1 Feb 2024 : Daily Answer Writing
Q1) Explain the origin and evolution of the Himalayan Mountain range. What impact do Himalayas have on the climate and geography of the Indian subcontinent? (250 words/ 15 Marks)
 The Himalayas are the highest mountain range in the world. It spreads across 2400 km over five countries with major parts in India and Nepal.
The Himalayas are the highest mountain range in the world. It spreads across 2400 km over five countries with major parts in India and Nepal.
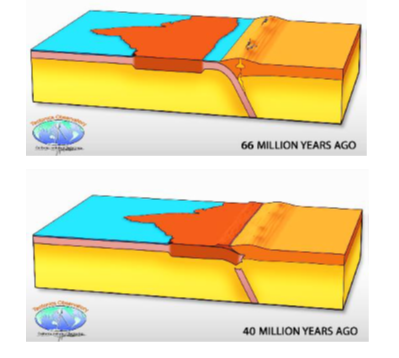
The origin and evolution of the Himalayan Mountain range can be explained through four major phases of tectonic upheaval as discussed below:
- Karakoram phase: The Indian and Eurasian plates started to collide, resulting in the upliftment of the Karakoram range. The compression of the sedimentary rocks during this phase led to the formation of folds and thrusts.
- Malla Johar phase: During this phase, the Himalayan Mountain range started to take shape. The Indian plate continued to move northwards, leading to the collision and subduction of the Tethys Sea’s oceanic crust under the Eurasian plate. The compression and folding of the sedimentary rocks led to the formation of the Great Himalayan range.
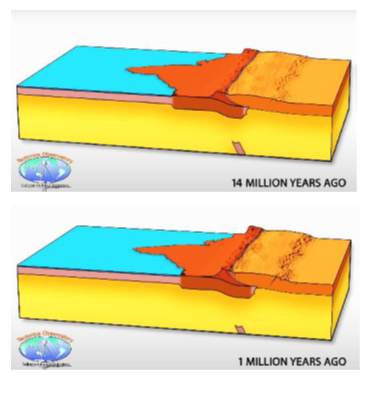
- Sirmurian phase: The Indian plate continued to move northwards, leading to the formation of the Lesser Himalayan range. The compression and folding of the sedimentary rocks in this phase resulted in the formation of the Main Central Thrust and the Main Boundary Thrust.
- Siwalik phase: The Himalayan Mountain range underwent upliftment and erosion due to the continued collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates. The sedimentary rocks that were formed during this phase make up the Siwalik range.
The impact of Himalayas on the climate of the Indian sub-continent is as follows:
- Monsoons: Himalayas provide a barrier to the monsoon winds, causing them to rise and precipitate. This results in rainfall in the plains of northern India, which is crucial for agriculture.
- Regulation of Temperatures: The Himalayas act as a barrier to cold winds from Central Asia and moderates winter temperatures in northern India. Himalayas also support a range of climate zones from evergreen to alpine.
- Indo-Gangetic Airshed: The vast northern plain between Vindhyas and Himalayas creates a single airshed over the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. It results in quick spread of monsoon as well as pollution across the airshed.
- Western Disturbances funnel through the northwest via the openings in the mountainous landscape into the Indian subcontinent. They cause winter rains.
The impact of Himalayas on the geography of the Indian subcontinent is as follows:
- River Systems: The Himalayas are the source of many important rivers, such as Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus. These rivers play a vital role in shaping the landscape and supporting human habitation.
- Plateaus: The formation of Himalayas caused the uplifting of the Tibetan plateau, and creation of trans-Himalayan landscapes such as Ladakh or the plains of Deosai.
- Geological Diversity: The Himalayas are geologically diverse, with a wide variety of rock types and mineral deposits from limestone to lithium.
- Biodiversity: Himalayas are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including several endemic species, such as Hangul deer and protected areas such the Valley of Flowers.
- Natural Hazards: The Himalayas are prone to natural hazards such as earthquakes, landslides, and flash floods. These hazards shape the landscape of the region and pose risks to human settlements.
The Himalayas continue to evolve due to tectonic activity and erosion processes, and seismic activity in the region is still prevalent. Their crucial impact on ecology, economy, and human life requires international cooperation for sustainable management
Upload Answer here


