13 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Stay on bail should only be granted in rare cases, says SC
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Supreme Court highlighted a concerning trend where higher courts frequently stall bail, posing a threat to personal liberty and due process.
- Justices A.S. Oka and Ujjal Bhuyan criticised the routine staying of reasoned bail orders by trial courts, labelling it “shocking”.
- They emphasised that bail should only be stayed in rare and exceptional cases, such as evident legal perversity or cases involving terrorists.
- The Court plans to issue a formal judgement on “casual” orders by High Courts that stay bail granted by trial courts.
- This discussion arose from Parvinder Khurana’s appeal, whose bail in a money laundering case was stayed by the Delhi High Court for over a year.
- Justice Oka questioned the necessity and duration of such stays, stressing that bail conditions should prevent absconding or witness tampering.
- Solicitor-General Tushar Mehta argued that bail conditions are only effective within the court’s jurisdiction, suggesting that High Courts should provide reasons when staying bail orders.
| Right to Default Bail: Supreme Court Decision |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the Supreme Court’s stance on the routine staying of bail orders by higher courts in the context of personal liberty and due process. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. India shows good progress on SDGs: NITI Aayog report
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
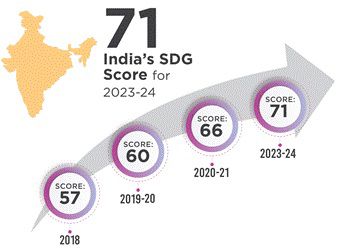
- NITI Aayog released its fourth evaluation report on India’s progress toward the 16 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the UN in 2015.
| Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): |
|
Adopted: In 2015 by the United Nations General Assembly, comprising 17 goals aimed at addressing global challenges by 2030. Scope: Covering social, economic, and environmental dimensions of sustainable development to eradicate poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all. Goals Include:
Importance: Provide a universal framework for global cooperation towards sustainable development, encouraging governments, businesses, and civil society to take action. Progress: Regular monitoring and reporting mechanisms track progress at national and international levels to ensure accountability and transparency. |
- India scored 71 out of 100 in 2023, up from 57 in 2018.
- NITI Aayog CEO B.V.R. Subrahmanyam emphasised the link between SDGs and people’s welfare, well-being, and quality of life.
- Improved health conditions were attributed to better public health and insurance coverage.
- Education benefited from high teacher-student ratios, but teacher quality requires targeted interventions.
- The report highlighted declines in income and gender inequality scores.
- Notably, the ratio of women’s earnings compared to men’s decreased from 0.75 last year to 0.73.
- The report’s release precedes the High-level Political Forum on Sustainable Development scheduled for July 18 in New York under UN auspices.
| PYQ: Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of NITI Aayog’s latest evaluation report on India’s progress towards Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), highlighting key improvements and remaining challenges. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. The Government to soon launch an ‘Agri Fund for Start-Ups & Rural Enterprises’ (AgriSURE) to provide support to Startup and Agripreneurs
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2032838 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government Policies, GS3 – Agriculture – E-technology in the aid of farmers. |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Indian Government announced the launch of ‘Agri Fund for Start-Ups & Rural Enterprises’ (AgriSURE) during a stakeholder meet in Mumbai.
- AgriSURE is a Rs 750 crore Category-II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) aimed at supporting start-ups and agripreneurs in the agriculture and allied sectors.
- It will provide equity and debt investments, focusing on innovation and sustainability across the agriculture value chain.
- The fund will be financed with Rs 250 crores each from the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare and NABARD, with an additional Rs 250 crores raised from financial institutions.
- NABVENTURES, a subsidiary of NABARD, will manage the fund, which aims to enhance farm produce value chains, rural infrastructure, and support Farmers Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Features include promoting IT-based solutions, machinery rental services for farmers, and fostering employment generation.
- Concurrently, NABARD launched the AgriSURE Greenathon 2024, addressing challenges such as cost-effective smart agriculture, utilising agri-waste profitably, and promoting regenerative agriculture practices.
- The initiative underscores collaboration between public and private sectors to drive agricultural innovation and growth.
| PYQ: How does e-Technology help farmers in production and marketing of agricultural produce? Explain it. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the importance and impact of financial support initiatives like the AgriSURE fund in fostering innovation and sustainability in agribusinesses in India. (150 Words /10 marks) |
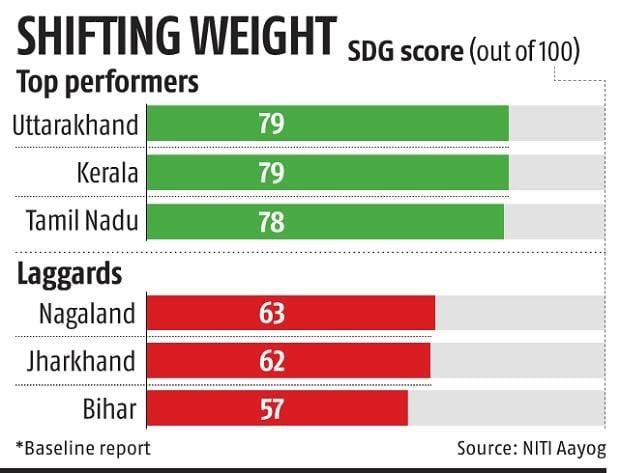
4. Release of SDG India Index 2023-24 By NITI Ayog
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2032857 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
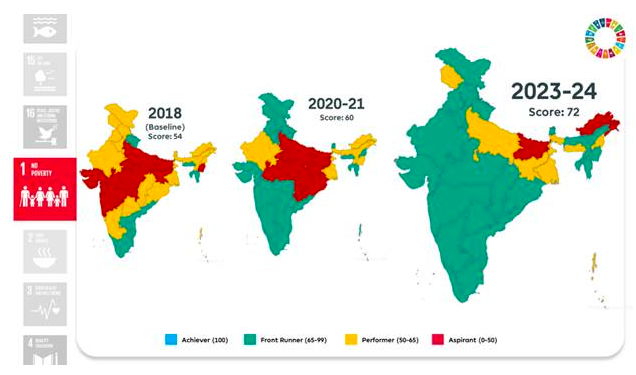
Goal 1: No Poverty
- Multidimensional poverty reduced significantly from 24.8% to 14.96% between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- Employment generation through MGNREGA reached 99.7% coverage in 2023-24.
- Housing coverage expanded with nearly 95.4% of households living in pucca or semi-pucca houses.
- Health insurance coverage increased to 41% of households.
Goal 2: Zero Hunger
- NFSA coverage extended to 99.01% of beneficiaries.
- Productivity gains in agriculture with increased rice and wheat yields.
- Improved Gross Value Added (GVA) per worker in agriculture.
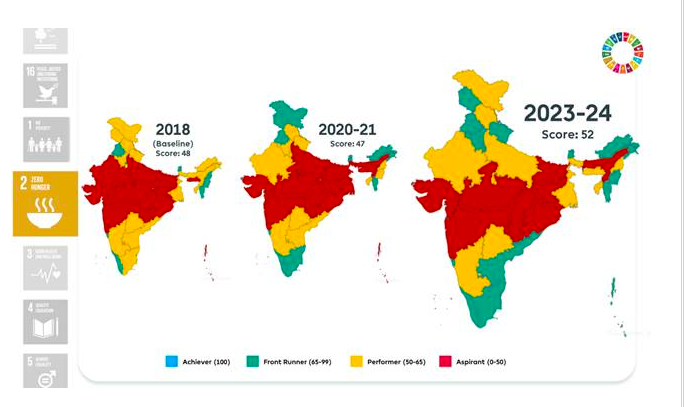
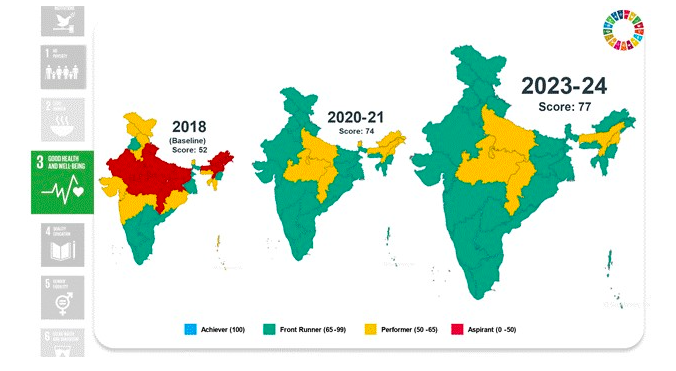
Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Maternal mortality rate reduced to 97 per 100,000 live births.
- Under-5 mortality rate decreased from 36 to 32 per 1,000 live births.
- High immunisation coverage with 93.23% of children fully immunised.
- Significant progress in tuberculosis case notifications and institutional deliveries.
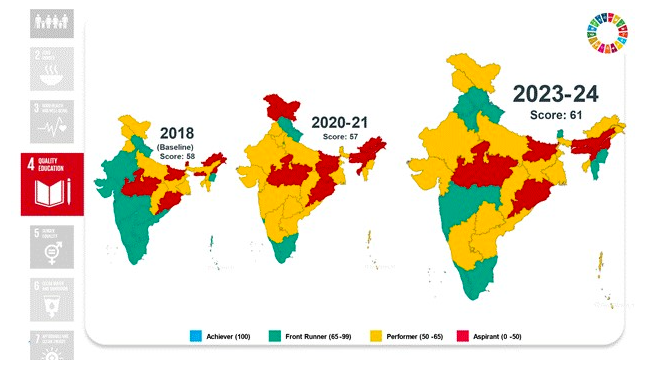
Goal 4: Quality Education
- Elementary education ANER at 96.5%, with 14 States/UTs achieving 100% enrolment.
- Pupil-teacher ratio improved to 18, meeting the target.
- Enhanced infrastructure with 88.65% schools having access to electricity and drinking water.
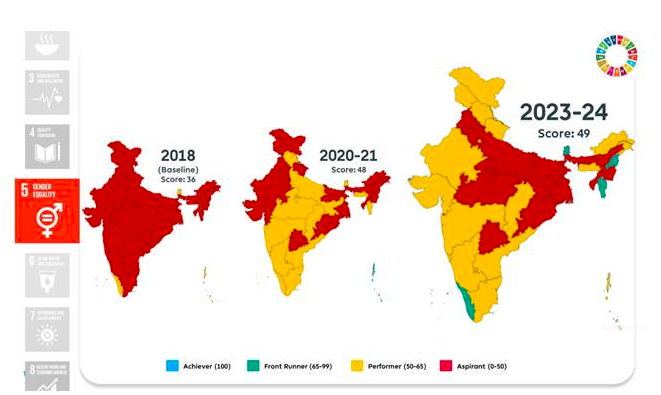
Goal 5: Gender Equality
- Improved sex ratio at birth of 929 females per 1,000 males.
- Increased female-to-male earnings ratio and labour force participation rate.
- Advancements in family planning met and mobile phone ownership among women.
Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Score improved from 63 to 89.
- Universal individual household toilet coverage under SBM (G).
- Significant rural household access to improved drinking water sources.
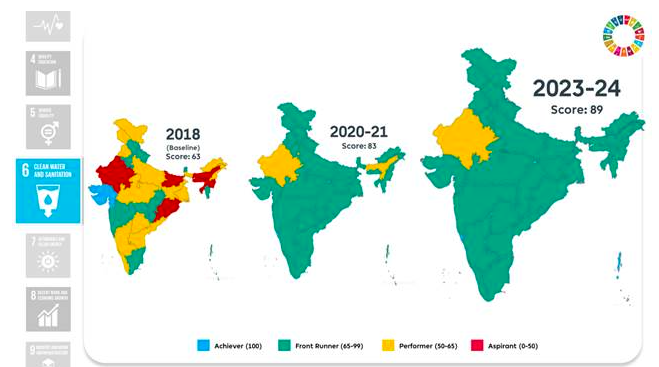
Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Highest score among SDGs with a score of 96.
- Saubhagya scheme achieving 100% household electricity access.
- Growth in clean cooking fuel connections (LPG + PNG) to 96.35% by 2024.
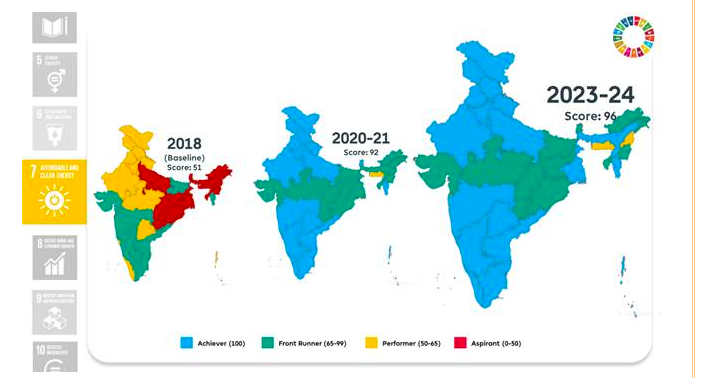
Goal 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- GDP per capita growth at 5.88% in 2022-23.
- Unemployment rate reduced to 3.40% in 2022-23.
- Increased LFPR and financial inclusion through PMJDY.
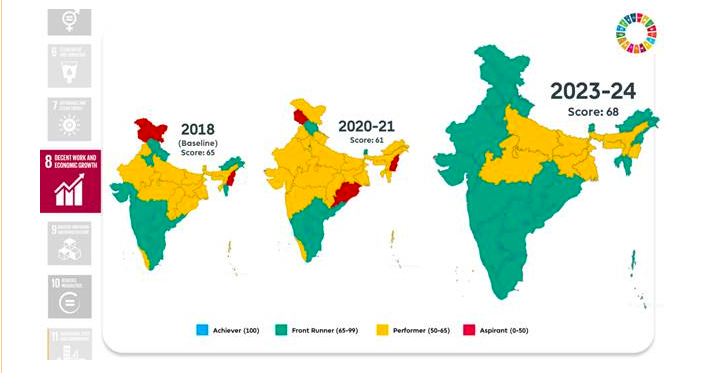
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Improved infrastructure connectivity with 99.70% habitations connected via PMGSY.
- High mobile phone penetration and improved internet coverage.
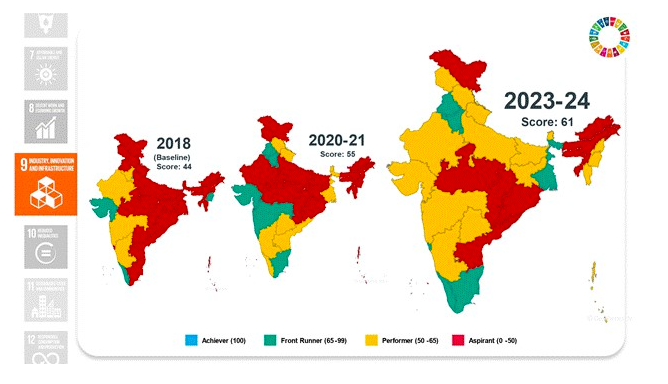
Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Increased women’s representation in Panchayati Raj institutions to 45.61%.
- Enhanced SC/ST representation in state legislative assemblies to 28.57%.
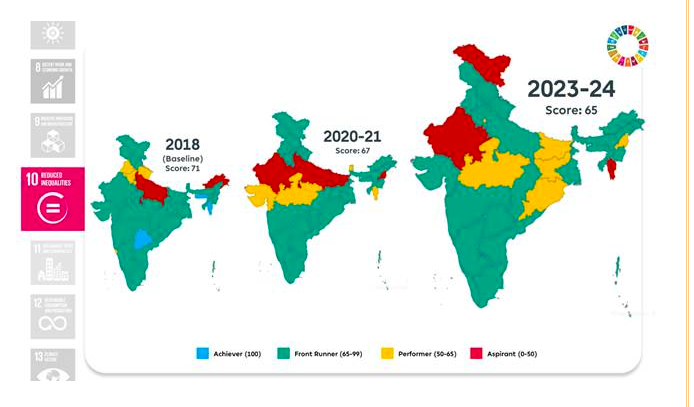
Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Score improved from 39 to 83.
- Enhanced sewage treatment and municipal solid waste processing capacities.
- High coverage of door-to-door waste collection and source segregation under SBM (U).
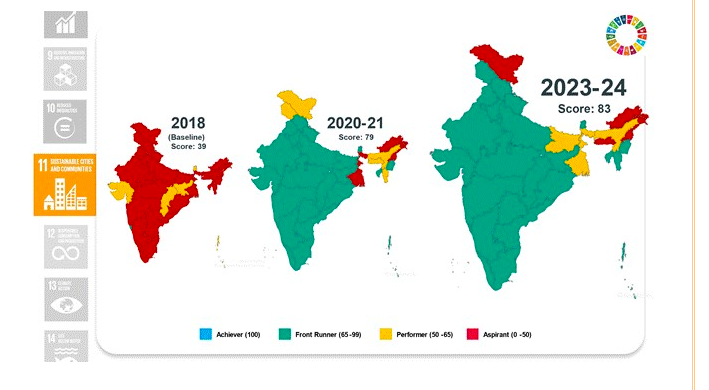
Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Biomedical waste treatment increased to 91.5% in 2022.
- Improved hazardous waste recycling to 54.99% in 2022-23.
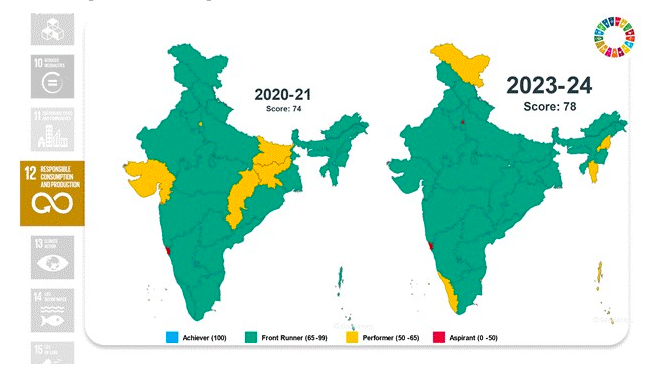
Goal 13: Climate Action
- Significant increase in score from 54 to 67.
- Improved disaster preparedness and renewable energy generation.
- High compliance with environmental standards among industries.
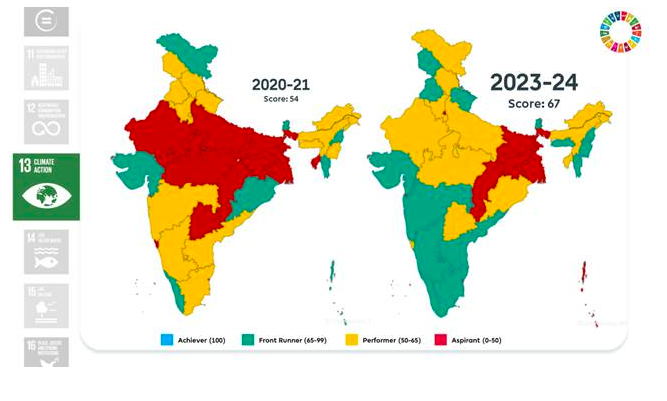
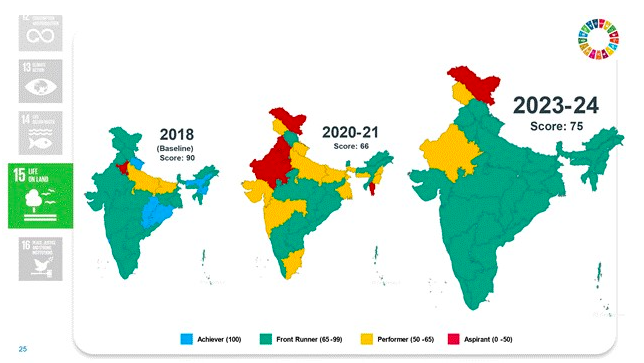
Goal 15: Life on Land
- Score increased from 66 to 75.
- Expanded forest and tree cover to nearly 25% of geographical area.
- Increase in carbon stock in forest cover.
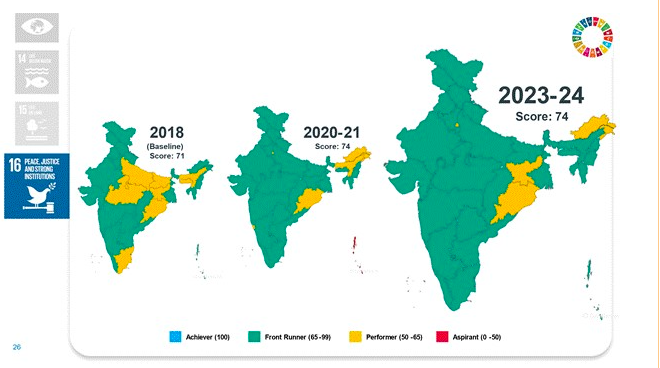
Goal 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- High Aadhaar coverage at 95.5%.
- Improved birth registration rates and IPC crime charge sheeting.
| PYQ: Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss India’s progress and achievements in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as highlighted in the SDG India Index 2023-24. Highlight key initiatives and their impact on national development. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. Indian Armed Forces Plan Joint Procurement of Explosive Vans to Enhance Integration and Safety
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 08)
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Objective of the Theaterisation Plan
- The theaterisation plan seeks to create a unified command structure that can efficiently deploy and utilize the combined resources of the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- By integrating their capabilities, the plan aims to enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Joint procurement of equipment, such as the explosive vans, is a significant move towards achieving this integration.
- A common platform for transporting ammunition will enable joint operation commanders to better support integrated operations.
Process and Specifications
- The Army, leading the joint procurement effort, has issued a Request for Information (RFI) to gather details from potential suppliers.
- The explosive vans will be designed to safely transport various types of ammunition owned by the three services to different locations, minimizing the risk of fire and other accidents.
- These vans are expected to be based on the in-service 5/7.5 MT 4×4 chassis vehicles and will undergo field evaluation trials in India to ensure they meet the required specifications.
Benefits of Joint Procurement
Joint procurement of explosive vans offers several advantages:
- Reduced Inventory and Optimized Infrastructure: A common platform will reduce the need for separate inventories for each service, optimize repair infrastructure, and decrease storage space requirements.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Resource Diversion: A standardized platform will allow easier diversion of resources between services, enhancing operational flexibility.
- Increased Interoperability: Joint procurement will increase interoperability among the services, enabling more coordinated and efficient operations.
Efficiency and Safety Improvements
- Currently, ammunition is transported in General Staff (GS) vehicles, which are considered hazardous and inadequate due to fire and security issues.
- The new explosive vans will enhance the functional efficiency and operational preparedness of the tri-services.
- They are designed to reduce the risk of accidents during transportation and increase overall efficiency by shortening the supply chain and optimizing maintenance processes.
Conclusion
- The joint procurement of explosive vans by the Indian Armed Forces represents a significant step towards achieving the objectives of the theaterisation plan.
- By integrating the capabilities and resources of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, this initiative aims to enhance operational efficiency, safety, and flexibility.
- The specialized vans will not only reduce the risk of accidents during ammunition transport but also improve the overall efficiency of the logistical operations of the tri-services.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of joint tri-service procurement of explosive vans by the Indian Armed Forces. How does this initiative contribute to enhancing integration, operational efficiency, and safety? Evaluate the potential challenges and benefits associated with such joint procurement in the context of India’s defense preparedness and theaterisation plan. (250 words/15 m) |
6. Union Budget Likely to Maintain Status Quo on Fertilizer Sector Amid Political Challenges and Fiscal Constraints
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Economic Implications for Fertilizer Sector
- Given the current political climate, significant changes in the maximum retail price (MRP) of urea are not expected.
- Urea prices have remained fixed at Rs 5,360 per tonne since November 2012 and at Rs 5,628 per tonne for neem-coated urea since January 2015.
- The continuation of these prices indicates a cautious approach by the government to avoid potential backlash from the agricultural sector.
Fertilizer Price Controls and Subsidies
Urea and Non-Urea Fertilizers
- The central government is unlikely to deregulate the MRPs of non-urea fertilizers like di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) and muriate of potash (MOP), which are technically under the nutrient-based subsidy (NBS) regime.
- Despite being labeled “decontrolled,” these fertilizers are subject to informal price controls.
- The government prescribes maximum profit margins over cost to determine the reasonableness of MRPs, ensuring that companies charging more cannot receive subsidies under NBS.
- Current reasonable MRPs are Rs 27,000 per tonne for DAP and Rs 30,000-31,000 per tonne for MOP.
Fiscal Impact
- The government’s fiscal pressure to increase MRPs of fertilizers is minimal.
- The fertilizer subsidy budget for 2024-25 is Rs 1,63,999.80 crore, down from Rs 1,89,487.44 crore in 2023-24 and Rs 2,51,339.36 crore in 2022-23.
- This reduction is partly due to the decline in landed prices of imported fertilizers and key inputs like phosphoric acid and ammonia.
- Consequently, the government may maintain current price controls to manage subsidy expenses effectively.
Potential Reforms and Industry Challenges
Deregulation and New Product Registration
- A feasible reform could be the deregulation of fertilizers not covered under any subsidy.
- Currently, registering a new fertilizer product in India takes an average of 804 days, significantly longer than in many other countries.
- Simplifying the registration process by granting automatic registration for products meeting specific nutrient and contaminant criteria could streamline market entry for new fertilizers, fostering innovation and competition.
Water-Soluble Fertilizers (WSF)
- The model for water-soluble fertilizers (WSF), which allows for automatic registration subject to basic quality parameters and truthful labeling, has been successful since its implementation in October 2015.
- Extending this model to all non-subsidized fertilizers could further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of fertilizer use.
- WSFs are particularly beneficial for high-value crops and drip irrigation systems, offering higher nutrient absorption rates compared to traditional fertilizers.
High-Value Nutrients and Liquid Fertilizers
- WSFs and liquid fertilizers offer higher nutrient use efficiency, with crops absorbing 60-70% of nutrients from WSFs and 80-90% from liquid fertilizers, compared to 30-35% from field-applied fertilizers.
- Despite their higher cost, the efficiency and effectiveness of these fertilizers justify their deregulation.
- A proposal to deregulate liquid fertilizers, similar to WSFs, is under consideration, potentially improving nutrient management practices in Indian agriculture.
Conclusion
- The Union Budget is expected to maintain the status quo for the fertilizer sector, avoiding significant reforms due to the current political and economic context.
- However, potential reforms in deregulating non-subsidized fertilizers and simplifying the registration process could foster innovation and improve nutrient use efficiency.
- Extending the WSF model to other fertilizers could also enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability.
| Practice Question: Examine the reasons behind the expected lack of major reforms in the fertilizer sector in the upcoming Union Budget, considering the political and economic context. Additionally, discuss the potential minor reforms that could be implemented to improve the sector’s efficiency and productivity. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Ancient Plague Linked to Neolithic Population Collapse in Northern Europe, New Study Reveals
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 10)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
New Study and Its Methodology
- A recent study titled “Repeated plague infections across six generations of Neolithic Farmers,” published in Nature, suggests that disease, specifically the plague, may have been the primary driver behind the Neolithic decline.
- Researchers analyzed DNA from human bones and teeth excavated from ancient burial tombs in Scandinavia.
- The remains of 108 individuals—62 males, 45 females, and one undetermined—were examined, revealing that 17% were infected with the plague at the time of death.
- The researchers charted a family tree of 38 individuals from Falbygden, Sweden, spanning six generations and approximately 120 years, finding that 32% were infected with the plague.
Key Findings
- The study reconstructed full genomes of different strains of the plague-causing bacterium Yersinia pestis.
- They discovered that the Neolithic plague was an ancestor to all later plague forms. The last strain identified in the study was more virulent, potentially spreading from person to person and causing epidemics.
- This early form of the plague is linked to later devastating plagues, such as the Justinian Plague of the 6th century AD and the 14th century Black Death.
- However, due to the early nature of the Neolithic strains, the symptoms may have differed significantly from those seen in later epidemics.
Implications of the Findings
- The high prevalence of plague indicated by the study suggests that plague epidemics played a substantial role in the Neolithic decline in northern Europe.
- The Neolithic era marked a significant shift from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to settled farming and animal domestication.
- However, by the time of the population crash between 3300 BCE and 2900 BCE, other regions, such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, had already developed cities and sophisticated civilizations.
Aftermath and Population Replacement
- Following the population collapse in Scandinavia and Northwestern Europe, these areas were later repopulated by the Yamnaya people, who migrated from the steppe region of present-day Ukraine.
- These migrants are considered the ancestors of modern Northern Europeans, indicating a significant demographic and cultural shift in the region post-Neolithic decline.
Prelims Facts
1. Centre declares June 25 as ‘Samvidhaan Hatya Diwas’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Union government announced June 25 as ‘Samvidhaan Hatya Diwas’ to commemorate the day the Emergency was imposed in 1975.
- Union Home Minister Amit Shah and Prime Minister Narendra Modi emphasised that this day would honour those who suffered during the Emergency, highlighting it as a dark phase in Indian history.
- The day aims to remind citizens of the importance of upholding the Constitution and democracy.
- The Gazette notification cited the Emergency’s proclamation and subsequent abuses of power, stating the observance would honour the victims and prevent future abuses.
- Congress leaders criticised the announcement, calling it hypocritical and referencing the defeat of NDA in the 2024 elections.
- Amit Shah stated that the day is intended to honour the spirit of those who revived democracy despite persecution, preventing future dictatorial actions.
- He criticised Indira Gandhi for imposing the Emergency, which silenced the media and imprisoned many without cause.
2. New species of dogfish shark discoveredin Kerala harbour
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Scientists from the Zoological Survey of India discovered a new deep-water dogfish shark species, Squalus hima, at Sakthikulangara fishing harbour in Kerala.
- Squalus is a genus of dogfish sharks, known as spurdogs, with smooth dorsal fin spines.
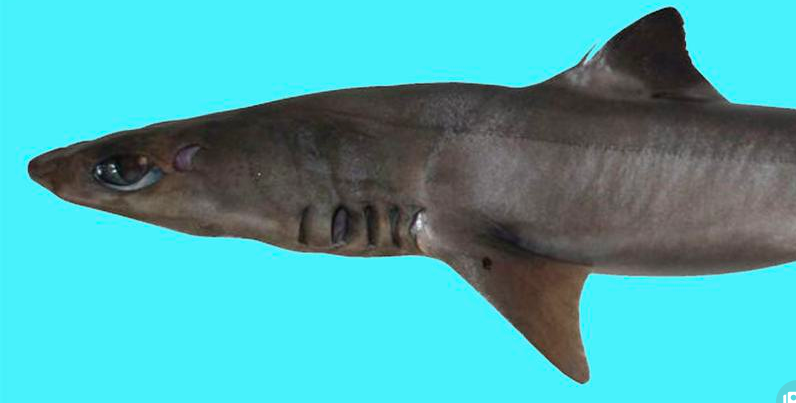

- The discovery was led by scientist Bineesh K. K and published in the journal Records of the Zoological Survey of India.
- Sharks from the genera Squalus and Centrophorus are often exploited for their liver oil, which is highly demanded in the pharmaceutical industry.




