US Seeks Greater Market Access in India for Soyabean, Corn, and Cotton Amid Trade Barriers
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 12)
|
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
|
Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
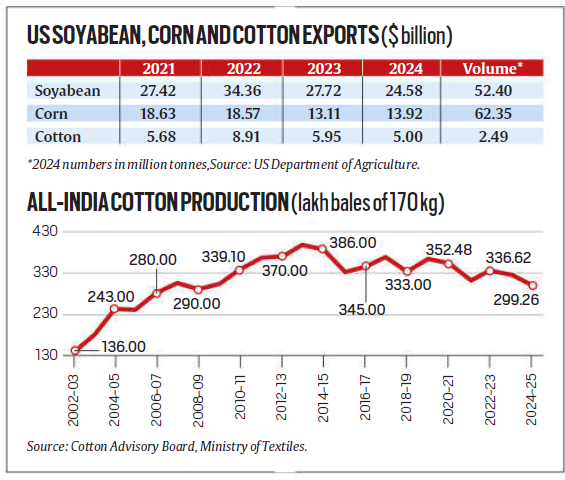
US Agricultural Exports and Market Focus
-
The US is a major exporter of soyabean, corn, and cotton.
-
With declining demand from China, the US seeks to expand its market in India.
-
However, India maintains high import tariffs and strict regulations on genetically modified (GM) crops, creating barriers to US exports.
India’s Growing Feed Demand
-
A USDA report predicts rising Indian demand for feed due to increasing consumption of milk, eggs, fish, and meat.
-
Domestic corn and soyabean meal consumption is projected to rise sharply by 2040 and 2050, making India a potential major importer.
-
However, current imports remain minimal due to high tariffs and regulatory constraints.
Challenges in US-India Trade
-
Tariff Barriers: India imposes a 45% duty on soybean and 50% on corn, limiting US exports.
-
GM Crop Restrictions: India bans GM imports, further restricting US access to the market.
-
Uncertain Consumption Growth: While India’s feed demand is growing, it may not match USDA projections, as past imports of feed ingredients have been limited.
Cotton: From Exporter to Importer
-
India was a leading cotton producer and exporter but is now becoming an importer due to stagnant GM crop approvals and pest resistance.
-
The US sees this as an opportunity to increase its cotton exports, especially if India removes the 11% duty on imports.
Conclusion
-
While India holds potential as a major market for US corn, soyabean, and cotton, regulatory and tariff barriers remain significant.
-
Any trade policy changes, particularly under the Trump administration’s stance on reciprocal tariffs, could impact future agricultural trade dynamics between the two countries.
|
Practice Question: Discuss the challenges and opportunities for India in opening its agricultural market to US exports of soybean, corn, and cotton. How can India balance trade liberalization with domestic agricultural interests and food security? (250 Words /15 marks) |
