Integrated Action Essential to Tackle Climate, Biodiversity, and Hunger: IPBES Report
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
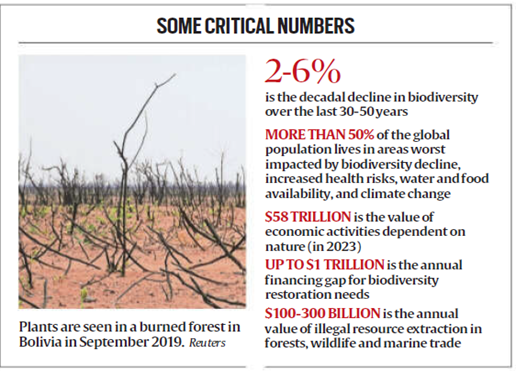
Interlinked Global Challenges: Climate, Biodiversity, and Hunger
- The latest report by the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) underscores the intricate connections between major global challenges: climate change, biodiversity loss, hunger, water scarcity, and health risks.
- Addressing these issues in isolation is ineffective and often counterproductive.
- Current economic activities significantly harm biodiversity, ecosystems, and health, with unaccounted adverse costs estimated at $10-25 trillion annually.
IPBES: Role and Contributions
- IPBES, akin to the IPCC but focused on biodiversity, consolidates scientific knowledge to inform global environmental agreements.
- Established in 2012, its assessments, such as the 2019 report on biodiversity threats, have shaped international frameworks like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
- This agreement aims to protect and restore 30% of ecosystems by 2030, highlighting IPBES’s impact on shaping actionable global targets.
Key Insights from the Nexus Report
- The IPBES Nexus Report identifies over 70 synergistic response measures addressing multiple challenges.
- Examples include restoring carbon-rich ecosystems, promoting sustainable diets, and implementing nature-based solutions.
- However, the report warns against actions that inadvertently harm other areas, such as increasing food production at biodiversity’s expense.
- Harmonizing responses is vital to ensure sustainable and inclusive benefits across sectors.
Economic Impacts of Biodiversity Decline
- The report stresses the economic value of biodiversity, with over half of global GDP dependent on nature.
- Biodiversity loss, currently at 2-6% per decade, poses significant risks to productivity and economic stability.
- Simultaneously, existing systems incentivize harmful practices. Transforming these systems could generate $10 trillion in business opportunities and 400 million jobs by 2030 through nature-positive models.
The Call for Transformative Change
- A parallel report, the Transformative Change Report, advocates for a paradigm shift in human-nature relationships, emphasizing equity, justice, inclusion, and adaptive learning.
- Immediate action is necessary to avoid escalating costs, with benefits including enhanced ecosystems and sustainable economic growth.
- A fundamental realignment of priorities is essential to halt and reverse ecological decline.
| Practice Question: Discuss the interlinkages between climate change, biodiversity loss, and food insecurity as highlighted by the IPBES Nexus Report. How can synergistic approaches help address these interconnected challenges effectively? (150 words/10 m) |
