Obesity: soft core of an epidemic of non-communicable diseases
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
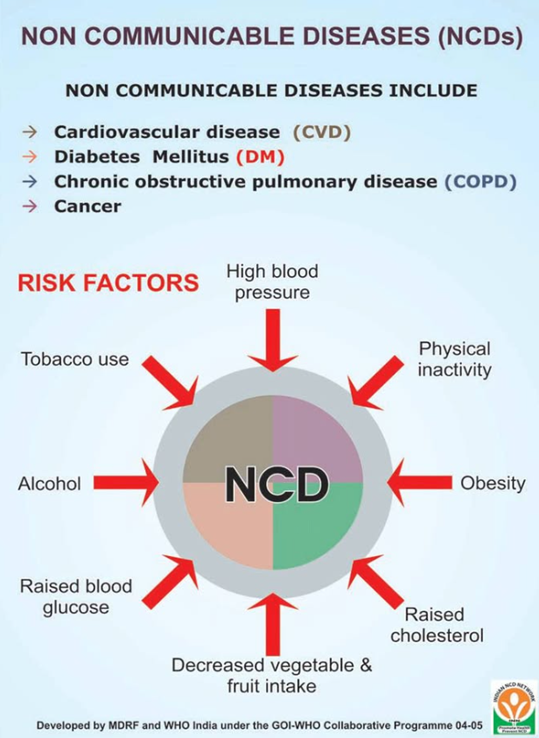
Obesity and Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)
- Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by excessive fat deposits that can harm an individual’s health.
- It significantly increases the risk of several NCDs, including diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and certain cancers.
- Additionally, obesity impacts quality of life factors such as sleep, mobility, and mental well-being.
- Obesity has been identified as a soft core for the epidemic of NCDs, exacerbating other health problems, and leading to early mortality.
Global and Childhood Obesity
- The World Health Organization (WHO) states that one in eight people worldwide are obese, and one in three are overweight.
- Worldwide, obesity in adults has doubled since 1990, and adolescent obesity has quadrupled.
- As of now, 37 million children under five years are overweight, while 390 million children and adolescents aged 5-19 years are overweight, and 160 million are obese.
- Childhood obesity in India is a growing concern, with the country ranking second globally for the highest number of obese children.
- Factors contributing to childhood obesity include a lack of physical activity, high-calorie foods, sugary drinks, and genetic influences.
| The Indian Scenario |
|
Obesity and Its Impact
- Obesity causes 3.4 million deaths annually worldwide, and India ranks third after China and the USA in terms of obesity-related deaths.
- Beyond the medical costs, obesity has economic repercussions, including loss of productivity, absenteeism from work, and premature mortality.
- The psychological effects of obesity are severe, leading to low self-esteem, mood disorders, and poor body image.
Addressing Obesity
- Weight loss is critical in preventing and treating obesity-related NCDs. Even modest weight reduction can lead to reduced blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and reduced diabetes risk.
- Treatments for obesity include newer medications and bariatric surgery, though they come with high costs and side effects.
- Prevention and treatment also focus on lifestyle changes like regular physical activity and avoiding unhealthy food.
- Recommendations include 6,000-8,000 steps daily, avoiding lifts, walking instead of driving, and limiting screen time.
- Employers can support by setting walking targets for their employees, and individuals should monitor their weight and waist circumference regularly.
Conclusion
- Addressing obesity requires a multifaceted approach, including awareness, advocacy, medical treatments, and changes in lifestyle.
- Simple interventions like regular exercise, balanced diets, and reducing sedentary behavior can significantly help in managing obesity and its related NCDs.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of obesity in the rise of non-communicable diseases. How can India address the growing obesity epidemic to improve public health? (150 Words /10 marks) |
For more such UPSC related Current Affairs, Check Out Govt. report reveals stark infrastructure gap in Indian schools
