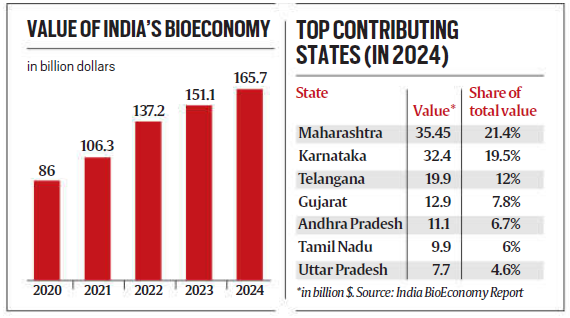
India’s bioeconomy has been valued at over $165 billion in 2024, contributing 4.2% to the national GDP.
-
According to the India BioEconomy Report, this sector has the potential to expand significantly, reaching $300 billion by 2030 and $1 trillion by 2047.
-
This growth is driven by advancements in biotechnology, sustainable bio-manufacturing, and increased industrial applications of biological resources.
Utilization of Bioresources
-
Bioeconomy involves the use of biological resources such as plants, animals, and microorganisms for industrial and commercial purposes.
-
While sectors like healthcare and agriculture have historically relied on bioresources, newer applications include biofuels, bioplastics, sustainable textiles, and bio-based chemicals.
-
Technologies like synthetic biology and precision biotherapeutics are expanding the role of biotechnology in pharmaceuticals and industrial processes, offering eco-friendly and cost-effective alternatives to conventional materials.
Expanding Industrial and Regional Footprint
-
India’s bioeconomy has almost doubled in the last five years, with the number of bio-based companies increasing by 90% since 2021.
-
The industrial sector leads in value generation ($78 billion), followed by pharmaceuticals, primarily vaccines (35%).
-
Research and IT, including biotech software and bioinformatics, emerged as the fastest-growing segments in 2024.
-
However, regional disparities exist, with Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh contributing over two-thirds of the sector’s value, while eastern and northeastern states account for less than 6%.
Challenges and Policy Interventions
-
Maintaining high growth rates will require increased innovation, better infrastructure, and policy reforms.
-
Addressing regional imbalances and regulatory hurdles, particularly in agricultural biotechnology, is essential.
-
Countries like Spain and Italy derive over 20% of their GDP from bioeconomy, indicating the need for India to scale up its efforts.
BioE3 Policy and Future Strategy
-
To strengthen its position as a global bio-manufacturing hub, India launched the BioE3 policy (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) in 2024.
-
This policy aims to boost R&D, encourage bio-industrialization, and support advancements in bio-based chemicals, functional foods, marine biotechnology, and climate-resilient agriculture.
-
The report also recommends setting up a National BioEconomy Mission and a single-window regulatory mechanism to streamline biotech innovations and unlock the full potential of India’s bioeconomy.
Conclusion
-
India’s bioeconomy is on a strong growth trajectory, driven by biotechnology innovations and increasing industrial applications of bioresources.
-
However, to sustain this momentum, addressing regional imbalances, regulatory hurdles, and infrastructure gaps is crucial.
-
Policies like BioE3 and the proposed National BioEconomy Mission can help India emerge as a global leader in bio-manufacturing and biotechnology-driven industries.
|
Practice Question: India’s bioeconomy has witnessed significant growth, contributing 4.2% to the GDP and holding the potential to reach $1 trillion by 2047. Discuss the key drivers of this growth, the challenges faced, and the policy measures needed to sustain and expand India’s bioeconomy. (250 Words /15 marks) |
