6 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
6-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Bombay High Court Acquits G N Saibaba: Emphasizes Procedural Safeguards in Anti-Terror Trials
| Topic: GS2 – Polity – Judiciary This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about the functioning of India’s legal system, particularly regarding procedural requirements and due process under anti-terror laws. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Grounds for Acquittal: Procedural Safeguards and Due Process:
- A division bench of Justices Vinay G Joshi and Valmiki SA Menezes reversed the trial court’s conviction, emphasizing the necessity to adhere to procedural safeguards.
- The High Court’s decision followed directions from the Supreme Court, underscoring the significance of due process in safeguarding the rights of the accused.
- The appellate court evaluated the case afresh, scrutinizing the evidence and procedural irregularities that tainted the trial proceedings.
Importance of Procedural Safeguards: Judicial Observations:
- In its earlier ruling in 2022, a bench of the Bombay High Court had stressed the importance of procedural safeguards legislated to protect citizens’ rights, particularly in cases involving stringent anti-terror laws.
- The court observed that while combating terrorism is crucial, sacrificing procedural safeguards undermines the principles of civil democracy.
- The requirement for prior sanction from the central or state government, as mandated by Section 45 of the UAPA, was highlighted as a vital procedural safeguard to prevent misuse of anti-terror laws.
Challenges and Legal Wrangling: State’s Response:
- The state government’s attempt to challenge the Bombay High Court’s initial acquittal through urgent legal maneuvers, including seeking a stay from the Chief Justice of India and constituting a special bench, underscores the legal complexities and political sensitivities surrounding the case.
- However, subsequent directions from the Supreme Court to reconsider the case on its merits underscored the judiciary’s commitment to upholding due process and constitutional principles.
High Court’s Ruling on Subsequent Consideration: Invalid Sanctions and Jurisdictional Issues:
- In its latest ruling, the High Court reiterated the need for adherence to procedural safeguards, particularly regarding the validity of sanctions obtained for prosecution.
- The court found fundamental errors in the granting of sanctions, noting the absence of independent review and the timing of sanctions vis-à-vis the framing of charges.
- These procedural lapses were deemed fatal to the prosecution’s case, leading to the acquittal of the accused.
Conclusion:
- The Nagpur Bench’s acquittal of G N Saibaba and others underscores the judiciary’s commitment to upholding due process and procedural safeguards, even in cases involving serious charges under anti-terror laws.
- The ruling highlights the importance of adherence to legal standards and constitutional principles in safeguarding individual rights and ensuring justice.
- As such, the case serves as a critical reminder of the judiciary’s role in upholding the rule of law and protecting citizens’ rights in the face of perceived threats to national security.
| PYQ: The Indian government has recently strengthened the anti-terrorism laws by amending the unlawful activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), 1967 and the NIA Act. Analyze the changes in the context of prevailing security environment while discussing the scope and reasons for opposing the UAPA by human rights organizations. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2019) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the role of procedural safeguards and due process in upholding constitutional principles in cases involving stringent legal frameworks. How can such legal developments contribute to enhancing transparency, accountability, and fairness in India’s legal system? (250 words/15 m) |
2. India Elevates Naval Presence: Commissioning of INS Jatayu Enhances Security in Lakshadweep
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding developments in India’s defense infrastructure and naval capabilities. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Background and Significance of Lakshadweep Islands:
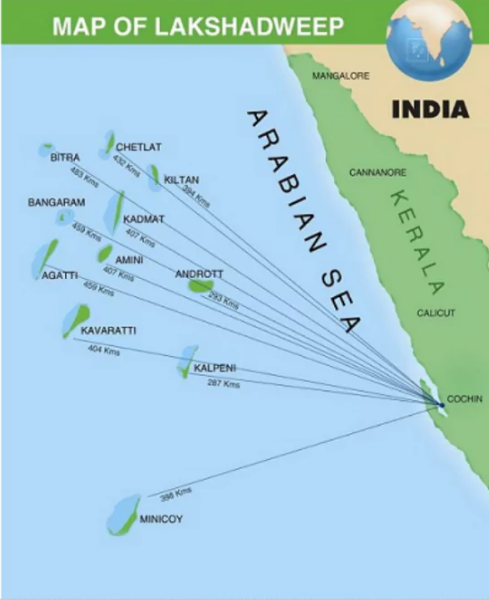
- Lakshadweep, an archipelago of 36 islands situated between 220km and 440km from Kochi, holds immense strategic importance due to its location in the Indian Ocean.
- Despite covering a total area of only 32 sq km, the islands straddle vital Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs), making them crucial for maritime navigation and security.
- Minicoy, in particular, is strategically positioned at key maritime highways, including the Eight Degree Channel and the Nine Degree Channel, further emphasizing the region’s significance.
Transformation of Naval Detachment to INS Jatayu:
- Naval Detachment Minicoy, which has been operational since the 1980s, will now be upgraded to INS Jatayu, effectively becoming the country’s second naval base in Lakshadweep.
- This transformation reflects India’s endeavor to strengthen its naval infrastructure and operational capabilities in the region, aligning with its broader strategic objectives and security priorities.
Infrastructure Development and Operational Enhancement:
- The commissioning of INS Jatayu signifies more than just a change in nomenclature; it represents a significant upgrade in infrastructure and resources.
- With additional facilities such as an airfield, housing, and personnel, INS Jatayu will serve as a vital asset for the Navy’s operations in the region.
- The establishment of this base is in line with the government’s focus on comprehensive development of the islands, emphasizing the holistic approach towards enhancing security and prosperity in the region.
Strategic Implications and Geopolitical Dynamics:
- The commissioning of INS Jatayu holds broader strategic implications, particularly in the context of India’s maritime security challenges and geopolitical dynamics in the Indian Ocean Region.
- The proposed airfield will not only enhance the Navy’s operational reach and surveillance capabilities but also serve as a deterrent against emerging threats, including piracy and narcotics trafficking.
- Additionally, it reinforces India’s strategic posture amidst growing Chinese influence in the region, underscoring the importance of maintaining maritime dominance and regional stability.
Conclusion:
- The commissioning of INS Jatayu as the second naval base in Lakshadweep marks a significant step towards enhancing India’s maritime security and strategic presence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- By bolstering infrastructure and operational capabilities, INS Jatayu reaffirms India’s commitment to safeguarding its maritime interests and upholding regional stability.
- As India navigates evolving geopolitical challenges, initiatives like INS Jatayu play a pivotal role in safeguarding national security and promoting peace and prosperity in the maritime domain.
| INS Jatayu Key Features |
| INS Jatayu, situated on the Minicoy islands within the Lakshadweep archipelago, is poised to become India’s strategic naval base, effectively serving as a stationary aircraft carrier in the expansive waters of the high seas. Here are the salient features of INS Jatayu:
INS Jatayu emerges as a pivotal asset, poised to bolster India’s maritime security architecture, project power across vital sea lanes, and fortify its capabilities as a proactive maritime force in the Indo-Pacific region. |
| PYQ: Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016) (a) Amphibious warfare ship (b) Nuclear-powered submarine (c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel (d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the commissioning of INS Jatayu in the Lakshadweep Islands for India’s maritime security and strategic interests. Evaluate the challenges and opportunities associated with enhancing naval presence in remote island territories and its impact on India’s defense preparedness and maritime dominance. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Milestone in Climate Monitoring: MethaneSAT Launched to Track Global Methane Emissions
| Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology GS3 – Environment This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about MethaneSAT’s advanced technology, including high-resolution sensors and AI-driven data analysis which highlights the intersection of science and technology in addressing environmental challenges. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Significance of Tracking Methane Emissions:
- Methane is the second most prevalent greenhouse gas after carbon dioxide and has a significant impact on climate change.
- Its atmospheric concentration has doubled over the past two centuries, contributing to approximately 30% of climate warming since the Industrial Revolution.
- Given its potency in trapping heat, reducing methane emissions is crucial in combating climate change and its adverse effects on the environment and public health.
Objectives and Purpose of MethaneSAT:
- MethaneSAT, developed by the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) in collaboration with Harvard University and other partners, aims to track methane emissions, particularly from fossil fuel operations, which account for a substantial portion of human-caused methane emissions.
- By providing real-time data on methane emissions, MethaneSAT seeks to identify sources of emissions, monitor changes over time, and enable stakeholders and regulators to take targeted actions to reduce emissions effectively.
Technical Features and Capabilities:
- MethaneSAT is equipped with advanced technology, including a high-resolution infrared sensor and spectrometer, allowing it to detect methane concentrations as low as three parts per billion in the atmosphere.
- This level of sensitivity enables the satellite to identify and track smaller emissions sources that may have previously gone undetected.
- Additionally, MethaneSAT’s wide-camera view enables it to identify larger emissions sources, known as “super emitters,” and track changes in emissions over time.
Addressing Challenges in Methane Emission Monitoring:
- Historically, tracking methane emissions and measuring their sources has been challenging due to limitations in satellite technology.
- Existing satellites often lack the resolution to detect smaller emissions sources accurately, leading to underreporting of global methane emissions.
- MethaneSAT addresses these challenges by offering high-resolution data and advanced monitoring capabilities, providing a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of methane emissions worldwide.
Data Analysis and Accessibility:
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be analyzed using cloud-computing and AI technology developed by Google, a mission partner.
- This data will be made publicly available through Google’s Earth Engine platform, enabling researchers, policymakers, and the public to access and utilize the information for informed decision-making and climate action.
- By promoting transparency and accessibility, MethaneSAT aims to catalyze efforts to reduce methane emissions and mitigate climate change on a global scale.
Conclusion:
- The launch of MethaneSAT represents a significant step forward in efforts to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane.
- By providing accurate, real-time data on methane emissions worldwide, MethaneSAT empowers stakeholders to take targeted actions to mitigate climate change and protect the environment and public health.
- As nations strive to meet their climate goals and transition towards a sustainable future, innovative initiatives like MethaneSAT play a crucial role in advancing climate action and fostering global cooperation in addressing the challenges of climate change.
| SOURCES OF METHANE EMISSIONS |
| Human activity: Around 60% of methane emissions are linked to human activity. Wetlands: While some 40% is from natural sources, mainly wetlands. Agriculture: Agriculture is the biggest culprit, responsible for roughly a quarter of emissions.
Energy sector: Coal, oil and gas is the second largest source of human caused methane emissions.
Household waste: Also releases large quantities of methane when it decomposes, if left to rot in landfills. |
| PYQ: Which of the following statements is/are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’? (2019) 1) Global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits. 2) Large deposits of ‘methane hydrate’ are found in Arctic Tundra and under the sea floor. 3) Methane in atmosphere oxidizes to carbon dioxide after a decade or two. Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of MethaneSAT in the context of global efforts to combat climate change and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Analyze the technological capabilities of MethaneSAT and its potential impact on monitoring methane emissions worldwide. (250 words/15 m) |
4. NOAA Warns of Impending Global Mass Coral Bleaching Event: Worst in History Looms
|
Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environment pollution and degradation This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about Coral reefs which are vital ecosystems, and their degradation due to coral bleaching has significant implications for biodiversity, climate regulation, and marine resources. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Global Coral Bleaching Risk:
- Experts coordinating NOAA’s Coral Reef Watch, suggests that the entirety of the Southern Hemisphere is likely to experience coral bleaching this year, indicating a severe global event that could be unprecedented in history.
Causes and Impact of Coral Bleaching:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals expel symbiotic algae living in their tissues due to heat stress.
- This process leaves corals pale and vulnerable to starvation and disease.
- The consequences extend beyond coral health, affecting ocean ecosystems, fisheries, and tourism-driven economies that rely on vibrant coral reefs to attract visitors.
Historical Context:
- The previous global mass coral bleaching events occurred in 2010 and 1998, with devastating effects on coral reefs worldwide.
- The Great Barrier Reef, in particular, suffered significant coral loss during the last event from 2014 to 2017, losing nearly a third of its corals.
Assessment Methods:
- Scientists rely on sea surface temperature data and satellite imagery to assess coral bleaching risk.
- By monitoring reef pixels and determining if they surpass critical thresholds of heat stress, researchers can identify regions experiencing widespread bleaching.
- For an event to be classified as a global mass bleaching, a certain percentage of reef pixels in each ocean basin must exhibit significant heat stress.
Implications and Concerns:
- The looming fourth mass coral bleaching event raises concerns about the long-term viability of coral reef ecosystems and the associated socio-economic impacts.
- Urgent action is needed to mitigate climate change and reduce stressors on coral reefs to safeguard these vital marine habitats for future generations.
| What are Coral reefs? |
What Causes Coral Bleaching?
|
|
PYQ: Consider the following statements: (2018) 1) Most of the world’s coral reefs are in tropical waters. 2) More than one-third of the world’s coral reefs are located in the territories of Australia, Indonesia and Philippines. 3) Coral reefs host far more number of animal phyla than those hosted by tropical rainforests. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the potential fourth mass coral bleaching event in the context of global environmental conservation efforts. Evaluate the role of climate change and ocean warming in triggering coral bleaching events and its implications for marine biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. (250 words/15 m) |
5. Centre Clarifies Advisory Scope on AI, Targets Significant Platforms, Not Start-up
|
Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about the nuances of government policies and the challenges of balancing innovation with regulatory oversight. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Advisory Content and Backlash:
- The advisory issued by the IT Ministry instructed generative AI companies like Google and OpenAI, as well as platform operators, to ensure that their services do not produce responses that violate Indian laws or jeopardize the integrity of the electoral process, especially with Lok Sabha elections looming.
- Platforms offering “under-testing/unreliable” AI systems or large language models to Indian users were required to seek explicit permission from the Centre and appropriately label the potential fallibility or unreliability of the output generated.
- However, this directive faced pushback from some start-ups in the generative AI sector, both domestically and abroad, who feared regulatory overreach and stifling innovation.
Government’s Messaging Intent:
- Following the clarification, it becomes evident that the advisory served more as a tool for political messaging than as a legally binding directive.
- It symbolized the government’s willingness to regulate and safeguard Indian internet users from potential risks associated with generative AI platforms.
- Despite unclear effectiveness or legal basis, the advisory conveyed the government’s stance on protecting users, although its practical implications remain uncertain.
Critique and Missing Acknowledgment:
- While criticism centered around the requirement for government approval before deploying untested AI services in India, the detractors failed to acknowledge the potential problems associated with such platforms.
- Few publicly acknowledged the regulatory challenges and the need for oversight, especially in a country as vast as India.
- The absence of a balanced discourse highlights the complexities inherent in policymaking in the AI sector, where tradeoffs between innovation and regulation must be carefully considered.
Call for Balanced Approach:
- In navigating the regulatory landscape for AI services, a balanced approach is necessary, requiring collaboration between lawmakers and companies.
- Striking a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring regulatory oversight is crucial for the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies.
- As policymakers and industry players navigate these challenges, finding common ground will be essential for effective regulation without stifling innovation.
| About Generative Artificial Intelligence |
How Does Generative AI Work?
Common Generative AI Applications
Role/Influence of GenAI on Elections in 2024
|
|
PYQ: With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020) 1) Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units 2) Create meaningful short stories and songs 3) Disease diagnosis 4) Text-to-Speech Conversion 5) Wireless transmission of electrical energy Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the recent advisory issued by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) regarding generative artificial intelligence (AI) services in India, and analyze its implications on technology regulation and governance. (250 words/15 m) |
6. Nearly 100 talukas are facing drinking water crisis: Karnataka CM
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation UPSC-relevant: Water crisis highlights drought impact, government response, and agricultural challenges, crucial for understanding regional governance and environmental issues. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Approximately 100 talukas in Karnataka are grappling with a severe drinking water crisis, prompting the deployment of water tankers for supply.
- Chief Minister Siddaramaiah conducted a videoconference to assess the situation, revealing that 98 out of 236 talukas are facing drinking water shortages due to drought.
- The State declared 223 talukas as drought-hit, affecting an estimated 7,408 villages and 1,115 urban local body wards with impending drinking water scarcity.
- Agreements have been made with private borewell owners to provide water to drought-affected villages and towns.
- Acknowledging extensive crop losses, the Chief Minister disclosed the disbursal of ₹631 crore to 33.25 lakh affected farmers.
| India’s water crisis |
Severity:
Reasons:
Way Forward:
|
| PYQ: Why is the world today confronted with a crisis of availability of and access to freshwater resources?(150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2023) |
| Practice Question: Critically examine the severity of the water crisis in India, highlighting its causes and suggesting potential solutions. (150 words/10 m) |
7. Indian troops out, Maldives inks defence pact with China
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral relations Critical for UPSC: India-Maldives strain impacts regional stability, maritime security, and underscores evolving geopolitical dynamics in the Indian Ocean. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Maldives signs a military pact with China after India replaces troops, fostering stronger bilateral ties and military cooperation.
- The agreement’s details are not disclosed, coinciding with elevated China-Maldives relations, marked by a comprehensive strategic cooperative partnership.
- China donates 12 ambulances to the Maldives, aligning with the enhanced partnership and commitment to economic and security collaborations.
- India compromises with the Maldives, withdrawing troops and replacing them with a technical team amid President Muizzu’s persistent calls for removal.
- Muizzu reassures Indian troops’ complete departure by May 10, responding to critics and dispelling concerns of soldiers returning in civilian attire.
- Bitter exchanges between India and the Maldives, with Minister Jaishankar’s comments and Muizzu emphasizing non-bullying and urging Chinese tourists.
- China becomes a significant player in Maldives tourism, accounting for 12.8% of visitors compared to India’s 6.4%, marking a new historical starting point in relations
| Deterioration of India – Maldives ties |
|
| PYQ: Discuss the political developments in Maldives in the last two years. Should they be of any cause of concern to India? (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2013) |
| Practice Question: Examine the geopolitical implications of the recent strain in India-Maldives relations and its potential impact on regional security and economic dynamics. (150 words/10 m) |
8. AI has a big and growing carbon footprint, but algorithms can help
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology Critical for UPSC: Examining AI’s carbon footprint, exploring energy-efficient solutions aligns with technology, environment, and global challenges. |
| Context |
|
Introduction:
- AI’s potential to address climate crisis contrasted with its contribution to environmental issues.
- Energy needs of AI models, exemplified by GPT-3, pose a significant challenge.
Emissions and Energy Consumption:
- GPT-3’s training emitted 502 metric tonnes of carbon, equivalent to driving 112 petrol cars for a year.
- Annual emissions from GPT-3’s inference stage amount to 8.4 tonnes of CO₂.
- Large language models’ energy requirements surged by a factor of 300,000 since the AI boom in the early 2010s.
Technological Approaches to Mitigate Carbon Footprint:
- Two promising technologies for reducing carbon footprint: Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) and Lifelong Learning (L2).
- ANNs, prevalent in current AI systems, become more energy-intensive as they grow in size and complexity.
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs):
- SNNs offer energy-efficient alternatives to ANNs by mimicking the brain’s intermittent electrical signals.
- Neurons in SNNs consume energy only during spikes, making them up to 280 times more energy-efficient than ANNs.
- Researchers are developing learning algorithms to enhance SNNs’ energy efficiency and decision-making speed.
- Potential applications of SNNs include space exploration, defense, and self-driving cars, where limited energy sources are crucial.
Lifelong Learning (L2):
- L2 aims to reduce overall energy requirements by enabling AI models to learn sequentially on multiple tasks without forgetting previous knowledge.
- Unlike sequential training in ANNs that leads to forgetting, L2 allows models to build on existing knowledge throughout their lifetime.
- Retraining ANNs from scratch when the operating environment changes contribute to increased AI-related emissions.
Future Solutions and Advancements:
- Building smaller AI models with equivalent predictive capabilities may reduce energy consumption.
- Quantum computing advancements hold potential for faster training and inference using both ANNs and SNNs.
- Quantum computing could offer superior computing capabilities, enabling energy-efficient solutions for AI at a larger scale.
Conclusion:
- Addressing the climate change challenge requires finding sustainable solutions for rapidly advancing AI technologies to prevent a significant carbon footprint.
| Practice Question: Discuss the environmental challenges posed by the energy consumption of large language models in AI and propose sustainable solutions. (150 words/10 m) |
9. Have India’s health centres really ‘collapsed’?
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health UPSC Significance: Examining India’s health centres is crucial for understanding public healthcare challenges, governance issues, and policy implications. |
| Context |
|
Introduction:
- Public health centres in India face a notorious reputation for dilapidation and inadequacy.
- However the news presents a nuanced view of health centres in five north Indian states.
Why Health Centres Matter:
- Health centres constitute the lowest tier of India’s public health system, offering accessible primary care.
- Despite being conceptualized as a three-tier system, less than 20% function effectively, pushing communities to expensive private healthcare.
- Economic Survey reveals nearly half of health spending is borne by patients, contributing to poverty.
Study Overview:
- Researchers studied 241 health centres across Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Rajasthan, comparing data from 2002 and 2013 to 2022.
Positive Trends and Case Studies:
- Positive trends noted include improved facilities, increased medicines, and wider service range.
- Himachal Pradesh serves as a “trailblazer,” while Chhattisgarh demonstrates radical expansion in public healthcare.
- Bihar lags behind, displaying dismal quality, highlighting regional disparities.
Factors Contributing to Change:
- Increased health expenditure in the Union Budget and the National Rural Health Mission.
- Ayushmann Bharat’s launch in 2018, incorporating health insurance and health and wellness centres.
- State-specific initiatives in Rajasthan and Chhattisgarh, and COVID-19 increasing public health facility trust.
Challenges and Flip Side:
- Progress remains modest with underutilized centres, high staff absenteeism, limited services, and likely poor quality.
- Neglected challenges include lack of staff, irregular funds, inadequate facilities, and social discrimination.
- Women’s crucial role in rural health settings acknowledged, advocating increased investment in frontline health workers.
Healthcare Budget Allocation Critique:
- Patchy improvements noted in healthcare budget allocation, prioritizing tertiary healthcare over primary care.
- Allocation trends questioned, emphasizing the need for major support to emulate successful initiatives.
Conclusion:
- Despite challenges, health centres offer hope, showcasing successful experiences in certain states.
- Call for substantial support beyond tokenism to facilitate the replication of successful initiatives in poorer states.
| PYQ: Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All ‘ in India. Explain. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the dynamics, challenges, and potential reforms in India’s public health centres, emphasizing governance, resource allocation, and policy interventions. (150 words/10 m) |
For Enquiry

6 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

6 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

6 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

6 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

5 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

4 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

5 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

5 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

5 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

5 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
March – The Hindu Editorial 6 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
6-March-2024
1. Green jobs and the problem of gender disparity
Topic: GS3 –…
March 2024 PIB 6 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
6-March -2024
1. India targets five-fold increase in its share of the global space…
Daily Current Affairs 6 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
6-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Bombay High Court Acquits G N Saibaba: Emphasizes…
Indian Express 6 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
6-March-2024
1. For the Gaya Lals of today
Topic: GS2 – Polity…
Daily Quiz 5 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 5 Mar 2024 : Daily Quiz…
Daily Quiz 4 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 4 Mar 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 5 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
5-March-2024
Q1) Examine the mandate and powers of the National Commission for…
Daily Current Affairs 5 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
5-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Supreme Court Challenges Parliamentary Privilege:…
Indian Express 5 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
5-March-2024
1. Let Pakistan be
Topic: GS2 – International Relations…
March 2024 PIB 5 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
5-March -2024
1. DefConnect 2024: Raksha Mantri launches ADITI scheme to promote…


