16 December 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. SC Examines Applicability of POSH Act to Political Parties, Directs Petitioner to Approach ECI
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is the PoSH Act, 2013?
- About:
- The POSH Act is a legislation enacted by the Government of India in 2013 to address the issue of sexual harassment faced by women in the workplace.
- The Act aims to create a safe and conducive work environment for women and provide protection against sexual harassment.
- The PoSH Act defines sexual harassment to include unwelcome acts such as physical contact and sexual advances, a demand or request for sexual favours, making sexually coloured remarks, showing pornography, and any other unwelcome physical, verbal, or non-verbal conduct of a sexual nature.
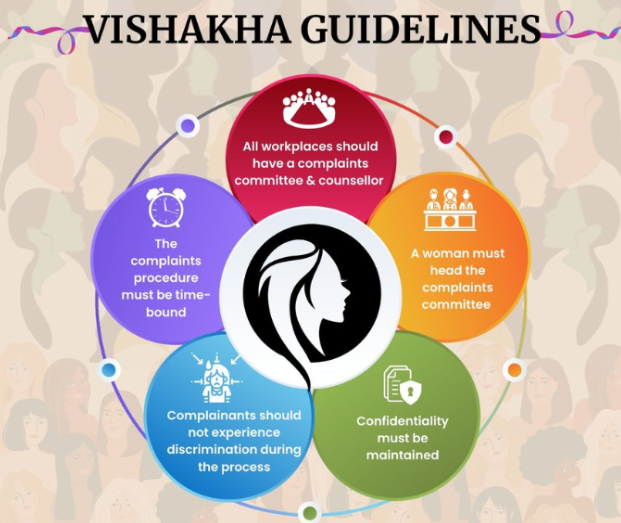
- Background: The Supreme Court in a landmark judgment in the Vishakha and others v State of Rajasthan 1997 case gave ‘Vishakha guidelines’.
- These guidelines formed the basis for the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013.
- The SC also drew its strength from several provisions of the Constitution including Article 15 (against discrimination on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, and place of birth), also drawing from relevant International Conventions and norms such as the General Recommendations of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), which India ratified in 1993.
- Key Provisions:
- Prevention and Prohibition: The Act places a legal obligation on employers to prevent and prohibit sexual harassment in the workplace.
- Internal Complaints Committee (ICC): Employers are required to constitute an ICC at each workplace with 10 or more employees to receive and address complaints of sexual harassment.
- The Complaints Committees have the powers of civil courts for gathering evidence.
- Duties of Employers: Employers must undertake awareness programs, provide a safe working environment, and display information about the POSH Act at the workplace.
- Complaint Mechanism: The Act lays down a procedure for filing complaints, conducting inquiries, and providing a fair opportunity to the parties involved.
- Penalties: Non-compliance with the Act’s provisions can result in penalties, including fines and cancellation of business licenses.
POSH Act and Its Scope
- The POSH Act mandates workplaces, public or private, to establish Internal Complaints Committees (ICCs) to address sexual harassment complaints.
- The Act broadly defines “workplace” to include traditional offices, public sector institutions, and even field locations visited during employment.
- However, applying this definition to political parties, which lack clear workplace structures and employer-employee relationships, presents legal challenges.
Kerala HC Precedent
- The Kerala High Court (2022) ruled that political parties are not workplaces under the POSH Act as they lack employer-employee relationships and do not operate as ventures or establishments.
- Hence, they are not obligated to form ICCs, highlighting a gap in how the Act applies to non-traditional setups like political parties.
Challenges in Applying POSH to Political Parties
- Ambiguous Employer Definition: Political parties employ temporary workers and volunteers without formal employment structures, complicating the identification of an “employer” responsible for ICCs.
- Field Operations as Workplaces: Fieldwork by party workers might fall under the Act’s broad “workplace” definition, but this remains legally undefined.
- Existing Discipline Mechanisms: Political parties manage internal discipline through their constitutions, but these lack specific provisions or independent oversight for addressing sexual harassment.
ECI’s Role and Precedents
- The ECI, empowered by Article 324 of the Constitution and the Representation of People Act, 1951, oversees political parties’ compliance with election laws.
- However, its role in enforcing other laws like the POSH Act is unclear. Previous instances, such as the CIC’s 2013 order applying the RTI Act to political parties, show limited compliance.
- The ECI’s approach typically involves advisories, as seen in its directives against using child labor in election campaigns.
Broader Implications
- The PIL raises critical questions about the accountability of political parties under laws like the POSH Act.
- If enforced, it would require redefining “workplace” and “employer” to fit the unique structure of political parties, thereby setting a precedent for broader applicability to other non-traditional organizations.
| Recommendations of the Justice Verma Committee on Sexual Harassment at Workplace |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges and implications of applying the POSH Act, 2013, to political parties in India. How can existing legal frameworks be adapted to ensure accountability for addressing sexual harassment in non-traditional workplaces? (250 words/15 m) |
2. Eastern Maritime Corridor Boosts India-Russia Trade with Faster, Cost-Effective Shipping
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 11)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
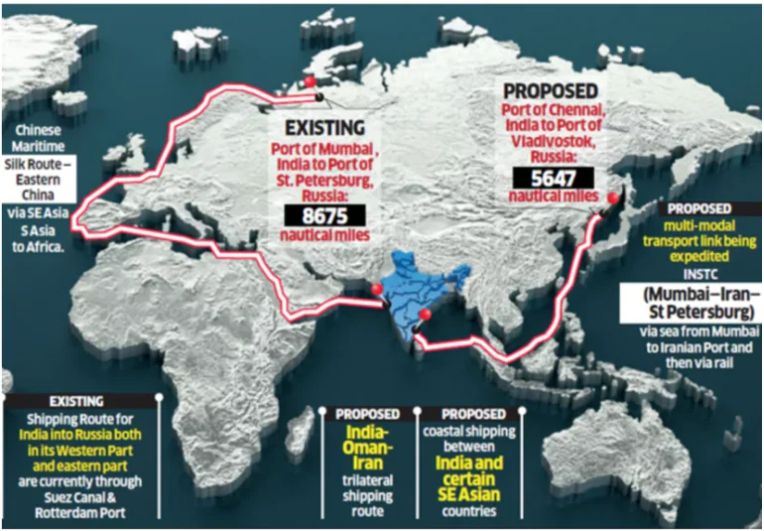
About Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC):
- The Chennai-Vladivostok Sea route, also known as the EMC, will link Russia’s east coast with South India.
- The EMC offers a significant reduction in both cargo transit time between India and the Russian Far East of up to 16 days and in distance by up to 40%, promising substantial efficiency gains in transportation.
- Currently, the route from Mumbai to St. Petersburg, Russia, via the Western Sea Route and Suez Canal spans 8,675 nautical miles or 16,066 km.
- At present, a large container ship from India takes around 40 days to reach Russia’s Far East region through Europe.
- In contrast, the distance from Chennai to Vladivostok via the EMC is significantly shorter, at only 5,647 nautical miles, or 10,458 km.
- This translates to substantial savings of 5,608 km in distance, providing significant reductions in logistical costs and enhancing the efficiency of cargo transportation between Russia, India, and Asia.
- En route, EMC passes through the Sea of Japan, the East China Sea, the South China Sea, the Malacca Straits, the Andaman Sea, and the Bay of Bengal.
- The route includes ports options if needed, such as Dalian, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Ho Chi Minh City, Singapore, Kuala Lumpur, Bangkok,Dhaka, Colombo, and Chennai.
Cost and Time Efficiency
- The Chennai-Vladivostok route spans approximately 5,600 nautical miles, reducing transit time to 24 days from the 40+ days required via the traditional Mumbai-St. Petersburg route.
- This reduction saves both time and transportation costs, making the EMC a strategic alternative for shipping commodities like crude oil, coal, and LNG.
Trade Patterns via EMC
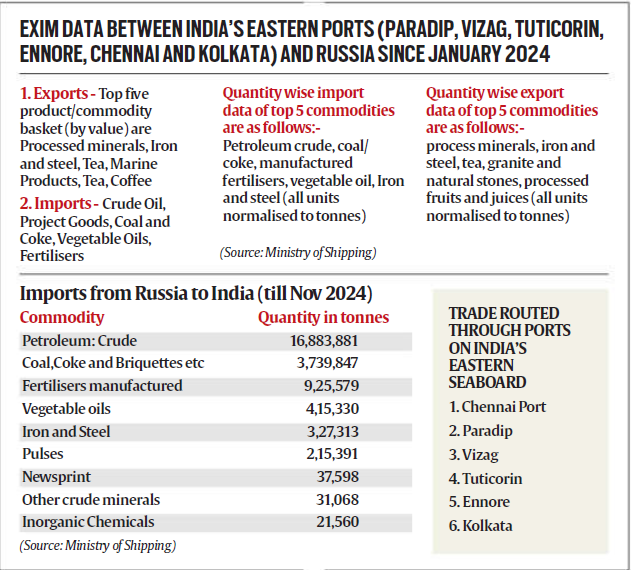
- India’s top imports through the EMC include crude oil, coal, fertilisers, vegetable oils, and iron and steel.
- Export items are dominated by processed minerals, tea, granite, marine products, and natural stones.
- The route is supported by multiple Indian ports, including Paradip, Visakhapatnam, and Tuticorin, depending on cargo type and destination.
India’s Growing Dependence on Russian Oil
- India, the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, surpassed China as the largest buyer of Russian oil in 2024.
- Russian oil, particularly the Urals crude grade, accounted for over 75% of India’s Russian imports.
- Despite reduced discounts on Russian crude, lower shipping costs via the EMC make Russian oil economically attractive.
Strategic and Economic Implications
- The EMC strengthens India-Russia trade ties while diversifying India’s supply routes. Beyond oil, closer engagement helps mitigate Moscow’s reliance on China and supports India’s defense and nuclear collaborations with Russia.
- The corridor also aligns with India’s strategic goals to bolster energy security and deepen bilateral relations.
Conclusion
- The Eastern Maritime Corridor represents a transformative development in India-Russia trade relations, providing economic benefits through reduced shipping costs and time.
- As the geopolitical landscape evolves, this route reinforces India’s strategic positioning in its engagement with Russia.
| Significance of the Corridor |
|
| Practice Question: Evaluate the economic and strategic benefits of the Eastern Maritime Corridor for India-Russia trade. How does this new sea route impact India’s energy security and geopolitical positioning? (250 words/15 m) |
3. How would a carbon market function?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
COP29 and Carbon Markets
- COP29, held in Baku, Azerbaijan, has approved standards to establish an international carbon market, potentially operational by next year.
- This step highlights the role of carbon markets in curbing carbon emissions and addressing climate change challenges.
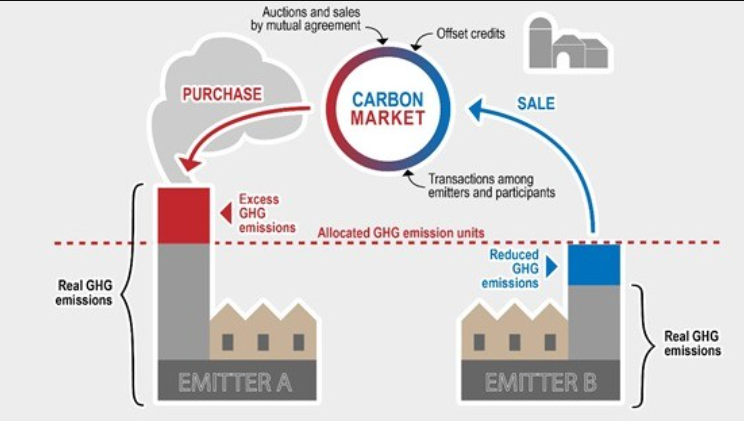
| What is a Carbon Market? |
|
|
Benefits of Carbon Markets
- Carbon markets address the problem of externalities, where the environmental cost of economic activities is not internalized in market prices.
- They impose financial costs on firms for carbon emissions, encouraging them to reduce pollution.
- Standardized accounting frameworks and technological advancements have enhanced corporations’ ability to monitor emissions and report accurately.
- Voluntary reporting systems like the Carbon Disclosure Project are preferred by corporations, while they oppose government interventions.
- Firms advocate free trading of carbon credits, which they claim ensures efficient allocation of resources.
Challenges of Carbon Markets
- Governments may manipulate the supply of carbon credits, either oversupplying them to reduce prices or allowing firms to bypass regulations.
- Firms purchasing carbon offsets may engage in virtue signaling, with limited actual impact on reducing emissions.
- Critics question governments’ ability to determine the optimal supply of carbon credits, as political interests may lead to restrictive or overly lenient policies.
- Restrictive policies may hinder economic growth, while lax regulations may fail to achieve meaningful emission reductions.
The Way Forward
- The effectiveness of carbon markets depends on transparent governance, strict enforcement, and incentivized participation by firms and governments.
- Ensuring accountability in carbon offset mechanisms and maintaining optimal credit supply are critical for achieving environmental goals.
- Collaboration between governments, corporations, and international bodies is essential to balance economic growth and climate commitments.
| PYQ: Should the pursuit of carbon credit and the clean development mechanism set up under UNFCCC be maintained even though there has been a massive slide in the value of carbon credit? Discuss with respect to India’s energy needs for economic growth. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of carbon markets in mitigating climate change. Highlight the challenges associated with their implementation and suggest measures to enhance their effectiveness. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Can we make black holes reveal themselves in echoes of light?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Importance of Black Holes
- Black holes have a strong pull that affects stars and galaxies.
- Studying black holes helps scientists understand how galaxies and stars are formed and evolve.
New Way to Study Black Holes
- A new study led by George Wong from Princeton University presents a method to measure black holes.
- This method uses the effect of black holes on light to understand their properties.
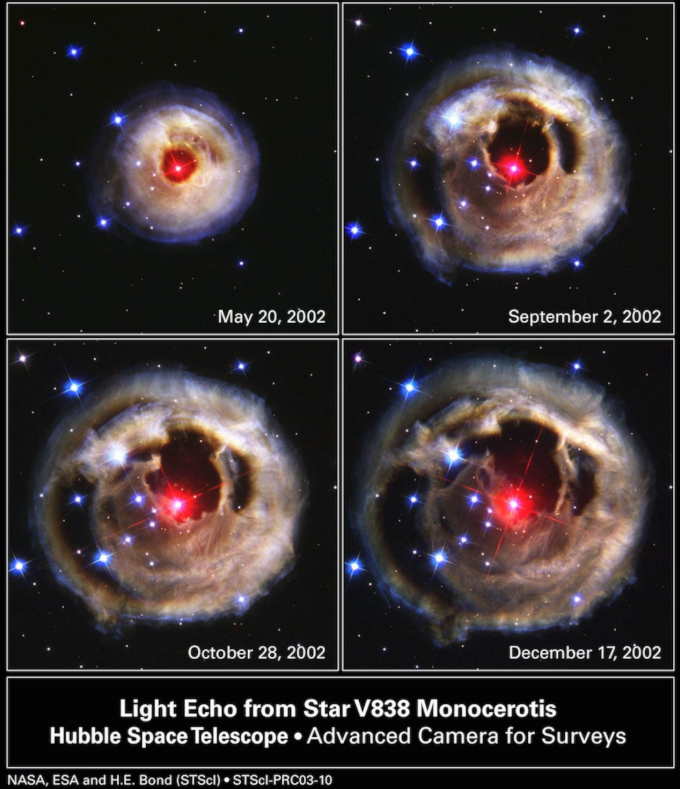
| What Are Light Echoes? |
|
|
Challenges in Measuring Black Holes
- Observing black holes is difficult because of the hot gases and radiation around them.
- Light echoes are helpful because they provide clearer signals, making measurements easier.
Gravitational Lensing and Interferometry
- Black holes bend light through their gravity, which is called gravitational lensing.
- The study suggests using long-baseline interferometry, where two telescopes (one on Earth and one in space) detect light echoes to create a special signal.
Studying Black Holes in M87 and the Milky Way
- The study focuses on supermassive black holes in the M87 galaxy and the Milky Way, which have bright rings of light at 230 GHz.
- Scientists want to study these rings to understand the black hole’s shadow.
Simulating Light Echoes Around M87
- The research team tested their method by simulating light around the M87 black hole.
- This helped them estimate the black hole’s mass and angular momentum.
Theory of Relativity and Light Echoes
- Einstein’s theory of relativity predicts that light echoes happen with all types of light, not just one frequency.
- Testing light echoes at different frequencies will help confirm the new method and the theory of relativity.
| Practice Question: Explain the phenomenon of light echoes and how it can be used to measure the properties of black holes. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Public Sector Banks: A Resurgent Force
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2084546®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Introduction: Public Sector Banks’ Achievements
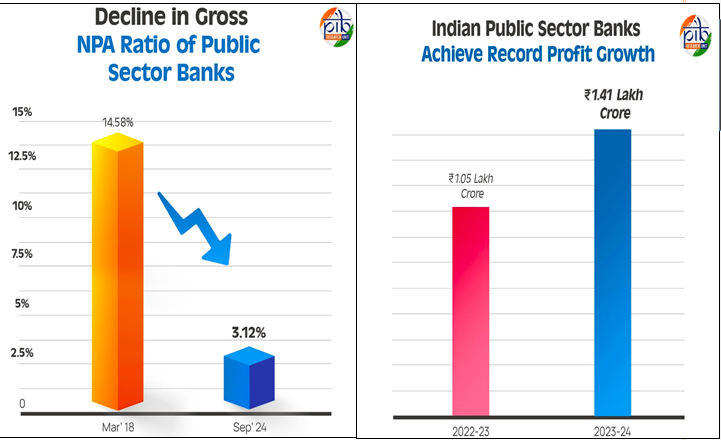
- Public Sector Banks (PSBs) in India achieved a record net profit of ₹1.41 lakh crore in FY 2023-24, marking their highest-ever aggregate profit.
- The sector saw a significant improvement in asset quality, with the Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio declining to 3.12% in September 2024.
- PSBs also recorded a net profit of ₹85,520.6 crore in the first half of 2024-25 and paid a total dividend of ₹61,964 crore over the past three years.
- These achievements reflect improved operational efficiency, stronger capital base, and better asset quality.
Decline in GNPA: Strengthening Resilience
- The GNPA ratio of PSBs dropped from a peak of 14.58% in March 2018 to 3.12% in September 2024.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) initiated the Asset Quality Review (AQR) in 2015, which helped in transparent recognition of NPAs and increased provisioning.
- To address banking stress, the Government introduced a comprehensive 4R’s strategy (Recognition, Resolution, Recapitalisation, and Reforms).
- The Capital to Risk (Weighted) Assets Ratio (CRAR) of PSBs rose by 3983 basis points to 15.43% in September 2024, indicating enhanced stability.
Expanding Financial Inclusion
- PSBs continue to drive financial inclusion, with 54 crore Jan Dhan accounts and 52 crore collateral-free loans under various schemes.
- The number of bank branches increased from 1,17,990 in March 2014 to 1,60,501 in September 2024, with most branches in rural and semi-urban areas.
- As of September 2024, the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme supported 7.71 crore accounts, with an outstanding loan of ₹9.88 lakh crore.
- MSME advances grew at a CAGR of 15% over the past 3 years, totaling ₹28.04 lakh crore in March 2024.
Strengthening PSBs through the EASE Framework
- The Enhanced Access & Service Excellence (EASE) framework promotes incremental reforms focusing on governance, risk management, technology, and data-driven banking.
- Key reforms have led to improved financial health and better banking services.
Conclusion: A Stronger Banking Sector
- PSBs have made significant progress in financial health and contributed to India’s economic growth.
- The decline in GNPA and improved CRAR reflect sound risk management.
- The EASE framework has facilitated reforms, and the focus on financial inclusion has expanded banking access. PSBs are now well-positioned to drive inclusive economic growth.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of Public Sector Banks (PSBs) in India’s economic growth, focusing on their financial performance, the decline in GNPA, and the impact of the EASE framework in strengthening the banking sector. (150 Words /10 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Santa Ana Winds
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
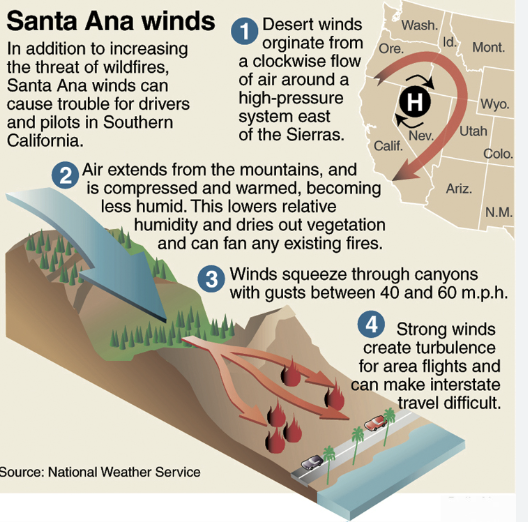
Role of Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds, a defining factor in Southern California’s wildfire dynamics, occur when high pressure builds over the Great Basin, creating a pressure difference with the California coast.
- This pressure gradient generates strong, dry winds that heat up as they descend toward the Pacific Ocean, reducing humidity to dangerously low levels.
- These winds dry vegetation, making it highly flammable.
- Santa Ana winds are most common from October to January, as seasonal weather patterns promote high-pressure systems inland.
Impact of Climate Change
- While Santa Ana winds are a natural phenomenon, climate change has exacerbated California’s wildfire crisis.
- Studies show the wildfire season has lengthened, with a peak shift from August to July, and fires have grown more intense.
- For instance, 10 of the largest wildfires in California occurred in the last 20 years, five in 2020 alone.
- Rising global temperatures, earlier snowmelts, and prolonged dry seasons have stressed vegetation, making forests more susceptible to fires.
Future wildfire risks are projected to escalate as greenhouse gas emissions drive global warming beyond 3°C by the century’s end, far surpassing the 1.5°C safety threshold outlined in global climate agreements.
2. Centre launches Jalvahak scheme for cargo movement via inland waterways
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Launch of Jalvahak Scheme
- The scheme was launched to promote cargo movement via inland waterways on National Waterways 1, 2, and 16.
- It offers financial incentives to encourage cargo transport through these waterways.
- The scheme is valid for an initial period of three years.
Objective of the Scheme
- The aim is to decongest road and railways by promoting more economical, ecologically friendly, and efficient waterway transport.
- The scheme provides an opportunity for trade sectors to explore cargo movement via waterways.
Incentives and Benefits
- The scheme offers a reimbursement of up to 35% of the total operating expenses for eligible cargo vessels.
- It encourages cargo owners to hire government-owned or operated vessels to enhance business prospects.
Operational Details
- The scheme features fixed scheduled sailing services for cargo vessels from Kolkata, operating along specific stretches of NW-1 and NW-2.
- It includes services like the Kolkata-Patna-Varanasi-Patna-Kolkata route and Kolkata-Pandu-Guwahati route.
3. Carcasses of Olive Ridley turtles continue to wash ashore in Vizag
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
Olive Ridley Turtles:
- Smallest sea turtle: Olive Ridleys are the smallest sea turtles, with adults reaching about 2 feet in length and weighing up to 100 pounds.
- Conservation status: Listed as ‘Vulnerable’ by the IUCN.

- Most abundant: They are the most numerous sea turtle species globally, though still considered vulnerable.
- Unique nesting: Olive Ridleys are famous for their “arribadas,” mass nesting events where thousands of females come ashore simultaneously.
- Wide distribution: They inhabit tropical and subtropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans.
- Diet: Olive Ridleys are omnivores, feeding on jellyfish, crabs, snails, shrimp, and algae.
- Threats: These turtles face dangers such as entanglement in fishing gear, habitat destruction, and climate change.