4 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
4-November-2023
1. Difficult to press for women’s quota before LS poll: SC
Topic: GS2 – Indian polity.
Context:
- The Supreme Court of India has expressed support for the constitutional amendment that reserves one-third of seats in Parliament, State legislatures, and the Delhi Legislative Assembly for women as a positive step toward achieving gender parity in politics.
- The court, led by Justice Sanjiv Khanna, has expressed doubts about intervening to enforce the implementation of the quota law before the 2024 general election, considering it would be akin to legislating.
- The case has been listed for further consideration on November 22, along with a similar petition.
Difficulties highlighted by the Supreme Court:
Difficulty in implementation before 2024 general election:
- The Supreme Court observed that it would be very difficult to step in to ensure the implementation of the quota law before the general election in 2024. This is because it would amount to virtually legislating.
- The court explained that it would have to consider the logistics of implementing the quota, which would involve redrawing constituency boundaries and making other changes.
- This would be a complex and time-consuming process, and it would be difficult to complete it in time for the 2024 election.
Clause in the law:
- The law says that the reservation should be implemented only after the next census followed by a delimitation exercise. The petition filed by Jaya Thakur questions this clause.
- The Supreme Court explained that this clause was included in the law to ensure that the quota is implemented in a fair and transparent manner. The census provides accurate data on the population of each state and constituency, which is essential for determining the number of seats to be reserved for women.
- The delimitation exercise ensures that each constituency has an equal number of voters, regardless of gender.
- The court also observed that this clause is consistent with the Constitution of India, which requires that elections be held on the basis of adult suffrage and universal adult franchise.
2. Delhi air quality worsens to ‘severe plus’.
Topic: GS3 – air pollution
Context:
- Delhi’s air quality deteriorated, reaching the ‘severe plus’ category for the first time in the current season.
- Lieutenant-Governor V.K. Saxena called an emergency meeting with Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal and Environment Minister Gopal Rai to address the situation.
Air quality in Delhi deteriorates to ‘severe plus’
- Causes: Stubble burning in neighboring states, local pollutants,and unfavorable meteorological conditions
- Impact: AQI score rose from 351 at 10 a.m. on Thursday to 471 at 9 a.m. on Friday and dipped to 468 by 4 p.m.
Emergency measures implemented
- GRAP Stage 3: Ban on construction and demolition activities and plying of BS-III petrol and BS-IV diesel light motor vehicles in Delhi and a few districts in the neighbouring states. All government and private primary schools in Delhi were closed till Saturday.
GRAP Stage 4 (not yet implemented)
- Shutting down educational institutes
- Reducing staff strength at government and private offices by 50%
- Implementing the odd-even scheme for the plying of vehicles
Other developments
- Lieutenant-Governor V.K. Saxena called for an emergency meeting with Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal and Environment Minister Gopal Rai.
- Saxena appealed to people to remain indoors as much as possible, avoid unnecessary travel, and, if necessary, use public transport.
- He also appealed to the neighbouring states, especially Punjab, to curtail crop residue burning.
Weather forecast
- Unfavorable weather conditions — low wind speed and lack of rain — are likely to persist for another two to three days.
3. National dam safety team faults planning, design of Kaleshwaram project’s barrage in Telangana
Topic: GS3 – disaster management
Context:
- An expert team from the National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) examined the sinking of piers in Block-7 of Medigadda (Laxmi) Barrage in the Kaleshwaram irrigation project in Telangana.
- The NDSA team found faults in the planning and design of the project.
- They concluded that a combination of issues involving planning, design, quality control, and operation and maintenance contributed to the damage.
Issues with Dam safety in India:
- Lack of awareness and training:There is a lack of awareness and training among dam owners and operators about dam safety. This leads to poor maintenance and operation of dams, which can increase the risk of dam failure.
- Inadequate funding:There is a shortage of funds for dam safety in India. This is due to a number of factors, including competing priorities for government spending and the lack of a dedicated funding source for dam safety.
- Ageing infrastructure:Many dams in India are ageing and in need of repair or replacement. However, there is a lack of resources to carry out these works.
- Climate change:Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts. This puts additional stress on dams and increases the risk of dam failure.
Way forward:
- Increase awareness and training:The government and other stakeholders should increase awareness and training about dam safety among dam owners, operators, and other relevant stakeholders. This will help to improve the maintenance and operation of dams and reduce the risk of dam failure.
- Increase funding:The government should increase funding for dam safety. This could be done by creating a dedicated funding source for dam safety or by increasing the allocation of funds for dam safety from existing sources.
- Improve dam safety management:The government should improve dam safety management by developing and implementing comprehensive dam safety plans. These plans should include measures for dam inspection, maintenance, and rehabilitation.
- Strengthen dam safety regulations: The government should strengthen dam safety regulations and ensure that they are effectively enforced. This will help to ensure that dams are designed and constructed to meet high safety standards.
- Address climate change:The government should take steps to address climate change and mitigate its impact on dam safety. This could be done by investing in renewable energy, improving water management, and strengthening disaster preparedness.
Question: Dam safety is a critical issue in India, given the large number of dams in the country. Discuss the challenges to dam safety in India and suggest measures to address these challenges.
4. Five Karnataka villages come under surveillance after Zika virus outbreak
Topic: GS3 – Health sector
Context:
- The Karnataka Health Department is closely monitoring Chickballapur after a positive Zika case was found in a mosquito pool in Thalakayalbetta village.
- Serum samples from 30 pregnant women from five villages in the containment zone have been sent to the National Institute of Virology (NIV) for testing.
- A containment zone has been established, covering 888 houses with a population of 4,282, and is under intense surveillance.
Zika Virus:
- What is Zika?: Zika is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause birth defects in babies born to infected mothers. It can also cause other health problems, such as fever, headache, rash,joint pain, and red eyes.
- How is Zika transmitted?: Zika is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito.Aedes mosquitoes are the same mosquitoes that transmit dengue and chikungunya.
- Who is at risk for Zika?: Anyone can be infected with Zika, but pregnant women and their babies are at the highest risk for serious complications.
- What are the symptoms of Zika?: Most people infected with Zika do not have any symptoms, or they have mild symptoms that are similar to other common illnesses. In those who do have symptoms, they usually start 3-14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The most common symptoms are fever,headache, rash, joint pain, and red eyes. Symptoms usually last for 2-7 days.
5. Strong quake jolts Nepal; tremors felt in North India
Topic: GS1 – Indian geography.
Context:
- A powerful earthquake with a magnitude of 6.4 struck Nepal on Friday night, leading to tremors felt across parts of North India.
- The earthquake occurred at 11.32 p.m., prompting people to quickly evacuate their homes during their preparations for the weekend.
- The National Centre for Seismology reported that the earthquake’s epicenter was located in Nepal.
Earthquake prone zones in India:
Earthquake-prone zones in India are classified into four main seismic zones based on their susceptibility to earthquakes:
- Zone 2: This is the least earthquake-prone zone in India and includes parts of northwestern India, the northeastern states, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It has the lowest level of seismic activity.
- Zone 3: This zone covers most of northern India, including Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, and parts of Rajasthan. It has moderate seismic activity.
- Zone 4: Zone 4 includes areas with high seismic activity, such as the Himalayan region, parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand. These areas are more vulnerable to earthquakes.
- Zone 5: This is the most earthquake-prone zone in India and includes the entire northeastern region and parts of Jammu and Kashmir. It has the highest level of seismic activity and is at the greatest risk of earthquakes.
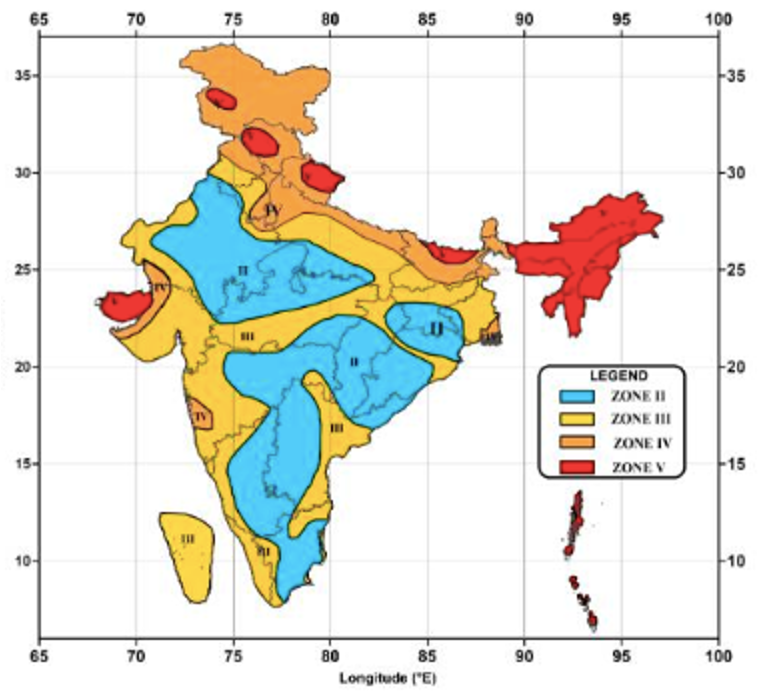
Note – Please refer NCERT and GC Leong for static part about earthquakes
6. India will work with Sri Lanka on its debt treatment: Nirmala
Topic: GS2 – International relations
Context:
- Indian Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman met with Sri Lankan President Ranil Wickremesinghe to discuss debt treatment and other areas of cooperation.
- Sri Lanka must bring all of its major creditors on board for a debt treatment plan in order to unlock the second tranche of the IMF’s EFF.
- India has provided nearly $4 billion in assistance to Sri Lanka during its economic crisis.
- The 12th round of negotiations on the stalled ETCA between the two countries took place from October 30 to November 1 in Colombo.
Debt crisis of Sri Lanka:
- Economic mismanagement:The Sri Lankan government has been accused of economic mismanagement, including overspending, corruption, and a failure to diversify the economy.
- High debt levels:Sri Lanka has a high debt-to-GDP ratio, which means that the government owes a lot of money relative to the size of the economy. This makes it difficult for the government to borrow more money or to repay its existing debt.
- The China factor: the Sri Lankan government has borrowed heavily from the Chinese investors, government – it has put Sri Lanka and economy under immense pressure of debt servicing.
- The COVID-19 pandemic:The COVID-19 pandemic had a severe impact on the Sri Lankan economy, disrupting tourism and other key sectors.
Specific examples of economic mismanagement:
- Large subsidies:The Sri Lankan government provides large subsidies for fuel, food, and other goods. These subsidies are expensive and have been criticized for being inefficient and benefiting the wealthy more than the poor.
- White elephant projects:The Sri Lankan government has invested heavily in white elephant projects, such as the Hambantota Port and the Mattala Rajapaksa International Airport. These projects have been criticized for being poorly planned and executed, and for draining the government’s finances.
- Corruption:Corruption is a widespread problem in Sri Lanka. This has led to waste and inefficiency in the government, and has made it difficult for the government to raise revenue.
7. How air pollution impacts economic growth: The evidence in research
Topic: GS3- Economy
Context:
- The prevalent belief that air pollution is an inevitable consequence of economic expansion is frequently rejected by the mainstream, which can lessen the urgency of developing efficient policy solutions for this problem.
- On the other hand, new studies indicate that air pollution negatively impacts GDP growth and per capita income levels, impacting many aspects of economic activity.
- This is especially problematic for nations like India, where frequent episodes of high pollution have a substantial negative influence on important economic centers.
Impact on Economic Growth:
- The effects of air pollution on economic growth are complex. It diminishes customer footfall in services that are driven by consumption and decreases worker productivity, which results in lost labor hours.
- In addition, it reduces the productivity of assets and raises health and welfare costs, particularly for the working-age population.
- The combined effects of these factors have a significant impact on a nation’s economic success.
RBI’s Assessment:
- The Department of Economic and Policy Research (DEPR) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued a warning, stating that lost work hours stemming from climate change-related problems, such as excessive heat and humidity, could jeopardize up to 4.5% of India’s GDP by 2030.
- The toll that pollution takes on annual cycles in major centers of manufacturing and services could be considerably more detrimental to economic productivity.
Micro-Level to Macro-Level Impact:
- According to a World Bank analysis released in June 2023, the macro-level effects of air pollution on yearly fluctuations in GDP are a result of the micro-level consequences that the pollution has on labor supply, productivity, health, and other economically significant outcomes.
- 90% of India’s actual GDP comes from major economic districts whose data served as the basis for this analysis.
Inter-State Variations and Economic Loss:
- A 2021 study that was published in The Lancet Planetary Health showed notable inter-state differences in the amount of money that India’s states lost as a result of air pollution relative to their GDP.
- These losses range from 0.67% to 2.15%, with states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh that have lower per-capita GDPs showing the worst effects.
Economic Costs of Air Pollution:
- According to a study conducted by Dalberg Advisors in collaboration with the Clean Air Fund, Blue Sky Analytics, and the Confederation of Indian Industry, air pollution costs Indian companies nearly $95 billion a year, or roughly 3% of the country’s GDP.
- The economic consequences are illustrated by anecdotal data gathered from different parts of India, such as decreased footfall in shopping centers and decreasing productivity in IT clusters and the solar industry.
Poor air quality has six main consequences:
- higher health expenditures,
- welfare losses,
- early mortality,
- decreased consumer footfall,
- decreased asset productivity, and
- poorer labor productivity.
Challenges for India:
- India’s reliance on outdoor labor-intensive industries like construction, agriculture, delivery services, and security agency employment makes managing air pollution difficult.
- But even indoor jobs like working in call centers can be negatively impacted by air pollution in terms of productivity.
Case Study
- A January 2019 study that looked at the daily output of Chinese call center employees discovered that low air quality affected worker productivity.
- Employee productivity decreased by 0.35% for every ten units increase in the air pollution index.
- This resulted in longer break durations for both highly and less productive workers.
International Rankings:
- More than 20 of the top 30 most polluted cities in the world are in India, with Delhi having the worst air quality in the world.
- Significant economic losses have resulted from this across the nation, especially when it comes to the per-capita economic losses brought on by pollution in India’s largest cities.
Conclusion:
- There is mounting evidence that air pollution has a direct and significant influence on GDP, productivity, health, and general economic well-being, challenging the widely held belief that it is an unavoidable byproduct of economic progress.
- For nations like India, addressing air pollution is becoming more and more important, with serious economic ramifications.
8. Fixing Mumbai’s air: A PRESCRIPTION
Topic: GS3- Environment
Context:
- From October 1 to October 30, there were 66 instances of poor air quality in 16 different locations in Mumbai.
- Mumbai’s air quality frequently declined to the extent that it exceeded Delhi’s.
There are multiple reasons that lead to Mumbai’s air pollution problem:
Geographical Advantage and Climate Change:
- Mumbai benefits from strong breezes that remove airborne pollution because of its coastal location.
- However, the pattern of wind reversal, which typically happens every 3–4 days, is taking longer than usual due to a shift in meteorological circumstances.
- This delay adds to the bad air quality in the city together with the weakened winds.
Construction and Urbanization:
- October’s unusually warm weather caused winds to blow dust into the city from large construction sites in Navi Mumbai and the neighboring areas.
- Mumbai has experienced a sharp increase in building activity over the past three years, which has resulted in massive dust displacement.
- This, combined with the city’s generally warm climate, prolongs the duration of dust particles trapped in the lower atmosphere.
- The issue is further made worse by refineries, industries, and the burning of trash.
- Experts do think that after these construction projects are over, the quality of the air should improve.
Steps that should be taken
Government and Civic Actions:
- The government and local authorities in Mumbai should first step-up air quality monitoring in order to address the air pollution situation.
- Although there are now 21 monitoring stations in the city, experts advise a larger network.
- Furthermore, installing sensor-based monitoring systems to provide hyperlocal data might help identify the sources of pollution.
- For more efficient preventive measures, these programs ought to be included into the current command and control framework.
Regional Cooperation
- Like Delhi, Mumbai ought to think about setting up an air quality management commission.
- The quality of air in Mumbai can be greatly affected by pollution in nearby areas such as Thane, Navi Mumbai, and Bhiwandi.
- Effective management of these difficulties could be aided by the establishment of an independent commission with the power to act beyond national boundaries.
Capacity Building and Academic Involvement:
- To develop long-term solutions, the government should invest in skilled labor, such as engineers, scientists, medical professionals, and legal advisors, in addition to updating the technical infrastructure.
- In order to effectively tackle air pollution, academic institutions should take a more active role in research and implementation.
Emissions-Based Policies:
- In order to develop and implement laws pertaining to vehicle pollution, particularly in regions with heavy traffic, Mumbai should carry out an emissions-based analysis.
- These laws need to be strictly enforced and addressed in order to relieve traffic congestion.
Citizen Engagement:
- People can help by walking and riding bicycles, which reduce vehicle pollution.
- The government ought to incentivize the populace to transition to more environmentally friendly energy sources, such as natural gas pipes, and include them in the reporting of instances of pollution and unpermitted development.
Learning from Other Cities:
- Mumbai may benefit from the knowledge that cities like Delhi and London have gained by establishing comprehensive networks for monitoring air quality and involving academic institutions in ongoing research.
- For example, private automobiles are prohibited in well-connected neighborhoods that are reachable by public transportation in London.
- Mumbai may explore taking similar actions, particularly in light of the Metro network’s development.
Way Forward:
- A multifaceted strategy is needed to address Mumbai’s air pollution problem, including extensive monitoring, policy creation, regional cooperation, capacity building, citizen participation, and learning from other cities’ experiences.
- Mumbai can only hope to adequately address its air quality issues by combining these initiatives.
9. India’s forex reserves rise by $ 2.57 bn
Topic: GS3- Economy
Context:
- In spite of international investors pulling out of the Indian market, India’s foreign exchange reserves increased by $2.579 billion to $586.111 billion.
- This milestone was revealed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), demonstrating the strength of the nation’s foreign exchange reserves.
Maturity of $5 Billion Dollar-Rupee Swap:
- The maturity of a sizable financial operation that the RBI has been conducting is responsible for the increase in foreign exchange reserves.
- A $5 billion dollar-rupee swap, consisting of the selling of dollars and the purchase of rupees, was carried out by the RBI the year before.
- The trade was reversed on October 23, the day this swap came to maturity.
Smooth Delivery to RBI:
- Indian banks successfully and without difficulty transferred the entire $5 billion forex swap to the RBI when it matured.
- The entire $5 billion was moved from the banking system to the account of the RBI very quickly.
- A treasury official from a public sector bank stated that this operation, which was part of a contract started by the RBI in cooperation with numerous banks around a year and a half ago, finished without any problems.
10. Why Pakistan is forcing lakhs of Afghan migrants to leave
Topic: GS2-IR
Context:
- Pakistan’s borders with Afghanistan saw long lines of trucks and a desperate trudge over the crossing as Islamabad ordered undocumented migrants to leave the country.
Details:
- While the order is meant for all foreigners, the main brunt is being borne by Afghans, who make up the biggest group of refugees in Pakistan.
- The government had given illegal migrants the deadline of October 31 to leave, following which they would face arrest and expulsion.
- Hours before the deadline, it began rounding up those without documents. Homes of some were razed, in order to make them leave.
- Over 4 million Afghans live in Pakistan, and the government estimates 1.7 million of these are undocumented.
Why is Pakistan deporting Afghan migrants?
- The government has stuck to its decision to deport them despite appeals from the United Nations, rights groups and Western embassies.
- Those being forced to return face an uncertain future, with Afghanistan struggling under the weight of a collapsed economy, devastating earthquakes, food insecurity, and human rights violations under the Taliban regime. Women and girls who return will not be allowed education or jobs.
- Many of the migrants fled Afghanistan in the 1970s during the Soviet war, and have little ties to, or opportunities in, their home country. Many were born in Pakistan. Also, many have not been able to secure documents simply because of the long process of getting one issued.
- Pakistan, however, maintains that it has the right to look after its own economic affairs and security. Pakistan’s economy is in dire straits, and it says undocumented migrants who pay no taxes are a drain on its scarce resources.
- More importantly, the Pakistan government has accused Afghan migrants of involvement in terror attacks, street crimes, and organised crimes such as drug trafficking. Pakistani authorities said Afghan nationals were found to be involved in attacks against the government and the army, including 14 of this year’s 24 suicide bombings.
- A particular risk upon returning will be those who had worked for the US before the Taliban takeover of Afghanistan. Many of them had moved to Pakistan to eventually secure a passage to the US.
- According to NPR, Washington has asked Islamabad “to ensure the protection of Afghan refugees and asylum seekers, including those in the US resettlement and immigration pipelines.”
Why take the decision now?
- The desperate condition of Pakistan’s economy and the terror attacks by Tehreek-e-Taliban Pakistan are triggers. But another important factor is that Pakistan at present is under a caretaker government, which is managing affairs till General Elections in February. This government is, thus, insulated from the potential political or electoral fallout of the expulsions.
- The deportation order has been met with some criticism in Pakistan. A few politicians and rights activists filed a petition with the Supreme Court challenging the “mass deportation”.
Conclusion
- This deportation is a contentious move driven by economic and security concerns.
- The international community, including the Taliban, is grappling with the challenges posed by this situation, particularly as winter approaches and Afghanistan faces additional hardships.
11. Work starts on shaping first national security strategy, long wait ends
Topic: GS3- Security Issues
Context:
- After years of deliberations inside military and strategic circles, India is taking a major step toward developing its first National Security Strategy.
- Leading the charge in developing this all-encompassing plan is the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS), working in tandem with other Central ministries and departments.
- Upon completion and Cabinet approval, the plan will become the first official national security strategy of India.
- India’s national security goals and the tactics needed to attain them are to be outlined in this project.
What is National Security Strategy?
- A nation’s National Security Strategy or Policy (NSS or NSP) provides a crucial framework for addressing both internal and foreign threats to the nation while also addressing the security concerns and fundamental needs of its population.
- A clear idea of the direction India should go in order to achieve its national goal is contained in a well-defined national strategy. It also offers guidelines on policy directions that all state organs must adhere to.
Need for National Security Strategy
-
A modern state faces numerous, concurrent problems in a number of areas.
- The concept of national security cannot be limited to the state’s use of force to counter dangers from both within and without. For instance, social and economic grievances may pose a threat to domestic peace and stability.
- Reacting hastily could result in these complaints going unanswered, and using force makes matters worse rather than better. For example, the ongoing exploitation of tribal tribes is the source of left-wing radicalism in India.
- Similar to this, there is a large-scale smuggling and contraband trade that is connected to the vulnerability of our borders. It is not possible to counter such threats only with increased military might without also addressing the factors that encourage illegal trade.
- The distinction between domestic and external affairs is getting more hazy for a contemporary state functioning in a globalized environment. For instance, terrorism poses a risk to national security even though it may have connections elsewhere. Therefore, it could be required to combine internal and external therapies.
- Such intricate interrelationships between domestic and external aspects can only be analyzed and coordinated policy responses established within the framework of a comprehensive NSS.
Way Forward:
- A major step forward has been taken with the creation of India’s first national security strategy, which attempts to address a wide variety of security issues, both conventional and unconventional.
- This plan will offer a thorough framework for defending India’s interests in national security and will be updated on a regular basis to take into account shifting conditions and new threats.
For Enquiry

4 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs

4 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

3 nov 2023 : Daily Quiz

3 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing

3 Nov 2023 : Indian Express

3 Nov 2023 : PIB

3 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs

3 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

2 nov 2023 : Daily Quiz

2 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing
Daily Current Affairs 4 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
4-November-2023
1. Difficult to press for women’s quota before LS poll: SC
Topic:…
November 2023 The Hindu 4 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
4-November-2023
1. The IITs are overcommitted, in crisis
Topic: GS3 – education…
Daily Quiz 3 nov 2023 : Daily Quiz 3 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 3 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
3-November-2023
Q1) Resorting to ordinances has always raised concerns about the…
Indian Express 3 Nov 2023 : Indian Express Indian Express
3-November-2023
1) Clearing the Dust, lifting the Haze
Context:
Mumbai’s air…
November 2023 PIB 3 Nov 2023 : PIB PRESS INFORMATION BUREAU
3-November -2023
1. Vice President calls Company Secretaries as ‘custodians…
Daily Current Affairs 3 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
3-November-2023
1. SC seeks data on donations through electoral bonds, reserves…
November 2023 The Hindu 3 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
3-November-2023
1. Biosphere reserves are evolving as pockets of hope.
Topic:…
Daily Quiz 2 nov 2023 : Daily Quiz 2 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 2 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
2-November-2023
1. How has judicial activism in India contributed to the protection…






