18 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Western and Southern States Lead Economic Growth, West Bengal Faces Sharp Decline: EAC-PM Report
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
| The article analyzes regional economic disparities in India from 1960-61 to 2023-24, highlighting strong growth in Western and Southern states while West Bengal experiences a continuous decline in its GDP share. |
Analysis of News:
What is EAC – PM?
- EAC-PM is a non-constitutional, non-statutory, independent body constituted to give advice on economic and related issues to the Government of India, specifically to the Prime Minister.
- The council serves to highlight key economic issues to the government of India from a neutral viewpoint.
- It advises the Prime Minister on economic issues like inflation, microfinance, and industrial output.
- For administrative, logistic, planning and budgeting purposes, the NITI Aayog serves as the Nodal Agency for the EAC-PM.
Regional Economic Performance: Key Trends
- Over the six-decade period from 1960-61 to 2023-24, Western and Southern states like Maharashtra and Gujarat consistently performed well economically, with Maharashtra maintaining the highest share in India’s GDP.
- In contrast, West Bengal saw a significant and continuous decline in its GDP share, from 10.5% in 1960-61 to 5.6% in 2023-24. Southern states—Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu—together contributed over 30% of India’s GDP in 2023-24.
Per Capita Income Disparities
- The analysis highlights disparities in relative per capita incomes across states. Delhi, Telangana, and Karnataka had the highest per capita incomes, with Delhi’s being 2.5 times the national average in 2023-24.
- States like Bihar lagged significantly. West Bengal, which had a higher-than-average per capita income in 1960-61, saw a decline to 83.7% of the national average by 2023-24.
- Smaller states like Sikkim and Goa witnessed remarkable improvements in per capita income, becoming some of the richest states by this metric.
Sectoral Shifts and Economic Dynamics
- Punjab and Haryana diverged in economic trajectories post-Green Revolution, with Haryana’s per capita income rising substantially, while Punjab’s declined relative to the national average.
- Odisha, traditionally a lagging state, saw notable improvement in its per capita income.
- Karnataka and Telangana emerged as key contributors to the national GDP post-liberalization, while Kerala experienced a slight dip in its share since the early 2000s.
Broader Implications and Future Outlook
- The report underscores the growing economic contributions of southern and western states and the declining performance of eastern states like West Bengal.
- This regional disparity comes amid ongoing debates over the Finance Commission’s tax distribution, which affects states contributing a higher share to India’s GDP.
| Impacts of regional disparities on economic development |
|
Creation of islands of prosperity in the sea of poverty Reduced Economic Growth Potential due to regional disparities Income Inequality and reduced GDP growth Unequal Access to Opportunities and impact on economic development Migration and Urbanization and impact on economic development Poor Social and Health Outcomes and impact on economic development Rise of social tensions and impact on economic development |
| Practice Question: Examine the regional economic disparities in India from 1960-61 to 2023-24, focusing on the contrasting performances of Western, Southern, and Eastern states. Discuss the factors contributing to the growth of some states and the decline of others, and suggest measures to promote balanced regional development. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Jammu and Kashmir’s First Assembly Polls Post-2019: New Powers and Limitations Under Union Territory Status
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Context: |
| The article discusses the first phase of polling for Jammu and Kashmir’s Assembly under its new Union Territory status, highlighting the altered powers and roles following the 2019 reorganization. |
Analysis of News:
Transition to Union Territory
- The Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, transformed Jammu and Kashmir from a state into a Union Territory (UT) with a legislature.
- Ladakh, split off as a separate UT, does not have a legislature. The new Assembly for J&K has reduced powers compared to previous state legislatures.
Powers of the Assembly
- Under the 2019 Act, the J&K Assembly can legislate on matters in the State List, except on public order and police, which remain with the Lieutenant Governor (LG).
- However, any financial bills require the LG’s recommendation, giving the LG significant control over legislative processes.
Role of the Lieutenant Governor
- The LG holds considerable power in J&K, overseeing critical areas like the bureaucracy, the Anti-Corruption Bureau, and any matter outside the legislative competence of the Assembly.
- His discretion in decision-making is broad and protected from legal challenge.
Comparison with Delhi
- While Delhi also has a legislature under Article 239AA, it is a special case due to its status as the national capital. The J&K Assembly, by contrast, operates under Article 239A, which applies to UTs like Puducherry, but with stricter limitations on its legislative scope.
Conclusion
- This election marks a shift in governance for Jammu and Kashmir. The Assembly will function under significantly altered powers, with the LG holding a dominant role in administrative and financial matters.
| Practice Question: Analyze the implications of the 2019 reorganization on the powers and functions of the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly. How do the changes in governance and legislative authority under the Union Territory status impact the political and administrative dynamics of the region? (250 words/15 m) |
3. Power asymmetry between China and Russia
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context |
|
Power Asymmetry between Russia and China:
- China dominates bilateral trade, with Russian exports making up 30.4% of Russia’s total exports but only 3% of China’s.
- Russia’s exports to China are largely energy-dependent (70%), whereas China’s exports to Russia are more diversified.
- Russia’s economy is heavily reliant on energy revenues, which make up 30-50% of its federal budget.
- Russia relies on China for critical high-priority goods, including dual-use products essential for arms manufacturing.
- China has replaced the EU as Russia’s top trade partner, absorbing losses from Western sanctions.
- Russia’s dependence on China has grown since 2021, making Moscow increasingly vulnerable to Beijing’s influence.
What it Means for India:
- Russia’s growing dependence on China limits its strategic autonomy, impacting its ability to balance relations with India.
- India-Russia trade is minimal compared to the expanding China-Russia trade, diminishing Moscow’s leverage to prioritise New Delhi.
- As the Sino-Russian relationship deepens, Russia’s geopolitical goals align more closely with China’s than with India’s.
- This power asymmetry raises concerns about Russia’s capability to resist Chinese pressure in the event of conflicting interests between India and China.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the growing Sino-Russian strategic partnership for India’s security and foreign policy. How should India navigate its relations with Russia in light of Moscow’s increasing economic dependence on China? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. What is a telescope? How good are modern telescopes?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
What is a Telescope?
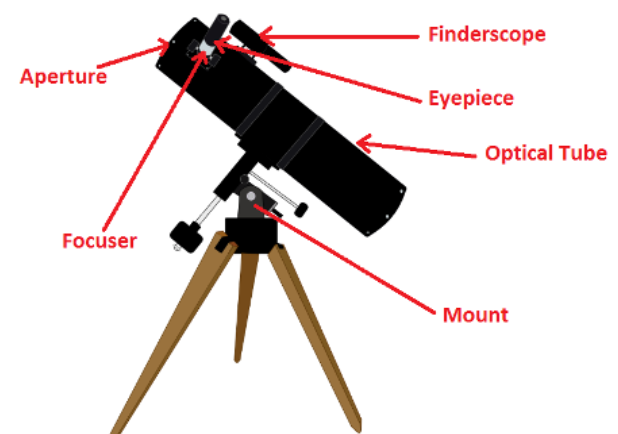
- A telescope is a tool used to observe distant objects by collecting light. It reveals celestial wonders by magnifying images and focusing on faint light rays.
The Aperture
- Aperture refers to the opening that collects light. A larger aperture allows more light to be gathered, creating clearer and more detailed images.
Lenses vs. Reflectors
- Refracting telescopes use lenses to bend light, focusing it at a specific point.
- Reflecting telescopes use mirrors to gather and focus light, offering better clarity and reduced distortion compared to refractors.
Features of Telescopes
- Brightness and visibility of celestial objects depend on apparent magnitude, which scales inversely with brightness (lower numbers are brighter).
- For example, Sirius is the brightest star, with a magnitude of -1.46.
Why Are Telescopes Setup on Mountains?
- Mountain observatories provide clearer skies due to reduced atmospheric distortion.
- Space telescopes, above the atmosphere, deliver even clearer views.
Advanced Telescopes
- The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), located in Chile, is one of the most advanced telescopes, with a 39-meter aperture for high-resolution images.
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) uses segmented mirrors to focus light more efficiently, crucial for infrared observations.
Evolution in Telescope Technology
- Modern telescopes use adaptive optics to correct atmospheric turbulence.
- The Hubble Space Telescope captures images with a resolution of 0.04 arc seconds, aiding in deep-space exploration.
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Azerbaijan Launches New Climate Finance Fund Ahead of COP29 to Aid Developing Nations
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 08)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
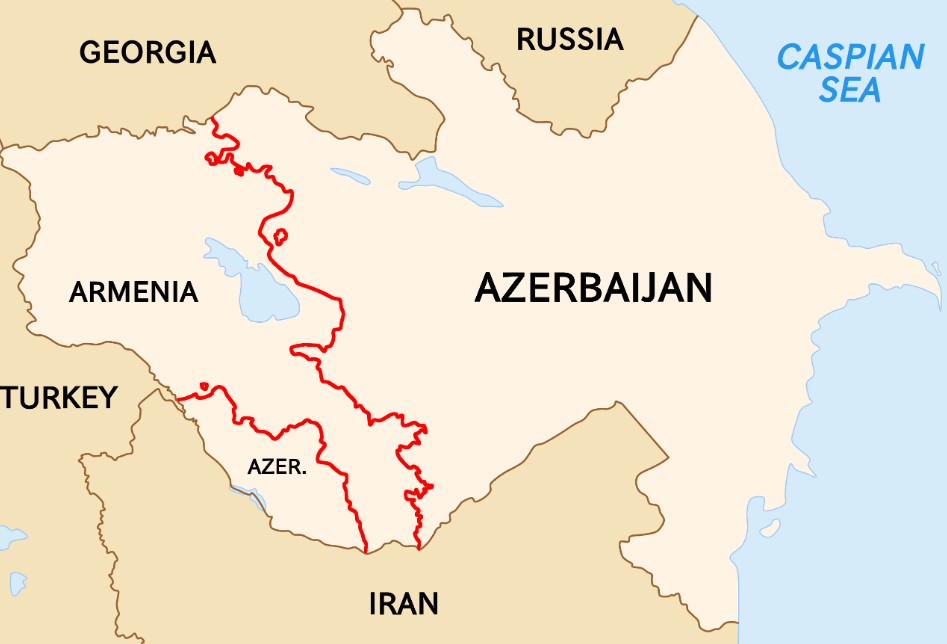
Focus on Climate Finance at COP29
- The primary agenda for COP29 is to finalize an agreement on post-2025 climate finance.
- Developed nations have been mandated to mobilize at least $100 billion annually since 2020, but the sum is expected to increase post-2025.
- However, negotiations on the specifics have seen limited progress, with several meetings scheduled before COP29 in Baku (November 11-22, 2024).
Azerbaijan’s Broader Climate Proposals
- In addition to CFAF, Azerbaijan has put forward other climate-related proposals for COP29, including pledges to increase global energy storage by six times by 2030, develop a global green hydrogen market, and minimize emissions from digitization and data centers.
- While these are outside the official COP29 agenda, they reflect Azerbaijan’s efforts to push for additional climate action.
Structure and Goals of the CFAF
- Half of the CFAF would be directed toward climate projects in developing countries, while the other half would support the implementation of national climate action plans.
- The fund will become operational once it accumulates $1 billion and secures commitments from at least 10 countries.
2. Metformin May Slow Aging in Male Monkeys, Raising Hope for Human Anti-Aging Benefits
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Context: |
| A recent study suggests that metformin, an inexpensive diabetes drug, may slow aging in male monkeys, particularly in the brain. This raises the possibility of using the drug to delay aging in humans. |
Analysis of News:
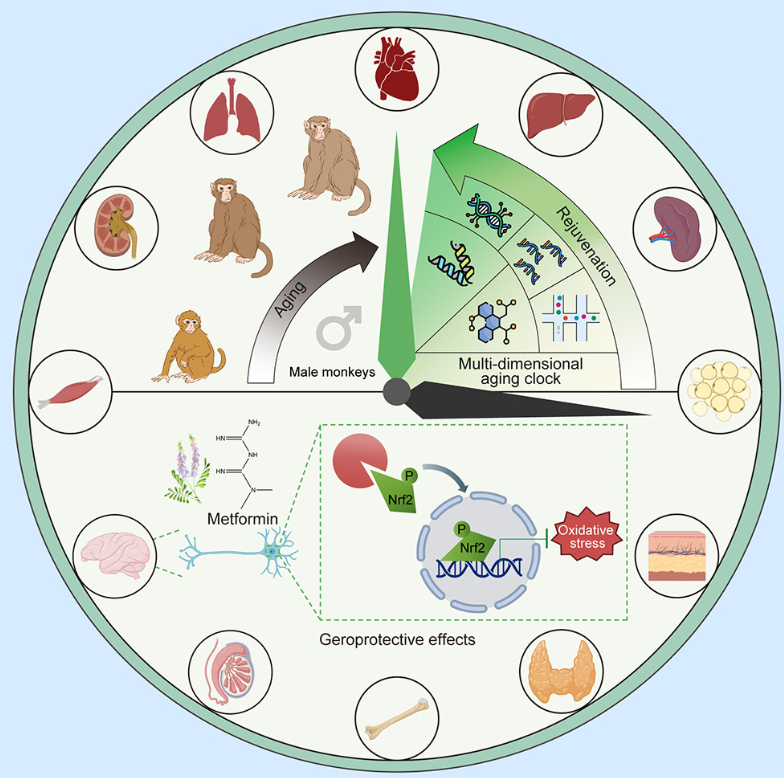
Study Details
- Published on September 12 in the journal Cell.
- Conducted by 43 researchers from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, and other institutions.
- Involved 12 elderly male cynomolgus macaques treated with metformin for 40 months, alongside control groups of older and younger monkeys.
Key Findings
- Neuronal activity in treated monkeys resembled that of monkeys six years younger.
- Metformin slowed biological aging in tissues from organs like the lungs, kidneys, liver, skin, and the brain’s frontal lobe.
- The drug reduced chronic inflammation, a major aging marker.
- It activated the NRF2 protein, which helps protect against cellular damage caused by injury and inflammation.
Metformin’s Background
- Widely used for treating type 2 diabetes since the 1950s.
- Derived from guanidine, found in the herb Goat’s Rue.
- Known for benefits beyond diabetes treatment, such as reducing the risk of cancer and showing anti-aging effects in worms, rodents, and flies.
Research Significance
- The study is the most comprehensive examination of metformin’s effects beyond its use in mice.
- Previous anti-aging effects had not been tested directly in primates before this study.
Future Implications
- Further research is needed before metformin can be approved as an anti-aging compound for humans.
- A 120-person trial is underway to test metformin’s effect on aging in humans, in collaboration with Merck, the drug’s manufacturer.
3. Rain harvesting work reveals megalithic burial site
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
What Are Megaliths?
- A megalith is a large stone structure or monument from prehistoric times, often used in burials or ceremonial sites.

- These monuments, found mainly in the Deccan Plateau, the northeastern regions, and parts of South India, include dolmens, cairn circles, and menhirs.
- Dolmens are burial chambers made of upright stones covered by a large capstone.
- Cairn circles are stone formations used as grave markers, while menhirs are tall, upright stones often placed in rows.
- Megalithic sites, such as those in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala, offer insights into ancient burial practices, social hierarchies, and ceremonial activities.
- They are crucial for understanding India’s early cultures and their advancements in stone technology and communal rituals.
4. No progress in resolution of Demchok and Depsang friction points in 2 years
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar reported that India and China have completed 75% of disengagement along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in eastern Ladakh.
- China has acknowledged disengagement from four border areas, but two friction points, Demchok and Depsang, remain unresolved.
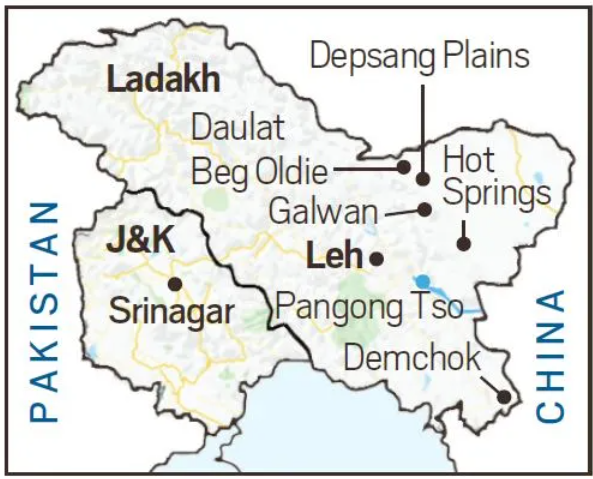
- There has been no progress on these two points in the past two years.
- The situation is described as “generally stable” by Chinese Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Mao Ning.
| Issues Over Demchok And Depsang Regions |
|
5. Rapa Nui genomes restore the real history of an old, troubled people
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
What Are Rapa Nui?

- The Rapa Nui, also known as the people of Easter Island, are Polynesians native to this remote island in the southeastern Pacific Ocean.
- Famous for their monumental stone statues called moai, they developed a complex society and culture.
- The Rapa Nui’s history includes periods of significant population growth and dramatic decline, influenced by both internal factors and external impacts from European contact.
How They Help Restore Real History
- Uncover Population History: Genomic data can reveal past population sizes and changes. For instance, recent studies show that the Rapa Nui population was larger and more stable before European contact than previously thought.
- Reveal Ancestry and Mixing: Genomic studies reveal how Rapa Nui people are related to other populations, including Native Americans and Europeans, providing a clearer picture of historical interactions and migrations.
More About New Study
- Recent research on the Rapa Nui (Easter Island) challenges the idea that resource overexploitation caused their population collapse.
- The study reveals that the Rapa Nui population grew until European contact, which introduced two major catastrophes: the abduction of a third of the population by Chilean slave traders and a devastating smallpox outbreak.
- The findings suggest that the Rapa Nui were managing their resources sustainably and that external factors, rather than internal mismanagement, led to their decline.
6. Ammonium nitrate imports cause concern
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
India’s rising ammonium nitrate (AN) imports from Russia have impacted domestic fertiliser production and mining industries. Cheaper imports, driven by Russia’s access to subsidised natural gas, are undermining India’s efforts to boost local AN capacity and reduce import dependence. |
Ammonium Nitrate (AN):
- A chemical compound primarily used as a fertiliser and an explosive in mining.
- Essential for creating controlled blasts during mining of coal, iron, and other ores.
- It is a key ingredient in nitrogen fertilisers, critical for agricultural productivity.
Concerns Over Ammonium Nitrate Import:
- Imports from Russia surged to 2.39 lakh tonnes in FY23, impacting domestic production.
- Domestic capacity utilisation dropped to 72% from 91% due to cheaper imports.
- Countries like Russia have access to low-cost, subsidised natural gas, making their AN cheaper.
- India’s domestic fertiliser industry, investing over ₹4,000 crore to boost AN capacity, faces competition.
- Dependence on imports raises concerns for mining sectors reliant on AN for operations.
- Curtailing imports is necessary to support domestic manufacturers and ensure self-reliance.
7. Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi launches ‘SUBHADRA’ – the largest women-centric scheme in Bhubaneswar, Odisha
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2055572 )
| Context |
|
SUBHADRA Scheme:
- The SUBHADRA scheme is a significant women-centric initiative launched by the Government of Odisha.
- It is designed to benefit over 1 crore women across the state.
- The scheme targets women aged 21-60 years for financial assistance.
- Each eligible woman will receive a total of Rs. 50,000 over a period of 5 years, from 2024-25 to 2028-29.
- The amount will be disbursed as Rs. 10,000 annually, divided into two equal installments.
- Payments will be made directly into the beneficiaries’ Aadhaar-enabled and DBT-enabled bank accounts.
- The scheme is integrated with a pilot project of the Reserve Bank of India’s digital currency, marking a step towards digital financial inclusion.
8. Rangeen Machhli App
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2055513 )
| Context |
|
The “Rangeen Machhli” App:
- The “Rangeen Machhli” app offers multilingual information on popular ornamental fish species in eight Indian languages, making it accessible to a broad audience.
- The app provides comprehensive guidance on fish care, breeding, and maintenance for hobbyists and farmers interested in ornamental fish.
- A key feature of the app is the “Find Aquarium Shops” tool, which helps users locate nearby aquarium stores, promoting local businesses and ensuring reliable sources for ornamental fish and aquarium products.
Ornamental Fishery in India:
- India has a diverse range of ornamental fish, with over 195 indigenous varieties from the North-East and Western Ghats, and nearly 400 species from marine ecosystems.
- Most ornamental fish exports are wild varieties from the North-East and Southern States, contributing about 85% of the country’s total exports.
- The Western Ghats, a biodiversity hotspot, is home to 40 ornamental freshwater fish species, 37 of which are endemic.
- Approximately 90% of India’s ornamental fish trade focuses on freshwater species, with the remaining 10% on marine species.
- Popular ornamental fish include goldfish, Oscar, Flower Horn, Tetras, Discus, and Cichlids, with goldfish being the most favoured among hobbyists.



