25 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
25-November-2023
1. Afghanistan Embassy in Delhi shuts down
Topic: GS2 – International relations.
Context:
- The Afghanistan Embassy in Delhi has permanently closed down as of November 23, according to an official statement.
Additional information on the news:
- The closure is attributed to pressure from both the Taliban rulers in Kabul and the Government of India.
- The embassy had ceased operations on September 30 when Afghan diplomats and the ambassador left India, citing unmet objectives related to visa extensions and the Indian government’s conduct.
- The official statement notes that despite an eight-week wait, the desired outcomes were not realized, leading to a challenging decision for the embassy.
- The closure is deemed to be in the “best interest of Afghanistan,” and the responsibility now lies with Indian authorities to decide on the future course of action.
- The diplomatic presence of the pre-Taliban regime in Afghanistan concludes with the permanent closure of the embassy.
2. Dalit youth seeks his salary, forced to hold footwear in mouth
Topic: GS1 – Indian Society.
Context:
- In Gujarat, a shocking incident involves a businesswoman and six others allegedly forcing a 21-year-old Dalit youth to apologize by putting her footwear in his mouth.
Why discrimination against Dalits still exist in India:
- Historical Social Hierarchy: Deep-rooted caste system and historical social hierarchy have perpetuated discrimination against Dalits, creating ingrained prejudices.
- Economic Disparities: Dalits often face economic marginalization, limited access to resources, and fewer opportunities, contributing to their vulnerable position.
- Landownership Patterns: Unequal landownership patterns, with Dalits often having limited or no land, contribute to economic disparities and social discrimination.
- Limited Educational Opportunities: Dalits may face obstacles in accessing quality education, limiting their upward mobility and reinforcing socio-economic inequalities.
- Cultural Practices: Certain cultural practices and social norms contribute to the perpetuation of discriminatory behavior against Dalits.
- Political Underrepresentation: Limited representation in political structures can lead to policies that inadequately address the specific challenges faced by Dalits.
- Enforcement Gaps: Weak implementation of protective laws and insufficient law enforcement contribute to the persistence of discrimination against Dalits.
- Social Stigma: Deep-seated social prejudices and stereotypes contribute to the perpetuation of discrimination, affecting various aspects of Dalits’ lives.
- Inadequate Legal Protection: While there are legal provisions to safeguard Dalit rights, the effectiveness of these laws is hindered by enforcement challenges and loopholes.
Way forward:
- Educational Reforms: Implementing educational reforms to ensure equal access and quality education for Dalits, addressing historical disparities.
- Economic Empowerment: Promoting economic empowerment through initiatives such as skill development, entrepreneurship, and land redistribution.
- Legal Reforms and Enforcement: Strengthening legal frameworks, ensuring effective enforcement, and closing gaps in the implementation of laws protecting Dalit rights.
- Political Representation: Encouraging increased political representation of Dalits to influence policies that address their unique challenges.
- Awareness and Sensitization: Conducting awareness campaigns and sensitization programs to challenge stereotypes, prejudices, and discriminatory cultural practices.
- Intersectional Approaches: Recognizing and addressing the intersectionality of discrimination by considering factors like gender and religion in policy formulations.
- Community Integration: Fostering community integration and social cohesion to break down barriers and reduce social stigma associated with Dalits.
- Empowering Civil Society: Supporting and empowering civil society organizations working towards Dalit rights to amplify advocacy efforts.
Question: How can India effectively combat discrimination against Dalits through education, economic empowerment, and legal reforms?
3. Centre exempts CERT-In from purview of RTI Act
Topic: GS2 – Government organisations.
Context:
- The Union government includes CERT-In in the list of organizations exempted from the RTI Act.
More information on the news:
- CERT-In, the national agency for responding to cyber incidents, enhances security awareness.
- The exemption applies to 27 intelligence and security organizations specified in the Second Schedule.
- The RTI Act, enacted in 2005, excludes these organizations but not information related to corruption and human rights violations.
- The recent amendment, made under section 24(2) of the RTI Act, adds CERT-In to the Second Schedule.
- CERT-In has played a crucial role in investigating major cyber attacks, including the AIIMS ransomware incident in November 2022.
What is CERT-In?
- CERT-In stands for Indian Computer Emergency Response Team.
- It is a government organization under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY),
- CERT-In is responsible for cybersecurity in India and plays a crucial role in preventing and responding to cyberattacks.
Key Responsibilities of CERT-In:
- Collect,analyze, and disseminate information about cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Issue advisories and guidelines to protect against cyberattacks.
- Respond to cybersecurity incidents and provide assistance to affected organizations.
- Coordinate with other cybersecurity agencies and organizations.
- Carry out research and development in cybersecurity.
Powers of CERT-In:
- CERT-In has the power to direct service providers, intermediaries,and data centers to take steps to protect against cyberattacks.
- It can also order the blocking of websites and applications that are found to be harmful.
- CERT-In can impose penalties on organizations that fail to comply with its directions.
Importance of CERT-In:
- CERT-In plays a critical role in protecting India’s critical infrastructure from cyberattacks.
- It also helps to raise awareness of cybersecurity among Indian organizations and individuals.
- CERT-In’s work is essential for maintaining India’s cybersecurity posture.
4. Generic drugs for 4 rare diseases made available in India
Topic: GS2 – Health sector
Context:
- The Union Health Ministry has initiated a crucial effort to provide relief to patients with rare diseases in India.
- The focus is on making generic drugs available for the treatment of specific rare ailments.
- The identified rare diseases include Tyrosinemia-Type 1, Gauchers Disease, Wilson’s Disease, and the Dravet-Lennox Gastaut Syndrome.
- The availability of generic drugs for these conditions is expected to substantially reduce their cost.
What are generic drugs?
- Definition: Generic drugs are copies of brand-name drugs that have the same active ingredient, strength, dosage form, and route of administration as the brand-name drug. They are also bioequivalent, which means that they work the same way in the body as the brand-name drug.
- Cost: Generic drugs are typically much cheaper than brand-name drugs. This is especially true in India, where the government has implemented policies to make generic drugs more affordable.
- Quality: Generic drugs in India must meet the same rigorous standards as brand-name drugs before they can be approved for sale by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- Prevalence: Generic drugs are widely available in India and account for a significant portion of the pharmaceutical market.
- Role in healthcare: Generic drugs have played a crucial role in improving access to affordable medications in India. They have helped to reduce healthcare costs and improve the health of millions of people.
Additional points:
- The Indian pharmaceutical industry is one of the largest in the world and is a major producer of generic drugs.
- India exports generic drugs to many countries around the world.
- The Indian government is committed to promoting the use of generic drugs as a way to improve access to affordable healthcare.
What are rare diseases?
Rare diseases are characterized by their low prevalence, typically affecting fewer than 65 per 100,000 individuals. In India, with its vast population, this prevalence translates to an estimated 8.4 crore to 10 crore cases.
Key characteristics of rare diseases:
- Low prevalence:Rare diseases affect a small percentage of the population, often less than 1 in 2,000 individuals.
- Diverse range of conditions:Rare diseases encompass a wide spectrum of disorders affecting various parts of the body and ranging in severity from mild to life-threatening.
- Complex and often undiagnosed:Rare diseases often present with complex symptoms and may be challenging to diagnose due to their rarity and lack of specialized expertise.
- Limited treatment options: Due to the rarity of these conditions, research and development of effective treatments for rare diseases often receive less attention and funding, leading to limited treatment options.
Challenges associated with rare diseases:
- Delayed diagnosis:The rarity of rare diseases often leads to delayed diagnosis, sometimes taking years for individuals to receive a proper diagnosis.
- Limited access to specialized care:Access to specialized healthcare providers and treatment facilities for rare diseases is often limited, particularly in resource-limited settings.
- Financial burden: The high cost of treatments and limited financial support can place a significant financial burden on individuals with rare diseases and their families.
- Psychosocial impact:The challenges associated with rare diseases can have a significant psychosocial impact on individuals and their families, including social isolation, anxiety, and depression.
Question: Discuss the challenges posed by rare diseases and the role of government and healthcare institutions in addressing these challenges.
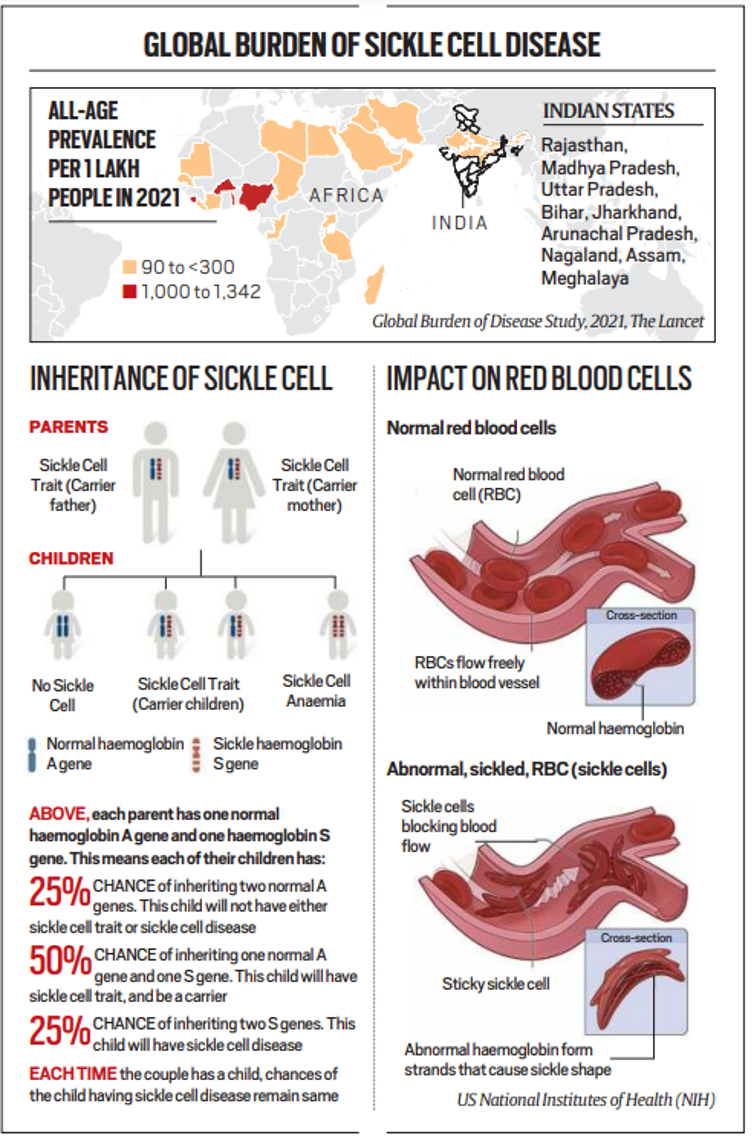
5. Sickle cell breakthrough
Topic: GS3- Science and Tech
Context:
- A novel gene therapy was recently approved by the UK drug Regulator, which is a major step forward in the treatment of sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
- This treatment, called Casgevy, uses the Crispr-Cas9 gene editing technique, which was awarded the Nobel Prize in 2012 and has completely changed the field of biotechnology.
Mechanism of Action:
- Casgevy functions by utilizing the patient’s own blood stem cells to modify the defective gene that causes sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
- The goal of the therapy is to increase the creation of fetal hemoglobin, which is devoid of the defects associated with adult hemoglobin, by targeting the BCL11A gene, which is essential for the transition from fetal to adult hemoglobin.
- Compared to the current bone marrow transplant process, this strategy offers a permanent remedy and may even be able to cure individuals with severe blood abnormalities.
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease and Thalassaemia:
- Red blood cells with sickle cell disease are malformed, which clogs blood arteries and causes excruciating pain, infections, anemia, and strokes.
- Conversely, thalassaemia causes low hemoglobin levels, which lead to exhaustion, dyspnea, and erratic heartbeats.
- A large number of children are born with these illnesses every year in places like India; therefore, the authorized gene therapy offers a ground-breaking alternative to the current treatments.
Clinical Trial Results:
- Casgevy’s clinical trial findings have been encouraging.
- For at least a year following treatment, 29 out of 45 trial participants with sickle cell disease did not develop acute pain crises.
- When it comes to thalassaemia, 39 out of 42 patients did not need a transfusion for at least a year following the medication, demonstrating its effectiveness in lowering the need for transfusions for the rest of their lives.
Administration of the Therapy:
- The administration of casgevy is a one-time procedure.
- Apheresis is used to extract blood stem cells from the patient’s bone marrow.
- The cells are then edited and tested at a manufacturing facility. After the bone marrow has been prepared, the patient receives another transplant of the modified cells.
- In order to guarantee that the modified cells integrate into the bone marrow and begin generating regular red blood cells that contain hemoglobin, patients usually remain in the hospital for at least a month.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
- Even if the therapy is revolutionary, there are still issues because of its potentially exorbitant cost—up to $2 million per patient.
- This is a major obstacle, especially in developing nations where a large number of people with these illnesses live.
- Establishing local manufacturing facilities and addressing pricing difficulties are essential steps toward greater accessibility.
- Researchers are still hopeful that as more people work on this technology, costs may come down and a wider range of people will be able to access it.
- Enhancing accessibility and cost could also be greatly aided by local manufacturing facilities.
6. Why a NASA space craft fired a laser at Earth, and why it is a big deal
Topic: GS3- Science and Tech
Context:
- NASA’s Psyche spacecraft has successfully sent a laser signal to Earth from a distance of more than 16 million kilometers while it is now traveling to a metal-rich asteroid between Mars and Jupiter.
- The mission’s objectives are to investigate the asteroid and learn more about Earth’s iron core.
- Moreover, Psyche conducts a groundbreaking laser-based deep space exploration expedition.
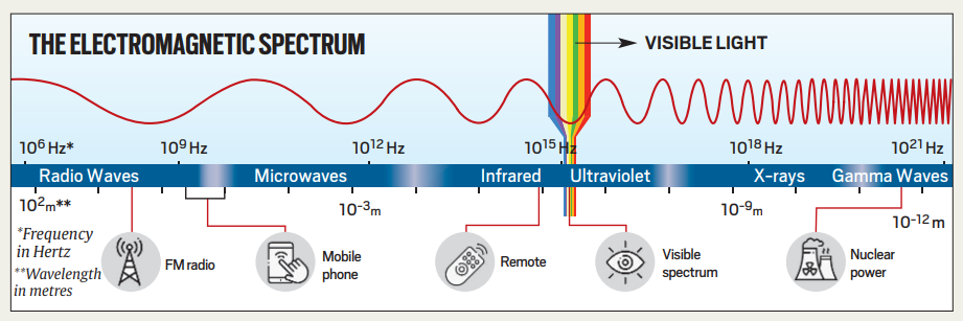
Space Data Transmission Challenges:
- The difficulty with space communication is moving large amounts of data quickly over long distances.
- Spacecraft use a variety of electromagnetic frequencies to encode data, just like terrestrial wireless communication does.
- Due to their advantageous propagation characteristics, radio waves are now used for the majority of space communication.
- However, researchers are looking at wider bandwidths for increased data transmission, which presents a unique set of difficulties.
NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC):
- The use of near-infrared laser signals for spacecraft communication is being introduced by NASA through the DSOC project.
- With data speeds at least ten times faster than current radio communications networks, this technology allows for the transport of bigger volumes of data, including streaming high-definition video.
- As it travels, Psyche—the first spaceship equipped with a DSOC transceiver tests high-bandwidth optical communications.
Precision and Technological Innovations:
- By separating the transceiver from spacecraft vibrations, correcting for changes in the craft’s and Earth’s position, and using signal-processing techniques to recover information from weak laser signals, DSOC achieves precise communication.
- Reaching this degree of accuracy is critical because it allows for communication that is similar to striking a dime as it is moving from a distance of a mile.
Transformative Impact on Space Travel:
- DSOC brings this technology into deep space, which is significant for humanity’s aspirations to travel beyond the Moon, even though similar technology has been proven in Earth-orbiting satellites.
- Future deep space missions must prioritize improved communication. NASA’s Trudy Kortes noted that the successful completion of “first light” is a significant step toward humanity’s next great leap—the landing of humans on Mars.
7. Shut Down of Afghan Embassy in India
Topic: GS2- IR
Context:
- The Afghanistan Embassy in New Delhi has been closed down permanently.
More about the news:
- Halt in functioning: The embassy had stopped functioning on September 30 when the senior Afghan diplomats and the ambassador representing the Government of Islamic Republic of Afghanistan left India.
- The embassy blamed both the Taliban rulers in Kabul as well as the Government of India for pressuring it to stop operations in India permanently.
- Reason for Closure: The closure is attributed to a lack of resources and the Taliban regime’s failure to meet Afghanistan’s interests.
- Concerns: The permanent closure of the embassy of Afghanistan will create a challenging situation for traders and travellers who want to apply for Afghan visas.
- Decline in the Afghan community: There is a significant decline in the Afghan community in India over the past two years which has been attributed to the departure of refugees, students, and traders.
About Embassy of Afghanistan:
- The embassy represented the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan until it was overthrown by the Taliban through a military campaign on August 15, 2021.
- The Taliban fighters quickly took over all the major cities and infrastructure of the country with the withdrawal of the U.S. forces. However, they were not recognised by India as de facto rulers.
- A stateless Mission: With the displacement of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, the embassy of Afghanistan in New Delhi had begun to work as a “stateless mission” as it did not represent the current rulers of Kabul, that is the Taliban, with whom India has no diplomatic relationship.
- Symbolic role: The embassy was performing a ceremonial role helping out Afghan citizens and travellers in India deal with the difficulties they have been facing due to the lack of diplomatic relations between the two countries.
Indian response to Taliban Regime:
- Diplomatic engagement: India has not recognised the Taliban formally but Indian diplomats have been engaged with the Taliban since the the fall of Kabul in August 2021.
- Indian diplomats have met the Taliban’s representatives in multiple locations under multilateral initiatives like the recent Moscow format dialogue.
- Recently, India sent a representative to Kazan, Tatarstan in Russia to engage with the Taliban under the Moscow format dialogue.
- No economic support: The Taliban has been urging India to support it with its economic revitalisation through projects like electricity generation and road building works.
- India, however, has not yet indicated that it will review its position on the Taliban.
- India has never allowed the Taliban to operate from embassy of Afghanistan in Delhi even when it governed Afghanistan from 1996 to 2001.
8. Low risk to India from influenza situation in China, says Govt
Topic: GS2- Health
Context:
- The Union Health Ministry of India has said that it is keeping a close eye on a situation in which reports of pneumonia patients in clusters have been received from northern China.
- According to the ministry, India is currently at low risk, based on information that is already available.
- According to the ministry’s statement, the rise in respiratory infections that has been recorded in China over the past few weeks is due to common causes in children, and no unique pathogen or unexpected clinical manifestation has been found.
Caution but No Cause for Alarm:
- Officials with knowledge of the situation say that while respiratory illnesses are on the rise, there is currently no need for concern.
- The seasonal rise in respiratory infections is consistent with the reported increase in illnesses.
- The ministry of health highlighted that no novel pathogen has been found to be linked to the cases that have been reported.
Preparedness Measures and Low Risk to India:
- The Union Health Ministry is keeping an eye on cases of pneumonia as well as a case of human H9N2 avian influenza that was detected in China in October.
- The Director-General of Health Services presided over a meeting where preparations for this circumstance were discussed.
- A low likelihood of human-to-human transmission and a low case fatality rate among humans are indicated by the WHO’s overall risk assessment.
- The H9N2 avian influenza case and the reported pneumonia clusters pose a low overall danger to India, according to the health ministry, which also guarantees that the country is ready for any future public health emergency.
9. Domestic production brings down cost of rare disease drugs
Topic: GS2- Health
Context:
- Manufacturing medicines for four rare conditions—Tyrosinemia Type 1, Gaucher’s Disease, Wilson’s Disease, and Dravet-Lennox Gastaut Syndrome is an impressive undertaking undertaken by Indian drug companies.
- Thanks to this approach, the cost of these medications has been drastically reduced leading to savings up to 100 times.
- By addressing a significant obstacle in the treatment of uncommon diseases, the action increases accessibility to these vital drugs.
What is a Rare disease?
- An illness is considered rare if there are less than 1,000 cases of it in the general population.
- It is estimated that 8.4 crore to 10 crore Indians, or 6% to 8% of the population, suffer from these uncommon illnesses.
- Since there are either no viable remedies or they are too expensive, many of these people do not have access to treatment.
- This highlights the major healthcare obstacles that a large segment of the Indian population with uncommon diseases must overcome.
Significant Price Reductions in Rare Disease Treatments
- There has been a significant decrease in the cost of drugs for rare conditions.
- The yearly cost of eliglustat capsules for Gaucher’s illness, which is known to cause fatty deposits in essential organs, has decreased from Rs 1.8 crore to Rs 3.6 crore to Rs 3 lakh to Rs 6 lakh.
- Trientine capsules, which were formerly priced at Rs 2.2 crore for a 10 kg infant, are now used to treat Wilson’s illness, which is characterized by copper deposition.
- The yearly cost of nitisinone capsules, which treat Tyrosinemia Type 1, has dropped from around Rs 2.2 crore to about Rs 2.5 lakh.
- Furthermore, the cost of the oral cannabidiol solution for Lennox-Gastaut and Dravet syndrome has significantly decreased, going from Rs. 7 lakh to Rs. 34 lakh annually to Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 5 lakh.
Way Forward
- The government is stepping up its efforts to guarantee that treatments for at least 13 priority illnesses may be obtained at a lower cost from domestic manufacturers.
- These disorders are increasingly prevalent, have treatments now in place, or are developing at a rapid pace in science and may one day result in treatments that could change people’s lives.
- In order to improve distribution beyond the existing centers of excellence for rare diseases, plans are in place to make these treatments available to patients nationwide.
- One potential solution being considered is the establishment of Jan Aushadhi stores.
- This all-encompassing strategy represents a major advancement in tackling the difficulties related to treating uncommon diseases in India.
10. India, EU sign semiconductor pact
Topic: GS2- Govt Policies
Context:
- In an effort to promote cooperation in the semiconductor ecosystem, India and the EU have inked a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU).
- Investments, joint ventures, and technological partnerships—including the opening of manufacturing facilities will be made easier by this agreement.
- This action is in line with India’s ambitious aim to offer incentives totaling $10 billion to support domestic chip manufacture.
Incentive Plans and Significance
- During the virtual second meeting of the India-EU Trade and Technology Council (TTC), the Memorandum of Understanding was formalized.
- The goal of this partnership is to strengthen innovation, supply chain, and semiconductor ecosystem interaction.
- India’s dedication to providing incentives for the production of chips highlights the strategic significance of semiconductor technology in the country’s economic growth.
Second India-EU Trade and Technology Council Meeting
- The India-EU Trade and Technology Council held its first meeting in Brussels in May, and this one is its second.
- India is the only nation to participate in a TTC mechanism with the European Union, after the United States.
The TTC aims to strengthen the relationship between the two organizations by expanding strategic collaboration in trade and technology
For Enquiry

25 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs

25 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

24 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz

24 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing

24 Nov 2023 : Indian Express

24 Nov 2023 : PIB

24 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs

24 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

23 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz

23 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing
Daily Current Affairs 25 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
25-November-2023
1. Afghanistan Embassy in Delhi shuts down
Topic: GS2 –…
November 2023 The Hindu 25 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
25-November-2023
1. Need for climate-smart agriculture in India
Topic: GS3 –…
Daily Quiz 24 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz 24 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 24 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
24-November-2023
Q1) How does the Archeological evidence help in piecing together…
Indian Express 24 Nov 2023 : Indian Express Indian Express
24-November-2023
1) Engaging With APEC
Context:
After a 12-year hiatus, the US hosted…
November 2023 PIB 24 Nov 2023 : PIB PRESS INFORMATION BUREAU
24-November -2023
1. PM participates in Sant Mirabai Janmotsav in Mathura,…
Daily Current Affairs 24 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
24-November-2023
1. Governor holds no veto power over Bills, says SC
Topic:…
November 2023 The Hindu 24 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
24-November-2023
1. A $5 trillion economy, but for whom?
Topic: GS2 – Indian…
Daily Quiz 23 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz 23 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 23 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
23-November-2023
1. How did the ancient trade routes connecting India to foreign…




