5 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
5-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Govt. to record parents’ religion to register births
| Topic: GS2 – Governance.
Understanding birth registration reforms is crucial for UPSC to grasp administrative and demographic changes, and civil registration system functions. |
| Context |
| ● The news pertains to the Union Ministry of Home Affairs’ mandate requiring separate recording of parents’ religion in birth registrations, to be adopted by State governments. |
Additional information on this news:
- Union Ministry of Home Affairs mandates recording parents’ religion separately in birth registrations, to be adopted by State governments.
- The “Form No.1-Birth Report” expands to include religion of the child, father, and mother.
- Birth and death database to update various national databases, including National Population Register, electoral rolls, Aadhaar, ration card, etc.
- Digital birth certificates to serve as proof for services like educational admissions.
- Proposed amendments include recording Aadhaar numbers, mobile, and email IDs of parents.
- RGI maintains a national database of registered births and deaths, coordinated by Chief Registrars appointed by State governments.
- CRS data used for compiling vital statistics reports aiding socio-economic planning and evaluating social programs.
| Rationale behind this government decision: |
| Advantages:
●Enhanced Data Collection: Separate recording of parents’ religion provides more comprehensive demographic data, aiding in policy formulation and socio-economic planning. ● Religious Data Analysis: Allows for analysis of religious demographics at the individual, family, and community levels, facilitating targeted interventions and resource allocation. ● Identity Documentation: Provides individuals with official documentation reflecting their religious background, potentially impacting access to religious or community-specific services. Challenges: ●Potential for Discrimination: Raises concerns about potential discrimination based on religious identity, particularly if this information is misused or improperly handled. ● Socio-Political Ramifications: Could influence electoral dynamics, community relations, and identity politics, potentially affecting social cohesion and harmony. ● Legal and Administrative Challenges: Implementation may face logistical challenges and legal complexities, including privacy concerns and data protection regulations. ● Policy Adaptation: May necessitate adjustments in existing administrative procedures, including birth registration protocols, database management, and information sharing mechanisms. ● Public Perception and Reaction: Public acceptance and perception of this decision could vary, impacting its implementation and effectiveness in different regions and communities. |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the Union Ministry of Home Affairs’ mandate regarding separate recording of parents’ religion in birth registrations. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. No sanctions against India for buying, refining Russian oil, say U.S. officials
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations.
Understanding India’s approach to oil purchases amid geopolitical tensions is crucial for UPSC’s international relations and economic aspects. |
| Context |
| ● The news pertains to discussions between U.S. Treasury officials and Indian counterparts regarding limitations on revenue to Russia without halting trade in Russian oil. |
Additional information on this news:
- S. Treasury officials visited Delhi to discuss limitations on revenue to Russia, rather than limiting trade in Russian oil.
- Their aim is to impose sanctions that impact the Kremlin’s revenue streams.
- They clarified that once Russian oil is refined in a country, it is no longer considered Russian for sanctions purposes.
- Indian companies have not faced sanctions from the U.S. for their oil purchases from Russia.
- The Indian External Affairs Ministry emphasised that oil purchases are guided solely by India’s energy security needs and commercial interests.
- India and China emerged as major purchasers of Russian oil since the conflict in Ukraine began.
- Russian President Putin praised India’s independent foreign policy despite Western pressure to reduce ties with Moscow.
- The U.S. announced a price cap on Ural oil, resulting in heavy discounts offered by Russian exporters to buyers.
- Moscow asserted that Russian oil supplies to India have remained consistently high, despite U.S. measures.
- Reports indicate that Indian buyers faced challenges with payments for oil in other currencies and rejected tankers from sanctioned Russian shipping companies.
- Indian-Russian economic ties, including significant investments in India by Russian companies, remain substantial despite geopolitical tensions.
| India’s oil procurement strategy amidst geopolitical tensions: |
| ● Diversification of Sources: India has diversified its sources of oil procurement to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions. It has reduced dependency on a single supplier, particularly from volatile regions.
●Focus on Strategic Partnerships: India has cultivated strategic partnerships with oil-producing nations such as Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Russia, ensuring a stable supply of crude oil even amidst geopolitical tensions. These partnerships are aimed at ensuring long-term energy security. ●Exploration of Alternatives: India has been exploring alternative sources of energy, including renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and minimize vulnerability to geopolitical disruptions in oil supply. ● Engagement in Diplomatic Efforts: India engages in diplomatic efforts to maintain stability in oil-producing regions and resolve conflicts that could disrupt oil supplies. It participates in international forums and maintains diplomatic relations to safeguard its energy interests. ●Investment in Infrastructure: India continues to invest in infrastructure for oil storage, refining capacity, and transportation networks to ensure smooth supply chains and minimize disruptions in oil procurement amidst geopolitical tensions. This includes the development of strategic petroleum reserves for emergency situations. |
| PYQ: It is said the India has substantial reserves of shale oil and gas, which can feed the needs of country for quarter century. However, tapping of the resources doesn’t appear to be high on the agenda. Discuss critically the availability and issues involved. (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2013) |
| Practice Question: Discuss India’s oil procurement strategy amidst geopolitical tensions and its implications for bilateral relations. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Next generation of medics to lead fightback against AMR
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – health.
This topic is crucial for UPSC as it relates to public health, policy-making, and global healthcare challenges. |
| Context |
| ● The news addresses the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in India and initiatives to combat it through education and medical stewardship. |
Additional information on this news:
- Antibiotics, discovered in the 1920s, revolutionized disease treatment, but overprescription and misuse have led to antimicrobial resistance (AMR), rendering antibiotics ineffective.
- Vijay Pal Singh et al.’s paper highlights India’s AMR burden factors: high infectious disease prevalence, lax infection control, easy antibiotic access, limited surveillance, and awareness.
- The AMR Declaration Trust and Rotaract Medicrew collaborate to address AMR.
- They aim to integrate stewardship into medical education and practice to combat resistance effectively.
- Their initiative, ‘Prescriber Today, Steward Tomorrow’, educates medical students on AMR, promoting responsible antibiotic use.
- The project aims to embed antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) principles into medical training, fostering rational antibiotic use.
- Through comprehensive training, it seeks to empower future medical professionals to combat AMR effectively.
- This collaboration sets a benchmark for AMR education, emphasizing its importance in healthcare practice and community awareness.
| What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): |
| Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR):
● Definition: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) refers to the ability of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, to evolve and withstand the effects of antimicrobial drugs, rendering them ineffective in treating infections. Impact of AMR: ● Global Health Crisis: AMR poses a significant threat to public health worldwide, as it undermines the effectiveness of commonly used antibiotics, leading to prolonged illness, increased mortality rates, and higher healthcare costs. ● Increased Morbidity and Mortality: AMR results in the failure of antimicrobial treatments, leading to prolonged illnesses, increased severity of infections, and higher mortality rates, especially among vulnerable populations. ●Economic Burden: AMR contributes to a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems, as the need for alternative, more expensive treatments increases, along with longer hospital stays and additional medical interventions. ● Challenges in Disease Control: AMR complicates disease control efforts, making it harder to contain infectious diseases and outbreaks, leading to potential public health emergencies. Way Forward: ● Enhanced Surveillance: Implement robust surveillance systems to monitor antimicrobial resistance patterns and trends, enabling timely interventions and treatment adjustments. ● Promotion of Antimicrobial Stewardship: Encourage the prudent use of antimicrobials through education, guidelines, and policies aimed at minimizing unnecessary prescription and misuse. ● Investment in Research and Development: Allocate resources towards the development of new antimicrobial drugs, diagnostics, and alternative treatment strategies to combat emerging resistant pathogens. ● International Collaboration: Foster collaboration among countries, healthcare sectors, and stakeholders to address AMR comprehensively, sharing best practices, resources, and knowledge. ●Public Awareness and Education: Raise awareness among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the general public about the threat of AMR and the importance of responsible antimicrobial use. ●One Health Approach: Adopt a One Health approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health in addressing AMR, promoting holistic interventions across sectors. ● Regulatory Measures: Implement and enforce regulations to restrict the over-the-counter sale of antimicrobials, strengthen prescription guidelines, and promote adherence to antimicrobial stewardship principles. ● Capacity Building: Build capacity in healthcare systems, including training healthcare professionals, improving laboratory infrastructure, and enhancing infection prevention and control measures. |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) on public health management and strategies to address it effectively. (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. On global indices measuring democracy
| Topic: GS2 – Governance.
Important for UPSC as it reflects on India’s democratic health, international relations, and credibility on global platforms. |
| Context |
| ● The news discusses India’s response to international democracy indices, highlighting plans to release its own index to counter negative assessments. |
Introduction:
- India’s democratic standing has faced criticism from various global indices, prompting the government to plan the release of its own democracy index to counteract negative ratings and criticisms.
Why India Cares About a Democracy Index:
- Indices like V-Dem and Freedom House indicate threats to India’s democracy, affecting its sovereign ratings and rankings on international governance indicators.
- India has denounced global assessments, calling the index makers “self-appointed custodians” with flawed methodologies and cultural biases.
- Foreign Minister S. Jaishankar argues that India performs comparably to other democracies but is unfairly ranked alongside less democratic nations.
Data Used by Indices:
- Indices use various data types: observational data, ‘in-house’ coding, expert surveys, and representative surveys.
- The UN High Commissioner for Human Rights advocates for objective data, but some argue for expert judgments to capture governance realities.
- Each index assesses democracy health differently, evaluating factors like electoral participation, participation, decision-making processes, and egalitarianism.
Limitations of Indices:
- Subjectivity undermines index credibility, as evaluations rely on researchers’ judgments rather than objective characteristics.
- Scope limitations exist, with some indices excluding non-independent and microstates, potentially overlooking smaller countries.
- Ideological discrepancies arise due to democracy’s ambiguous definition, leading to instances where less democratic countries receive higher scores.
Conclusion:
- Despite limitations, democracy indices offer valuable insights into global democracy trends, allowing for comparisons across time and geography.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of international democracy indices and India’s response to them in shaping global perceptions and policies. (150 Words /10 marks) |
War in Ukraine, possible return of Trump trouble NATO as it turns 75
| Topic: GS2 – International relations – Important International institutions, agencies and fora – their structure, mandate.
This news is significant for UPSC as it highlights NATO’s response to geopolitical challenges and implications for global security. |
| Context |
| ● The news discusses NATO’s response to Russian aggression and concerns over the potential return of Donald Trump to power, emphasizing unity and support for Ukraine. |
NATO’s Response to Russian Aggression and Trump’s Influence:
- NATO chief Jens Stoltenberg urged the U.S. to stand united with Europe amidst Russian aggression and the potential return of Donald Trump to power.
- The Kremlin’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022 revitalized NATO, prompting increased focus on countering Russia’s threats.
NATO’s Growth and Concerns:
- NATO has expanded to 32 members, including Finland and Sweden, bolstering forces in eastern Europe.
- While NATO is re-focused on countering Moscow, concerns also arise from potential threats posed by the U.S., particularly under Trump’s leadership.
Stoltenberg’s Call for Unity:
- Stoltenberg emphasised the importance of U.S.-Europe unity in NATO for collective strength and security.
- Increased defence spending by European allies aims to address criticisms from Trump, showcasing commitment to NATO’s goals.
Challenges in Supporting Ukraine:
- NATO supports Ukraine in its resistance against Russia, but crucial U.S. support remains blocked amidst political disputes.
- Ukraine seeks additional Patriot defense systems to counter Russian attacks and prevent further losses.
NATO’s Proposal and Concerns:
- Stoltenberg proposed a 100-billion-euro fund over five years to support Ukraine and enhance NATO’s involvement in coordinating deliveries.
- Concerns exist over the potential escalation of conflict with Russia and the financial implications of the proposal.
Future Preparedness and Concerns:
- NATO allies fear potential future conflicts with Russia and stress the importance of preparedness.
- There are concerns over the alliance’s readiness and coordination in facing future challenges, particularly in the context of Trump’s possible return to power.
Conclusion:
- NATO faces complex challenges from both Russian aggression and internal divisions, compounded by uncertainties surrounding the U.S. political landscape.
- The proposed initiatives aim to strengthen NATO’s response capabilities while addressing the immediate needs of Ukraine.
- However, concerns persist regarding the feasibility and implications of these measures, highlighting the ongoing complexities in navigating geopolitical tensions and ensuring collective security in the Euro-Atlantic region.
| More about NATO: |
| ● NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is an intergovernmental military alliance of 32 member countries.
● Founded in 1949, NATO’s primary purpose is to guarantee the freedom and security of its members through collective defence. ● The organisation is based on the North Atlantic Treaty, which was signed on April 4, 1949. ● NATO’s headquarters is located in Brussels, Belgium. ● Its core principle is Article 5, which states that an attack on one member is considered an attack on all, triggering a collective response. ● NATO’s missions include collective defence, crisis management, cooperative security, and partnership building. ●It has conducted numerous military operations, including peacekeeping and counterterrorism missions. ● The organisation underwent significant expansion after the end of the Cold War, admitting former Eastern Bloc countries. ● NATO engages in partnerships with non-member countries and international organisations to promote stability and security. ● The alliance faces challenges such as cyber threats, terrorism, and geopolitical tensions with Russia and China. |
| PYQ: The expansion and strengthening of NATO and a stronger US-Europe strategic partnership works well for India.” What is your opinion about this statement? Give reasons and examples to support your answer. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss NATO’s response to Russian aggression and challenges posed by potential shifts in U.S. leadership dynamics. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. Prostate Cancer Cases Surge in India: Urgent Action Needed to Address Rising Incidence
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the analysis offers insights into the rising incidence of prostate cancer in India, highlighting the challenges and opportunities for addressing this public health issue. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Global Trends and Projections:
- Globally, prostate cancer cases are projected to rise substantially, with low and middle-income countries expected to witness the highest increase.
- This underscores the importance of international collaboration and concerted efforts to address the growing burden of prostate cancer worldwide.
- The Lancet Commission report highlights the significance of early detection and education programs in saving lives and mitigating the impact of the disease.
Factors Contributing to Rising Cases:
- Several factors contribute to the rising incidence of prostate cancer in India.
- Aging populations, increasing life expectancy, and the widespread adoption of corporate health checkups incorporating prostrate specific antigen (PSA) tests are identified as key contributors.
- Moreover, lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, and poor dietary habits exacerbate the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Early awareness and detection are crucial in tackling the disease effectively.
Importance of Early Screening and Detection:
- Prostate cancer often presents no symptoms in its early stages, making early screening imperative for timely intervention.
- Doctors stresses the importance of PSA tests for men above 60 years, as well as those experiencing symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine stream, or blood in urine.
- Simple and inexpensive screening methods, such as digital rectal examinations, can aid in early detection, facilitating prompt treatment and improved outcomes.
Challenges in Access to Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Despite advancements in radiotherapy and palliative care, challenges persist in ensuring equitable access to diagnosis and treatment, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
- The shortage of radiotherapy units, limited coverage within government health schemes, and regulatory barriers to opioid use for pain relief pose significant hurdles in addressing the burden of prostate cancer effectively.
- Concerted efforts are needed to bridge these gaps and ensure access to comprehensive care for all patients.
Conclusion:
- The rising incidence of prostate cancer in India poses a significant public health challenge that demands urgent attention.
- Proactive measures, including widespread screening, early detection, and improved access to diagnosis and treatment, are essential in mitigating the impact of the disease and reducing mortality rates.
- Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities are imperative to address the multifaceted challenges associated with prostate cancer and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
| Prostate Cancer |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges and opportunities presented by the rising incidence of prostate cancer in India. How can proactive public health policies and collaborative efforts between stakeholders mitigate the impact of prostate cancer and improve outcomes for affected individuals? (250 words/15 m) |
7. Unveiling the Mysteries of the Universe: DESI’s Three-Dimensional Map Offers Clues to Dark Energy
| Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology – Achievements of Indian S&T
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as this analysis offers insights into the groundbreaking research conducted by the international team of researchers using the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) to map the universe. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
DESI: A Revolutionary Instrument:
- DESI, a sophisticated instrument mounted atop the Mayall 4-Meter Telescope in Arizona, United States, has the remarkable capability to capture light from 5,000 galaxies simultaneously.
- Through DESI, researchers have successfully measured light from six million galaxies, spanning distances as far back as 11 billion years ago.
- This unprecedented achievement has enabled scientists to construct an intricate map of the universe, providing precise information about the spatial distribution of galaxies and their distances from each other.
Unraveling the Mystery of Dark Energy:
- One of the primary objectives of DESI’s observations is to shed light on the enigmatic nature of dark energy, which constitutes nearly 70 percent of the universe’s composition.
- The hypothesis of dark energy stems from observations indicating the universe’s accelerating expansion, contradicting gravitational forces that tend to pull celestial objects together.
- Understanding dark energy is crucial as it holds profound implications for our comprehension of the universe’s origin, evolution, and ultimate fate.
Significance of Expansion Rate Measurements:
- The data obtained from DESI’s observations offers tantalizing clues into the behavior of dark energy.
- Notably, DESI has measured the expansion rate of the universe with unprecedented precision, revealing an acceleration rate of 68.5 kilometers per second after every 3.26 million light years of distance.
- This precise measurement holds immense scientific significance, potentially providing crucial insights into the underlying mechanisms driving the universe’s expansion and the role of dark energy therein.
Implications and Future Prospects:
- Despite being in its early stages, the data from DESI has already sparked excitement among researchers, with indications of potential new physics awaiting further exploration.
- With DESI scheduled to continue observations for five years, scientists anticipate further revelations that could revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos.
- The collaborative efforts of over 900 researchers worldwide, including the pioneering contributions from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in India, underscore the global significance of initiatives such as DESI in advancing our knowledge of the universe.
Conclusion:
- The unveiling of the detailed three-dimensional map of the universe by DESI represents a significant milestone in cosmology.
- By providing unprecedented insights into the spatial distribution of galaxies and the dynamics of cosmic expansion, DESI holds immense potential in unraveling the mysteries of dark energy and advancing our understanding of the cosmos.
- As scientists continue to analyze the wealth of data collected by DESI, the prospects of unlocking the secrets of the universe loom ever closer, offering glimpses into the fundamental nature of reality itself.
| What is Dark Energy? |
|
| PYQ: Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidence for the continued expansion of the universe? (2012)
1) Detection of microwaves in space 2) Observation of redshift phenomenon in space 3) Movement of asteroids in space 4) Occurrence of supernova explosions in space Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) None of the above can be cited as evidence Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent unveiling of the most comprehensive three-dimensional map of the universe by the international team of researchers using the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI). Analyze the potential implications of this groundbreaking research for our understanding of dark energy and the expansion of the universe. (250 words/15 m) |
8. India Successfully Tests New-Generation Nuclear-Capable Agni Prime Missile, Bolsters Strategic Deterrence
Topic: Important topic for Prelims
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Test Validation and Objectives Met:
- According to the defense ministry, the test-flight of Agni Prime, successfully met all trial objectives.
- The missile’s performance was deemed reliable, as confirmed by data captured from a network of range sensors deployed at various locations.
- This validation underscores the efficacy and readiness of India’s indigenous missile technology.
Strategic Significance of Agni Prime:
- Agni Prime, developed jointly by the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), boasts a striking range of 1,000 to 2,000 kilometers.
- This extended range enhances India’s deterrence capabilities, enabling it to effectively counter emerging threats and safeguard its national security interests.
Conclusion:
- The successful night launch of Agni Prime represents a significant milestone in India’s missile technology development.
- The validation of its performance and the strategic significance it holds underscore India’s commitment to enhancing its deterrence capabilities.
- With Agni Prime poised to serve as a force multiplier for the military, India strengthens its position as a formidable player in the realm of national defense and security.
| What are the Other Agni Class of Missiles? |
|
| PYQ: With reference to Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
1) It is a surface-to-surface missile. 2) It is fuelled by liquid propellant only. 3) It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
9. Indian Army Initiates Induction of Advanced Control and Reporting Systems for Enhanced Air Defense Capabilities under Project Akashteer
| Topic: Important topic for Prelims |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Flagging off of Control Centres:
- The deployment of the Akashteer systems began with the flagging off of the first batch of Control Centres from Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) in Ghaziabad.
- Developed by BEL, these Control Centres are equipped with state-of-the-art technology aimed at automating air defense control and reporting processes, thereby streamlining operations and enhancing responsiveness.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
- Project Akashteer represents a cutting-edge initiative designed to digitize and automate air defense control and reporting processes comprehensively.
- By embracing advanced technology, the Indian Army seeks to achieve higher levels of operational efficiency, situational awareness, and responsiveness in dealing with air threats.
Year of Tech Absorption: Meeting Future Requirements:
- With the year 2024 designated as the ‘Year of Tech Absorption,’ the induction of Akashteer Control Centres aligns with the Army’s vision to embrace technological advancements in defense operations.
- These Control Centres are poised to meet both current and future requirements of complex air defense operations, ensuring readiness to counter evolving threats effectively.
Conclusion:
- The induction of control and reporting systems under Project Akashdeep marks a significant step forward in enhancing the Indian Army’s air defense capabilities.
- By leveraging cutting-edge technology and automation, these systems promise to streamline air defense operations, enhance situational awareness, and bolster responsiveness in countering aerial threats.
- As the Indian Army continues to modernize its defense infrastructure, initiatives like Project Akashteer play a crucial role in ensuring the nation’s security preparedness in the face of emerging challenges.
| Importance of the project: |
|
| PYQ: What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news? (2018)
(a) An Israeli radar system (b) India’s indigenous anti-missile programme (c) An American anti-missile system (d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea. Ans: (c) |
For Enquiry

5 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

5 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

5 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

5 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

5 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

5 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

4 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

4 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

4 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

4 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
Daily Quiz 5 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 5- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 5 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
5-April-2024
Q1) The relevance of diaspora as a tool to further the country’s national…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 5 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
5-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Govt. to record parents’ religion to register…
April 2024 PIB 5 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
5-April-2024
1. PRESIDENT OF INDIA LAUNCHES INDIA’S FIRST HOME-GROWN GENE THERAPY…
April 2024 The Hindu Editorial 5 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
5-April-2024
1. Universities must budge on college autonomy nudge
Topic: GS2…
April 2024 Indian Express 5 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
4-April-2024
1. The demographic window
Topic: GS1 – Society – Population…
mains answer writing 4 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
4-April-2024
Q1) Historical and cultural affinities between India and Nepal create…
Daily Quiz 4 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 4 April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 4 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
4-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Taiwan Rattled: Deadly Earthquake Strikes…
April 2024 PIB 4 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
4-April-2024
1. Union Health Ministry launches myCGHS iOS app
Topic: GS2 –…


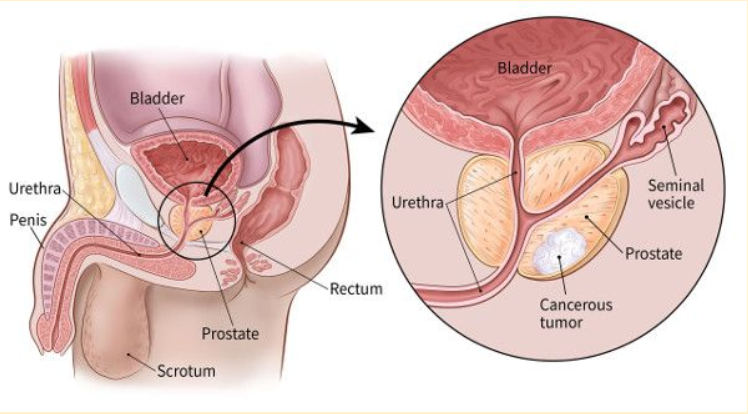 Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells, and can then spread to other areas of the body.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells, and can then spread to other areas of the body.

