7 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
7-November-2023
1. Governors delaying crucial Bills a matter of concern, says SCf
Topic: GS2 – Indian polity.
Context:
- The Supreme Court expressed displeasure over Governors withholding key Bills, especially in non-BJP-ruled states like Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Telangana.
- The court criticized the practice of State governments having to approach the Supreme Court for judicial intervention to push forward these Bills.
More information on the news:
- Chief Justice of India D.Y. Chandrachud, leading a three-judge Bench, emphasized the need for Governors and Chief Ministers to resolve such matters without court intervention.
- The Chief Justice urged everyone, including Governors and Chief Ministers, to engage in self-reflection and emphasized that Governors are not elected by the people.
- The case in question involves a petition filed by the Punjab government, alleging that the Governor had delayed the approval of seven crucial Bills related to fiscal matters and state-affiliated colleges.
Impact of delaying the bills by State Governors:
- Delaying key bills by State Governors hampers the legislative process.
- It can lead to uncertainty and impede government initiatives.
- Delays may affect the functioning of state programs and policies.
- It can result in disputes and legal challenges, necessitating Supreme Court intervention.
- The delay may also hinder economic and social development within the state.
- Governors are appointed, not elected, and should consider the democratic process and constitutional roles.
Question: Critically examine the impact of delaying bills by State Governors on the functioning of the state government and the lives of its citizens. Suggest measures to ensure timely assent to bills passed by the legislature.
2. Bengaluru to get exclusive rapid response team to capture leopards
Topic: GS3 – environment and ecology
Context:
- Karnataka’s Forest and Environment Minister, Eshwar Khandre, has directed the Forest Department to establish a dedicated rapid response leopard task force for Bengaluru city.
- The directive follows repeated leopard sightings in residential areas of Bengaluru, driven by wild animals venturing into the city due to a lack of rainfall and food shortages.
Reasons for increasing man animal conflict:
- Competition for resources:As human populations grow and demand for resources increases, humans and wildlife are increasingly competing for food, water, and space. This can lead to animals raiding crops or livestock, and humans encroaching on wildlife habitats.
- Changing human behavior:Changes in human behavior, such as increased recreational activities in wildlife areas and the keeping of exotic pets, can also contribute to MAC. For example, feeding wildlife can make them more dependent on humans and less wary of them, increasing the risk of attacks.
- Climate change: Climate change is also exacerbating MAC. Extreme weather events such as droughts and floods can displace wildlife and make them more desperate for food and water, leading them to interact with humans more frequently.
Way Forward for Reducing Man-Animal Conflict:
- Habitat protection and restoration:Protecting and restoring wildlife habitats is essential to reduce MAC. This includes creating wildlife corridors to connect fragmented habitats, replanting forests, and establishing protected areas.
- Human-wildlife conflict mitigation measures:Implementing specific measures to reduce conflict between humans and wildlife can be very effective. For example, using fencing to protect crops and livestock, building barriers to prevent animal access to roads and settlements, and using deterrents such as sound or light devices can all help to reduce conflict.
- Education and awareness:Raising awareness among both humans and wildlife communities is crucial to reduce MAC. This includes educating people about wildlife behavior, the risks of feeding or approaching wild animals, and the importance of coexisting with wildlife.
- Community engagement:Involving local communities in MAC management is essential for long-term success. This includes empowering communities to identify and address conflict issues, providing them with resources and training, and incorporating local knowledge and traditional practices into conflict mitigation strategies.
- Research and monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring are needed to better understand the causes and patterns of MAC. This information can be used to develop more effective mitigation strategies and policies.
- Policy and legislation:Strong policies and legislation are needed to support MAC management efforts. This includes laws that protect wildlife habitats, regulate the keeping of exotic pets, and provide funding for conflict mitigation programs.
Question: Examine the factors contributing to the increasing man-animal conflict in India. Suggest measures to mitigate this conflict and promote harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife.
3. 50 acres of farmland wiped out in landslips in Idukki
Topic: GS3 – disaster management
Context:
- Over 50 acres of agricultural land were destroyed by landslips near Munnar in Idukki, Kerala, due to extremely heavy rainfall.
- The affected areas are in the Santhanpara gram panchayat, leading to significant damage to agricultural land.
Impact of landslips:
- Loss of life and property: Landslides can cause significant loss of life and property damage. The sudden and destructive nature of landslides can leave little time for people to escape, and the weight of debris can crush buildings and infrastructure.
- Disruption of infrastructure and transportation: Landslides can disrupt transportation networks, roads, and railways, making it difficult for people and goods to move around affected areas. This can hinder economic activities and access to essential services.
- Environmental damage: Landslides can trigger erosion, sedimentation, and damage to natural ecosystems. They can also disrupt water supplies and contaminate water sources.
- Social and psychological impacts: Landslides can have a devastating impact on the social fabric of communities. Survivors may experience trauma, anxiety, and depression, and the loss of homes and property can disrupt livelihoods and social ties.
Mitigation Strategies for Landslides:
- Hazard mapping and risk assessment: Identifying landslide-prone areas through detailed mapping and risk assessment is crucial for planning and implementing mitigation measures. This involves understanding the geology, topography, and land-use patterns of an area.
- Land-use planning and regulation: Implementing land-use regulations and zoning restrictions can help to minimize human encroachment in landslide-prone areas. This may involve restricting development in areas with steep slopes, unstable soils, or a history of landslides.
- Slope stabilization and protection measures: Engineering measures can be employed to stabilize slopes and reduce the risk of landslides. These measures include terracing, retaining walls, drainage systems, and vegetation cover.
- Early warning systems and evacuation plans: Developing early warning systems that can detect landslides and provide timely alerts to communities is essential for reducing loss of life. This may involve installing monitoring systems, training local observers, and establishing evacuation plans.
4. States in Court against their Governors.
Topic: GS2 – Indian polity.
Context:
- Non-BJP ruled States such as Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Punjab accuse their Governors of delaying the passage of crucial Bills into law.
- Bills related to public health, higher education, Lokayukta, and cooperative societies have been kept pending.
- Tamil Nadu alleges that Governor R.N. Ravi has caused a “constitutional deadlock” by sitting on Bills for months.
- Kerala states that eight proposed laws have been pending with the Governor for years.
- Punjab reports that seven Bills have been stuck with the Governor since June, affecting the functioning of the administration.
Governors’ Discretion:
- Article 200 of the Constitution outlines the options available to the Governor when presented with a Bill passed by both Houses of the Legislature.
- The Governor can declare assent, withhold assent, or reserve the law for the consideration of the President.
- If assent is withheld, the Bill should be returned to the Legislative Assembly for reconsideration or amendments, with the Governor ultimately assenting after reconsideration.
- The first proviso in Article 200 clarified that the Governor’s discretion should not be exercised independently but on the advice of the State Cabinet.
Interpretation of “As Soon As Possible”:
- The Constitution states that the Bill should be returned “as soon as possible,” leaving room for interpretation.
- The Supreme Court has defined this phrase as “as early as practicable without avoidable delay.”
- Justice Rohinton F. Nariman suggested that a “reasonable time” would mean three months.
- The States request the Supreme Court to interpret and set a time limit for Governors to assent or return Bills, as recommended by the Sarkaria Commission in 1988.
Review of Purushothaman Nambudiri Case:
- Kerala calls for the formation of a seven-judge Bench to review the 1962 Purushothaman Nambudiri case.
- The case stated that Article 200 did not specify a time limit for Governors to decide on Bills, which the State argues did not consider the possibility of indefinite delays by Governors.
5. India, Bhutan to discuss new routes of regional connectivity
Topic: GS2 – International relations.
Context:
- India and Bhutan have agreed to discuss new routes of regional connectivity and upgrade border and immigration posts.
- This development supports Bhutan’s plans for a smart city at Gelephu on the border between Bhutan and Assam.
More about this news:
- The two countries will conduct a final survey for a 58-km crossborder rail link between Gelephu and Kokrajhar in Assam, and explore an 18 km rail link between Samtse in Bhutan and Banarhat in West Bengal.
- India will allow Bhutanese trade items to be transported from Haldibari in West Bengal to Chilahati in Bangladesh.
- This rail connectivity could facilitate air connectivity for India’s northeastern region, as Bhutan plans to build an international airport at Gelephu.
Importance of India Bhutan relation:
- Shared history and culture: India and Bhutan share a long history and cultural ties, with deep-rooted ties of friendship and mutual respect.
- Strategic partnership: India and Bhutan have a strong strategic partnership, with close cooperation on security, border management, and defense.
- Economic cooperation: India is Bhutan’s largest trading partner and development partner, providing significant economic assistance and support.
- Hydropower cooperation: Bhutan is a major source of hydropower for India, and the two countries are working together to develop joint hydropower projects.
Challenges in India-Bhutan Relations
- India’s dominance: India’s size and economic power can sometimes lead to perceptions of dominance in the relationship.
- Water sharing: There have been occasional disputes over water sharing between India and Bhutan.
- Third-party interference: There have been concerns about third-party interference in the India-Bhutan relationship. For example, China – Bhutan relations.
Way Forward for India-Bhutan Relations
- Strengthening the institutional framework: India and Bhutan should work together to strengthen the institutional framework of their relationship, including regular meetings of high-level officials and joint mechanisms for cooperation.
- Promoting people-to-people contact: India and Bhutan should promote people-to-people contact through increased tourism, cultural exchanges, and educational opportunities.
- Addressing the issue of water sharing: India and Bhutan should work together to develop a comprehensive framework for water sharing that is fair and equitable for both countries.
- Maintaining vigilance against third-party interference: India and Bhutan should maintain vigilance against third-party interference in their relationship and work together to protect their shared interests.
Question: Critically examine the historical and strategic importance of India-Bhutan relations. Discuss the challenges faced by the relationship and suggest measures to further strengthen the bilateral ties.
6. Delhi’s Odd Even Formula
Topic: GS3- Environment
Context:
- The Delhi administration decided to bring back the odd-even road restriction plan a day after Diwali because of the city’s already dangerously high air pollution levels.
- Delhi’s air quality index (AQI), which is classified as “severe plus” pollution, has continuously above 450, according to data from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
The Odd-Even Scheme:
- Cars are only permitted to operate under the odd-even method on certain days, which are determined by their registration numbers.
- Even-numbered cars are permitted on even dates, whereas odd-numbered cars are permitted on odd dates.
- By cutting traffic by about half, this action may help to lower AQI readings.
Current Vehicle Statistics:
- Roughly one-third of the approximately 75 lakh registered vehicles in Delhi are cars.
- The odd-even program will result in almost 12.5 lakh cars being taken off the road every day.
- Furthermore, about 20 lakh vehicles registered in the neighboring cities of the National Capital Region (NCR) also travel in Delhi, albeit their presence at any given time doesn’t greatly affect the traffic there.
Vehicular Emissions and Pollution in Delhi:
- Delhi’s geographical location in an atmospheric “bowl” that traps pollutants, particularly at times of low wind and lowering temperatures, exacerbates the city’s air pollution.
- Smog in the city is caused by the yearly crop stubble burning practices in nearby states like Punjab and Haryana as well as the Diwali celebrations.
- According to studies, automobiles can contribute up to 30% of Delhi’s yearly PM2.5 concentration, while NO2 and other pollution emissions are rising.
Effectiveness of the Odd-Even Scheme:
- There has been discussion about the odd-even scheme’s effectiveness on a worldwide scale.
- Following the 2019 implementation in Delhi, a research was carried out to compare the AQI values in Delhi with those in neighboring areas such as Gurgaon, Ghaziabad, and Noida, which did not adopt the plan.
- The average AQI in Delhi had the biggest decline, according to the data, dropping by 41 points during the odd-even interval.
- Experts stress that there are many variables that affect air quality, making it difficult to pinpoint the precise effect of a measure like this on air pollution.
Conclusion
- The odd-even road rationing program was reinstated by the Delhi government in order to alleviate the extreme air pollution in the city.
- Although the program has had some success in the past, experts agree that resolving Delhi’s air quality problems calls for a multipronged strategy that takes into account a number of contributing elements.
7. Odd-even’s health impact: what studies, doctors say
Topic: GS3- Environment
Context:
- Although there is some evidence that the odd-even vehicle policy can lower pollution levels, experts stress that there is inconsistent data available and that the reduction may not be enough to address health-related effects.
Details:
- According to experts this policy is insufficient because it does not consistently reduce the number of vehicles on the road by 50%.
- Furthermore, because pollutant concentration is dependent on meteorological variables like wind speed, a decrease in emissions may not always translate into a comparable decrease in pollutant concentration.
- Reductions have occurred in certain regions but not in others, or they have occurred but not for long.
Health Implications of Odd-Even Policy:
- Experts believe that since a 20% reduction in PM2.5 (a common pollutant) levels beyond 500 would still result in dangerous levels above 400, it is insufficient to reduce health hazards.
- Long-term exposure to pollution has been associated with a higher chance of developing a number of illnesses, such as depression, diabetes, heart disease, lung disease, cancer, and hypertension.
Findings from Studies:
- The odd-even strategy in Delhi has been shown to lower particulate matter (PM) levels, with reductions ranging from 5% to 10%, according to several studies.
- Two studies published in 2016 revealed that PM2.5 concentrations had decreased by 2 to 3%, while one study found that average PM2.5 levels had decreased by 5.73%.
- It was suggested that slower-moving vehicles, less engine idling, and less traffic congestion were the reasons for the drop in PM levels during odd-even hours.
- However, midday rather than early morning saw the biggest decrease in PM levels.
Reduction of NO2 as a Benefit:
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which is mostly produced by vehicle emissions, is one gaseous pollutant that the odd-even strategy may help reduce.
- NO2 levels are predicted to drop as there are fewer cars on the road and less traffic.
- This is significant because, according to a recent AIIMS study, short-term exposure to NO2 resulted in a 53% rise in the number of patients visiting the hospital’s emergency room up to a week later.
- The study also indicated that emergency room visits increased more with an increase in NO2 levels than with PM2.5.
Long-Term Solutions:
- The odd-even strategy may not be a long-term solution to Delhi’s air pollution issue, according to experts.
- Rather, they advocate for actions that will probably produce greater outcomes in the upcoming years, such as encouraging electric vehicles and gradually phase-out of older BS-IV cars.
- They also suggest putting policies into action on a regional level as opposed to just in Delhi.
- Doctors also recommend installing air purifiers in schools to shield students from the negative impacts of air pollution.
- Lastly, scientists advise against using firecrackers to lessen the negative effects of air pollution, even though the odd-even policy might assist reduce pollution after Diwali.
8. A National Security Strategy for India: what it should be guided by
Topic: GS3- Internal Security
Context:
- India’s first written National Security Strategy (NSS), which is being drafted by the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) will represent a substantial change in the country’s national security strategy.
- The necessity of a clearly stated NSS has come up for discussion in recent years as its significance in tackling many facets of national security has become increasingly apparent.
Importance of a Publicly Articulated NSS:
- A clearly stated National Security Strategy (NSS) is essential since it explains the Indian government’s approach to managing national security from all angles.
- It is essential to nation’s well-being and continued existence because it promotes unity, mutual understanding, and a common understanding of the goals of national security.
Comprehensive Nature of NSS:
- Numerous security facets, such as those pertaining to the military, economy, diplomacy, internal affairs, people, environment, food, and water security, will be covered by the NSS.
- Although they have important responsibilities to play, internal and military security should make other types of security possible.
- Strong defense and internal security management is therefore crucial.
India’s Growing Significance in World Affairs:
- India is becoming an important player in world politics due to its rising stature and growth forecasts.
- The NSS will require ownership and approval at the highest levels of government in order to withstand thorough examination and scrutiny from a wide range of nations and geopolitical scenarios.
Timeline for the NSS:
- It is important to draft the NSS slowly and thoroughly, allowing for revisions and adjustments as conditions evolve.
- Although a detailed progress report is not provided, two years seems to be an acceptable amount of time to complete the NSS.
Way Forward:
- In tackling the complex facets of national security, India’s adoption of a widely stated National Security Strategy is a noteworthy milestone.
- It is anticipated that the NSS will include a wide range of security aspects, entail in-depth discussions, and act as a foundational framework for security planning at all planning levels.
- The completion schedule ought to strike a balance between the necessity of thorough consideration and the dynamic nature of security threats.
9. Nepal Earthquake
Topic: Physical Geography
Context:
- A powerful 6.4 magnitude earthquake, the worst since 2015, struck Nepal’s remote mountainous region.
Details:
- According to the National Earthquake Monitoring and Research Centre, the epicentre of the earthquake was in Jajarkot district, about 500km west of Kathmandu.
- Areas affected: Jajarkot and Rukum districts of Nepal, New Delhi and neighbouring areas of India.
Earthquake:
- Earthquakes are natural geological phenomena that occur when there is a sudden release of energy in the Earth’s crust.
- Epicenter: The epicentre is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the underground point where an earthquake originates. It is the location where the seismic waves, generated by the release of energy during the earthquake, first reach the Earth’s surface.
- Hypocenter (or Focus): The hypocenter, also known as the focus, is the actual point within the Earth where the seismic energy is released during an earthquake. It is underground, and its depth can vary. Earthquakes can have shallow hypocenters, which are closer to the Earth’s surface, or deep hypocenters, which are further below the surface.
Why is Nepal prone to so many earthquakes?
- Nepal lies in one of the most active tectonic zones (seismic zone IV and V) of the world, making the country extremely vulnerable to earthquakes.
- Large tectonic plates make up the crust of the Earth. These land masses, which contain entire continents, are in motion and colliding with one another all the time.
- Earthquakes are common in Nepal which is situated on the ridge where the Tibetan and Indian tectonic plates meet and advance two meters closer to one another every century which results in pressure which is released in the form of earthquakes.
- A collision between the Indian and Tibetan plates has been going on underground for a long time which has accumulated tremendous energy due to which western Nepal is under the threat of bigger earthquakes.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) ranks Nepal 11th on the list of the most vulnerable countries to earthquakes and Nepal’s capital Kathmandu is one of the top cities prone to earthquakes.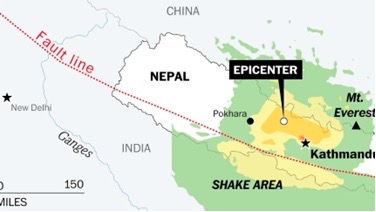
The Devastating Impact of Earthquakes: Destruction and Environmental Consequences
- Damage to life and property: Earthquakes of high magnitude cause total collapse of the entire structure/building. This is accompanied by disruption of underground pipelines and railway lines, collapse of dams which cause sudden floods that in turn endanger life and livelihood.
- Changes in river courses: Sometimes River channels are blocked or their courses are changed due to the impact of earthquake.
- Tsunami and other associated disasters: Earthquakes cause Tsunamis which disrupts life in settlements of coastal areas. It sinks large ships. Example: Tsunami in Indonesia Tsunami near Sumatra coast had cost properties worth billions of rupees.
- Landslides and avalanches are also caused by earthquakes.
10. Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project
Topic: Prelims
Context:
- A major controversy has erupted in poll-bound Telangana over alleged engineering lapses in the Rs 1.5 lakh crore Kaleshwaram project
What is the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project?
- Located in Kaleshwaram, Bhupalpally, Telangana, the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Scheme is a multi-use irrigation project on the Godavari River.
- The project begins where the Pranahita and Godavari rivers converge.
- In 2014, the Kaleshwaram project in Telangana was modified, expanded, and renamed from its original Pranahita-Chevella project in the former Andhra Pradesh.
What does the project entail?
- This project is special because Telangana will build a barrage at the Medigadda confluence to capture water from two other rivers that flow into the Godavari.
- The water will then be pumped back into the main Godavari River and directed through lifts and pumps into an extensive network of reservoirs, water tunnels, pipelines, and canals.
- With the longest water tunnels, largest pumps, underground surge pools, and aqueducts in the world, the project has broken numerous records.
- The reservoirs are interconnected through a network of tunnels running about 330 km, the longest being 21 km long connecting Yellampalli reservoir with Medaram reservoir in Peddapalli district.
How important is KLIS to Telangana?
- Kaleshwaram will transform Telangana into an agricultural powerhouse.
- The project will enable farmers in Telangana to reap multiple crops with a year-round supply of water wherein earlier they were dependent on rains resulting in frequent crop failures.
- KLIS covers several districts which used to face rainfall deficit and the groundwater is fluoride-contaminated.
- Apart from providing water for irrigation to 45 lakh acres, a main component of the project is supply of drinking water to several towns and villages and also to twin cities of Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
- Mission Bhagiratha, the Rs 43,000-crore project to supply drinking water to every household in villages, draws a large quantity of water from the KLIS and some quantity from projects on River Krishna.
- There is a fresh water fishing industry in the state as the numerous water bodies created under the project are also being used to grow fish and locals are given rights to fish and sell.
11. India, Bhutan to broaden partnership on energy, health, space technology
Topic: GS2- IR
Context:
- During a meeting with Bhutan King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck, Prime Minister Narendra Modi reaffirmed India’s strong commitment to its special partnership with Bhutan.
- In line with its aims, he reaffirmed India’s unwavering support for Bhutan’s socioeconomic growth.
Advancements in Connectivity:
- The two leaders decided on a final location survey for a proposed cross-border railway connecting Kokrajhar in Assam to Gelephu in Bhutan, according to a joint statement released after their discussions.
- They also talked of building a railroad to connect Samtse, Bhutan, with Banarhat, West Bengal.
Expanding India-Bhutan Partnership:
- The extension of the India-Bhutan collaboration was warmly evaluated by both Modi and Wangchuck, especially in the areas of connectivity, infrastructure for cross-border trade, trade, mutual investments, energy, health, education, space technology, and people-to-people interactions.
- This indicates a dedication to expanding the range of cooperation between the two countries.
Significance
- During his journey to India, King Wangchuck was part of a renewed push by China and Bhutan to resolve their long-standing boundary issue as soon as possible.
- This visit emphasizes the value of Bhutan’s connection with India and signals a strengthening of such ties.
12. Govt launches ‘Bharat Atta’ at subsidised rate to support consumers
Topic: Schemes
Context:
- Prior to the Diwali celebration, the Indian government formally started selling subsidized wheat flour to alleviate the burden of exorbitant pricing on people.
- The wheat flour, which is marketed under the brand name “Bharat Atta,” is available at a heavily discounted price of Rs 27.50 per kilogram, which is far less than the going rate of Rs 36–70 per kilogram, depending on region and quality.
Distribution Channels:
- Cooperatives like Kendriya Bhandar, the National Cooperative Consumers’ Federation (NCCF), and the National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED) will distribute the “Bharat Atta.”
- Approximately 2,000 stores and 800 mobile trucks will help with distribution across the nation.
Formal Launch and Wider Availability:
- The official launch of ‘Bharat Atta’ was marked by the flagging off of 100 mobile vans by Union Food and Consumer Affairs Minister Piyush Goyal, who also said that the subsidized wheat flour, priced at Rs 27.50 per kg, will be made available nationwide.
- Sales were modest during the trial period, but it is anticipated that increased demand will result from a wider availability through mobile vans and stores.
For Enquiry

7 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs

7 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

6 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz

6 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing

6 Nov 2023 : Indian Express

6 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs

4 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz

4 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing

4 Nov 2023 : Indian Express

4 Nov 2023 : PIB
Daily Current Affairs 7 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
6-November-2023
1) DESPITE GOVT’S EFFORTS, WHY ONION PRICES ARE STILL HIGH
Topic:…
November 2023 The Hindu 7 November 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
7-November-2023
1. A telco double dip attempt that threatens Net neutrality.
Topic:…
Daily Quiz 6 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz 6 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 6 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
6-November-2023
1. Fundamental rights are not gifts bestowed upon by the state…
Indian Express 6 Nov 2023 : Indian Express Indian Express
6-November-2023
1) CLEAR AND PRESENT DANGER
Context:
The Delhi Declaration, signed…
Daily Current Affairs 6 November 2023 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
6-November-2023
1) DESPITE GOVT’S EFFORTS, WHY ONION PRICES ARE STILL HIGH
Topic:…
Daily Quiz 4 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz 4 Nov 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 4 Nov 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
4-November-2023
Q1) Examine the importance of establishing a National Tribunals…
Indian Express 4 Nov 2023 : Indian Express Indian Express
4-November-2023
1) A matter of greying
Context:
The prospects for the population…
November 2023 PIB 4 Nov 2023 : PIB PRESS INFORMATION BUREAU
4-November -2023
1. Atal Innovation Mission Opens Application for School Innovation…




