01 January 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. The nature of dissent in the Indian judiciary
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
Dissent in Democracies: A Comparative Overview:
Role of Dissent in Democracy
- Dissent is an essential component of a vibrant democracy, including in the judiciary.
- While both the Indian and U.S. Supreme Courts feature powerful judicial dissents, the underlying reasons differ between the two countries.
Dissents in the U.S. Supreme Court (SCOTUS)
- SCOTUS dissents are often influenced by the political leanings of the appointed judges.
- Example: Justice Stephen Breyer (appointed by Democrats) supported pro-affirmative action, anti-capital punishment views, as seen in his dissent in Glossip v. Gross (2015).
- Example: Justice Samuel Alito (appointed by Republicans) opposed same-sex marriage and abortion rights, as demonstrated in his dissent in Obergefell v. Hodges (2015).
Political Dissent in the Indian Supreme Court
- Unlike the U.S., Indian judges are selected by a collegium of senior judges, reducing political influence in decisions.
- Example: ADM Jabalpur (1976) – Justice H.R. Khanna dissented against suspending fundamental rights during the Emergency, a stance that later became law through a constitutional amendment.
- Example: P.V. Narasimha Rao (1998) – Justices Agarwal and Anand dissented on parliamentary immunity regarding accepting bribes, a stance later overruled in Sita Soren (2023).
Social Dissent in the Indian Supreme Court
- Dissent can reflect different social views on legal issues, particularly when they touch on personal or religious matters.
- Example: Shayara Bano (2017) – Justices Khehar and Nazeer dissented from the majority opinion that struck down triple talaq, arguing it was an integral part of Sunni personal law.
- Example: Aishat Shifa (2022) – Justices Gupta and Dhulia had different views on whether the hijab ban in schools infringed upon secularism.
Intellectual Dissent in the Indian Supreme Court
- Some dissents are rooted in intellectual debates over constitutional interpretation.
- Example: Lalta Prasad Vaish (2024) – Justice Nagarathna dissented on the interpretation of “intoxicating liquor” in the Constitution, focusing on textual clarity.
Conclusion
- Dissent serves as a critical tool for maintaining judicial independence and shaping legal precedents in democracies.
- It fosters deeper engagement with legal principles and societal values.
| Practice Question: Judicial dissent is crucial for democracy. Discuss the nature and significance of dissent in the Indian Supreme Court, comparing it with the U.S. Supreme Court. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Geopolitical Shifts in 2025: Opportunities and Challenges for India
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 09)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
A Dynamic Geopolitical Landscape in 2025
- The year 2025 begins with notable geopolitical shifts, including Donald Trump’s return to the US presidency, regime changes in India’s neighborhood, ongoing conflicts, and evolving global alliances.
- These developments present both opportunities and challenges for India’s foreign policy and global engagement.
India’s Regional Neighborhood: Political Upheavals
- Bangladesh: Sheikh Hasina’s 16-year rule ended amid protests, leading to her exile in India. The interim government under Muhammad Yunus faces domestic unrest and strained ties with New Delhi over her extradition.
- Sri Lanka: Leftist leader Anura Kumara Dissanayake’s rise to power brings a fresh dynamic, with his approach to Tamil minority aspirations being closely watched.
- Maldives: Relations improved slightly under Mohamed Muizzu despite his initial anti-India stance.
- Nepal: K P Sharma Oli’s pro-China policies remain a concern, although his alliance with the Nepali Congress offers a degree of stability.
Global Conflicts and India’s Role
- Ukraine War: Peace talks are in motion, with China and possibly India playing critical roles in negotiations. India must weigh its contributions and potential risks of mediation.
- China Relations: Border de-escalation talks show promise, with troop drawdowns likely in 2025. Trust issues persist, but diplomatic engagements like PM Modi’s potential visit to China could help rebuild ties.
- Pakistan: Relations remain stagnant, with New Delhi maintaining its firm stance against engagement due to terrorism concerns and SAARC’s limited revival prospects.
Western Alliances: Opportunities and Challenges
- United States: Donald Trump’s return introduces unpredictability, but a Modi-Trump meeting could bolster ties.
- Canada: Relations are strained due to accusations of India’s involvement in a Khalistani separatist’s killing, complicating broader diplomatic engagements.
- Europe: Rising far-right movements and immigration debates pose challenges for Indian students and professionals. Negotiations on free trade pacts with the EU and UK continue amidst political uncertainty.
Engagement Beyond the West
- Africa: Renewed efforts for engagement could culminate in a summit, possibly hosted in Ethiopia, building on the success of the 2015 India-Africa Summit.
- Russia: President Putin’s visit to India and ongoing bilateral cooperation will be significant amid global scrutiny over the Ukraine war.
Conclusion: Balancing Promise and Peril
- India’s geopolitical strategy in 2025 will involve navigating regional instability, fostering alliances, and leveraging opportunities in Africa and the West.
- As global dynamics evolve, India’s diplomatic agility will be critical in shaping its role as a leading global player.
| Practice Question: Examine the geopolitical challenges and opportunities India faces in 2025, considering regional political changes, global conflicts, and evolving international alliances.(250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Quad members vow to work vigorously towards a free, open, and stable Indo-Pacific
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad):
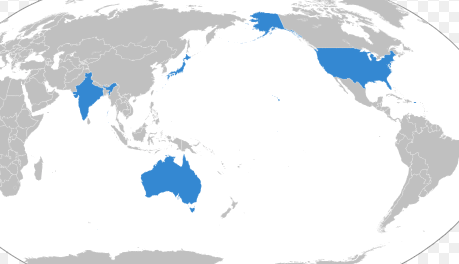
- The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) consists of India, the U.S., Australia, and Japan.
- It was formed in 2007 and initially aimed to provide humanitarian assistance in response to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.
- The Quad’s main objective is to promote a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- Key areas of cooperation include maritime security, infrastructure development, connectivity, and countering China’s growing influence.
- The Quad emphasizes the centrality of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in regional security and the Pacific Islands Forum in the Pacific region.
- The next Quad Summit is scheduled to be hosted by India in the second half of 2025.
- The Quad supports regional institutions like the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
2. India-Nepal joint military exercise begins
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
|
Exercise Surya Kiran:
- The exercise is aimed at enhancing interoperability and fostering collaboration between the two countries’ armies.
- It is an annual training event conducted alternately in India and Nepal.
- The exercise is being held at the Nepal Army Battle School, Saljhandi, in the Shivalik ranges of Western Nepal.
- The main focus is on counter-terrorism (CT) operations, jungle warfare, and mountain warfare.
- It also includes humanitarian assistance activities.
- Exercise Surya Kiran strengthens the bond of friendship and military cooperation between India and Nepal.
3. 10 payloads of ISRO’s POEM-4 module deployed successfully
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
POEM-4 module:
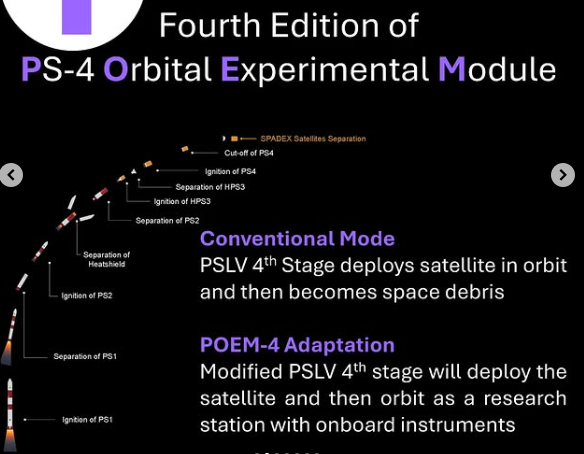
- POEM-4 stands for PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4.
- It is a module used to carry out scientific experiments in space.
- POEM-4 is part of the PSLV-C60/SpaDeX mission, launched by ISRO.
- The module is a repurposed PS4 stage (a part of the PSLV rocket), which is used to deploy payloads in space.
- It operates at an altitude of 350 km with a 55-degree inclination.
- POEM-4 allows non-government entities (NGEs) like start-ups, academic institutions, and research organizations to test space technologies without needing to launch entire satellites.
- It helps reduce entry barriers for these entities to engage in space activities.
- A total of 10 hosted payloads were successfully established and operationalised by IN-SPACe on the POEM-4 module.
| IN-SPACe |
IN-SPACe stands for Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center.
|
4. Willow is a small chip for Google but a quantum leap for computing
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
What is Willow?

- Willow is a quantum processor developed by Google.
- It has 105 physical qubits, which are used to store and process information.
- Willow operates at extremely low temperatures, close to absolute zero (-273°C).
- The processor uses both data qubits and measurement qubits to handle errors.
- Quantum computers like Willow work differently from classical computers by using qubits, which can represent both 0 and 1 at the same time (superposition).
- Willow uses error-correction methods, making it faster and more reliable than other quantum computers.
- It completed a difficult task, random circuit sampling, in minutes, which would take classical computers millions of years.
- Willow shows promise for solving complex problems in areas like drug design, climate science, and optimization.
5. Social Inequality Linked to Accelerated Brain Aging and Dementia: Study
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained – Page No. – 09)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Link Between Social Inequality and Brain Health
- A study has established a direct connection between social inequality and changes in brain structure associated with aging and dementia.
- With dementia cases expected to rise, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, the research underscores the importance of addressing socioeconomic disparities as a fundamental aspect of brain health interventions.
Study Scope and Methods
- The research, conducted by teams from South America and Trinity College Dublin, analyzed over 2,100 individuals from Latin America and the US, including those with neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s.
- The study examined national structural inequality indices and their impact on brain volume and connectivity, focusing on regions critical for memory and cognitive function.
Key Findings: Impact of Inequality
- The findings revealed that greater socioeconomic disparities were associated with reduced brain volume and connectivity, with the most pronounced effects observed in Latin America.
- Latinos with Alzheimer’s experienced the most severe impacts, highlighting the exacerbation of neurodegeneration in environments with high inequality.
- Notably, these links persisted even after adjusting for individual factors like education, age, and cognitive ability.
Macro-Level Determinants of Brain Health
- The study highlights the role of macro-level social determinants, such as structural inequality and physical environment, in shaping brain health independently of individual factors.
- Researchers emphasize the need to incorporate these broader determinants into global brain health strategies.
Implications for Future Research
- The findings pave the way for exploring the biological mechanisms linking social inequality to neurodegeneration.
- They stress the urgency of integrating macro-level social factors into interventions to address disparities in brain health and aging outcomes globally.
6. Pangong Lake
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Govt & Politics- Page No. – 06)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
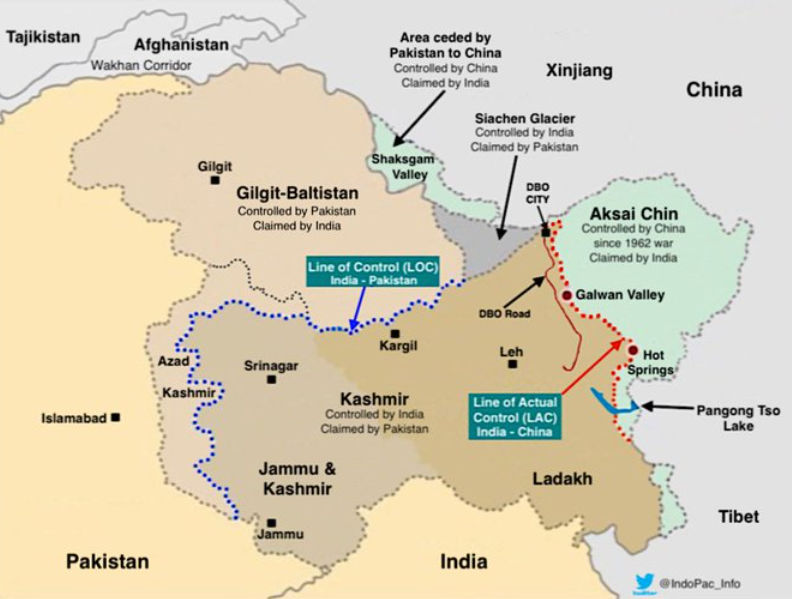
About Pangong Tso lake:
- It is one of the most famous lake in Leh Ladakh, derives its name from the Tibetan word, “Pangong Tso”, which means “high grassland lake”.
- It is also known as Pangong Lake which is a long narrow, endorheic (landlocked) lake situated at a height of more than 14,000 ft (4,350 meters) in the Ladakh Himalayas.
- It is the world’s highest saltwater lake.
- India holds one-third of the 135 km-long boomerang-shaped Pangong lake.
- One-third of the Pangong Lake lies in India and the other two-thirds in China.
- It is also known to change colors, appearing blue, green, and red at different times.
7. INDEX OF EIGHT CORE INDUSTRIES (BASE: 2011-12=100) FOR NOVEMBER, 2024
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2089066®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Index of Eight Core Industries:

Overview
- The ICI measures the combined and individual performance of eight core industries that form the backbone of India’s industrial economy.
- These industries are Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement, and Electricity.
- The eight core industries collectively hold a 40.27% weight in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
Components and Their Weights
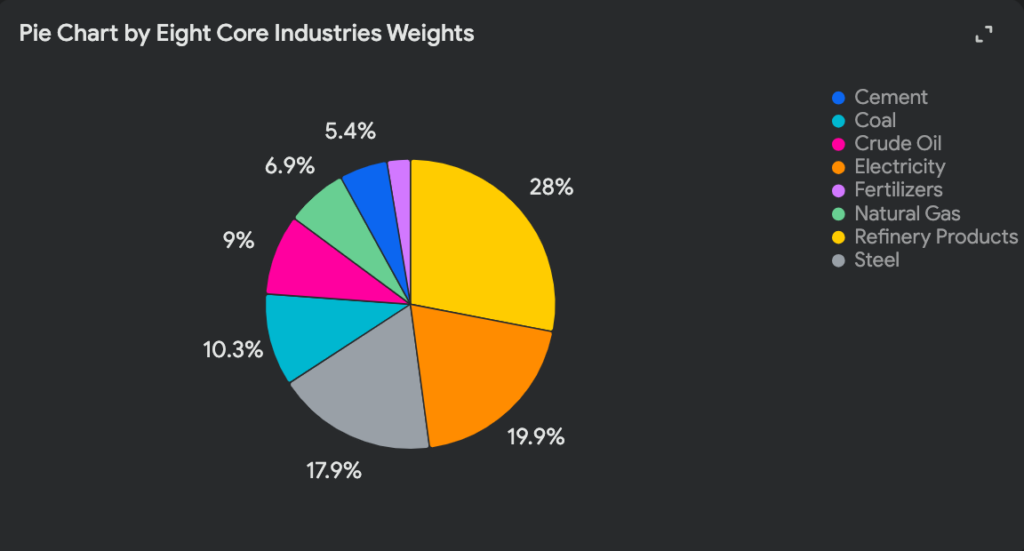
Monitoring:
- The Office of the Economic Adviser (OEA) under the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP), Ministry of Commerce and Industry compiles and releases the ICI monthly.
Base Year:
- The base year for the ICI is 2011-12.
Data Sources:
- Production data for each industry is sourced from respective government agencies.
Purpose
- Tracks industrial performance for economic planning and policy formulation.
- Provides insights into trends and growth patterns of key sectors.
- The ICI provides valuable insights into the performance of key sectors, aiding policymakers in economic decision-making.
| Index of Industrial Production (IIP): |
|
For more such UPSC-related Current Affairs, Check Out- 31 December 2024: Daily Current Affairs

