10 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs
1. What does NEP, 2020 state about languages?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|

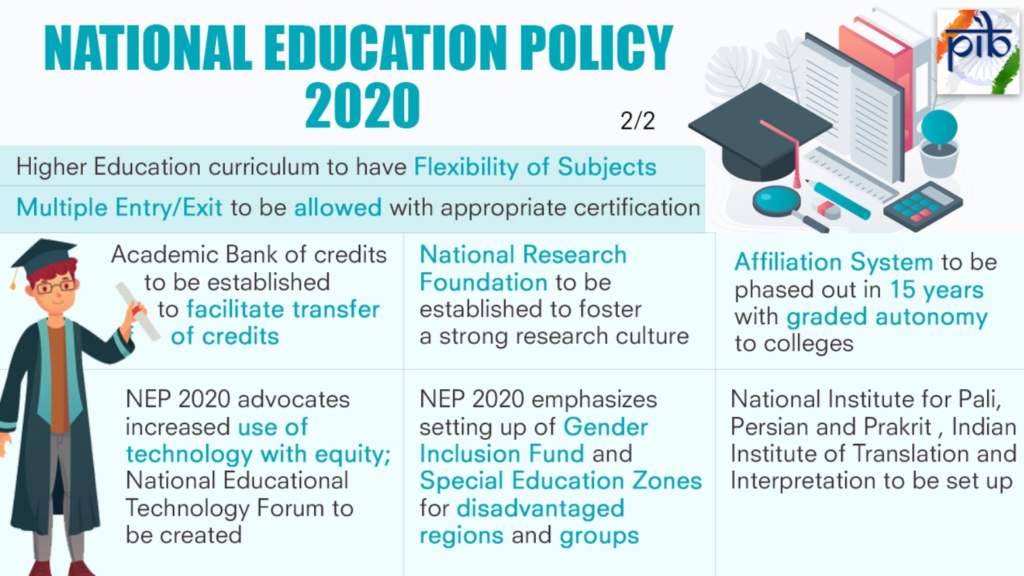
NEP 2020 on Language Instruction
- NEP 2020, which replaced the 1986 education policy, emphasizes the importance of mother tongue or regional languages in education.
- It states that, wherever possible, the medium of instruction in both public and private schools should be in the mother tongue, home language, or regional language until at least Grade 5, preferably till Grade 8 and beyond.
- Even after Grade 8, the local or home language should continue to be taught as a subject whenever possible.
- Research shows that children between the ages of two and eight learn best in their mother tongue, and multilingualism provides cognitive benefits.
- The policy encourages bilingualism, combining the mother tongue with English, to aid better comprehension and learning.
Implementation in Schools
- Some states have already implemented bilingual learning at the preschool level.
- For example, anganwadis in certain regions use textbooks with Hindi and English side by side, along with colorful imagery, to teach alphabets and numbers.
Findings of the AISES Survey on Language in Schools
- The eighth All India School Education Survey (AISES), conducted by a national institution, provides data on language instruction in schools.
- The survey found that the number of schools using the mother tongue as a medium of instruction has decreased over time.
- In 2002, about 92.07% of schools taught in the mother tongue at the primary stage, which dropped to 86.62% in 2009.
- The decline is noticeable in both urban and rural areas, highlighting a shift toward other languages in education.
Understanding the Three-Language Formula
- The three-language formula was first introduced in 1968, requiring Hindi-speaking states to learn Hindi, English, and a southern Indian language.
- Non-Hindi-speaking states were required to study Hindi, English, and their regional language.
- NEP 2020 modifies this formula, offering flexibility and ensuring that no language is imposed on any state.
- However, the policy encourages the study of Sanskrit and emphasizes classical languages such as Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Pali, Persian, and Prakrit.
Steps to Promote Regional Languages
- NEP 2020 aims to make high-quality textbooks available in home languages to enhance learning.
- In 2024, digital books were released in 104 regional languages and dialects, including Bengali, Khandeshi, Tulu, Ladakhi, Pashto, Bhili, Dogri, Lahuli (Pattani), and Car Nicobarese.
- The responsibility of translating these materials into local languages is assigned to state-level education councils.
- Some states, such as Assam and Andhra Pradesh, have already introduced bilingual textbooks in science and mathematics, combining English with regional languages like Assamese, Bodo, Bengali, and Telugu.
Challenges in Implementation
- The three-language formula has faced implementation challenges in many states.
- For instance, some states attempted to introduce additional languages but later removed them due to a lack of qualified teachers.
- In certain regions, Tamil was once offered as a second language but was later discontinued due to the small number of Tamil-speaking students.
- Similarly, states like Himachal Pradesh have been unable to offer languages like Telugu and Tamil due to the absence of trained teachers.
Foreign Languages in NEP 2020
- NEP 2020 also promotes learning foreign languages such as Korean, Japanese, Thai, French, German, Spanish, Portuguese, and Russian at the secondary school level.
- According to the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), students must study two Indian languages until Class 10.
- In Classes 11 and 12, students have the option to study one Indian language and one foreign language to enhance their linguistic skills.
| PYQ: National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient the education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2020) |
| Practice Question: Examine the challenges in implementing the three-language formula under NEP 2020 and its implications for linguistic diversity and education in India. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Trump Seeks to Renegotiate Nuclear Deal with Iran Amid Regional Tensions
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Background: The JCPOA and US Withdrawal
- In 2015, Iran signed the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) with global powers, agreeing to restrict its nuclear program in exchange for sanctions relief.
- However, in 2018, Trump unilaterally withdrew the US from the deal, citing its failure to curb Iran’s ballistic missile program and influence in the region.
- This led to renewed US sanctions and Iran gradually rolling back its commitments.
| What was the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)? |
|
Post-Withdrawal Developments
- Despite European efforts to salvage the deal, US sanctions forced companies to exit Iran, weakening its economy.
- Indirect negotiations under Biden failed, while Iran expanded its nuclear enrichment beyond the JCPOA limits.
- By 2023, talks had stalled, with Iran facing economic turmoil, regional tensions, and growing nuclear concerns.
Why is Trump Reconsidering?
- With Iran’s economy in crisis and new diplomatic realignments in the Middle East, Tehran has shown signs of willingness to negotiate.
- Meanwhile, Trump faces a changed regional landscape, where Iran’s growing influence through its proxies, alongside Israel’s declining Arab support, complicates US strategy.
Challenges Ahead
- Despite Trump’s outreach, deep mistrust remains between Washington and Tehran.
- Iran may reject any deal that imposes stricter terms than the JCPOA, while Trump’s willingness to offer concessions remains uncertain.
- The evolving Middle East conflict adds another layer of complexity to the negotiations.
Conclusion
- Trump’s outreach to Iran signals a potential shift in US-Iran relations, driven by Iran’s economic struggles and changing Middle Eastern dynamics.
- However, deep mistrust, Iran’s nuclear advancements, and regional conflicts pose significant challenges to any renewed agreement.
| What is the significance of JCPOA for India? |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of Trump’s attempt to renegotiate a nuclear deal with Iran. How do shifting geopolitical dynamics and Iran’s economic struggles influence the feasibility of such an agreement? (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. SC Limits Arrest Powers of Tax Officials
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 12)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
SC’s Ruling on Arrest Powers
- In Radhika Agarwal v. Union of India, the Supreme Court ruled that officials under the Customs Act, 1962, and CGST Act, 2017, exercise powers similar to the police and must be bound by the same procedural safeguards as per the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (CrPC).
- This decision aligns with the court’s broader attempt to restrict the unchecked arrest powers of enforcement agencies, as seen in the Arvind Kejriwal v. Directorate of Enforcement (2025) case concerning the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA).
Ensuring Due Process in Arrests
The SC emphasized that while tax officials are not police officers, they possess investigative and arrest powers. Thus, their actions must follow CrPC safeguards, including:
- Presenting the accused before a magistrate within 24 hours.
- Informing family members or friends of the arrest.
- Allowing the presence of a lawyer during interrogation.
The ruling ensures that tax officials cannot misuse their powers beyond those granted to regular police officers.
Conditions for Arrest Under Customs & CGST Acts
Under Section 104(4) of the Customs Act, certain offences (e.g., evading duty over ₹50 lakh) are cognizable, allowing arrest without a warrant. The CGST Act, 2017, has similar provisions. The SC ruled that even in these cases, officials must:
- Possess material evidence justifying the arrest.
- Clearly record their “reasons to believe” in writing.
- Provide the grounds for arrest to the accused to facilitate legal defense.
These conditions, initially set in Kejriwal v. ED, have now been extended to tax law enforcement.
Preventing Misuse of Arrest Powers
The SC acknowledged concerns about tax officials coercing businesses into paying overdue taxes under the threat of arrest. It ruled that such coercion is illegal and:
- Victims can seek refunds for tax payments made under duress.
- Disciplinary action will be taken against erring officials.
- The CBIC must issue guidelines to prevent arbitrary arrests.
Conclusion
- The ruling curbs arbitrary arrests under tax laws while maintaining officials’ powers.
- By enforcing CrPC safeguards, the SC aims to protect individuals from coercion and uphold the rule of law.
| Practice Question: The Supreme Court has ruled that tax officials under the Customs Act and CGST Act must follow the same procedural safeguards as police officers under the CrPC while making arrests. Discuss the significance of this judgment in curbing the misuse of arrest powers and ensuring constitutional rights. (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Indian team makes doubly secure ink to thwart counterfeiting
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Counterfeiting and Security Printing
- Governments and financial institutions continuously enhance security features in banknotes, cheques, and passports to prevent counterfeiting.
- Despite these efforts, counterfeiters develop new techniques to replicate security features, necessitating constant improvements.
- Security printing involves techniques such as optically variable ink, holograms, watermarks, and security threads to detect counterfeits.
- Some security features, like raised textures, can be felt by touch, while others require machines, such as RFID chips and digital watermarks.
New Fluorescent Ink with Nanoparticles
- Scientists in India have developed a new ink using nanoparticles to enhance security printing.
- The ink consists of strontium bismuth fluoride (Sr₂BiF₇) nanoparticles doped with lanthanide ions.
- It is created through the coprecipitation technique, a simple and scalable method requiring minimal energy.
Unique Fluorescence Properties
- When exposed to ultraviolet light (365 nm), the ink emits a blue glow.
- Under a different ultraviolet wavelength (395 nm), it glows magenta.
- When near-infrared light (980 nm) is applied, the ink fluoresces orange-red.
- This dual-spectrum fluorescence (both ultraviolet and infrared) enhances security features compared to existing inks.
Advantages and Practical Applications
- The ink is low-cost and performs well under different lighting, temperature, and humidity conditions.
- It can be used for security features in documents, currency, and product packaging.
- While screen printing was used in experiments, further research is being conducted to adapt the ink for offset printing, commonly used in banknotes.
2. Madhav National Park becomes India’s 58th Tiger Reserve
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|

Madhav National Park:
- Location: Situated in Shivpuri district, Madhya Pradesh, in the Chambal region.
- Establishment: Declared a national park in 1958.
- Area: Covers approximately 375 sq km.
- New Status: Declared as India’s 58th Tiger Reserve and Madhya Pradesh’s 9th in 2024.
- Tiger Population: Currently home to five tigers, including two cubs.
- Reintroduction Efforts: Three tigers were introduced in 2023, and two more may be added.
- Flora and Fauna: Rich biodiversity, including leopards, wolves, hyenas, chinkaras, sambar, and various bird species.
- Historical Significance: The park was once a royal hunting ground for the Gwalior dynasty.
- Water Bodies: Includes the Sakhya Sagar Lake, supporting aquatic life and bird species.
3. Thakkolam temple, a treasure trove of Tamil history, needs restoration
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 2)
| Context |
|
Thakkolam Temple:

- Location: Thakkolam (historically known as Thiruvural), Ranipet district, Tamil Nadu.
- Historical Significance:
- Built in the 6th century by the Pallavas.
- Inscriptions from the Chola period provide key historical records.
- The site of the Battle of Thakkolam (949 CE) between the Cholas and Rashtrakutas.
- Architecture & Inscriptions:
- Contains 51 inscriptions, including those of Pallava king Aparajita and Chola king Aditya I.
- Mentions grants of land, gold, and goats to the temple.
- Current Condition:
- The northern outer wall has collapsed.
- Temple tank is in a derelict state.
- Kumbabishekam (consecration) not conducted for over 15 years.
- Cultural Importance: Mentioned in Saivite hymns and has deep religious significance.
4. Global Obesity Crisis: Over Half of Adults and One-Third of Children at Risk by 2050
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained, Page – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Current Trends in Global Obesity
- Over half of all adults (380 crore) and a third of all children and adolescents (74.6 crore) worldwide are projected to be overweight or obese by 2050.
- In 2021, 45% of the global population (211 crore people) was overweight or obese.
- India ranks among the top countries, with 18 crore people classified as overweight or obese, and this number is expected to rise significantly by 2050.
Obesity in India
- India is witnessing a rapid increase in obesity rates across all age groups.
- The country may surpass China in absolute numbers in some obesity-related metrics by 2050.
- Urbanization, lifestyle changes, and increasing consumption of processed and calorie-dense foods are key contributors.
Defining Obesity and New Medical Criteria
- Traditionally, obesity is classified based on Body Mass Index (BMI):
- Overweight: BMI 25-30
- Obese: BMI >30
- The new definition of obesity includes parameters such as waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and metabolic dysfunctions.
- “Clinical obesity” now includes physical symptoms, while “pre-clinical obesity” identifies at-risk individuals before major health issues arise.
Impact of the Obesity Epidemic
- Rising Childhood Obesity – The number of obese children and adolescents is growing, increasing future adult obesity rates.
- Increased Risk of Lifestyle Diseases – Higher chances of diabetes, heart disease, and cancer at younger ages.
- Healthcare Burden – Aging populations with obesity require expensive treatments and more surgeries.
- Higher Infection Vulnerability – Obese individuals face greater risks of severe diseases and complications.
- Double Burden of Malnutrition – Many low-income countries face both under-nutrition and obesity, leading to long-term health risks.
Causes Behind the Obesity Epidemic
- Dietary Changes – Growing reliance on high-calorie, processed foods rich in sugar, salt, and fat.
- Market Influence – Multinational food corporations shifting focus to developing nations, where regulations are weaker.
- Urbanization & Sedentary Lifestyles – Reduced physical activity and increased fast-food consumption.
Solutions
- Strengthening Local Food Systems – Supporting traditional food markets to compete with large food companies.
- Government Regulation – Taxing unhealthy foods and restricting aggressive marketing of junk food.
- Healthcare Investment – Expanding obesity management and treatment facilities.
- Policy Implementation – Encouraging national-level action plans to tackle obesity, especially in low-income countries.
- Medical Advancements – Increasing access to new GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs (e.g., semaglutide), while addressing cost and availability challenges.
5. Hantavirus
(Source – Indian Express, Section – Explained- Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

What is Hantavirus?
- Hantavirus refers to a family of rodent-borne viruses that can cause serious illnesses in humans.
- These viruses are transmitted through rodent urine, feces, and saliva but do not spread from person to person.
Types of Hantavirus Diseases
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) – Found in the Western Hemisphere, mainly transmitted by deer mice.
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) – Found in Europe and Asia, causing kidney-related complications.
Symptoms of HPS
- Early symptoms: Fatigue, fever, and muscle aches.
- Advanced stage: Shortness of breath, chest tightness, and lung fluid buildup.
- Mortality rate: 38% of patients with respiratory symptoms die from the disease.
Is There a Cure?
- There is no specific cure or treatment for HPS. Early detection, respiratory support, and antiviral drugs may help manage symptoms.
Prevention Measures
Experts recommend:
- Using gloves, N95 masks, and wet paper towels to clean rodent droppings.
- Avoiding brooms and vacuums to prevent aerosolization.
- Disinfecting surfaces with bleach solutions or commercial disinfectants.
The tragic case underscores the deadly risks posed by hantavirus and the importance of rodent control and hygiene in affected areas.
6. INDIAN ARMY CONTINGENT DEPARTS FOR INDIA- KYRGYZSTAN JOINT SPECIAL FORCES EXERCISE KHANJAR-XII
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2109604 )
| Context |
|
KHANJAR-XII: India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise
- The 12th edition of the India-Kyrgyzstan KHANJAR-XII exercise is scheduled from 10 March to 23 March 2025 in Kyrgyzstan.
- It is a joint special forces training exercise held annually since 2011, alternating between India and Kyrgyzstan.
- The Indian Parachute Regiment (Special Forces) and the Kyrgyz Scorpion Brigade are participating.
- The exercise aims to improve counter-terrorism and special forces operations in urban and high-altitude mountainous terrain.
- Key training areas include sniping, complex building intervention, and mountain craft.
- Cultural exchanges, including Nowruz celebrations, will strengthen ties.
The exercise enhances military cooperation, counter-terrorism capabilities, and regional security
check more – 08 March 2025 : Daily Current Affairs

