Why is the textile industry struggling to perform better?
Why is the textile industry struggling to perform better?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth. |
| Context |
| ● The Indian textile and apparel sector aims to achieve a $350 billion annual business by 2030, generating 3.5 crore jobs.
● However, challenges such as export slumps, high raw material prices, and shifting consumer preferences threaten its growth prospects. |
Current Status of the Indian Textile and Apparel Sector
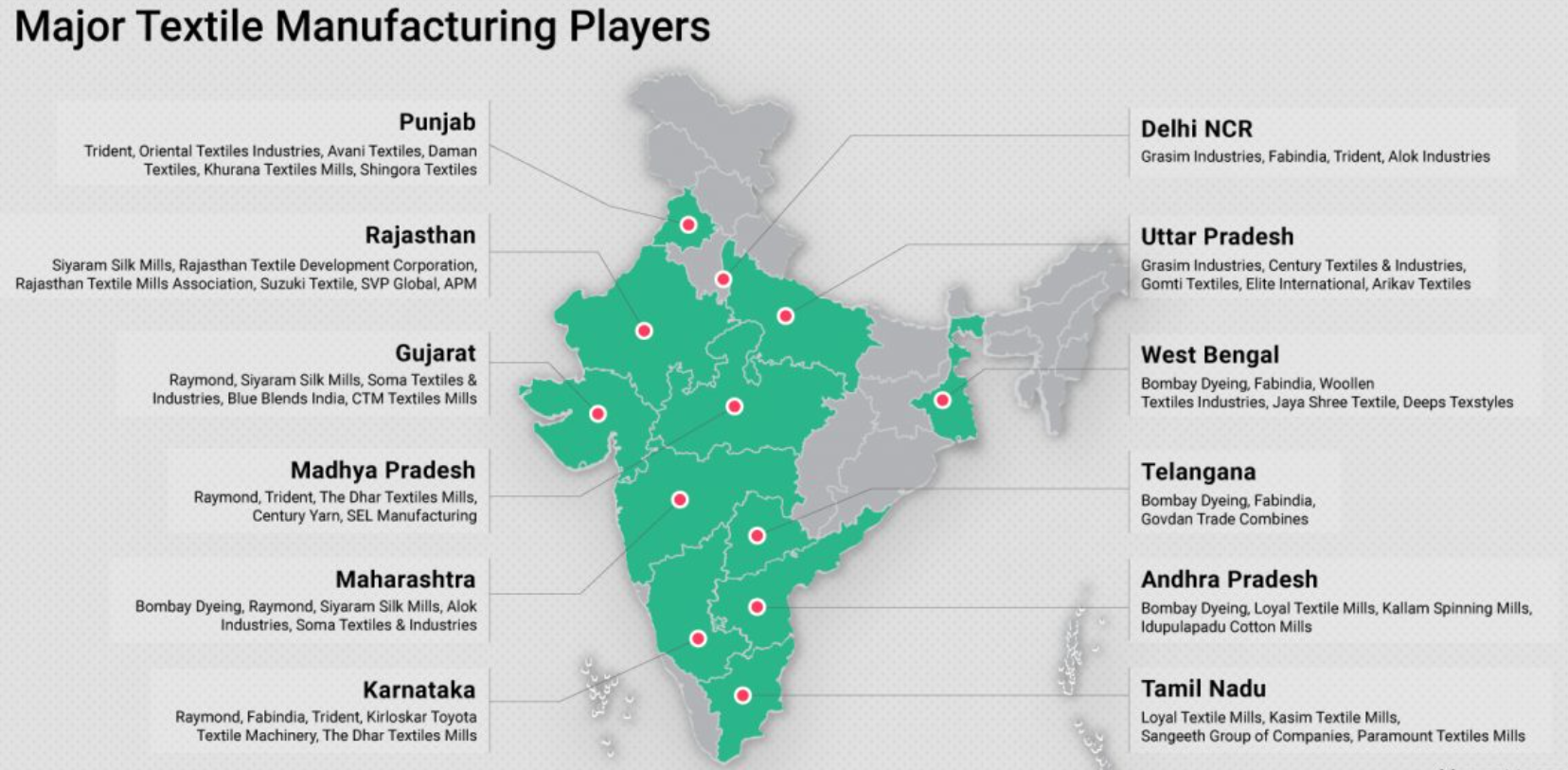
- Union Minister for Textiles Giriraj Singh announced that the Indian textile and apparel sector aims for a total business of $350 billion annually by 2030, which could generate 3.5 crore jobs.
- The industry’s size was estimated at $153 billion in 2021, with approximately $110 billion derived from domestic business.
- In FY22, India ranked as the third-largest textile exporter globally, with a market share of 5.4%, and possessed the second-largest manufacturing capacity in the sector.
- The textile industry contributed 2.3% to the country’s GDP and 10.6% to total manufacturing Gross Value Added (GVA).
- The sector employs around 105 million people directly and indirectly.
Reasons for Export Slump
- Economic Downturn: The industry faced a decline starting in 2022-2023, marked by significant reductions in exports and domestic demand due to geopolitical issues and decreased demand from purchasing countries.
- High Raw Material Prices: Rising prices for cotton and Man-Made Fibres (MMF) worsened the situation, with a 10% import duty on cotton making Indian cotton less competitive globally.
- Quality Control Orders: The introduction of quality control orders on MMF disrupted raw material availability and pricing, leading to industry calls for the removal of the import duty during the off-season from April to October.
Challenges Facing the Industry
- E-commerce Disruption: The sector is experiencing shifts due to e-commerce trends, with more manufacturers opting for direct retail to consumers.
- Sustainability Demand: International brands are prioritising sustainability, leading to increased demand for vendors who can meet specific environmental standards.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: There is a growing consumer preference for comfort wear, coupled with shifts in shopping habits, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Labour Costs: Labour constitutes around 10% of production expenses, with trained textile workers earning ₹550 daily and unskilled workers earning ₹450.
Future Outlook
- Investment Goals: To achieve the $350 billion target, the industry anticipates a $100 billion investment across various segments by 2030.
- Focus on Technology: The industry must emphasise technology adoption and workforce skilling to enhance productivity and reduce waste.
- Strengthening Supply Chains: Efforts will be made to strengthen supply chains to mitigate disruptions and ensure timely availability of raw materials and finished products.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges faced by the Indian textile and apparel industry in achieving its target of $350 billion annual business by 2030. How can the sector address these challenges to ensure sustainable growth? (150 Words /10 marks) |
