13 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. On the allegations against the SEBI chief
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Hindenburg Research’s New Allegations
- Accusations Against SEBI: Hindenburg Research, a New York-based short seller, has released documents claiming that the investigation into the Adani Group by India’s financial regulator, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), is compromised.
- Evidence Presented: The documents include emails and records showing stakes held by SEBI Chairman Madhabi Puri Buch and her husband Dhaval Buch in Adani Group-related entities through offshore funds.
- Conflict of Interest: Hindenburg alleges that these investments indicate a conflict of interest, suggesting that Ms. Buch’s position influenced the investigation in favour of the Adani Group.
| Understanding Short Selling |
|
SEBI Chief’s Alleged Misconduct
- Hindenburg Research alleges SEBI Chairman Madhabi Puri Buch and her husband held hidden stakes in offshore funds linked to Adani stock manipulation.
- It also accused Ms. Buch’s ongoing involvement with Agora Partners and her husband’s appointment at Blackstone.
- Investments in Global Dynamic Opportunities Fund and IPE Plus Fund 1, starting in 2015, raise conflict of interest concerns.
- SEBI counters these claims, asserting that Blackstone was properly recused and maintaining transparency in policy changes.
- The Supreme Court has directed SEBI to investigate potential investor losses and legal infractions. SEBI has completed one of two investigations and defends its integrity against Hindenburg’s attacks.
Key Takeaways
- Allegations of Conflict of Interest: The core issue is the alleged conflict of interest involving SEBI Chairman Madhabi Puri Buch and her husband’s investments and professional engagements.
- Short Selling and Market Manipulation: Short selling can be a tool for market manipulation, raising concerns about the intentions of short sellers.
- SEBI’s Response and Legal Proceedings: SEBI is defending its actions and the Supreme Court is overseeing the investigation, with ongoing scrutiny of the regulator’s handling of the case.
| Practice Question: Examine the governance challenges posed by allegations of conflicts of interest and biassed regulatory actions in financial investigations. How can regulatory bodies ensure transparency and accountability to maintain public trust in their oversight functions? (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Centre and States are in for a confrontation over redistribution of taxes: Thomas Isaac
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Federal Structure |
| Context |
|
Levy of Cesses and Surcharges by the Union Government
- The Union government imposes cesses and surcharges, which are not part of the divisible pool of taxes shared with States.
- Between 2015-16 and 2018-19, States reportedly lost approximately ₹5.26 lakh crore due to these levies, reducing the resources available for distribution.
Discriminatory Redistribution of the Divisible Pool
- The central redistribution of the divisible pool of taxes is perceived as discriminatory, with some States receiving a smaller share compared to others.
- Examples include Tamil Nadu receiving only 29% of its contributions back, Maharashtra 10%, while Kerala gets 57%, compared to higher shares for States like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
Challenges in Fiscal Federalism
Lack of Objective Criteria for Resource Transfer
- There is a need for transparent and objective criteria for transferring resources to ensure fairness and equity among States.
- Current devolution practices are seen as inequitable, leading to fiscal stress for some States.
Impact on State Finances
- States argue that the current system restricts their financial autonomy and ability to effectively manage their resources.
- The fiscal pressure is particularly acute for States investing heavily in social sectors, facing reduced funding from the Centre.
Implications for Backward States
Limited Economic Improvement Despite Higher Share
- Despite receiving a higher share from the divisible pool, many backward States have not shown significant improvement in per capita income.
- This raises questions about the effectiveness of the current redistribution model in promoting balanced regional development.
Constraints Post-GST Implementation
Reduced Taxation Powers for States
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has limited the taxation powers of States, restricting them to levying taxes mainly on petrol, diesel, and alcohol.
- This has further constrained States’ ability to generate revenue independently, increasing reliance on central transfers.
Political Dimensions
Perceived Discrimination Against Opposition-Ruled States
- There is an allegation that the Union government discriminates against Opposition-ruled States, particularly those investing significantly in social sectors.
- This perceived bias adds a political dimension to the fiscal confrontation, with claims of financial squeezing of these States.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges of fiscal federalism in India with reference to the imposition of cesses and surcharges by the Union government and their impact on state finances. How can a more equitable system of tax redistribution be achieved? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. The tech that helps vehicles from bumping into each other
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Collision Avoidance Systems (CAS):
- Definition: Collision Avoidance System (CAS) is a technology designed to prevent vehicle collisions by monitoring the location of other vehicles and obstacles.
- Land-Based Vehicles:
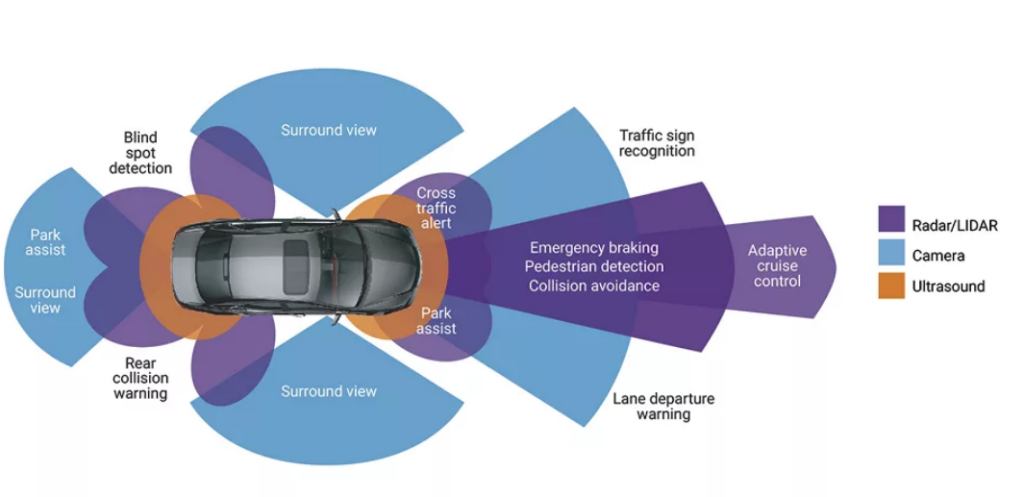
Collision Avoidance Systems (CAS)
- Function: Tracks the speed, distance, and relative positions of vehicles.
- Components: Includes sensors (radar, lidar, cameras), onboard computers, and automatic emergency braking systems.
- Example: In cars, CAS can automatically apply brakes if a collision with a preceding vehicle is imminent.
- Railways:
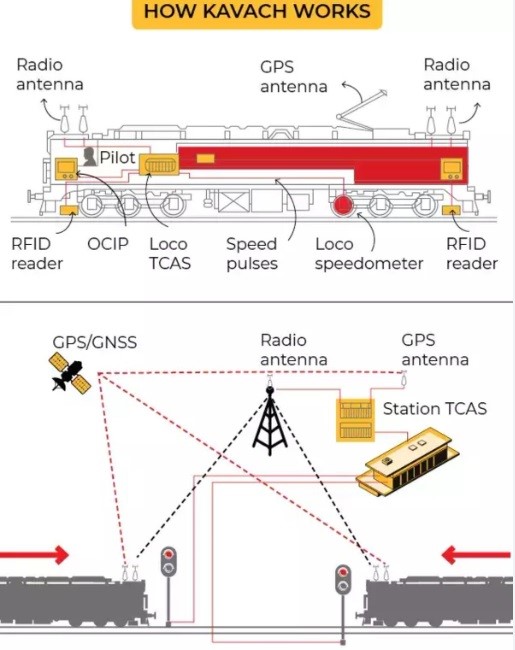
- System: India’s ‘Kavach’ consists of onboard computers, trackside computers, and communication systems.
- Components: RFID readers, ultra-high frequency radio, GSM-Railway.
- Function: Communicates with station masters, facilitates decision-making, maintains speed, and applies emergency brakes if necessary.
- Aircraft:
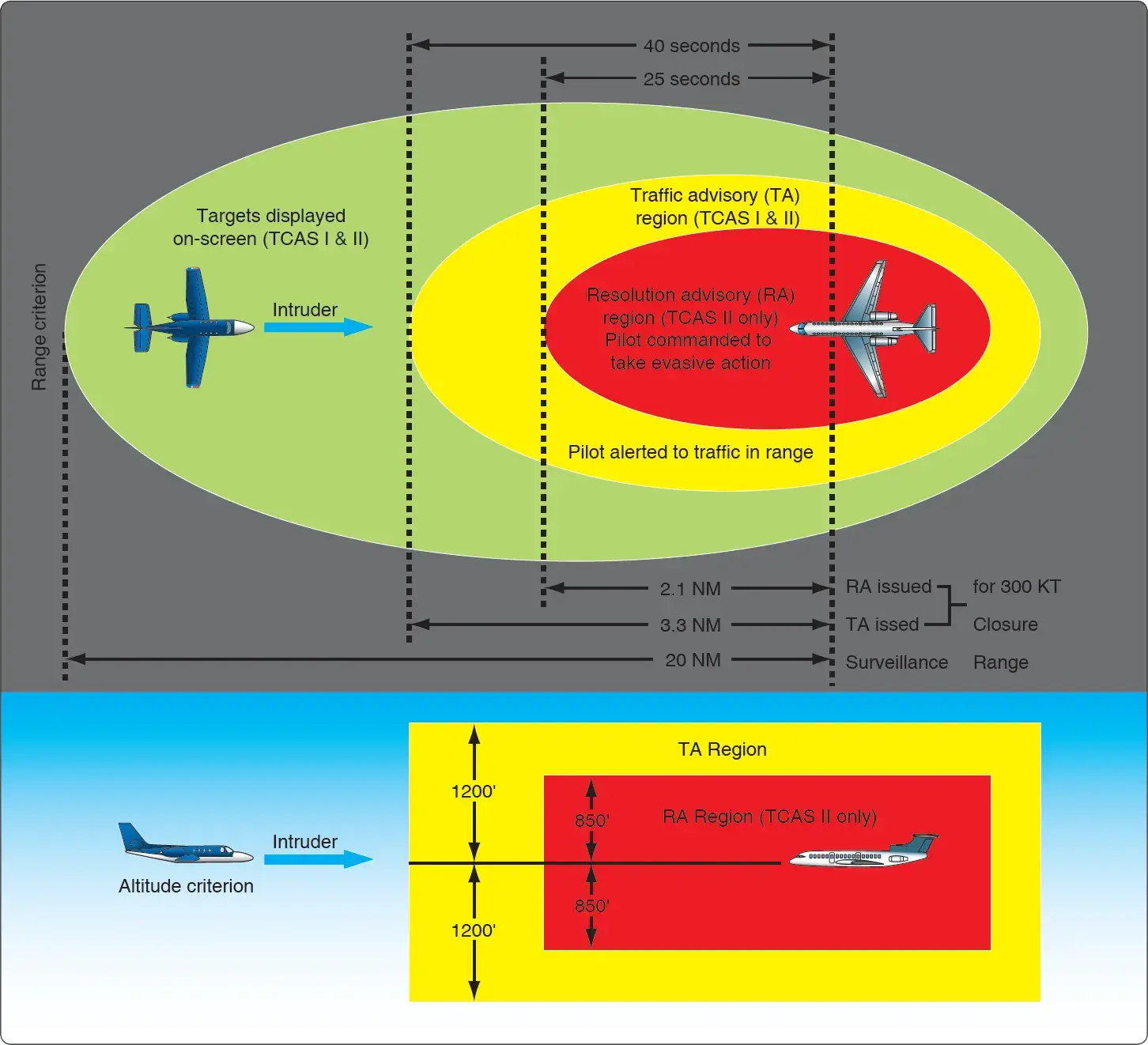
- System: Traffic Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) uses transponders and radar altimeters.
- Function: Builds a 3D view of nearby aircraft and issues traffic advisories or resolution advisories if a collision risk is detected.
- Ships:
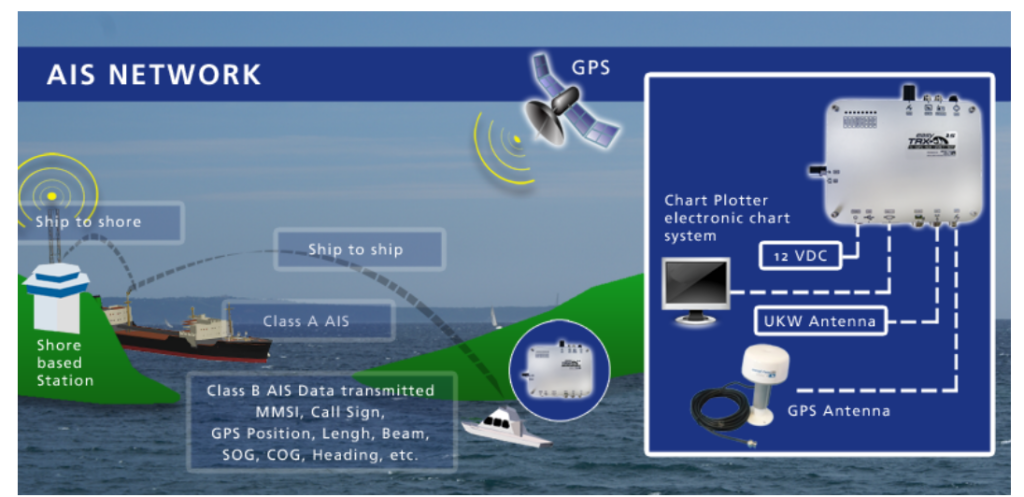
- Systems: Automatic Identification System (AIS) and Long Range Identification and Tracking (LRIT).
- Function: Tracks and reports ships’ positions, speed, and bearing, with satellite-enhanced AIS for remote tracking.
- Satellites:
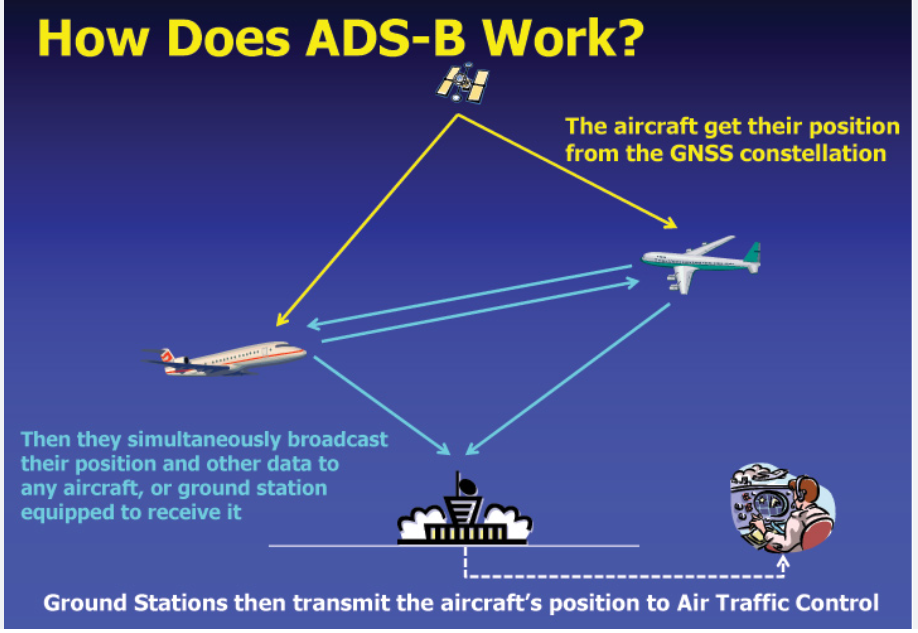
- Technology: Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) for aircraft and Satellite-AIS for ships enhance CAS capabilities using GPS data and satellite communication.
4. Highly porous Xerogel dressing can save lives by clotting blood faster
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2044556 )
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Development: Researchers at Agharkar Research Institute (ARI), Pune, have created a porous composite xerogel dressing incorporating silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) and calcium for rapid blood clotting and uncontrolled haemorrhage management.
| What Is Xerogel? |
|
- Performance: The xerogel demonstrated a 13-fold increase in blood clotting efficiency compared to commercial dressings.
- Structure: The dressing features multiple pores of approximately 30 µm in size, enhancing its absorbance capacity and effectiveness.
- Mechanism: The composite improves blood clotting by promoting platelet aggregation and enhanced calcium release.
- Significance: This advanced dressing addresses the limitations of traditional gauze and natural clotting mechanisms, offering a potential solution to manage severe haemorrhage, a leading cause of trauma-related deaths.
- Publication: The study detailing the xerogel’s efficacy is published in the Journal of Applied Polymer Science.
5. 2D electron gas creates possibilities for ultra-fast, low-power electronics
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2044555 )
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Discovery of Transparent Spin-Polarised Electron Gas
- Breakthrough: Researchers at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, developed a transparent layer between two insulating materials with room temperature spin-polarised electron gas.
- Material Composition: The interface comprises LaFeO₃ and SrTiO₃ oxides, creating a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) with spin polarisation at room temperature.
- Potential Applications:
- Spintronics: Enhances data transfer speed and storage capacity in quantum devices.
- Transparent Electronics: Enables see-through devices, such as transparent phone screens or solar cells with advanced functionalities.
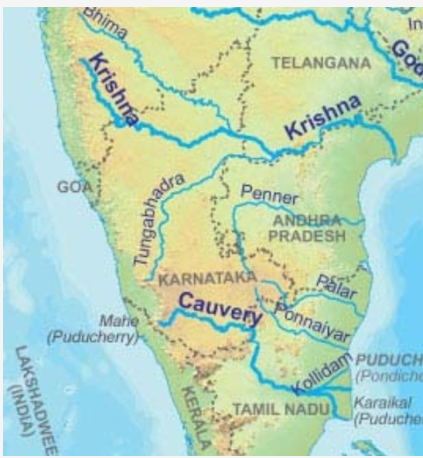
6. Flood Alert Issued After Crest Gate Failure at Karnataka’s Tungabhadra Dam
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

- Dam Specifications: The Tungabhadra dam, built across the Tungabhadra river, has a reservoir capacity of 105.8 TMC ft. On August 10, the dam was at its maximum level of 1,633 ft. The dam plays a crucial role in supplying water for irrigation, industrial use, and drinking purposes in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- Repair and Risks: Repairs can only commence after two-thirds of the dam’s water is discharged, which raises concerns among farmers about the impact on irrigation. There are also fears of potential flooding due to increased water release. The Karnataka State Natural Disaster Monitoring Centre has issued a flood alert for downstream areas.
- Historical Context: The Tungabhadra dam, initially conceived in 1860 and completed in 1953, is one of South India’s major reservoirs. The dam is managed by the Tungabhadra Board, established in 1953, which includes representatives from the Union government and the states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Current Outlook: While heavy rainfall could worsen the situation, no significant rain is forecast in the coming days. However, the incident has heightened concerns for farmers, especially after last year’s drought. The projected inflow of 50-60 TMC ft in September and October is expected to aid farmers in cultivating at least one crop this year.
| About Tungabhadra River |
|
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the recent crest gate failure at the Tungabhadra dam in Karnataka on disaster management and water resource management. (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. India- Sri Lanka Joint Military Exercise Mitra Shakti Commences In Maduru Oya, Sri Lanka
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2044570 )
| Context |
|
Exercise MITRA SHAKTI:
- Participating Countries: India and Sri Lanka
- Location Of Exercise: Sri Lanka
- Dates: August 12 to August 25, 2024
- Participants:
- Indian Contingent: 106 personnel from Rajputana Rifles and other arms/services
- Sri Lankan Contingent: Personnel from the Gajaba Regiment
- Objective: Enhance joint military capabilities for counter-insurgency operations in semi-urban scenarios under UN Chapter VII mandate
- Focus Areas:
- Response to terrorist actions
- Establishing joint command posts and intelligence centres
- Securing helipads and landing sites
- Small team insertion and extraction
- Special heliborne operations and cordon & search
- Use of drones and counter-drone systems
- Goals: Improve interoperability, share best practices, and strengthen defence cooperation and bilateral relations between India and Sri Lanka
2. Government of India has declared August 23rd as “National Space Day” to celebrate the remarkable success of the Chandrayaan-3 Mission
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2044457 )
| Context |
|
Chandrayaan-3 Mission:
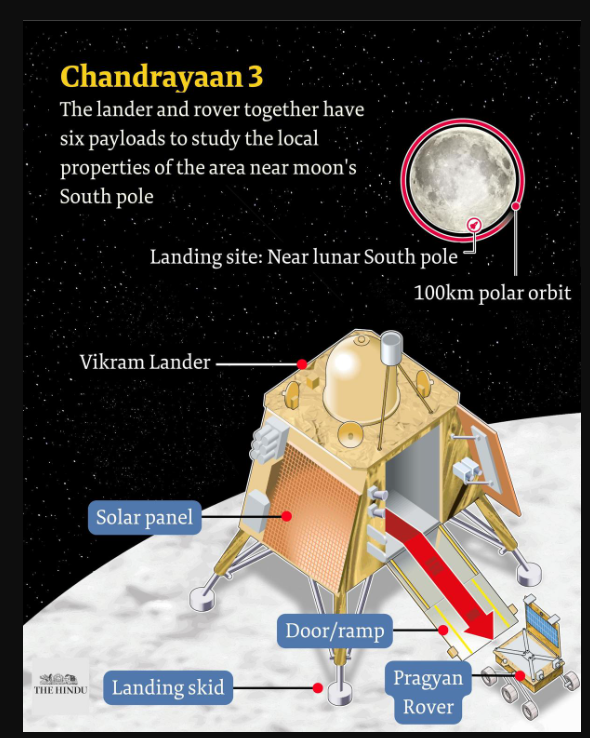
- Objective: The Chandrayaan-3 mission, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), aims to achieve a successful soft landing on the Moon’s surface, focusing on the lunar south pole.
- Launch Date: The mission was launched on July 14, 2023, using a GSLV Mk III rocket.
- Components: The mission comprises a lander named Vikram and a rover named Pragyan, with no orbiter, as Chandrayaan-2’s orbiter is still operational.
- Scientific Goals: It seeks to enhance lunar surface exploration, study lunar geology, and test new technologies for soft landing and mobility on the Moon.
- Significance: Chandrayaan-3 aims to build on the partial success of Chandrayaan-2 by achieving a fully successful soft landing and deploying a rover to conduct experiments on the lunar surface.
3. IIT-Madras retains top spot in NIRF ranking for sixth consecutive year
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- IIT-Madras ranked as the best educational institution in India for the sixth time since 2019.
- IIT-Madras also retained the top position in engineering for the ninth consecutive year.
- Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru ranked highest in universities and research categories.
- New NIRF categories: open universities, skill universities, and State public universities.
- IIM-Ahmedabad continued as the top management institute for the fifth year.
- AIIMS, New Delhi remains the best in medical sciences for seven years.
- IIT-Bombay is the top institution for innovation.
- Increased participation in 2024: 6,517 institutions, 10,845 applications.

| National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) |
|
4. Suspected case of Chandipura virus found in M.P.’s Indore
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Chandipura Virus:

- Origin: Chandipura virus was first identified in 1965 in the village of Chandipura in Maharashtra, India.
- Transmission: The virus is primarily transmitted by sandflies, particularly the Phlebotomus species.
- Geographic Distribution: While initially reported in India, outbreaks have also been observed in neighbouring countries like Nepal and Bangladesh.
- Symptoms: The virus can cause an acute encephalitic illness characterised by sudden high fever, convulsions, altered mental status, and sometimes coma. It primarily affects children.
- Outbreaks: Notable outbreaks have occurred in central and western India, with significant mortality rates among children.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically made through serological tests and RT-PCR to detect the virus in blood or cerebrospinal fluid.
- Prevention and Control: Control measures focus on reducing sandfly populations and avoiding exposure, as there is currently no specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for the Chandipura virus.
5. India Withdraws Support for UNESCO Kalinga Prize, Sparking Protests from Odisha’s Naveen Patnaik
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 08)
| Context: |
| The Indian government has withdrawn its annual contribution to the UNESCO Kalinga Prize for Popularisation of Science. |
Analysis of News:
Withdrawal of DST’s Contribution to UNESCO Kalinga Prize
- The Ministry of Science and Technology has withdrawn its annual contribution to the UNESCO Kalinga Prize for Popularisation of Science, one of UNESCO’s oldest awards, established in 1951 through a donation by former Odisha Chief Minister Biju Patnaik.
- The decision is part of the government’s recent move to “rationalize” science awards, leading to the replacement of previous awards, including the prestigious Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Awards, with a new set of honors called the Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP).
- The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is one of the highest recognitions in the field of science, technology, and innovation in India
- The RVP is awarded in four categories i.e., the Vigyan Yuva-SSB, the Vigyan Shri, Vigyan Ratna and Vigyan Team awards.
About the prize
- The UNESCO Kalinga Prize for the Popularization of Science is UNESCO’s oldest prize.
- It was created in 1951 following a donation from Mr Bijoyanand Patnaik, Founder and President of the Kalinga Foundation Trust in India. The prize is awarded biennially.
Purpose
- The Kalinga Prize rewards the contribution of an individual, institution, non-governmental organization (NGO) or other entity that has made a significant contribution to the popularization of science or technology and has helped interpret science and technology for the public and contributed to bridging the gap between science and society.
Donors
- The Prize is funded by the Kalinga Foundation Trust, the Government of the State of Orissa, and the Government of India (Department of Science and Technology).
6. Kerala’s Last Paradesi Jewish Woman Passes Away, Marking the End of an Era
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Context: |
| Queenie Hallegua, the last woman of Kerala’s Paradesi Jewish community, passed away in Kochi at the age of 89, leaving her nephew, Keith, as the last Paradesi Jew in the state. |
Analysis of News:
The Decline of Kerala’s Jewish Community
- Kerala’s Jewish population, once vibrant, has dwindled significantly. From a population of 20,000-50,000 in the mid-1940s, India’s Jewish community now comprises around 4,000-5,000 members, primarily from the Bene Israel community.
- Kerala’s Jewish history, however, dates back to ancient times, with two main Jewish groups:
- the Malabar Jews, who have roots tracing back almost 3,000 years, and
- the Paradesi Jews, who arrived from the Iberian Peninsula in the 15th and 16th centuries.
Cultural Legacy and Migration
- Over time, the Paradesi Jews became a distinct community, often regarded separately from the older Malabar Jews.
- Despite their integration into local society, the Jewish communities in Kerala have faced a steady decline due to migration, primarily to Israel.
- Today, only 14 Malabar Jews and one Paradesi Jew remain in Kerala. The state’s Jewish heritage is now preserved in relics like “Jew Streets,” synagogues, and former Jewish-owned businesses.
7. Ukrainian Forces Advance 30 km into Russian Territory in Kursk Oblast, Largest Incursion Since 2022
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
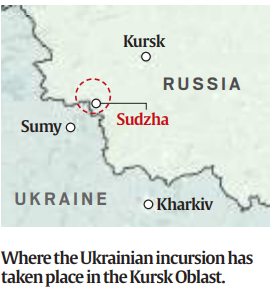
Potential Objectives:
- The motivations behind Ukraine’s attack are not entirely clear. Analysts suggest it could be a strategic move to gain leverage in potential negotiations, possibly by capturing Russian territory to exchange for Ukrainian land held by Russia.
- Another theory posits that Ukraine may aim to capture the Kursk nuclear power plant, just 60 km from the border, in retaliation for Russia’s seizure of the Zaporizhzhia plant.
Implications:
- It is uncertain whether Ukraine can maintain its current gains. Holding the territory would require significant additional resources.
- The move is seen as either a bold strategic initiative to shift the war’s momentum or a risky decision that might complicate Ukraine’s defensive efforts in the east.
8. Ancient Calendar Discovered at Gobekli Tepe: Earliest Record of Comet Strike 12,000 Years Ago
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The World; Page: 14)
| Context: |
| Martin Sweatman, a researcher at the University of Edinburgh, claims to have discovered the earliest known lunisolar calendar at Gobekli Tepe, an ancient archaeological site in southern Turkey. |
Analysis of News:

Significance:
- Sweatman suggests that V-shaped markings on a pillar at the site represent a calendar combining the movements of the sun and moon, documenting a major comet strike around 10,850 B.C.
- This event is believed to have caused a 1,200-year ice age and significantly impacted Earth’s environment and human civilization.
Implications:
- Sweatman’s research suggests that ancient people at Gobekli Tepe were capable of recording astronomical events and tracking time through a solar calendar, indicating a sophisticated understanding of the cosmos and timekeeping.
- This discovery could offer new insights into early human civilization and its development.
Breakthrough:
- The identification of the V-shaped symbols as calendar markers was prompted by an external tip, leading to the conclusion that these symbols represent a 365-day solar calendar with 12 lunar months and an additional 11 days, marking the summer solstice and other significant astronomical events.
9. China Tests Largest Civilian Cargo Drone, Advancing Low-Altitude Economy Ambitions
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 15)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
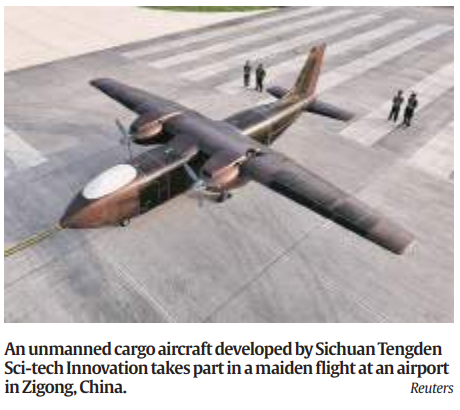

- Strategic Significance: This test is part of China’s broader initiative to expand its low-altitude economy, with the government aiming to grow the UAV industry to a 2-trillion-yuan ($279 billion) market by 2030. The development of larger UAVs is a key aspect of this strategy, focusing on applications in cargo delivery and potentially passenger transport.
- Economic Impact: The expansion of UAV capabilities is expected to be a major driver of China’s low-altitude economy, particularly in logistics, transport, and other commercial sectors. The industry is rapidly growing, with over 2,000 enterprises involved, led by global drone giant DJI.
- Future Prospects: The ongoing development and testing of larger UAVs suggest a future where drones play a central role in both cargo and passenger transport, marking a significant shift in logistics and mobility solutions.

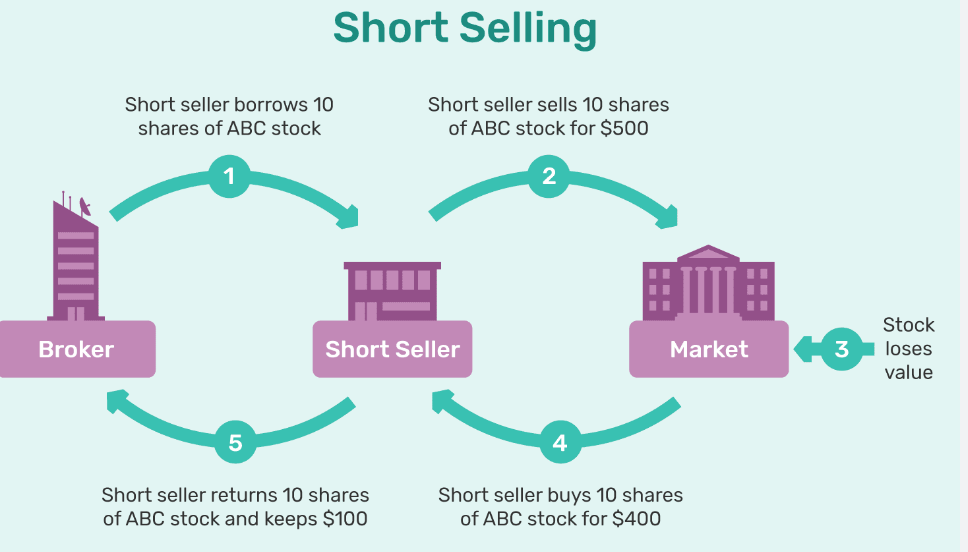 Definition: Short selling involves profiting from a decline in the price of a stock. It involves selling borrowed shares with the expectation of buying them back at a lower price.
Definition: Short selling involves profiting from a decline in the price of a stock. It involves selling borrowed shares with the expectation of buying them back at a lower price.