18 November 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. New infectious diseases among bees threaten world’s economies
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment |
| Context |
|
Importance of Pollinators
- Over 75% of food crops and flowering plants depend on insect pollinators like bees, wasps, beetles, flies, moths, and butterflies for successful harvests.
- Declines in pollinator populations due to pesticides, pollution, climate change, habitat loss, and emerging infectious diseases threaten agricultural productivity and economies worldwide.

Role of Wild Bees and Pathogen Spillover
- Wild bees are often more efficient pollinators than managed western honey bees (Apis mellifera).
- Research indicates pathogen spillover between managed honey bees and wild pollinators, with diseases like deformed wing virus and black queen virus threatening the health of wild species.
- A study in Switzerland found that shared habitats increased the viral loads in wild pollinators by up to 10 times.
Pollinator Diversity and Habitat Overlap
- India hosts over 700 bee species, including four indigenous honey bees: Asiatic honey bee, giant rock bee, dwarf honey bee, and stingless bee.
- Habitat loss forces pollinators to share smaller spaces, increasing disease transmission risks between managed and wild species.
Case Study: Thai Sacbrood Virus
- The Thai sacbrood virus outbreak in 1991-1992 devastated 90% of Asiatic honey bee colonies in South India.
- Recent reemergence of the virus highlights the vulnerability of native bee populations to infectious diseases.
- Transmission pathways of the virus remain unknown, posing a significant research gap.
Migration and Competition for Resources
- Managed honey bee migrations disrupt local ecosystems and compete with native pollinators.
- In Maharashtra, diseases linked to introduced honey bees have drastically reduced forest honey production.
Need for Focused Research
- Dedicated studies on emerging diseases like the Thai sacbrood virus can aid in early detection and prevention strategies.
- Monitoring and controlling diseases in managed colonies can minimise spillover risks to wild pollinators, safeguarding biodiversity and agricultural productivity.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of pollinators in global agriculture and biodiversity. Highlight the threats they face and suggest measures to address these challenges, with a focus on India’s pollinator diversity. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. India, Bangladesh have maintained relations despite changes, says High Commissioner
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Overview of Bilateral Relations Between India and Bangladesh
- India and Bangladesh have continued their strong relationship despite “turbulent changes” and political shifts in Bangladesh, as indicated by India’s High Commissioner in Dhaka.
- The political unrest, including the removal of the Prime Minister and subsequent violence, has not significantly affected the ongoing bilateral cooperation between the two nations.
Key Bilateral Developments
- India and Bangladesh have maintained multifaceted relations, especially in trade, energy, and transport connectivity.
- A notable recent development includes the inauguration of a power supply line from Nepal to Bangladesh via India, highlighting strong cooperation in energy and infrastructure projects.
- Despite the political volatility in Bangladesh, trade and people-to-people exchanges have shown positive momentum, underscoring the resilience and depth of the relationship.
Counter-Terrorism Cooperation
- India and Bangladesh have taken decisive actions against terrorism, especially since 2009, which played a crucial role in improving bilateral cooperation.
- Bangladesh’s “zero-tolerance on terrorism” has strengthened cooperation between India and Bangladesh, contributing to regional peace and prosperity.
Concerns Over Minority Safety
- Tensions have arisen between India and Bangladesh regarding the safety of minorities in Bangladesh, particularly the Hindu community.
- India has raised concerns over attacks on Hindus, urging the Bangladesh government to take strong measures to protect the community, especially in light of reports from Chittagong.
- The issue has been discussed at the highest levels, including during virtual summits, although the two countries’ leaders have not met in person recently.
Ongoing Diplomatic Engagements
- Despite some diplomatic irritants, the overall relationship continues to progress, with both nations recognizing their interdependence.
- India has reiterated its commitment to Bangladesh’s economic growth, with Bangladesh being India’s largest trading partner in South Asia.
|
PYQ: Q.1 Analyze internal security threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2020) Q.2 Critically examine the compulsions which prompted India to play a decisive role in the emergence of Bangladesh. (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2013) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of India-Bangladesh bilateral relations in the context of regional security, economic cooperation, and the protection of minorities. How can both nations address the existing challenges to maintain a sustainable partnership? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Assam’s Semiconductor Plant: A Game-Changer for India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2074074®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
India’s Semiconductor Industry Growth
- Morigaon Semiconductor Facility:
- Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test Pvt Ltd (TSAT) is developing a semiconductor unit in Morigaon, Assam.
- Investment of Rs. 27,000 crore.
- Expected to produce up to 48 million semiconductor chips per day using flip chip and Integrated System in Package (ISIP) technologies.
- Facility designed for sectors like automotive, electric vehicles, telecommunications, and consumer electronics.
- Completion expected by mid-2025.

- Socio-Economic Benefits:
- Will create 15,000 direct jobs and 11,000-13,000 indirect jobs.
- Contributes to regional economic growth in Assam and surrounding areas.
- Daily output will serve both domestic and international markets, enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global semiconductor supply chain.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- Mission Objectives:
- Aims to build a self-sufficient semiconductor ecosystem.
- Reduce reliance on imports and make India a global leader in electronics manufacturing and design.
- Involves collaborations between industry, government, and academic institutions.
- Government Initiatives:
- Launched in 2021 with an investment of ₹76,000 crore under the Semicon India program.
- Promotes semiconductor manufacturing through incentives and strategic partnerships.
- Supports various sectors: semiconductor fabrication (fabs), packaging, Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Testing (OSAT), sensors, and more.
Future Developments
- Expansion Across India:
- Additional semiconductor facilities planned in Gujarat and Mohali.
- New units by Tata Electronics in Dholera, Gujarat, and CG Power in Sanand, Gujarat.
- The government also approved a unit by Kaynes Semicon Pvt Ltd in Sanand.
- These initiatives aim to strengthen India’s position in the global semiconductor supply chain and digital economy.
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) in fostering self-reliance in semiconductor manufacturing. How will initiatives like the Morigaon semiconductor facility contribute to India’s position in the global supply chain? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. India Leads in CO2 Emissions Growth Amid Global Climate Alarm
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Understanding Greenhouse Gases (GHGs)
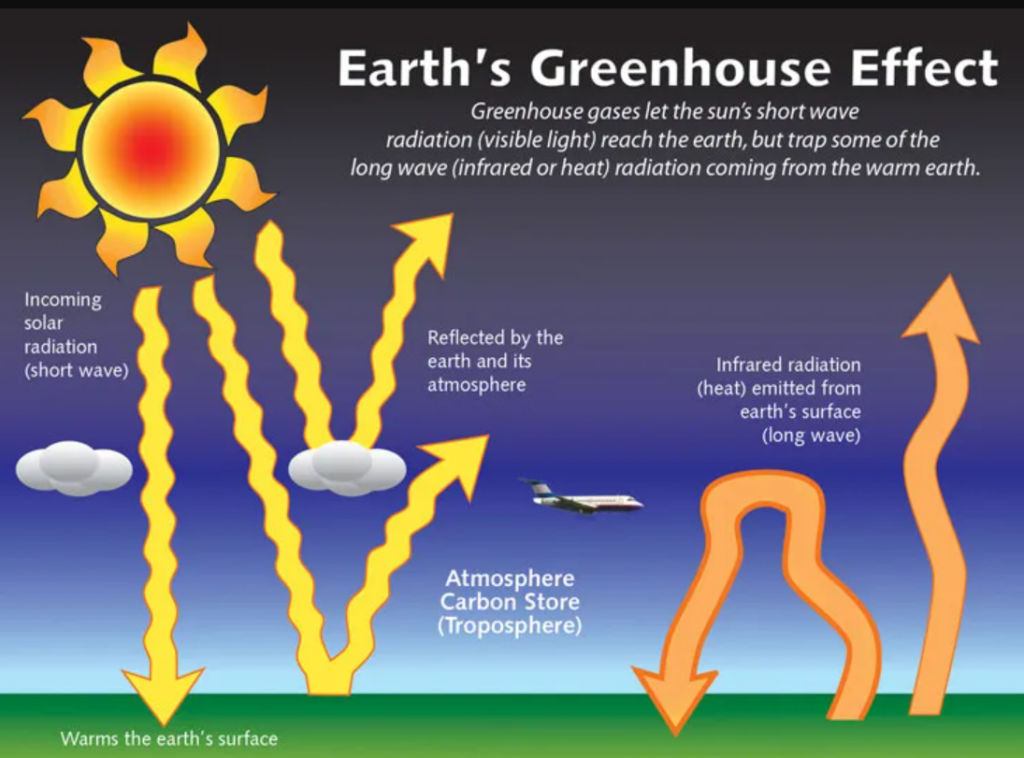
Definition and Mechanism:
- GHGs trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, creating a natural greenhouse effect essential for sustaining life.
- They absorb infrared radiation due to their molecular structure, preventing heat from escaping into space.
Key GHGs:
- Naturally occurring: CO2, CH4 (methane), and water vapour.
- Man-made: Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and other industrial gases.
- Issue: Rising GHG concentrations since the Industrial Revolution have amplified the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming.
Why CO2 Drives Most Global Warming
Dominance of CO2:
- Contribution to Warming: Responsible for 70% of global warming due to its abundance and long atmospheric lifespan.
- Radiative Forcing (RF): CO2 has the highest RF among climate drivers, meaning its heating effect is more significant than other GHGs, aerosols, or land use changes.
Comparison with Other GHGs:
- Methane (CH4): Although ~80 times more potent than CO2, CH4 is less abundant and has a shorter atmospheric presence (~10 years).
- Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs): Thousands of times more powerful but exist in negligible concentrations.
- Water Vapour: Most abundant GHG but has a short atmospheric cycle (~10 days), limiting its direct contribution to warming.
Persistence of CO2:
- A significant portion of CO2 remains in the atmosphere for centuries, with residual amounts persisting for thousands of years.
India’s Contribution and Global Implications
- India’s Emissions Growth: Driven by industrialization and energy demands, India’s rising CO2 emissions are a stark reminder of the need for sustainable growth strategies.
- Global Impact: Continued increases in CO2 emissions risk exceeding the 1.5°C warming threshold within six years, with severe climate consequences worldwide.
Conclusion: Addressing the CO2 Challenge
- Reducing CO2 emissions is critical to mitigating climate change. Nations like India must balance economic growth with aggressive decarbonization strategies, focusing on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon capture to curb their environmental footprint and uphold global climate commitments.
| What are the Initiatives to Reduce Emissions in India? |
|
Bharat Stage-IV to Bharat Stage-VI Emission Norms: India skipped BS-V and directly adopted BS-VI in 2020, reducing vehicle emissions by 80% for PM and 70% for NOx. This shift improved fuel standards, promoting cleaner vehicular technologies. UJALA Scheme: Launched in 2015, UJALA distributed over 36 crore LED bulbs by 2021, reducing 47 billion kWh annually and saving 38 million tonnes of CO2 emissions. This initiative enhances energy efficiency and lowers household electricity costs. International Solar Alliance (ISA): India co-founded the ISA in 2015, aiming to mobilise $1 trillion for solar projects by 2030. It promotes solar energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and meet renewable energy targets. National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): Established in 2008, NAPCC addresses climate challenges through eight missions, including National Solar and Enhanced Energy Efficiency, aiming to promote sustainable development and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Ethanol Blending in India by 2025: India aims to achieve 20% ethanol blending in petrol by 2025. This reduces dependence on imported oil and lowers emissions, saving 27 lakh tonnes of CO2 annually and benefiting the agriculture sector. India Updated its NDC: In 2022, India updated its Nationally Determined Contributions to reduce emissions intensity by 45% from 2005 levels by 2030 and achieve 50% cumulative electric power from non-fossil sources, supporting Paris Agreement goals. |
| PYQ: The ‘Common Carbon Metric’, supported by UNEP, has been developed for (2021) assessing the carbon footprint of building operations around the worldenabling commercial fanning entities around the world to enter carbon emission tradingenabling governments to assess the overall carbon footprint caused by their countriesassessing the overall carbon foot-print caused by the use of fossil fuels by the world in a unit time Answer: A |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of CO2 as the primary driver of global warming and analyze the implications of India’s rising CO2 emissions in the context of global climate goals. Suggest measures to address these challenges effectively. (250 words/15 m) |
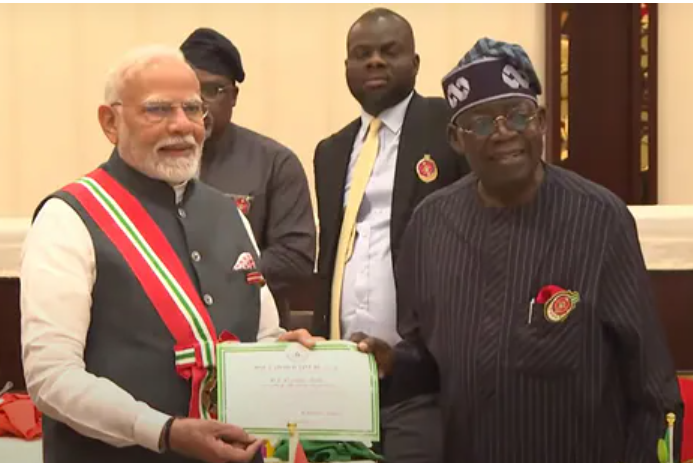
5. PM Modi Honoured in Nigeria, Strengthens Strategic and Economic Ties
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 05)
| Context: |
|

Analysis of News:
What is the Current State of India-Nigeria Relations?
- India is Nigeria’s second-largest trading partner, with bilateral trade at $7.9 billion, though it is half its peak a decade ago.
- Over 150 Indian companies operate in Nigeria, investing $27 billion.
- The Indian diaspora in Nigeria, numbering nearly 50,000, is the largest non-African group and contributes significantly to the economy.
- India has no upstream hydrocarbon assets in Nigeria despite being a top buyer of Nigerian crude.
- India channels its development assistance to Nigeria through the African Union, limiting direct bilateral engagement.
- The last meeting of the bilateral joint commission took place after 13 years.
Key Highlights of the Visit
Award and Recognition:
- PM Modi became the second foreign dignitary after Queen Elizabeth to receive Nigeria’s prestigious award, symbolizing the depth of bilateral relations.
- The Indian expatriate community, 60,000-strong, was acknowledged as a pillar of the India-Nigeria relationship.
Strategic Talks:
- Discussions between PM Modi and President Tinubu focused on defence, energy, trade, technology, and education.
- Agreements were signed in cultural exchange, customs cooperation, and survey cooperation.
Joint Challenges and Security:
- Terrorism, piracy, and radicalization were identified as mutual concerns, with a reaffirmed commitment to address them collaboratively.
- The Strategic and Counter-Terrorism Dialogue held earlier between the nations’ NSAs reinforced these objectives.
Development Cooperation:
- India’s concessional loans ($100 million) and capacity-building initiatives have fostered local expertise in Nigeria.
- Indian companies have invested $27 billion in Nigeria, becoming major employers and contributors to its economy.
Significance of the Visit
Deepening Strategic Partnership:
- Strengthened cooperation in defence and security aligns with shared priorities of countering extremism and international crime.
- Trade and investment opportunities, particularly in energy and manufacturing, enhance economic ties.
Global Leadership and Multilateralism:
- Modi highlighted India’s role in Africa’s development, especially following the African Union’s inclusion in the G20 during India’s presidency.
Humanitarian Aid and Cultural Ties:
- Modi announced 20 tonnes of flood relief supplies for Nigeria, reflecting India’s commitment to humanitarian cooperation.
- Cultural exchanges and recognition of shared heritage reinforce people-to-people connections.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in India-Nigeria Relations
- PM Modi’s visit underscores the mutual commitment to a robust and multi-faceted partnership.
- With shared priorities in development, security, and economic cooperation, this visit has laid the foundation for deeper ties between the two nations, fostering stability and progress in the broader African and global context.
| How Can India Help Nigeria? |
|
Defense: Nigeria faces challenges like Boko Haram, piracy, and oil theft. India can offer defense supplies, training, and remote sensing technology to tackle terrorism (e.g., Boko Haram) and piracy in the Gulf of Guinea. Seven Nigerian Presidents since 1960 were trained in India as defense officers. Economic Stabilization: Nigeria faces foreign exchange shortages and inflation (32%). Strategic initiatives such as partnerships in hydrocarbon sectors and infrastructure development can help stabilize Nigeria’s economy. India can offer large financial facilitations and consider barter arrangements to ease Nigeria’s foreign exchange shortage. Trade Enhancement: Bilateral trade stands at $7.9 billion, but India’s exports fell 29.7% in 2023-24. India can increase exports to Nigeria, including essential commodities like pharmaceuticals, foodstuffs, and textiles, leveraging the potential for rupee-based trade to boost bilateral trade from the current $7.9 billion. Capacity Building: Offering expertise in IT, healthcare, and education can support Nigeria’s infrastructure and human resource development. |
| Practice Question: Examine the significance of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Nigeria in the context of India-Africa relations. How does the deepening India-Nigeria partnership contribute to regional and global strategic objectives? (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Cultural experts ask UN to shield war-torn Lebanon’s heritage
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
- Hundreds of cultural professionals, including archaeologists and academics, petitioned the United Nations to protect Lebanon’s cultural heritage amidst ongoing conflict.
- Recent Israeli strikes near Baalbek and Tyre, UNESCO World Heritage sites, have threatened ancient Roman ruins.
- The petition, signed by 300 cultural figures, urges UNESCO to establish “no-target zones,” deploy international observers, and enforce the 1954 Hague Convention on cultural heritage protection.
- It highlights threats to historic sites like Baalbek, Tyre, and Anjar and calls for influential states to push for military restraint and impose sanctions if necessary.
| UNESCO World Heritage Sites In Lebanon |
|
Baalbek Ancient Roman city with grand temples, including the Temple of Jupiter.Known for its architectural and historical significance. Tyre Historic Phoenician city and former trading hub.Features ancient ruins, including a Roman hippodrome and necropolis. Byblos One of the world’s oldest continuously inhabited cities.Important for its role in early alphabet development and Phoenician culture. Anjar Umayyad city showcasing early Islamic architecture.Features a unique urban layout with palaces, mosques, and baths. Qadisha Valley (Holy Valley) and the Forest of the Cedars of God A sacred valley with ancient Christian monasteries.Contains Lebanon’s famous cedar trees, a national symbol. |
2. India conducts ‘historic’ flight test of hypersonic missile with a range of 1,500 km
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The flight test was conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) from Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha.
- The missile is designed to carry various payloads for all branches of the Indian armed forces.
- DRDO tracked the missile using multiple range systems, confirming its successful terminal manoeuvres and impact with high accuracy.
- Hypersonic weapons travel at speeds of Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound) and are highly manoeuvrable, making them hard to detect and intercept.

| What is a hypersonic missile? |
|
Definition: A hypersonic missile is a type of missile that travels at speeds greater than Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound), typically exceeding 6,174 km/h, making it extremely difficult to intercept due to its speed and manoeuvrability. Advantages: Speed: Hypersonic missiles can strike targets quickly, reducing reaction time for defence systems. Evasion: Their high speed and ability to manoeuvre at various altitudes make them harder to detect and intercept. Penetration: They can bypass current missile defence systems, providing strategic superiority. Precision: Hypersonic missiles can deliver highly accurate strikes on critical targets. Surprise Element: Their rapid strike capability leaves little time for opponents to respond, enhancing tactical advantage. Global Reach: They can cover vast distances in a short time, enabling global strike capabilities. Versatility: Useful for both conventional and nuclear strikes. |
3. Centre aims to make Andaman and Nicobar Islands a tuna export hub
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Export of tuna fish from India increased by 31.83% in 2023-24.
- The Centre is exploring new areas to boost tuna exports, focusing on Andaman and Nicobar Islands as a hub.

- The global tuna market is valued at $41.94 billion, with the Indian Ocean producing 21% of the world’s tuna.
- The Exclusive Economic Zone around the islands holds substantial tuna species with untapped resources.
- Potential annual yield estimates: 64,500 tonnes, including 24,000 tonnes of yellowfin, 22,000 tonnes of skipjack, 500 tonnes of bigeye, and 18,000 tonnes of neritic tuna.
- In 2023-24, India exported 51,626 tonnes of tuna worth $87.96 million.
- The region’s tuna fishery remains underdeveloped due to infrastructure, fishing technologies, and processing challenges.
- Investors’ meet aims to increase networking and optimise tuna fishing.
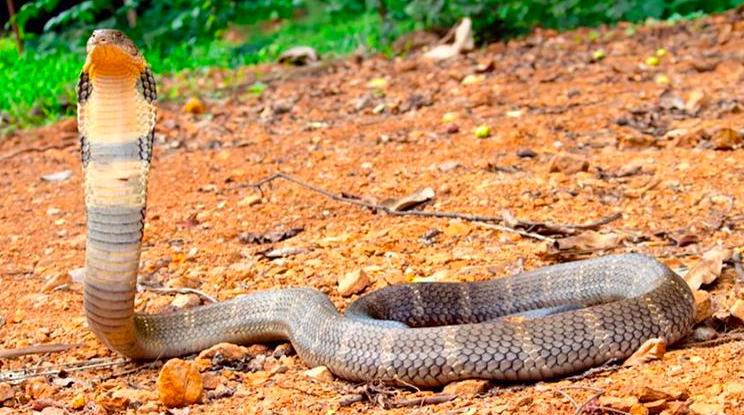
4. Kaalinga will be scientific name for Kalinga Sarpa
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The king cobra species from the Western Ghats, known as “Kalinga Sarpa” in Kannada, will be officially named Ophiophagus kaalinga.
- The species was previously thought to be a single lineage but extensive research revealed four distinct king cobra lineages.
- These lineages include Western Ghats, Indo-Chinese, Indo-Malaysian, and Luzon Island.
- The naming of Kaalinga will be formally announced on November 22 in Bengaluru.
- The research involved genetic work, DNA mapping, and sampling from over 200 specimens across the region.
- The Western Ghats king cobra was found to be genetically distinct from others, leading to its unique classification.
| More About Kalinga Sarpa |
|
The Ophiophagus kaalinga is a newly identified species of king cobra from the Western Ghats. It was previously classified under a single species, Ophiophagus hannah, for 186 years.Genetic research revealed that the Western Ghats population forms a unique lineage. King cobras are venomous and primarily prey on other snakes. The species is known for its large size, with lengths reaching up to 18 feet. They are found in forested regions of South and Southeast Asia. The Western Ghats king cobra’s venom is potent, used for subduing large prey like other snakes. Their habitat includes dense forests and hilly terrains.
|




