13 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
12-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. ADB projects India’s GDP growth at 7% this year
| Topic: GS2 – Important International institutions, agencies and fora – their structure, mandate, GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to growth,
Critical for understanding India’s economic trajectory, inflation dynamics, investment climate, and implications for domestic and global growth. |
| Context |
| ● The Asian Development Bank forecasts India’s GDP growth at 7% in 2024, with easing inflation and a focus on investment and consumer demand. |
Additional information on this news:
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) projects India’s GDP growth to slow from 7.6% in 2023-24 to 7% in 2024, with a slight improvement to 7.2% in 2025-26.
- Retail inflation is expected to ease to 4.6% this year and 4.5% in 2025-26, with food inflation dropping to 5.7%.
- A ‘higher for longer’ interest rate regime due to U.S. inflation resurgence may impact Asia’s inflation outlook and slightly dent growth.
- India’s inflation pace is more sensitive to exchange rate fluctuations and relies heavily on imported goods, intensifying the impact.
- A potential spike in shipping costs from Red Sea strife could further add to inflation pressures across developing Asia.
- Projected normal monsoon will boost rural consumption, with increased demand under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act.
- India remains the fastest-growing sub-region in South Asia, driving regional growth with improving domestic demand.
- Higher incomes will spur urban consumer demand, although a rise in imports may moderately widen the Current Account Deficit to 1.7% of GDP.
- India’s growth is driven by public and private investment demand, with exports likely to improve in 2025-26.
- Foreign direct investment inflow may remain muted initially due to global financial conditions but is expected to pick up in 2025-26.
- India’s economic outlook depends on price and financial market stability, with downside risks including weather shocks affecting agriculture and global inflation spikes.
- Upside risks include faster-than-expected foreign direct investment inflow and better global growth boosting exports and growth.
| More about Asian Development Bank (ADB): |
| ●Established in 1966, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
● Membership: Comprises 68 members, including 49 from the Asia-Pacific region and 19 from outside the region. ● Mission: ADB aims to reduce poverty in Asia and the Pacific through inclusive economic growth, environmental sustainability, and regional integration. ● Financial Resources: ADB provides loans, grants, technical assistance, and equity investments to its member countries to support development projects and programs. ● Priority Areas: Focuses on sectors such as infrastructure (transport, energy, water), education, health, agriculture, and rural development. ●Environmental and Social Safeguards: ADB integrates environmental and social considerations into its projects to promote sustainability and mitigate adverse impacts. ● Regional Cooperation: ADB facilitates regional cooperation and integration through cross-border infrastructure projects, trade facilitation, and policy dialogue. ● Partnerships: Collaborates with governments, other development agencies, private sector entities, and civil society organizations to maximize development impact. |
| PYQ: India has recently signed to become a New Development Bank (NDB) and also the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB). How will the role of the two Banks be different? Discuss the significance of these two Banks for India. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the evolution and impact of the Asian Development Bank (ADB) in India, analysing its role in financing infrastructure projects, fostering regional cooperation, and addressing socio-economic challenges. Evaluate the effectiveness of ADB initiatives in promoting sustainable development and inclusive growth. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Sound and stable Sino-Indian relations serve the interests of both sides, region, says Beijing
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations
Relevant for UPSC as it concerns India-China relations, border security, diplomatic engagements, and regional stability. |
| Context |
| ● The news pertains to Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s remarks on India-China tensions at the Line of Actual Control (LAC), urging for urgent resolution and positive bilateral engagement, which drew reactions from China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs. |
Additional information on this news:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi broke his silence on India-China tensions at the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in an interview with Newsweek.
- Prime Minister Modi called for urgent resolution of the border situation and emphasized positive bilateral engagement to restore peace.
- China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs reacted, urging India to work together for stable bilateral relations.
- Pankaj Saran, former Deputy National Security Advisor, highlighted the significance of Modi’s comments as a signal to China and the world.
- The PM’s words suggest a potential shift in approach towards addressing China-related issues in his third term, if re-elected.
- Recent visits by senior U.S. officials to Beijing and Chinese President Xi Jinping’s upcoming trip to France indicate broader diplomatic engagements.
| Significance of healthy India – China relationship: |
| Significance of Healthy India-China Relationship:
● Economic Cooperation: A strong relationship between India and China can foster economic cooperation, leading to increased trade, investment, and business opportunities for both nations. This collaboration has the potential to drive economic growth and prosperity in the region. ● Regional Stability: India and China are major powers in Asia, and their stable relationship is crucial for regional stability. By maintaining peaceful coexistence and resolving disputes through dialogue, they can contribute to peace and security in the Asia-Pacific region. ● Global Influence: As two populous and rapidly developing countries, India and China have significant global influence. A positive relationship between them can enhance their collective voice on global issues such as climate change, terrorism, and international trade, leading to more effective cooperation on these pressing challenges. ● Cultural Exchange: India and China have rich cultural heritages dating back centuries. Strengthening cultural exchange programs can promote mutual understanding, appreciation, and people-to-people ties between the two nations, fostering a sense of goodwill and friendship. Way Forward for Healthy India-China Relationship: ● Diplomatic Dialogue: Continued engagement through diplomatic channels is essential for resolving differences, building trust, and maintaining open communication between India and China. ● Conflict Resolution: Both countries should prioritise peaceful resolution of disputes, including border issues, through dialogue and negotiation, avoiding escalation and conflict. ●Trade and Economic Cooperation: Enhancing bilateral trade relations and promoting economic cooperation through initiatives like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) can create win-win situations for both countries. ● Cultural Exchanges: Encouraging cultural exchanges, such as student exchanges, artist collaborations, and tourism promotion, can foster people-to-people connectivity and strengthen bilateral ties at the grassroots level. ●Mutual Respect: Both nations should demonstrate mutual respect for each other’s sovereignty, territorial integrity, and core interests, while also recognizing each other’s role as major regional and global players. ●Multilateral Engagement: Collaborating in multilateral forums like the United Nations, BRICS, and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) can provide platforms for India and China to address common challenges and work together on global issues of mutual concern. |
| PYQ: ‘China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia’, In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of maintaining a healthy relationship between India and China in the context of regional stability, economic cooperation, and global influence. Suggest measures for fostering constructive engagement between the two nations. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Fire destroys nearly 100 hectares of Wayanad sanctuary
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation, GS3 – Disaster and disaster management.
The topic holds importance for UPSC as it assesses candidates’ understanding of environmental conservation, disaster management, and regional issues. |
| Context |
| ● The news is about a forest fire in the Sulthan Bathery forest range of the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary in Kerala, destroying nearly 100 hectares of forest. |
Additional information on this news:
- A fire in the Sulthan Bathery forest range in Kerala destroyed close to 100 hectares of forest, starting around 10:30 a.m. in the Karassery district.
- The fire spread to Kumbram Kolly, Ezhekkar, Narikkolly, and Kottanode areas of the forest under the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Three units of Fire and Rescue Services, along with around 150 individuals including forest and fire services personnel and local residents, battled the flames for nearly six hours.
- The fire was finally brought under control with the use of four fire tenders and manual fire beaters.
- This was the fourth fire incident in the sanctuary this year, with the latest one attributed to dried bamboo pods, high temperatures, gusty winds, and withered undergrowth.
- The fire also affected a rubber plantation nearby, and lower mammals and reptiles in the area sustained injuries.
| Forest fires in India: |
| Vulnerability of forests in India:
● Worrying Trend: India grapples with frequent forest fires, particularly during the dry summer months (March-May). ● Satellite Data: According to satellite data from the Forest Survey of India (FSI), a staggering 3,45,989 fire incidents were detected between November 2020 and June 2021 – an all time high. ● Vulnerable Forests: Over 50% of India’s total forest cover is unfortunately fire-prone, leaving vast areas susceptible to damage. Impact on Environment: ● Habitat Destruction: Forest fires destroy habitats, leading to loss of biodiversity and disruption of ecological balance. ● Air Pollution: Smoke and ash from forest fires contribute to air pollution, affecting air quality and human health. ● Carbon Emissions: Forest fires release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. ● Soil Erosion: Loss of vegetation exposes soil to erosion, leading to land degradation and reduced fertility. ●Water Quality: Runoff from burnt areas can pollute water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and water quality. Ways for Disaster Management: ● Early Detection: Use of satellite imagery and remote sensing technology for early detection and monitoring of forest fires. ● Firebreaks: Creation of firebreaks and controlled burns to prevent the spread of wildfires. ● Community Involvement: Engage local communities in fire prevention and firefighting efforts through training and awareness programs. ● Equipment and Infrastructure: Provide firefighting equipment and infrastructure such as fire towers, watchtowers, and fire lines. ● Coordination: Establish coordination mechanisms between forest departments, firefighting agencies, and local authorities for efficient response. ● Preparedness Plans: Develop and implement comprehensive forest fire preparedness and response plans at the national, state, and local levels. ●Rehabilitation: Conduct post-fire rehabilitation activities such as reforestation and soil conservation to restore affected areas. Steps taken by Indian government in this regard: ● Forest Survey of India identified fire-prone forest areas over 17 years (2004-2021), categorizing them into extremely to less fire-prone. ● Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change formulated the National Action Plan on Forest Fire to minimize forest fires. ● The plan focuses on informing, enabling, and empowering forest fringe communities to work with forest departments. ●Objectives include reducing forest vulnerability to fire hazards, enhancing firefighting capabilities, and expediting post-fire recovery. ● Central Monitoring Committee oversees plan implementation. ● Financial assistance provided to states/UTs for forest fire prevention and mitigation under various schemes. ●Activities funded include creating and maintaining fire lines, water conservation, procurement of firefighting equipment, and community awareness. ● States receive advisories to raise awareness among forest fringe communities and provide incentives for forest protection efforts. |
| PYQ: Examine the status of forest resources of India and its resultant impact on climate change. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2020) |
| Practice Question: What are the environmental impacts of forest fires in India, and how can effective disaster management strategies mitigate their effects? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Crafted at home, NexCAR19 takes India to next level in cancer care
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health, GS3 – Science and Technology.
This topic showcases indigenous medical innovation and addresses healthcare accessibility, aligning with UPSC’s focus on national development and healthcare. |
| Context |
| ● The news is about the development of NexCAR19, an affordable CAR-T cell therapy for cancer treatment, spearheaded by Indian researchers and clinicians. |
Additional information on this news:
- NexCAR19 is a CAR-T cell therapy developed in India to treat cancer, particularly B-lymphomas and B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL).
- Developed by a team led by Professor Rahul Purwar from IIT Bombay, in collaboration with Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH) Mumbai.
- The therapy involves genetically modifying a patient’s T cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) targeting CD19 protein on cancer cells.
- CAR-T cells are multiplied in the lab and infused back into the patient after chemotherapy.
- NexCAR19 is humanized, using human proteins in the CAR construct, potentially reducing toxicity.
- It underwent successful clinical trials at TMH, with CDSCO approval obtained in October 2023.
- While promising, CAR-T therapy has side effects like cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity.
- NexCAR19’s cost ranges from ₹40 to 45 lakh, relatively high but cheaper than its US counterpart.
- Efforts are underway to reduce costs through scale-up manufacturing and improving purchasing power.
| Practice Question: How does the development of NexCAR19 contribute to indigenous medical innovation and healthcare accessibility in India? (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Progress in combating malnutrition remains ‘sluggish’
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health
Understanding undernutrition in India is vital for UPSC aspirants to address public health challenges and achieve Sustainable Development Goals. |
| Context |
| ● The news discusses a study by the Indian Institute of Public Health (IIPH) Hyderabad on undernutrition in India, highlighting marginal increases in wasting but decreases in stunting and underweight prevalence among children. |
Additional information on this news:
- Malnutrition is a significant health issue in India, contributing to the disease burden, prompting global initiatives like the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aiming to eradicate it by 2030.
- Despite national nutrition programs, progress in reducing undernutrition has been slow in India, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to designate 2016–2025 as the decade of nutrition.
- A study by the Indian Institute of Public Health (IIPH) Hyderabad analysed undernutrition among children under three at the state level using data from the National Family Health Surveys (NFHS).
- The study found marginal increases in wasting but decreases in stunting and underweight prevalence from NFHS-1 to NFHS-5, highlighting the need for tailored interventions.
- Factors affecting children’s nutritional status include maternal education and gender, with male children at a higher risk.
- While urban areas show increased risk, trends in malnutrition indicators vary across states, emphasizing the need for state-level action.
- Insights from the study underscore the importance of addressing malnutrition and its socio-demographic correlates to meet global targets and improve India’s Global Hunger Index ranking.
- Initiatives like Mission Indradhanush play a role, but efforts from parents, caregivers, and educators are also crucial in combating undernutrition.
| Reasons for persisting malnutrition in India: |
| Reasons for Persisting Malnutrition in India:
●Socio-economic Factors: Poverty, inadequate access to nutritious food, and limited healthcare services contribute to malnutrition. ● Poor Infant and Young Child Feeding Practices: Lack of breastfeeding, timely introduction of complementary foods, and poor feeding practices impact child nutrition. ● Inadequate Maternal Health and Nutrition: Maternal undernutrition during pregnancy affects fetal development and increases the risk of low birth weight and stunting. ● Lack of Sanitation and Hygiene: Poor sanitation practices lead to infections and diseases, further aggravating malnutrition. ● Food Insecurity and Inequality: Disparities in food distribution and access, coupled with inequitable distribution of resources, perpetuate malnutrition. ●Limited Awareness and Education: Lack of nutrition education and awareness among caregivers hinders optimal feeding practices and dietary diversity. ●Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Environmental factors such as natural disasters and climate change impact food production, availability, and access. Way Forward: ● Strengthening Social Safety Nets: Implementing poverty alleviation programs and ensuring access to food assistance for vulnerable populations. ●Enhancing Maternal and Child Healthcare: Improving antenatal care, promoting breastfeeding, and enhancing nutritional support for pregnant women and children. ●Investing in Sanitation and Hygiene: Building adequate sanitation infrastructure and promoting hygienic practices to prevent disease transmission. ● Promoting Nutrition Education: Conducting awareness campaigns and integrating nutrition education into school curricula and community programs. ● Addressing Food Insecurity: Improving agricultural productivity, enhancing food distribution systems, and promoting sustainable food production methods. ● Strengthening Policy Frameworks: Implementing comprehensive policies and programs targeting malnutrition prevention and mitigation at national and state levels. ●Fostering Multi-Sectoral Collaboration: Engaging multiple stakeholders, including government agencies, NGOs, and civil society, to address the complex determinants of malnutrition. |
| PYQ: Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2016) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the trends and factors contributing to undernutrition among children in India, and propose strategies for improvement. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. Apple Issues Threat Notifications to Users Worldwide Over Pegasus Spyware Concerns
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security – Challenges to internal security through communication networks This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the article sheds light on internal security concerns related to cyber threats and surveillance activities, specifically the potential infiltration of spyware like the NSO Group’s Pegasus malware. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Change in Language and Attribution:
- Unlike previous notifications attributing attacks to “state-sponsored” actors, Apple has refrained from specifying any stakeholders and has altered its language to term these attacks as “mercenary spyware” instead.
- This shift marks a departure from previous policies, indicating a change in how the company addresses such security concerns.
Previous Notifications and Government Pressure:
- In the past, Apple had notified Opposition leaders in India about “potential state-sponsored spyware attacks” on their iPhones.
- However, under pressure from the government, the company clarified that it does not attribute these threats to any specific state-sponsored attacker.
Recommendations and Advice for Users:
- Apple advises impacted users to exercise caution with links and attachments from unknown senders, suggesting they change passwords for sensitive websites and services.
- However, the company refrains from providing specific details about the cause of the notifications to prevent attackers from adapting their behavior to evade detection.
Support and Assistance for Users:
- Apple has updated its support page to provide tips for users who may have been potential targets, emphasizing the extreme sophistication and global nature of mercenary spyware attacks.
- The company aims to inform and assist users targeted by such attacks, without attributing them to specific attackers or geographical regions.
Investigations and Past Responses:
- Previous investigations into similar issues, including allegations of unauthorized surveillance using Pegasus software, have not yielded conclusive evidence.
- The Supreme Court-formed committee found no conclusive evidence of spyware use but noted a lack of cooperation from the Centre.
- The Pegasus controversy, which emerged from media reports of illegal surveillance, led to petitions seeking probes into the allegations.
Conclusion:
- Apple’s issuance of threat notifications underscores the seriousness of potential security threats posed by mercenary spyware.
- Despite challenges in attributing attacks and conducting investigations, addressing such security concerns remains crucial for safeguarding user privacy and digital integrity.
| About Pegasus |
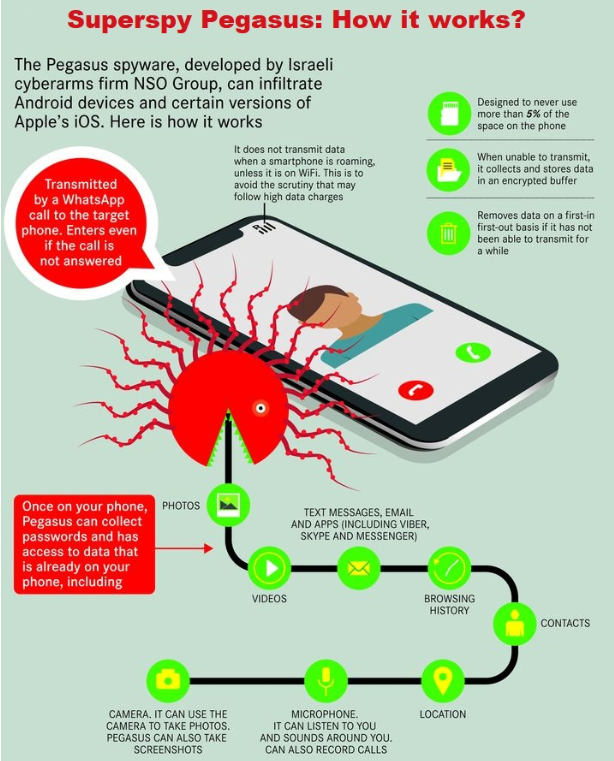 |
| PYQ: In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020) 1) Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer 2) Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so 3) Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion 4) Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third- party files a suit Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 4 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Explain the significance of Apple’s recent threat notifications regarding potential spyware attacks on iPhones. Discuss the challenges posed by such cyber threats and the measures taken by companies and governments to address them. (250 words/15 m) |
7. India Amends DTAA with Mauritius to Combat Tax Treaty Abuse
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations
GS3 – Indian Economy – This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the article discusses the amendment to the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) with Mauritius, which has significant implications for India’s economy, particularly in terms of foreign investments and tax policies. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Inclusion of Principal Purpose Test (PPT):
- The amended protocol incorporates Article 27B, defining the ‘entitlement to benefits’ and outlining the conditions under which treaty benefits, such as reduced withholding tax on interest, royalties, and dividends, will be denied if obtaining those benefits was a principal purpose of the transaction.
Historical Context and Impact:
- Mauritius has been a preferred jurisdiction for investments in India, particularly due to the non-taxability of capital gains until 2016.
- However, the amendment in 2016 allowed India to tax capital gains from the sale of shares acquired by Mauritian tax residents.
- The recent amendment aims to address ambiguities and prevent tax treaty abuse but lacks clarity on the treatment of past investments.
Potential Rise in Litigation:
- While the amendment aims to curb tax treaty abuse, experts anticipate a surge in litigation as investors from Mauritius will now need to substantiate the commercial rationale behind their transactions.
- Ambiguities remain regarding the application of the PPT to grandfathered investments, necessitating guidance from the Indian government.
Alignment with Global Efforts and BEPS Framework:
- The amendment reflects India’s commitment to align with global efforts against treaty abuse, particularly under the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) framework.
- However, India is yet to announce Pillar Two amendments in its domestic tax laws, which are expected to be addressed post-elections, possibly in the budget in July 2024.
Conclusion:
- Over 135 jurisdictions have agreed to implement a minimum tax regime for multinationals under Pillar Two, with the OECD releasing the Global Anti-Base Erosion (GloBE) rules.
- These rules propose a global minimum corporate tax rate set at 15%, aiming to generate additional global tax revenues annually.
- The Pillar Two framework emphasizes coordinated taxation to prevent profit shifting and ensure a level playing field in the global tax landscape.
| About DTAA |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the recent amendment to the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between India and Mauritius. Evaluate the potential impact of these amendments on foreign investments, bilateral relations, and India’s efforts to align with global tax governance frameworks. (250 words/15 m) |
8. Chital Overpopulation in Andaman and Nicobar Islands Sparks Concern Over Invasive Species Management
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental Pollution and Degradation
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of Understanding the concept of invasive alien species, their definition, examples, and impact on native ecosystems. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Invasive Alien Species (IAS):
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) defines invasive alien species (IAS) as those whose introduction and spread outside their natural distribution threaten biological diversity.
- In India, the legal definition of IAS, under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (amended in 2022), is narrower, excluding species within India that may be invasive to a specific region, such as chital in the Andamans.
Examples of IAS in India:
- India’s list of invasive wildlife is dominated by certain fish species like the African catfish, Nile tilapia, red-bellied piranha, and turtle species such as the red-eared slider.
- These species, often introduced by human intervention, outcompete native species for resources and disrupt local ecosystems.
Impact of IAS on Native Species:
- IAS disrupt food chains and ecosystem balance, often dominating habitats where there is no competition.
- For example, chital in the Andamans have impacted the regeneration of native vegetation by consuming seeds and seedlings.
- In places like Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan, invasive species like the African catfish have been known to prey on water fowl and migratory birds, affecting biodiversity.
Economic Impact of IAS:
- According to a report by the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), the global economic cost of IAS was over $423 billion annually in 2019.
- These costs arise from the damage inflicted by IAS on natural ecosystems, leading to yield losses in crops like cotton due to invasive pests like the cotton mealy bug.
Conclusion:
- The management of invasive alien species like chital in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands is crucial for preserving native biodiversity and mitigating economic losses caused by their proliferation.
- Collaborative efforts between wildlife authorities, research institutions, and local communities are essential to address this challenge effectively.
| Factors Responsible for Rising Invasive Species: |
|
Globalization of Trade and Travel:
|
| PYQ: With reference to the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
1) IUCN is an organ of the United Nations and CITES is an international agreement between governments. 2) IUCN runs thousands of field projects around the world to better manage natural environments. 3) CITES is legally binding on the States that have joined it, but this Convention does not take the place of national laws. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Explain how invasive alien species can disrupt native ecosystems, using the example of chital in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Discuss the challenges posed by invasive species and the measures taken by authorities to address this issue. (250 words/15 m) |
For Enquiry
/* widget: Icon Mobile Menu */
#uc_icon_mobile_menu_elementor_25dc4a0910
{
text-align:center;
display:flex;
flex-direction: row;
box-shadow:0px -10px 10px rgba(0,0,0,0.1); overflow:hidden;
}
#uc_icon_mobile_menu_elementor_25dc4a0910 a
{
text-decoration:none;
flex:1;
text-align:center;
}
#uc_icon_mobile_menu_elementor_25dc4a0910 a i
{
font-size:20pxpx;
}
#uc_icon_mobile_menu_elementor_25dc4a0910 a
{
display:block;
padding:Arraypx;
}
Phone
Whatsapp
Mail
/* widget: AJAX Search */
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911.uc-ajax-search-wrapper{
position:relative;
display:flex;
width:100%;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__suggested, #uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__suggested-wrapper
{
display:flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-items:center;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__title
{
display:block;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search-wrapper-inside
{
width:100%;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911.uc-ajax-search-wrapper span{
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911.uc-ajax-search-wrapper input{
width:100%;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__input-wrapper-inner
{
position:relative;
flex-grow:1;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__items{
position:absolute;
left:0px;
width:100%;
z-index:999999;
overflow:hidden;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-search-item__link{
display:flex;
align-items:center;
gap:10px;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-search-item__link-title{
display:block;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-search-item__link-image{
display:block;
flex-grow:0;
flex-shrink:0;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__input-wrapper{
position:relative;
display:flex;
align-items:center;
justify-content:center;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-search-item{
transition: background-color .3s;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-search-item.uc-selected{
background-color: #ccc;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-pagination-list{
display: flex;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
width: 100%;
transition: transform .3s;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-pagination-list-inner{
flex: 0 0 100%;
max-width: 100%;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-pagination-header{
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
direction: ltr;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search-pages{
display: flex;
gap: 5px;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search-navigation-panel{
display: flex;
gap: 15px;
justify-content: space-between;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-arrows{
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
gap: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-arrows .uc-inactive{
opacity: .5;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-arrow-left{
position: relative;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-arrow-left::before{
font-family: “Font Awesome 5 Free”;
content: “f104”;
font-weight: 900;
line-height:1em;
display: inline-flex;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-arrow-right::before{
font-family: “Font Awesome 5 Free”;
content: “f105”;
font-weight: 900;
line-height:1em;
display: inline-flex;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__btn
{
display:flex;
align-items:center;
justify-content:center;
flex-grow:0;
flex-shrink:0;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__btn.uc-inactive{
cursor: default;
opacity: 0.7;
pointer-events: none;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__btn_icon
{
line-height:1em;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__btn svg
{
height:1em;
width:1em;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911.uc-loading .uc-ajax-search__spinner__loader-wrapper{
display:flex !important;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__error{
color:red;
padding-top:15px;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__spinner__loader-wrapper{
position:absolute;
top:50%;
transform:translateY(-50%);
height: 100%;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
inset-inline-end: 15px;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__spinner {
animation: ajaxsearchrotate 2s linear infinite;
z-index: 2;
width: 25px;
height: 25px;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__spinner-path {
stroke-linecap: round;
animation: ajaxsearchdash 1.5s ease-in-out infinite;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-pagination-list-inner
{
display:grid;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 ::-webkit-input-placeholder { /* Edge */
color: #8f8f8f;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 :-ms-input-placeholder { /* Internet Explorer 10-11 */
color: #8f8f8f;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 ::placeholder {
color: #8f8f8f;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__input.uc-active{
caret-color: unset;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-ajax-search__input{
caret-color: transparent;
}
#uc_ajax_search_elementor_30e2a1911 .uc-highlight{
font-weight: 700;
}
@keyframes ajaxsearchrotate {
100% {
transform: rotate(360deg);
}
}
@keyframes ajaxsearchdash {
0% {
stroke-dasharray: 1, 150;
stroke-dashoffset: 0;
}
50% {
stroke-dasharray: 90, 150;
stroke-dashoffset: -35;
}
100% {
stroke-dasharray: 90, 150;
stroke-dashoffset: -124;
}
}

12 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

12 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

12 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

12 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

12 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

12 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

10 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

10 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
/* widget: Post Scroll */
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue_post_scroll_item
{
display:flex;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue_post_image
{
flex-shrink:0;
flex-grow:0;
display:flex;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue-scroller-content
{
flex-grow:1;
display:flex;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue_post_image img
{
width:100%;
object-fit: cover;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue_image_spacer
{
flex-shrink:0;
flex-grow:0;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue_calendar_spacer
{
flex-shrink:0;
flex-grow:0;
}
.ue-post-title
{
font-size:21px;
}
.ue-post-desc
{
font-size:14px;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue-post-calendar
{
text-align:center;
display:flex;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue-post-calendar-holder
{
overflow:hidden;
}
.ue-calendar-date
{
font-size:32px;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .uc_more_btn{
display:inline-block;
text-align:center;
text-decoration:none;
}
.ue-post-category
{
font-size:12px;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .bx-wrapper
{
box-shadow:none;
overflow:hidden;
margin-bottom:0;
border:none;
background:transparent;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .bx-viewport
{
overflow:hidden;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .bx-wrapper .bx-pager
{
position:relative;
bottom:auto;
padding-top:20px;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .bx-wrapper .bx-pager.bx-default-pager a
{
width:8px;
height:8px;
border-radius:50%;
background-color:#d3d3d3;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .bx-wrapper .bx-pager.bx-default-pager a.active
{
background-color:#535353;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .bx-wrapper .bx-pager.bx-default-pager a:hover
{
background-color:#c6c6c6;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .bx-wrapper .bx-pager.bx-default-pager a.active:hover
{
background-color:#535353;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue-calendar-month, #uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue-calendar-day
{
display:flex;
align-items:center;
justify-content:center;
}
#uc_post_scroll_elementor_7d0c4d1d12 .ue-scroller-content-container
{
width:100%;
}
Daily Quiz 12 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 12- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 12 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
12-April-2024
Q1) Bilateralism has helped India in building robust ties with the…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 12 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
12-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. ADB projects India’s GDP growth at 7% this…
April 2024 The Hindu Editorial 12 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
12-April-2024
1. In poll season, the perils of scorching bilateral ties
Topic:…
April 2024 PIB 12 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
12-April-2024
1. 7th round of the India-Peru Trade Agreement Negotiations concludes…
April 2024 Indian Express 12 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
12-April-2024
1. Decoding state budgets
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy…
Daily Quiz 10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 10- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 10 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
10-April-2024
Q1) By placing strategic evaluation of opportunities and threats…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 10 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
10-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. States, U.T.s asked to submit data on heatstroke…
April 2024 PIB 10 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
10-April-2024
1. Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) to organise…





