Stagnant Wages and Slowing Growth: Addressing India’s Economic Imbalance
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
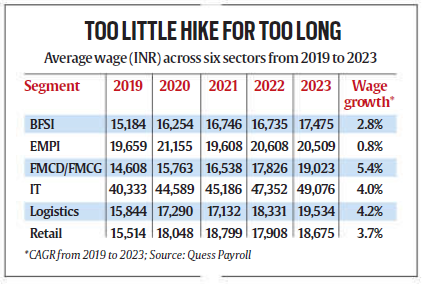
Real Wage Decline and Inflationary Pressures
- Real wage growth, when adjusted for inflation, has been stagnant or negative, exacerbating workers’ financial struggles.
- With retail inflation consistently high over five years, wage stagnation has led to reduced purchasing power, impacting consumption levels and slowing recovery to pre-pandemic economic activity.
Wage Growth Across Sectors
- The FICCI-Quess report highlights wage disparities among sectors. IT wages averaged the highest at ₹49,076 in 2023, while FMCG wages were the lowest at ₹19,023.
- Growth rates varied, with logistics and IT sectors seeing moderate increases (4.2% and 4%, respectively), but these gains remain insufficient to counter inflation.
Corporate Profitability vs. Wage Allocations
- Corporate profitability reached a 15-year high at 4.8% of GDP in 2024, yet staff costs have declined, with non-managerial compensation dropping sharply.
- Experts warn that this imbalance between capital and labor income weakens demand, creating a self-destructive cycle for businesses reliant on consumer spending.
Broader Challenges: Productivity and Job Quality
- Economists attribute slow wage growth to low labor productivity, surplus labor, and underemployment.
- India’s workforce faces a lack of quality jobs, with nominal wages declining as bargaining power diminishes.
- Raising productivity is seen as the key to sustainable wage growth and economic expansion.
Informal Sector Vulnerabilities
- Experts argue that wage stagnation disproportionately affects the informal sector, where job creation remains inadequate.
- While formal sector companies maintain consistent salary increments, the informal sector struggles with low wages and employment instability, highlighting the need for workforce formalization and targeted policy interventions.
Path Forward: Enhancing Productivity and Job Creation
- Raising labor productivity and promoting employment-generating sectors such as textiles and tourism are critical.
- Policymakers must focus on creating quality jobs, balancing wage and profit growth, and formalizing the workforce to ensure broad-based economic recovery and sustainable consumption growth.
| Practice Question: The sharp slowdown in wage growth despite rising corporate profits has raised concerns about subdued demand and inequality in India’s economic recovery. Discuss the factors contributing to stagnant wages and suggest measures to balance wage growth, labor productivity, and economic expansion. (250 words/15 m) |
