10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
10-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. States, U.T.s asked to submit data on heatstroke cases
| Topic: GS2 – Governance, GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation
Crucial for UPSC as it addresses public health management, disaster preparedness, and governance strategies during environmental challenges. |
| Context |
| ● The news highlights directives from the National Centre for Disease Control regarding heatstroke data submission and health precautions during mass gatherings amidst rising temperatures. |
Additional information on this news:
- The National Centre for Disease Control advises States and Union Territories to submit heatstroke data on the Integrated Health Information Portal (IHIP) as summer temperatures rise.
- Precautionary measures for preventing health issues during mass gatherings are issued, including early warnings and avoiding activities between noon and 3 p.m.
- Organizers are directed to prevent overcrowding, identify vulnerable individuals, and set up medical camps with uniformed medical aid teams and clear exit indications.
- Doctors warn about rising temperatures and advise vigilance for symptoms of sun allergies and dehydration, particularly among vulnerable groups like the elderly and children.
- Sun protection measures, including sunscreen application and limiting sun exposure, are recommended to prevent sun-related allergies and skin issues.
- Hospitals report a rise in sun-related allergies, emphasizing the need for caution, especially for outdoor workers and children.
| Increasing instances of Heatwave: |
| Reasons for Increasing Instances of Heatwaves:
● Climate Change: Global warming leads to higher average temperatures, exacerbating heatwave frequency and intensity. ● Urban Heat Island Effect: Urbanization and land use changes result in heat-absorbing surfaces like concrete, amplifying local temperatures. ● Deforestation: Reduction in green cover decreases natural cooling effects, contributing to higher temperatures. ● Air Pollution: Greenhouse gas emissions trap heat in the atmosphere, exacerbating heatwave conditions. Impact on Human Health: ● Heatstroke: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to heatstroke, a life-threatening condition. ● Dehydration: Increased sweating leads to fluid loss, raising the risk of dehydration and related complications. ● Cardiovascular Issues: Heatwaves strain the heart, leading to increased incidents of heart attacks and other cardiovascular problems. ●Respiratory Problems: High temperatures worsen air quality, exacerbating respiratory conditions like asthma. ● Vulnerable Populations: Elderly, children, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are at higher risk of heat-related illnesses. Way Forward: ● Mitigate Climate Change: Implement measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat global warming. ● Urban Planning: Increase green spaces, promote reflective roofing, and enhance ventilation to mitigate urban heat island effects. ● Public Health Measures: Raise awareness about heatwave risks, provide access to cooling centers, and distribute information on staying hydrated and cool. ● Early Warning Systems: Develop and implement effective heatwave early warning systems to alert vulnerable populations. ● Infrastructure Resilience: Invest in heat-resilient infrastructure and urban design to withstand extreme temperatures. ● Community Engagement: Engage communities in heatwave preparedness and response strategies to ensure collective resilience. ● Research and Innovation: Support research on heatwave impacts and develop innovative solutions for adaptation and mitigation. |
| PYQ: Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world. (100 words/5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2013) |
| Practice Question: How can effective public health measures mitigate the impact of rising temperatures and prevent health issues during mass gatherings? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. India likely to record normal monsoon this year, says Skymet.
| Topic: GS1 – Geography
Crucial for UPSC as it addresses agricultural productivity, disaster management, and regional socio-economic impacts of monsoon variability. |
| Context |
| ● The news discusses forecasts by Skymet and the India Meteorological Department regarding a normal monsoon in India, with regional variations anticipated. |
Additional information on this news:
- Skymet forecasts a normal monsoon in India this year, with more rainfall expected in the second half of the season.
- India Meteorological Department (IMD) scientists also predict a favorable monsoon, citing fading El Nino conditions and reduced snow cover over Eurasia.
- Normal cumulative rainfall is expected, but climate change may increase the variability of rain distribution.
- Climate scientists note a decline in rainy days and an increase in heavy rain events, leading to more frequent droughts and floods.
- Skymet predicts the monsoon to be at 102% of the long-period average, with normal rainfall between 96% and 104% of the LPA.
- Sufficient rainfall is anticipated in the south, west, and northwest regions, while Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh will receive adequate rainfall.
- Eastern states like Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal may experience deficit rainfall during peak monsoon months.
- Northeast India is expected to observe below-normal rains during the first half of the season.
| Significance of monsoon rainfall for Indian economy: |
| Formation of Monsoon:
●Southwest Monsoon: The Indian monsoon is primarily driven by the southwest monsoon winds, which originate from the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea. ● Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ): The monsoon is influenced by the seasonal shift of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone, a low-pressure belt where trade winds converge. ●Land-Water Temperature Difference: The monsoon is also affected by the temperature difference between the Indian subcontinent and the Indian Ocean. During summer, land temperatures rise, creating low-pressure areas, while the ocean retains cooler temperatures, resulting in high-pressure zones. This contrast causes the influx of moist air from the ocean to the land, leading to rainfall. ● Topography: India’s geographical features, including the Western Ghats and the Himalayas, play a role in directing the monsoon winds and influencing rainfall patterns. Significance of Monsoon for Indian Economy: ● Agriculture: The monsoon is crucial for agriculture as it provides the majority of India’s rainfall. It replenishes water sources, irrigates farmland, and supports the growth of crops, ensuring food security for the nation. ● Hydropower Generation: Heavy rainfall during the monsoon season fills reservoirs, facilitating hydropower generation. This helps meet electricity demands and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. ● Economic Growth: Agriculture, being a significant contributor to India’s GDP, heavily relies on the monsoon. A good monsoon season boosts agricultural output, which, in turn, stimulates economic growth and contributes to overall prosperity. ● Livelihoods: Millions of farmers depend on the monsoon for their livelihoods. A successful monsoon season ensures adequate water availability for farming activities, supporting rural communities and reducing poverty. ● Industrial and Service Sectors: The monsoon indirectly impacts industries and service sectors by influencing agricultural output, rural demand, and consumer spending patterns. ● Water Resources Management: The monsoon replenishes water bodies, including rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, essential for drinking water supply, irrigation, and industrial purposes. ● Tourism: Monsoon-related activities, such as nature tourism, trekking, and adventure sports, attract tourists to regions experiencing heavy rainfall, contributing to the tourism industry’s revenue. |
| PYQ: What characteristics can be assigned to monsoon climate that succeeds in feeding more than 50 percent of the won population residing in Monsoon Asia?(250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of Indian monsoon variability on agricultural productivity, regional economies, and disaster management. Propose measures to mitigate its socio-economic impacts. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Health sector can’t ignore green gains from telemedicine: study
| Topic: GS2 – Social justice – Health, GS3 – Science and Technology – Development & their applications
From the UPSC perspective, understanding telemedicine’s environmental impact aligns with contemporary issues and sustainable healthcare solutions. |
| Context |
| ● The news highlights the benefits of teleophthalmology, as studied by the L.V. Prasad Eye Institute, including reduced patient visits and carbon emissions. |
Introduction:
- Study by L.V. Prasad Eye Institute (LVPEI) in Hyderabad assesses benefits of teleconsultations in eye care.
- Telemedicine, including teleophthalmology, gains popularity for its convenience and cost-effectiveness.
- Notably, teleconsultations also reduce carbon emissions, aligning with environmental concerns.
Teleophthalmology Process:
- Patients remotely consult ophthalmologists via internet-based video chat.
- Sessions facilitated through smartphone apps or technicians at primary healthcare centers.
- Technicians conduct examinations, capture eye images, and upload data to cloud servers.
- Doctors analyze data remotely, prescribe treatment or refer patients to higher-level hospitals if needed.
- Teleconsultations primarily cater to follow-up patients, reducing the need for repeated hospital visits.
Impact of Teleophthalmology:
- Study involves 324 patients over three months, assessing travel modes and emissions.
- Around 70% of rural patients deemed suitable for teleconsultations, reducing travel.
- Urban tertiary-care hospitals see patients from various locations, saving significant travel distances.
- Each deferred visit saves substantial carbon emissions and travel expenses.
- Rural patients save ₹370 on travel expenses, while urban patients save ₹8,339 on average.
Significance of Teleophthalmology:
- Bridges healthcare access gap between rural and urban areas, critical for India’s predominantly rural population.
- Offers convenience and cost savings for patients, particularly those with minor eye issues.
- Contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing vehicular emissions associated with hospital visits.
- Aligns with global efforts to promote telemedicine and reduce carbon footprint in healthcare.
Conclusion:
- Teleophthalmology emerges as an effective tool for eye care delivery, especially in resource-constrained settings.
- Its environmental benefits, including reduced carbon emissions and cost savings, underscore its importance.
- Encourages broader adoption of telemedicine practices to enhance healthcare access and address environmental concerns.
| PYQ: Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does AI help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of Al in healthcare? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the environmental implications of telemedicine in the context of sustainable healthcare delivery. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. The ‘import restrictions’ on solar PV cells
| Topic: GS3 – Indian economy – Effects of liberalization on the economy.
Understanding India’s efforts to increase local manufacturing of solar modules is crucial for its energy security and economic development. |
| Context |
| ● The news is about recent government orders aiming to increase local sourcing of solar modules, referred to as ‘import restrictions’, to boost India’s renewables manufacturing ecosystem. |
Introduction:
- Recent government orders on increasing local sourcing of solar modules have been reported as ‘import restrictions’.
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) re-implemented the 2021 notification of an ‘Approved List of Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Modules’ (ALMM list).
ALMM List and Re-Implementation:
- ALMM list consists of manufacturers eligible for government projects.
- Notification was kept in abeyance for the past financial year.
- Re-implementation due to domestic sector’s boosted production capacities and improved price competitiveness.
India’s Reliance on Solar PV Imports:
- Overwhelming import dependence for solar cells and modules, majorly from China and Vietnam.
- India imported about $11.17 billion worth solar cells and modules in the past five years.
- China accounts for the majority of India’s solar cell and module imports.
Policies Response:
- Efforts to address over-dependence: ALMM order, PLI scheme, and customs duties.
- PLI scheme aims to scale domestic manufacturing of the entire solar supply chain.
- Introduction of customs duties to encourage domestic production.
China’s Leading Exporter Status:
- China’s cost competitiveness attributed to lower power costs and government prioritization of solar PV.
- Chinese policies support continuous innovation and economies of scale throughout the supply chain.
Scope for Solar in India:
- Government targets 500 GW of installed capacity from non-fossil fuels by 2030.
- India’s fastest rate of growth for electricity demand among major economies.
- Solar power accounts for a significant portion of renewable energy generation, with untapped potential of 748.99 GW.
Conclusion:
- Government initiatives aim to reduce import dependence and scale up domestic solar manufacturing to meet ambitious renewable energy targets and tap into India’s solar energy potential.
| PYQ: India has immense potential of solar energy though there are regional variations in its development. Elaborate. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of India’s recent initiatives to boost local manufacturing of solar modules for its energy sector and economic growth. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Peter Higgs, who proposed existence of ‘God particle’, dies
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology
Understanding the contributions of Peter Higgs to particle physics is crucial for comprehending the Standard Model’s theoretical framework. |
| Context |
| ● Renowned physicist Peter Higgs, known for proposing the existence of the Higgs boson, or “God particle,” has passed away at 94. |
Additional information on this news:
- Physicist Peter Higgs, renowned for proposing the existence of the “God particle,” the Higgs boson, has passed away at 94.
- Higgs predicted the particle’s existence in 1964, crucial for understanding how matter forms post-Big Bang.
- His theory explained how subatomic particles acquire mass, a cornerstone of the Standard Model of physics.
- In 2012, scientists at CERN confirmed the Higgs boson’s existence using the Large Hadron Collider.
- Higgs and Francois Englert were jointly awarded the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physics for their work.
- Higgs’ legacy as a pioneering scientist continues to inspire generations.
More about Higgs Boson: ● The Higgs boson is a subatomic particle predicted by the Standard Model of particle physics. ● It was discovered in 2012 by experiments conducted at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN.
● Its discovery confirmed the existence of the Higgs field, which gives mass to other elementary particles through the Higgs mechanism.
● The Higgs boson is a crucial component in explaining how particles acquire mass.
● It has a spin of zero, making it a scalar boson.
● The mass of the Higgs boson is approximately 125 gigaelectronvolts (GeV), making it relatively massive compared to other elementary particles.
● Its discovery was a significant milestone in particle physics, filling in a crucial missing piece of the Standard Model.
● Further studies of the Higgs boson aim to understand its properties more precisely and explore potential connections to physics beyond the Standard Model.
| PYQ: The efforts to detect the existence ‘of Higgs boson particle have become frequent news in the recent past. What is/are the importance/ importance’s of discovering this particle?
1. It will enable us to understand as to why elementary particles have mass. 2. It will enable us in the near future to ‘develop the technology of transferring matter from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them. 3. It will enable us to create better fuels for nuclear fission. Select the correct answer using the codes given below. (A) 1 only (B) 2 and 3 only (C) 1 and 3 only (D) 1, 2 and 3 Answer – option (B) – 2 and 3 only (UPSC Prelims 2013) |
| Practice Question: What are the contributions of Peter Higgs to particle physics, and how did they impact our understanding of the Standard Model? (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. Strategic Military Infrastructure Upgrade in Andaman and Nicobar Islands Bolsters India’s Maritime Security
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about the infrastructure upgrade in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands which is directly related to national security and defense. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Purpose of Infrastructure Enhancement:
- The enhanced infrastructure aims to facilitate the deployment of additional military forces and accommodate larger and more advanced warships, aircraft, missile batteries, and troops.
- This expansion is crucial in enhancing the defense capabilities of the islands and strengthening India’s military presence in the region.
Strategic Context: Countering Chinese Influence:
- The ongoing infrastructure development is occurring against the backdrop of growing Chinese attempts to expand its influence in the region.
- Notably, China’s construction of a military facility at Myanmar’s Coco Islands, located north of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, underscores the strategic significance of these upgrades in countering external threats and safeguarding India’s interests.
Scope of Infrastructure Upgrade:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC), established in 2001 as India’s first and only tri-service command in the islands, is central to these infrastructure enhancements.
- Plans include significantly enhancing surveillance infrastructure on one of the northern islands and constructing a permanent habitat for troops.
- Additionally, expansions of airstrips, jetties, roads, and other vital infrastructure are underway to accommodate larger aircraft, ships, and increased traffic.
Key Developments and Initiatives:
- Recent developments include the inauguration of modern hangars, precision approach radar systems, and underwater harbor defense and surveillance systems.
- Furthermore, the establishment of Naval Communication Network (NCN) centers aims to augment communication and operational capabilities in the region.
- Additionally, efforts to bolster satellite imagery analysis and surveillance of both inhabited and uninhabited islands demonstrate a multifaceted approach towards strengthening maritime security.
Inter-Agency Collaboration and Policy Initiatives:
- Policy meetings involving multiple agencies, including the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Navy, and National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), highlight the collaborative efforts to enhance maritime security.
- These initiatives underscore the importance of coordinated action and technological advancements in safeguarding India’s maritime interests in the Indian Ocean region.
Conclusion:
- The ongoing military infrastructure upgrade in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands represents a significant strategic investment aimed at enhancing India’s maritime security posture and countering external threats.
- The multifaceted approach, coupled with inter-agency collaboration and policy initiatives, underscores India’s commitment to safeguarding its strategic interests in the region.
| What is the Significance of ANI for India? |
|
About:
|
| PYQ: Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar (b) Nicobar and Sumatra (c) Maldives and Lakshadweep (d) Sumatra and Java Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the ongoing military infrastructure upgrade in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the context of India’s national security and strategic interests. Analyze the geopolitical implications of China’s expanding influence in the region. (250 words/15 m) |
7. India Faces Mounting Challenge as Global Hepatitis Report Highlights High Prevalence and Low Treatment Rates
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the analysis sheds light on the prevalence of viral hepatitis in India and the challenges associated with diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
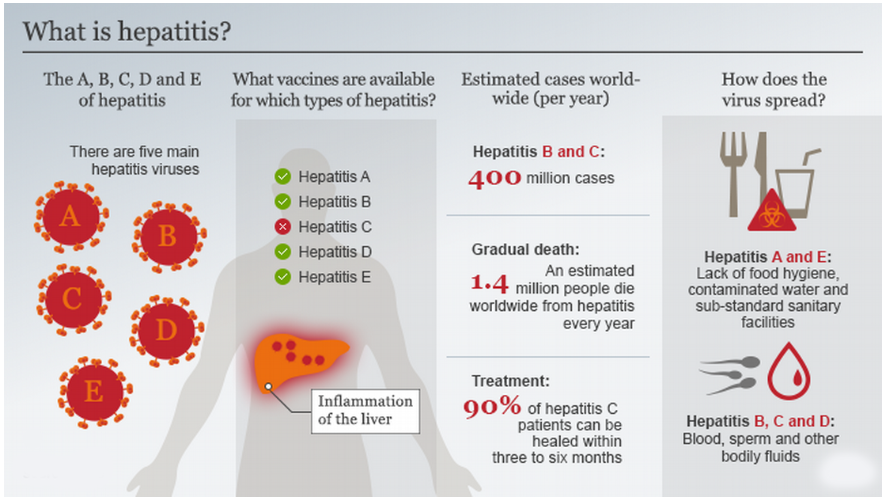
Low Diagnosis and Treatment Rates:
- Despite the high prevalence of viral hepatitis, diagnosis and treatment rates remain alarmingly low in India.
- Only 2.4% of Hepatitis B cases and 28% of Hepatitis C cases were diagnosed in 2022, with even fewer individuals receiving treatment.
- This indicates a significant gap in healthcare infrastructure and access to essential services for managing viral hepatitis.
Health Implications of Viral Hepatitis:
- Viral hepatitis can lead to liver inflammation, damage, and potentially life-threatening conditions such as liver cancer.
- Hepatitis B, in particular, can cause acute symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, with severe cases leading to liver failure.
- Chronic Hepatitis B infections, especially when contracted in childhood, can result in long-term liver disease and increase the risk of liver cancer.
Preventive Measures and Treatment Options:
- While Hepatitis B can be prevented through vaccination, coverage remains inadequate in India.
- Ensuring universal vaccination for newborns and high-risk adults is crucial to reducing the burden of Hepatitis B in the country.
- Additionally, medical treatment is available for Hepatitis C, with Indian pharmaceutical companies manufacturing generic drugs at affordable prices.
- However, the coverage of treatment remains suboptimal, highlighting the need for improved healthcare delivery and accessibility.
Challenges and Recommendations:
- Effective management of viral hepatitis requires concerted efforts from healthcare providers, policymakers, and the community.
- The report underscores the importance of expanding diagnostic and treatment services, as well as raising awareness about preventive measures such as vaccination.
- Furthermore, ensuring universal access to treatment for diagnosed individuals is essential to mitigating the health consequences of viral hepatitis and reducing disease burden in the long term.
Conclusion:
- The high prevalence of viral hepatitis in India underscores the urgent need for comprehensive public health interventions.
- From increasing vaccination coverage to enhancing diagnostic and treatment services, addressing the challenges posed by viral hepatitis requires a multi-faceted approach.
- By prioritizing prevention, diagnosis, and treatment, India can significantly reduce the burden of viral hepatitis and improve the overall health outcomes of its population.
| What is Hepatitis? |
|
About:
|
| PYQ: Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV. (b) Hepatitis B unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine. (c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses arc several times more than those infected with HIV. (d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: What are the key challenges faced in addressing viral hepatitis in India, and what measures can be taken to improve diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies? (150 words/10 m) |
8. Botswana’s Elephantine Problem: Balancing Conservation, Human-Elephant Conflict, and Trophy Hunting
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservations
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding the challenges associated with balancing conservation efforts with wildlife management strategies. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Factors Contributing to Elephant Population Growth:
- Botswana’s stable government and relatively small human population have made it a safe haven for elephants.
- Conservation policies and shoot-to-kill orders against poachers have also helped maintain elephant numbers in the country.
Human-Elephant Conflict:
- The increasing elephant population has led to human-elephant conflict, with elephants damaging homes, crops, and infrastructure, as well as posing risks to human and livestock safety.
- This conflict has become a significant concern for rural communities, impacting their livelihoods and daily lives.
Impact on Biodiversity and Habitat:
- The large elephant population threatens biodiversity and habitat integrity, leading to habitat degradation and loss of vegetation.
- Elephants consume large amounts of water and tear down trees for fodder, which can have adverse effects on non-elephant wildlife species.
Role of Elephant Hunting:
- Hunting has been proposed as a solution to control the elephant population and generate revenue for local communities.
- Trophy hunting brings substantial economic benefits, with hunters paying significant sums for each animal killed.
- The revenue generated from trophy hunting is often reinvested in conservation efforts and shared with local communities.
Controversies Surrounding Elephant Hunting:
- Despite its potential economic benefits, elephant hunting is controversial and deemed unethical by animal rights advocates.
- Critics argue that trophy hunting contributes minimally to the economy and may exacerbate population declines in imperiled species.
- Corruption and lack of benefit-sharing with local communities are also raised as concerns.
Need for Balanced Approaches:
- While some advocate for outright bans on trophy hunting, others argue for regulated hunting as a management tool.
- Conservation experts emphasize the importance of considering alternative sources of revenue and understanding the potential consequences of banning hunting entirely.
Conclusion:
- Botswana’s elephant overpopulation presents complex challenges that require careful consideration of various factors, including conservation, economic sustainability, and ethical considerations.
- Finding a balanced approach that addresses both human-elephant conflict and conservation concerns is essential for ensuring the long-term survival of both elephants and other wildlife species in Botswana.
| About Botswana |
|
PYQ: Prelims PYQ (2022):
With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements:1. Wild animals are the sole property of the government. 2. When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled for equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside. 3. Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 (d) 3 only Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: What are the main challenges posed by the elephant overpopulation in Botswana? Suggest potential solutions to address this issue and discuss the ethical considerations surrounding elephant hunting in the context of wildlife management. (250 words/15 m) |
For Enquiry

10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

10 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

10 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

10 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

10 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

9 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

9 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

9 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

9 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
Daily Quiz 10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 10- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 10 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
10-April-2024
Q1) By placing strategic evaluation of opportunities and threats…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
10-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. States, U.T.s asked to submit data on heatstroke…
April 2024 PIB 10 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
10-April-2024
1. Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) to organise…
April 2024 The Hindu Editorial 10 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
10-April-2024
1. The climate crisis is not gender neutral
Topic: GS2 – Social…
April 2024 Indian Express 10 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
9-April-2024
1. Quality of growth
Topic: GS3 – Indian economy…
Daily Quiz 9 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 9- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 9 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
9-April-2024
Q1) Shared values, histories, and interests of the members enable…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 9 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
9-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Supreme Court Urges Centre and States to…
April 2024 PIB 9 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
9-April-2024
1. PRESIDENT’S GREETINGS ON THE EVE OF CHAITRA SUKLADI, UGADI, GUDI…


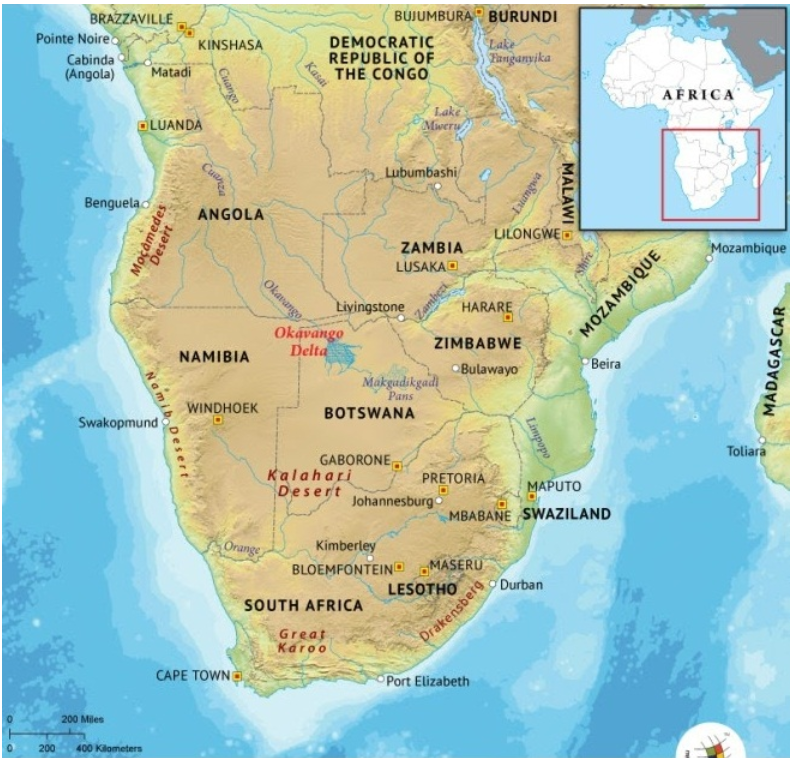 Botswana: It is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Its 70% territory is covered by Kalahari Desert.
Botswana: It is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Its 70% territory is covered by Kalahari Desert.


