05 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. What are the issues around delimitation?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|
| What is Delimitation? |
|
|
Why is Delimitation Being Debated?
- India’s population has grown unevenly in the past five decades.
- Some States, like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan, have seen higher population growth compared to southern States like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Two key scenarios are being considered for delimitation:
- Redistributing the existing 543 seats among the States.
- Increasing the number of seats to 848 in proportion to population growth.
- There is uncertainty about whether the allocation will be based on the current share of seats or projected population.
Concerns About Delimitation
- If seats are allocated based on population, southern and smaller northern States may lose their proportional representation.
- This could impact the federal structure and reduce the political significance of States that controlled their population.
- Currently, southern States hold 24% of Lok Sabha seats, which could decline by 5% under the proposed changes.
Possible Solutions
- Fix the number of Lok Sabha seats at 543 to maintain federal balance and ensure fair representation for all States.
- Increase the number of MLAs in each State based on population growth to provide adequate local representation.
- Follow the U.S. model, where the House of Representatives has remained fixed at 435 despite a fourfold population increase.
- Prevent regional disparities by avoiding disproportionate representation shifts that could weaken smaller States.
- Ensure long-term stability by considering that India’s population is expected to peak at 165-170 crore in the next three decades before declining.
Conclusion
- Delimitation must balance democratic representation and federal integrity.
- Fixing Lok Sabha seats at 543 while adjusting State assemblies ensures fairness, prevents regional disparities, and upholds India’s diverse and evolving political landscape.
| Practice Question: How will the upcoming delimitation exercise impact the federal structure and political representation in India? Suggest measures to ensure a balanced approach while addressing concerns of underrepresented States. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Bombay High Court Conducts First-Ever Legislative Review of Maharashtra Slum Act to Address Redevelopment Delays
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 15)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
First-of-its-Kind Legislative Review
- Unlike traditional judicial reviews that assess constitutional validity, this review—mandated by the Supreme Court—aims to identify gaps in the legislation affecting slum redevelopment.
Background and Issues Leading to Review
- The review stems from delays in slum redevelopment projects, violating slum-dwellers’ fundamental rights.
- In a 2003 Borivali project, Yash Developers failed to deliver for 18 years, prompting legal intervention.
- Despite repeated Bombay High Court rulings, delays persisted due to loopholes in the law and ineffective oversight by the Slum Rehabilitation Authority (SRA).
- The Supreme Court, recognizing these systemic failures, ordered a performance audit of the Act and a legislative review.
Key Issues Identified for Review
- Land Identification as Slum: Possible builder influence compromises the independence of the decision-making process.
- Slum Dwellers’ Identification: Disputes over eligibility lead to prolonged litigation.
- Developer Selection: Developers manipulate slum dwellers’ cooperative societies to secure projects.
- Land Allocation for Redevelopment & Sale: Developers prioritize saleable area, often at the expense of slum dwellers.
- Transit Housing Obligations: Delays in providing transit accommodation force residents into unstable living conditions.
- Lack of Independence of Authorities: Short tenures and regulatory capture weaken the Slum Rehabilitation Authority’s accountability.
Bombay HC’s Response and Future Proceedings
- On February 14, a special bench noted that Maharashtra is unique in providing free housing to encroachers.
- The court raised concerns over vertical slums, lack of open spaces, and mass housing policies.
- It has sought stakeholder input and will continue hearings on March 18, potentially shaping future slum redevelopment policies.
Conclusion
- The Bombay High Court’s review of the 1971 Maharashtra Slum Act marks a crucial step toward resolving systemic delays and inefficiencies in slum redevelopment.
- By addressing gaps in land identification, developer accountability, and transit housing, the review aims to ensure fair, transparent, and timely rehabilitation of slum dwellers while balancing urban development needs.
- The upcoming hearings will be pivotal in shaping future housing policies in Mumbai.
| Practice Question: The inefficiencies in slum redevelopment laws have led to prolonged delays, impacting the rights of slum dwellers. Discuss the key challenges in slum rehabilitation in India and suggest reforms to ensure timely and transparent redevelopment. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. US Halts Military Aid to Ukraine, Pressures Kyiv for Peace Talks
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Significance of US Aid to Ukraine
- Since the onset of the Russian invasion, the US has been a primary supplier of military aid, contributing advanced weaponry, intelligence support, and logistical assistance.
- Key supplies include Javelin missiles, HIMARS rocket systems, NASAMS air defense systems, and essential provisions such as medical aid and winter gear.
- This aid has been crucial in sustaining Ukraine’s resistance against Russian aggression.
Implications of the Aid Suspension
- Military Setback for Ukraine – The halt in aid could weaken Ukraine’s defense capabilities, making it more vulnerable to Russian advances, especially in critical battlefronts.
- Increased Pressure to Negotiate – The move is seen as a strategic effort to coerce Ukraine into peace talks with Russia, aligning with Trump’s diplomatic priorities.
- Strain on European Allies – While European nations contribute significantly to Ukraine’s war effort, their capacity to sustain aid at US levels is limited, potentially forcing a reassessment of their commitments.
- Geopolitical Ramifications – Russia may exploit this development by intensifying its military offensive, sensing a strategic advantage. Additionally, it could prompt Ukraine to seek alternative alliances for continued military support.
Historical Precedent
- This is not the first instance of Trump leveraging aid to pressure Ukraine. In 2019, he temporarily blocked congressionally approved assistance, seeking political concessions from Zelenskyy.
- The current suspension follows a similar pattern, with broader geopolitical stakes.
Future Outlook
- While European nations may attempt to fill the aid gap, their military production capacities are already stretched.
- Russia, on the other hand, has strengthened its arms supply chains, drawing support from countries like North Korea and Belarus.
- The suspension of US aid may thus accelerate the war’s conclusion on terms unfavorable to Ukraine.
Conclusion
- The US decision to halt aid marks a pivotal moment in the Ukraine conflict, potentially reshaping the war’s trajectory.
- Whether this will force Ukraine to negotiate or further destabilize the region remains to be seen.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the US decision to pause military aid to Ukraine on the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict. How might this impact global geopolitics and the role of European allies in supporting Ukraine? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. India’s circular economy to generate a market value of over $2 trillion and create close to 10 million jobs by 2050 – Union Minister
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2108165 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Circular Economy’s Economic Potential
- India’s circular economy could create a market value of over $2 trillion and generate nearly 10 million jobs by 2050.
- It aims to shift from the traditional ‘take, make, waste’ model to a more sustainable approach.
- Globally, the circular economy has the potential to contribute $4.5 trillion in additional economic output by 2030.
| What is a circular economy? |
|
India’s Bid for World Circular Economy Forum 2026
- India has expressed its willingness to host the World Circular Economy Forum in 2026.
- The event for 2025 is scheduled to be held in Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Government Initiatives to Promote Circular Economy
- Plastic Waste Management Rules (2016) – Established guidelines for managing plastic waste across municipal, industrial, residential, and commercial sectors.
- Ban on Single-Use Plastics (2022) – Prohibited specific categories of plastics to reduce environmental pollution.
- Eco-Mark Rules – Introduced to promote environmentally friendly products and energy-efficient manufacturing.
- Circular Economy Action Plans – Finalized for 10 waste categories, with regulatory and implementation frameworks in progress.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Regulations – Implemented for plastic waste, e-waste, battery waste, and packaging materials.
- Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules – Established guidelines for reusing and recycling construction waste.
- Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) Waste to Wealth Portal – Launched to enhance waste management and resource efficiency.
- Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for Scientific Collaboration – Signed between research institutions and government bodies to develop innovative waste management technologies.
- Promotion of Waste-to-Energy and Bioremediation Projects – Encouraged sustainable waste processing solutions.
Conclusion
- India’s commitment to a circular economy promotes sustainability, efficient waste management, and economic growth.
- These initiatives ensure long-term environmental benefits and resource optimization for a sustainable future.
| Practice Question: Some argue that transitioning to a circular economy poses economic and logistical challenges, yet it offers long-term environmental and economic benefits. Discuss its relevance for India and the key government initiatives supporting this transition. (250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. What is carbon intensity?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
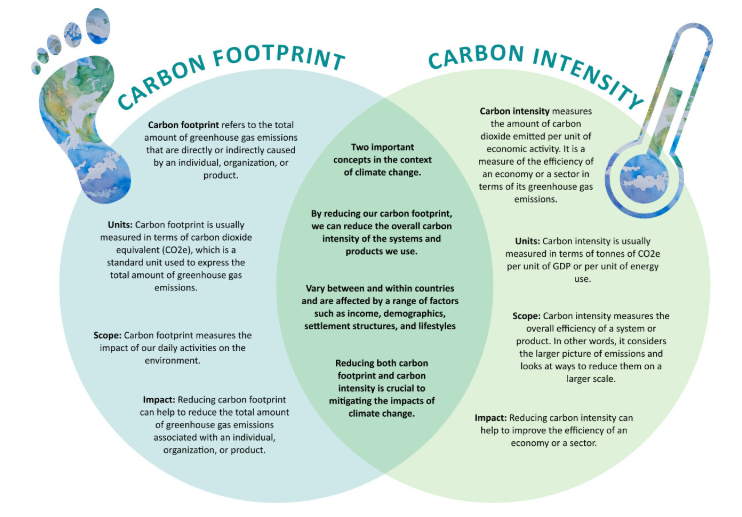
Carbon Intensity:
- Carbon intensity measures how much carbon dioxide (CO₂) is emitted for a specific activity.
- It helps track emissions from industries, services, or entire countries.
- Different sectors measure it based on their output, like steel production or insurance claims.
- Governments track carbon intensity using GDP per capita and CO₂ emissions.
- It adjusts existing economic metrics to include environmental impact.
- Lower carbon intensity means producing more with fewer emissions.
- It is crucial in fighting climate change and reducing greenhouse gases.
2. How the Wallace line explains the difference in species across continents
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Context |
|
What is the Wallace Line?

- The Wallace Line is an invisible boundary between Asia and Australia, separating distinct species on either side.
- It runs between Bali and Lombok, and between Borneo and Sulawesi, marking a shift in biodiversity.
- This concept helped establish modern biogeography, the study of species distribution.
Wallace’s Findings on Sulawesi
- Sulawesi, despite being close to Borneo, has a mix of Asian and Australian species.
- It hosts unique species like tarsiers, lowland anoa, mountain anoa (Asian origin), and dwarf cuscus (Australian marsupial).
- The island’s biodiversity puzzled early researchers as it contained species from multiple regions.
Geological History and Species Migration
- The Malay Archipelago has over 25,000 islands, shaped by past continental movements.
- Millions of years ago, Australia drifted from Antarctica and moved northward, forming volcanic islands.
- Changing sea levels, monsoons, and climates influenced species migration and adaptation.
- Asian species could migrate through tropical islands, but Australian species faced barriers due to cooler origins.
Current Relevance of the Wallace Line
- Modern research shows that the Wallace Line is a simplified concept; species movement depends on deeper environmental factors.
- Advanced technology, like evolutionary modeling, helps understand species adaptation.
- The Indo-Malayan region faces rapid habitat destruction, making species conservation a priority.
- Rather than redrawing boundaries, efforts should focus on protecting biodiversity from climate change and deforestation.
3. IRCTC and IRFC Attain Navratna Status: Boost to Indian Railways’ Financial Autonomy
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Economy- Page No. – 14)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Navratna Status and Eligibility Criteria
- Navratna status is the second tier of the ‘Ratna’ classification for Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs), positioned between Maharatna and Miniratna.
- To qualify, a CPSE must have a composite score of 60+ across six financial and performance indicators, along with an “Excellent” or “Very Good” MOU rating in at least three of the last five years.
- The Department of Public Enterprises (DPE) under the Ministry of Finance grants this status.
Financial Standing of IRCTC and IRFC
- IRCTC, which manages online ticketing for Indian Railways, had an annual turnover of ₹4,270 crore, a profit of ₹1,111 crore, and a net worth of ₹3,230 crore in FY 2023-24.
- IRFC, responsible for raising extra-budgetary resources for Indian Railways, reported a turnover of ₹26,644 crore, profit of ₹6,412 crore, and a net worth of ₹49,178 crore.
- These figures highlight their strong financial performance, justifying their Navratna elevation.
Benefits of Navratna Status
- Navratna companies enjoy greater financial and operational autonomy.
- They can invest up to ₹1,000 crore or 15% of their net worth in a single project without government approval.
- They gain flexibility in forming joint ventures, mergers, and acquisitions, allowing them to compete with private players.
- Additionally, they can expand internationally and attract more investors due to their improved financial credibility.
Other Navratna CPSEs in Indian Railways
Before IRCTC and IRFC, five other railway CPSEs held Navratna status:
- Container Corporation of India (CONCOR) – Freight transport and multimodal logistics.
- Rail Vikas Nigam Ltd (RVNL) – Railway infrastructure development.
- RITES Ltd – Transport infrastructure consultancy.
- IRCON International Ltd – Railway and highway construction.
- RailTel Corporation of India Ltd – IT and connectivity services.
With this addition, all seven listed CPSEs under Indian Railways now have Navratna status, reinforcing the sector’s financial and strategic importance in India’s economic growth.
check more – 04 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs




