17 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Illegal mining, encroachments, deforestation a threat to Aravali as natural green wall
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 2)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation |
| Context |
|
Environmental Threats to the Aravali Range
Overview and Threats
- The Aravali range, stretching from Gujarat to Delhi through Rajasthan, is facing severe threats from illegal mining, deforestation, and human encroachments.
- These activities have led to significant environmental degradation and depletion of groundwater reserves.
- The destruction has resulted in loss of vegetation, soil cover, and has negatively impacted the region’s biodiversity.
| Geographic and Ecological Details Of Aravali Range |
|
Findings from Recent Studies
- A study by Laxmi Kant Sharma presented at the IUFRO World Conference in Stockholm highlighted the urgent need for sustainable practices.
- Forest area decreased by 0.9% from 1999 to 2019, with a loss of 705 sq. km of dry deciduous forest.
- Human settlements increased from 4.5% in 1975 to 13.3% in 2019, while waterbodies and mining areas have shown fluctuating trends.
Impact on Carbon Flux and Vegetation
- Areas with high positive rates of carbon flux are in the upper and lower Aravali due to higher rainfall and protected areas.
- Negative carbon flux is noted in the central Aravali near the Thar Desert.
- Protected regions like Todgarh-Raoli and Kumbhalgarh positively impact the ecosystem with minimal forest depletion.
Recommendations for Preservation
- LiDAR-based drone surveys are recommended for identifying and mitigating illegal mining activities.
- Establishing an independent Aravali Development Authority and enforcing a ban on all mining activities are crucial for preserving the hill ecosystem.
- Implementing these measures is essential to safeguard the Aravali range’s ecological balance and biodiversity.
| Practice Question: Discuss the environmental threats faced by the Aravali range due to illegal mining and deforestation. What measures are recommended to address these issues and ensure the sustainable preservation of this ecological zone? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Panama Canal Faces Existential Threat from Climate Change as Water Levels Drop
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 19)
| Topic: GS1 – Geography – Climate Change |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
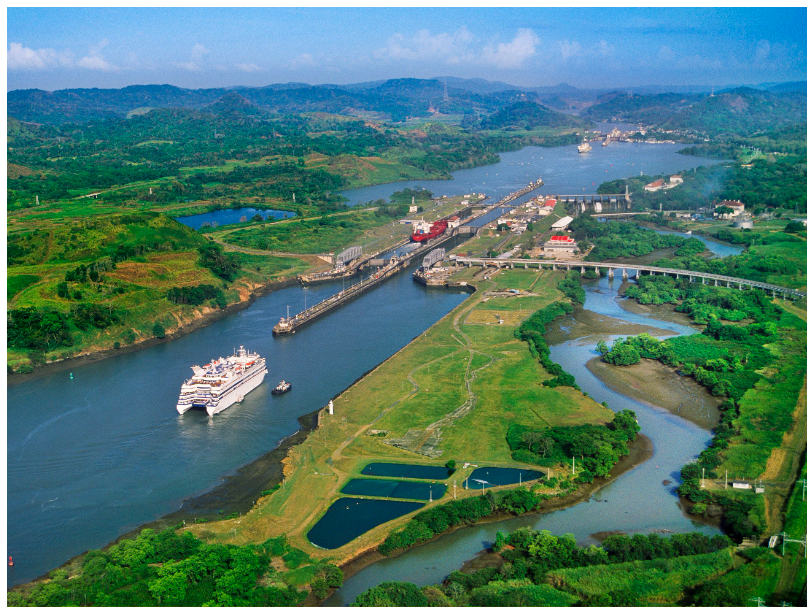

About Panama Canal:
- It is a constructed waterway that connects the Atlantic and Pacific oceans across the Isthmus of Panama.
- It is one of the two most strategic artificial waterways in the world, the other being the Suez Canal.
- It is approximately 80 kilometers long.
- The canal was built by the United States between 1904 and 1914, and it was officially opened on August 15, 1914.
- It is owned and administered by the Republic of Panama since the oversight of the Canal was transferred from the United States to Panama in 1999.
- The Panama Canal consists of a series of locks that raise and lower the water level to facilitate the passage of ships through the continental divide.
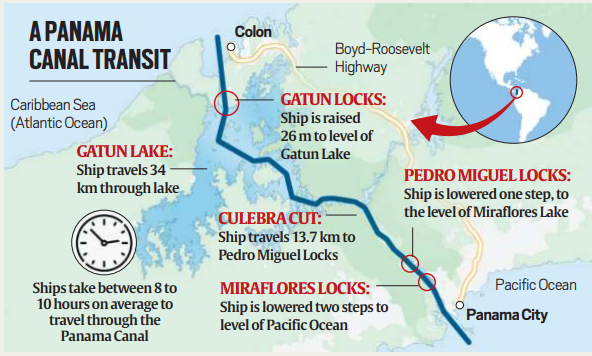
Functioning of the Canal
- The canal operates through a complex system of locks that elevate ships to different sea levels.
- This system is essential because the Pacific Ocean at the canal’s southern end is slightly higher than the Atlantic at the northern end.
- The locks use gravity-fed water from Lake Gatun to lift and lower ships, facilitating their passage across the Isthmus of Panama.
The Impact of Climate Change
- The operation of the canal is heavily dependent on the water levels in Lake Gatun.
- Each ship’s passage requires nearly 200 million liters of water, and the canal uses more water daily than consumed by New York City’s population.
- In recent years, droughts have caused significant drops in the lake’s water level, reducing the number of ships that can pass through the canal and forcing some to reduce their cargo loads.
Proposed Solutions and Controversies
- To address the water shortage, Panama Canal authorities have proposed constructing a dam on the Rio Indio river.
- While this $1.6 billion project could secure the canal’s water supply for the next 50 years, it also poses social challenges, as it would displace about 2,000 people living in the area.
- The solution is contentious, reflecting the complex balance between preserving a vital global trade route and addressing the social and environmental impacts of such large-scale interventions.
| Practice Question: Examine the impact of climate change on global trade routes with a focus on the Panama Canal. What measures can be taken to mitigate these challenges while balancing environmental and social concerns? (250 words/15 m) |
3. James Webb Telescope’s Findings Challenge Cosmic Understanding
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 19)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context: |
| The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the most powerful telescope in space, has provided images that challenge current astronomical theories, complicating our understanding of the Universe’s history. |
Analysis of News:
About James Webb Space Telescope
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a general-purpose observatory with a large aperture telescope optimised for infrared observations and a suite of state-of-the-art astronomical instruments capable of addressing many outstanding issues in astronomy.
Background of JWST
- Initiation and collaboration: The JWST project began in 1996 as a collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
- Successor to Hubble: It has been conceived as the next-generation space telescope succeeding the Hubble Space Telescope, with a focus on infrared astronomy.
Features of James Webb Space Telescope
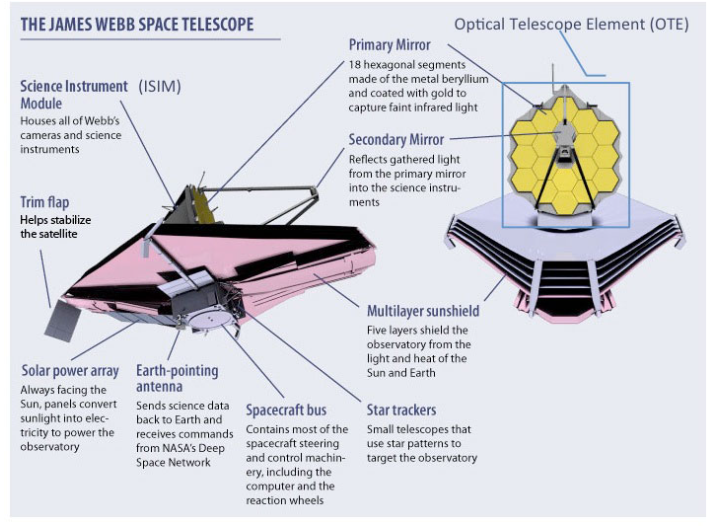
The JWST’s features represent a significant advancement in space telescope technology, promising to deepen our understanding of the universe and its origins. Its key features are:
- Infrared optimisation: Designed primarily for infrared astronomy to observe objects which were too old, distant, or faint for visible light detection.
- Large primary mirror: Equipped with a 6.5-meter diameter primary mirror to capture more light and provide higher-resolution images.
- Segmented mirror design: The primary mirror comprises 18 hexagonal, gold-coated beryllium segments, thus enabling it to fold for launch and unfold in space.
- Sunshield protection: A five-layer sun-shield, which blocks solar light and heat, maintaining the instruments at extremely low temperatures necessary for infrared observations.
- Location at Lagrange Point 2 (L2): Operates from a stable orbit around the Sun-Earth L2 point thereby minimising light interference and reducing fuel consumption for orbital corrections.
- High sensitivity: Its instruments are highly sensitive to infrared light thus enabling the study of the earliest stars and galaxies formed after the Big Bang.
- Cryogenic cooling system: Uses a passive cooling system to reach temperatures as low as 40 Kelvin (-233°C) which is essential for infrared observations.
- Precision guidance sensors: Equipped with sophisticated guidance sensors for accurate pointing and stability. This is crucial for long-duration observations of faint celestial objects.
- Extended wavelength coverage: Capable of observing a wide range of wavelengths from 0.6 to 28 micrometres.
Objectives of James Webb Space Telescope
Its key objectives are:
- To look for galaxies that formed just after the Big Bang.
- To determine the evolution of galaxies from their creation to the present.
- To examine the stages of star creation till the formation of planetary systems.
- To investigate the potential for life in planetary systems by measuring their physical and chemical features.
Unexpected Findings

- Early Universe Galaxies: JWST was expected to find small, newborn galaxies but instead discovered mature, full-sized galaxies in the early Universe, contradicting predictions.
- Expansion Rate Discrepancy: The telescope’s measurements have deepened the existing discrepancy in the Universe’s expansion rate, with its findings showing a faster rate than those based on early Universe data.
Methods of Measuring Expansion
- Early Universe Method: Relies on ancient relic radiation, revealing the Universe’s expansion since its hot, early stages.
- Local Celestial Method: Uses the brightness variation of stars to determine distances and expansion, focusing on relatively closer celestial objects.
Implications for Cosmology
- Challenges to the Standard Model: The JWST’s findings suggest potential flaws in the current cosmological model, which relies on concepts like dark matter and dark energy—phenomena that remain poorly understood.
- Potential Paradigm Shift: The unexpected results may indicate a need for a significant revision of our understanding of the Universe, reminiscent of historical shifts in scientific thought.
Conclusion
- The JWST has opened new questions rather than providing answers, suggesting that our current understanding of the Universe’s history and structure may require fundamental changes.
| Significance of JWST |
|
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) offers numerous benefits for humanity in various ways:
|
| PYQ: Launched on 25th December, 2021, James Webb Space Telescope has been much in the news since then. What are its unique features which make it superior to its predecessor Space Telescopes? What are the key goals of this mission? What potential benefits does it hold for the human race? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2022) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the James Webb Space Telescope’s (JWST) findings on our current understanding of the Universe’s history. How do these findings challenge the standard cosmological model, and what potential shifts in scientific thought could arise as a result? (250 words/15 m) |
4. DRDO hands over Authority Holding Sealed Particulars of ‘Nipun’ munition to Directorate General of Quality Assurance
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2045992 )
| Context |
|
More About NIPUN Munition:
- Design and Development: Created by the Armament Research & Development Establishment (ARDE) in collaboration with the High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL).
- Type: Soft Target Munition, designed for precision and effectiveness.
| What is Soft Target Munition? |
|
- Induction: Successfully inducted into the Indian Army after meeting General Staff Qualitative Requirements (GSQR).
- Production: Bulk production is underway, with more than 20 lots delivered to the Indian Army.
- Features: User-friendly, effective against targets, safe during handling, transportation, and deployment.
- Recent Development: Authority Holding Sealed Particulars (AHSP) handed over NIPUN to Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA) for further quality assurance.
5. NEHHDC achieves Oeko-Tex Certification for Eri Silk, marking a milestone for Northeast’s unique vegan silk
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2046099 )
| Context |
|
Oeko-Tex Certification:
- Definition: Oeko-Tex Certification is a global standard for textiles that ensures products are tested for harmful substances and produced in environmentally friendly conditions.
- Purpose: Aims to promote safety, sustainability, and transparency in the textile industry.
- Types:
- Standard 100: Certifies that textiles are free from harmful levels of over 100 substances that could be harmful to human health.
- Sustainable Textile Production (STeP): Focuses on sustainable production processes and environmental management.
- OEKO-TEX Made in Green: Ensures textiles are made in facilities that meet high environmental and social standards.
- Testing: Products undergo rigorous testing for harmful chemicals, including pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxic substances.
- Certification Process: Involves thorough testing of samples, inspection of production processes, and compliance with environmental and social criteria.
- Benefits: Provides consumer assurance of product safety, supports sustainable practices, and enhances marketability by meeting global standards.
- Global Recognition: Widely recognized in the international market as a mark of quality and safety.
6. BHAVISHYA – Promoting Digital Empowerment and Ease of Living for Pensioners
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2046070 )
| Context |
|
More About Bhavishya Software:
- Bhavishya is a centralized pension processing software developed by the Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare (DOPPW) to streamline and enhance the efficiency of pension processing for central government employees.
- Implemented on January 1, 2017, it integrates with payroll systems to auto-fill data, enables self-registration and form-filling by retirees, and enforces strict processing timelines.
- The software offers real-time updates, automates pension calculations, and issues electronic PPOs.
- It is digitised end-to-end, integrates with Digilocker for document storage, and connects with bank portals for post-retirement services, significantly improving transparency and reducing processing delays.
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Streetlights running all night make leaves inedible to insects: Study
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 19)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Research Focus
- The study concentrated on two common species of street trees in Beijing: Japanese pagoda and green ash trees.
- Researchers selected 30 sampling sites on main roads illuminated by streetlights throughout the night.
Methodology
- Illuminance Measurement: The amount of light at each site was measured.
- Leaf Collection: Approximately 5,500 leaves were collected to assess traits like size, toughness, water content, and levels of nutrients and chemical defense compounds.
Resource Allocation Indicators:
- Larger Leaves: Indicate resources are directed towards growth.
- Tougher Leaves: Suggest resources are allocated towards defense.
Key Findings
- Tougher Leaves: Increased illuminance led to tougher leaves in both tree species.
- Insect Herbivory: Tougher leaves showed less evidence of insect feeding.
- Altered Nutrient and Chemical Levels: Artificial lights changed the levels of nutrients and chemical defense compounds in the leaves.
Ecological Implications
- Impact on Food Chains: The study indicates that tougher leaves, due to artificial lighting, could lead to lower populations of herbivorous insects. This decline could cascade up the food chain, affecting predatory insects, insect-eating birds, and other species.
- Potential Ecosystem Disruption: Experts expressed concern that lower herbivory might reduce the abundance of various species, ultimately threatening urban ecosystems.
2. India’s fuel exports to Europe shift entirely to longer route around Africa
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 15)
| Context: |
| India’s petroleum product exports to Europe have shifted from the Red Sea route to the longer and costlier Cape of Good Hope route due to security threats from Iran-backed Houthi rebels in the Red Sea region. |
Analysis of News:
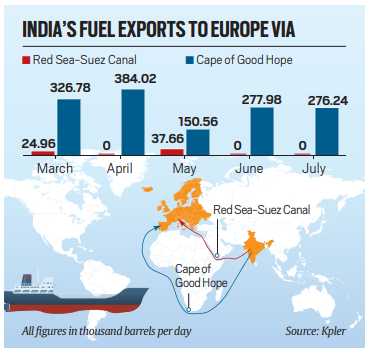
Key Points
- Security Concerns: The Red Sea route, previously the mainstay for India’s fuel exports to Europe, has become dangerous due to attacks by Houthi rebels, prompting a shift to the Cape of Good Hope route.
- Impact on Trade: The longer route adds 15-20 days to the journey and significantly increases freight costs, leading to a 25% drop in India’s petroleum exports to Europe in the first half of 2024.
- Shift in Focus: India has increased its fuel exports to Asian markets and Australia to offset the decline in European exports.
- Russian Oil Exemptions: Russian oil shipments to India continue through the Suez Canal-Red Sea route, as Russia is perceived as an ally of Iran, which backs the Houthi rebels.
Implications
- Global Shipping: The security crisis has reduced the use of the Suez Canal-Red Sea route for global oil and petroleum product flows, except for Russian crude.
- Geopolitical Risks: The ongoing Israel-Hamas conflict and potential regional escalation could further deter the use of this route in the near future.
3. IndiaAI Mission Launches Tender for 1,000 GPUs to Boost National AI Capacity
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 15)
| Context: |
| The Indian government has finalized a tender to procure 1,000 Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) as part of its IndiaAI Mission, aiming to provide computing capacity for Indian start-ups, researchers, and public sector agencies. |
Analysis of News:
What is IndiaAI Mission?
Background– During the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit in 2023 held in New Delhi, the Prime Minister of India declared India’s intention to initiate an artificial intelligence (AI) mission.
Aim– The mission aims to create a comprehensive ecosystem, drive AI innovation, and encourage AI use across sectors. It prioritizes skill development and socio-economic change, in line with the vision of ‘Making AI in India’ and ‘Making AI Work for India’.
Nodal Ministry– Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
Implementing Agency: ‘IndiaAI’ Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC)
Key Points
- IndiaAI Mission: A Rs 10,370 crore initiative to establish over 10,000 GPUs for developing AI systems and foundational models, especially in sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Initial Phase: The current tender is for 1,000 GPUs, marking the first phase of the mission, with Rs 551.75 crore allocated in the Union Budget 2024.
- Data Localization: The tender requires all AI services to be delivered from data centers in India, ensuring data sovereignty.
- Consortium Bidding: Indian entities can form consortia to bid, with strict eligibility criteria, including a Rs 100 crore average annual turnover for the primary partner.
- Public-Private Partnership: The mission will be implemented via a public-private partnership model with 50% viability gap funding. As prices drop, the private sector must expand computing capacity to meet demand.
Implications
- Boost for AI Ecosystem: The mission aims to lower barriers for smaller businesses and start-ups in AI development by providing accessible compute resources.
- Strategic National Infrastructure: By enforcing data localization, the government is ensuring that sensitive data remains within India’s borders, enhancing security and sovereignty in AI research and applications.
4. Aattam top film, Kantara’s Rishab the best actor as regional movies steal the show at National Film Awards
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The National Film Awards for 2022 highlighted the success of regional films, with Malayalam film Aattam winning Best Feature Film.
- Rishab Shetty won Best Actor for Kantara (Kannada), while Nithya Menen and Manasi Parekh shared Best Actress for Thiruchitrambalam (Tamil) and Kutch Express (Gujarati).
- Aattam also won awards for Best Editing (Mahesh Bhuvanend) and Best Screenplay, shared with Gulmohar (Hindi).
- Kantara won Best Popular Film Providing Wholesome Entertainment.
- Best Direction was awarded to Sooraj R. Barjatya for Uunchai: Zenith (Hindi), which also earned Neena Gupta Best Supporting Actress.
- Fouja (Haryanvi) won Best Supporting Actor (Pavan Raj Malhotra) and Best Debut Film.
- PS-1 won multiple awards, including Best Music Director (A.R. Rahman), Best Cinematography, and Best Sound Design.
- Brahmastra-Part 1: Shiva won Best Music Director (Pritam) and Best Male Playback Singer (Arijit Singh).
- Ayena: Mirror won Best Non-Feature Film.
| National Film Awards |
|
5. ISRO’s SSLV-D3 successfully launches earth observation satellite EOS-08 into orbit
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the EOS-08 Earth Observation Satellite on August 16, 2024.
- The launch was conducted using the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV-D3) from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Sriharikota.
- It includes new technologies such as an Integrated Avionics System, flexible solar panels, and advanced antennas.
- The satellite’s EOIR payload will capture images in the Mid-Wave IR (MIR) and Long-Wave IR (LWIR) bands.
- GNSS-R will support applications like ocean surface winds and soil moisture monitoring.
- The mission has a planned life of one year.
| What Is An Earth Observation Satellite? |
|
Purpose: Earth observation satellites monitor and gather data about the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, and oceans for various applications, including weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. Types:
Key Missions: India’s Earth observation satellites, such as the RISAT, Cartosat, and Astrosat series, enhance the country’s capabilities in monitoring and data collection. Sensors: Equipped with various sensors like optical, radar, and infrared, enabling detailed imaging and data collection. Data Uses: Provide vital data for weather forecasting, disaster management, resource mapping, and environmental monitoring, supporting various national initiatives. International Collaboration: Many countries and organisations share satellite data and collaborate on joint missions for broader insights. |
6. Pakistan records Asia’s first cases of mpox; European agency urges caution
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Definition: Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is an infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes smallpox.
- Transmission: The virus is transmitted through direct contact with infected animals (like rodents and primates), humans, or contaminated materials. It can spread from person to person via respiratory droplets or through contact with lesions or bodily fluids.
- Symptoms: Initial symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue, followed by a rash that starts on the face and spreads to other parts of the body, evolving into fluid-filled pustules.
- Incubation Period: Typically 7-14 days from exposure to symptoms.
- Complications: May lead to severe outcomes, including secondary bacterial infections or respiratory issues.
- Prevention: Includes vaccination, avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals, and practising good hygiene.
- Current Situation: Recent outbreaks have led the WHO to declare mpox a global health emergency. Increased monitoring and precautionary measures are in place worldwide.


