Why precision medicine in India can’t advance without biobank laws
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
| ● Precision medicine, driven by genomics and emerging technologies like gene editing and mRNA therapeutics, is transforming healthcare globally.
● India’s biobanking ecosystem is growing but faces challenges due to inconsistent regulations around data protection and ethical practices. ● Aligning India’s biobanking laws with global standards is crucial for advancing next-generation therapeutics. |
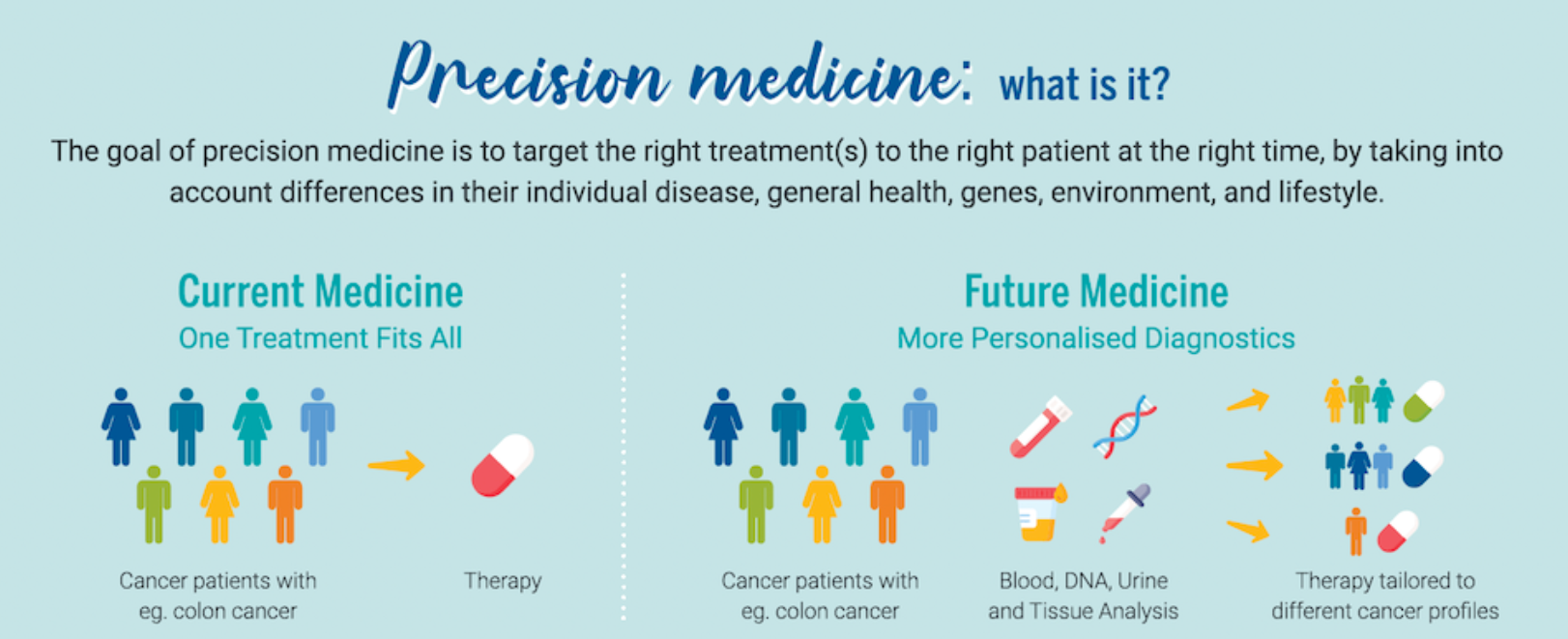
Introduction to Precision Medicine
- Precision medicine is transforming healthcare by offering personalised treatments, especially in fields such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- The Human Genome Project laid the groundwork for advancements in genomics, which have enhanced diagnostics and therapies for multiple health conditions.
- Emerging technologies like gene editing, mRNA therapeutics, and organ-on-chips are contributing to the progress of precision medicine.
Technological Advancements in Precision Medicine
- Gene editing and mRNA therapeutics are two key emerging technologies.
- Success stories include restoring vision through gene therapy and reversing diabetes with reengineered stem cells.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, the mRNA platform played a critical role in the development of vaccines, which led to a Nobel Prize.
- Organ-on-chips offer promising solutions by replicating human organs in laboratories, aiding in more accurate drug testing.
| Precision Medicine in India |
| ● The precision medicine market in India is growing rapidly at a CAGR of 16% and is projected to exceed $5 billion by 2030.
● It contributes significantly to India’s bioeconomy, alongside innovations in cancer immunotherapy, gene editing, and biologics. ● In 2023, India approved NexCAR19, its first domestic CAR-T cell therapy, and opened a dedicated center for its development. ● Collaborative efforts between healthcare institutions, such as Apollo Cancer Centre and the Indian Institute of Science, are driving the use of artificial intelligence in precision medicine. |
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine
- Biobanks store biological samples (e.g., blood, DNA, tissues) and are crucial for the success of precision medicine.
- Large and diverse biobanks ensure that research benefits a broad section of society.
- Recent research using biobank data has led to the discovery of rare genetic disorders and the identification of potential sarcoma therapies through organoid-based studies.
Biobanks in India
- India currently has 19 registered biobanks storing various biological specimens, including cancer cell lines.
- Key initiatives like the ‘Genome India’ project, which sequenced 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, and the ‘Phenome India’ project, focused on cardio-metabolic diseases, are aiding precision medicine research.
- The Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) mission aims to develop therapies for genetic disorders affecting children.
- Despite progress, India’s biobanking regulations are fragmented and hinder the full potential of precision medicine.
Challenges in Biobanking Regulations
- Unlike other countries such as the U.S. and the U.K., India lacks comprehensive regulations on biobanking, leaving gaps in informed consent, data protection, and privacy.
- Current guidelines from the Indian Council for Medical Research and the Department of Biotechnology are inadequate and do not protect individual rights effectively.
- Issues like mishandling of samples, data misuse, and non-consensual sharing pose ethical challenges.
- Without robust laws, Indian citizens risk losing control over their biological samples and the resulting research profits.
The Need for Regulatory Reform
- Stronger regulations, overseen by an expert committee, would encourage public participation in biobanks and ensure ethical practices.
- Proper biobanking laws aligned with global standards would position India as a leader in next-generation therapeutics, enhance trust, and facilitate international collaborations.
- India’s involvement in international organisations like the Quad and BRICS, as well as its leadership in pharmaceuticals, underscores the importance of aligning its biobanking policies with international standards.
Conclusion
- To harness the full potential of precision medicine, India must strengthen its biobanking regulations, ensuring ethical practices, data protection, and public trust.
- These reforms will not only benefit domestic healthcare but also enhance India’s position in global medical research and pharmaceutical diplomacy.
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential of precision medicine in transforming healthcare in India. What are the challenges faced by India’s biobanking regulations, and how can they be improved to support research and innovation? (150 Words /10 marks) |
