19 June 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Controversy Surrounds Great Nicobar Island Infrastructure Project: Balancing Development and Environmental Concerns
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies– Issues arising out of their design & implementation GS3 – Environment – Environment Pollution and Degradation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
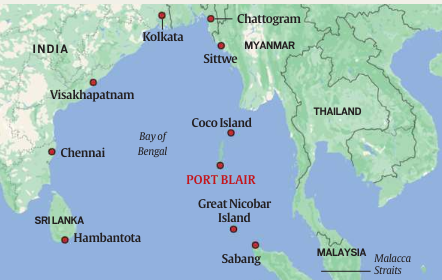
Project Details and Objectives:
- The mega infrastructure project, implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO), includes an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), a greenfield international airport, a township, and a gas and solar-based power plant spread across 16,610 hectares.
- Initiated after a NITI Aayog report, the project aims to leverage the island’s strategic location to enhance India’s maritime economy and tourism potential.
- The site for the proposed ICTT and power plant is Galathea Bay, an area devoid of human habitation, and the project has received forest and environmental clearances as of October 2022.
Strategic Importance:
- The Bay of Bengal and the Indian Ocean region are crucial for India’s strategic and security interests, particularly in countering the expanding presence of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army Navy.
- India’s focus on the Indo-Pacific region, especially strategic chokepoints like Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok, underscores the importance of enhancing military capabilities on Great Nicobar Island.
- The island’s development is part of a broader strategy to strengthen India’s maritime security, with significant military infrastructure upgrades already underway in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Environmental Concerns:
- The proposed infrastructure development has faced opposition due to its potential environmental impact. Critics argue that the project threatens the Shompen, a particularly vulnerable tribal group, and the island’s delicate ecosystem.
- Concerns include the felling of nearly a million trees, destruction of coral reefs, and threats to local wildlife such as the Nicobar Megapode bird and leatherback turtles.
- The Congress party, along with various environmental and civil society groups, has highlighted the seismic volatility of the region and accused the administration of insufficient consultation with local tribal councils.
Conclusion:
- The Great Nicobar Island infrastructure project represents a significant development initiative with both strategic and economic implications for India.
- However, it also poses substantial environmental and social challenges that need careful consideration. Balancing developmental goals with ecological preservation and indigenous rights will be crucial for the project’s long-term success and sustainability.
- The ongoing debate underscores the need for comprehensive and inclusive planning to address the diverse concerns associated with such large-scale infrastructure projects.
| About Great Nicobar |
|
|
PYQ: In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009) (a) Nilgiri Hills (b) Nicobar Islands (c) Spiti Valley (d) Lakshadweep Islands Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Examine the proposed infrastructure development on Great Nicobar Island, discussing its strategic and economic significance for India. Critically analyze the environmental and social concerns and suggest measures to balance developmental goals with ecological preservation and the rights of indigenous communities. (250 words/15 m) |
2. CII Urges Removal of Angel Tax Amid Plummeting Startup Funding and Job Losses
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 15)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to development and employment |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
History and Purpose of Angel Tax:
- Angel Tax was first introduced in 2012 to deter the generation and use of unaccounted money through the subscription of shares of a closely held company at a value higher than the fair market value of the firm’s shares.
- The government cited the difference between valuations and actual performance as a potential sign of money laundering.
- However, the industry argued that investors fund startups based on their future potential, and the tax on the difference between the issue price of unlisted securities and their fair market value (FMV) has hurt funding.
Current Challenges and Funding Decline:
- The changes in the Angel Tax provisions came at a time when an estimated 100 Indian startups laid off over 15,000 employees in 2023, with the funding winter that began in 2022 persisting.
- Indian startups witnessed over a 60 percent decline in funding in terms of value in 2023.
- The Finance Act 2023 had amended Section 56(2)(viib) of the Income-tax Act to include foreign investors in the ambit, meaning that when a startup raises funding from a foreign investor, it will now be counted as income and be taxable.
Government’s Response and Exemptions:
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT)-recognized startups were excluded from the Angel Tax levy.
- However, following pushback from the industry and reports of decline in funding, the Finance Ministry exempted investors from 21 countries, including the US, UK, and France, from the levy of Angel Tax for non-resident investment in unlisted Indian startups.
- Despite this, the list excluded investments from countries like Singapore, the Netherlands, and Mauritius, which have traditionally been key geographies for startups to raise money.
Conclusion:
- The Angel Tax remains a contentious issue for the Indian startup ecosystem. While its original intent was to curb money laundering, its implementation has had unintended consequences on legitimate fundraising activities.
- The recent amendments and exemptions have provided some relief, but the exclusion of significant investment sources continues to be a concern.
- A thorough reassessment of the tax’s impact on startups is necessary to foster a more conducive environment for innovation and growth in India.
|
PYQ: What does venture capital mean? (2014) (a) A short-term capital provided to industries (b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs (c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses (d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of the Angel Tax on Indian startups and the broader implications for capital formation and employment in the country. How has the recent amendment to the Finance Act, 2023, affected this scenario? What are the industry’s concerns, and what measures could be taken to address these issues? (250 words/15 m) |
3. NSAs of India and the U.S. assure industry to resolve any barriers that hold back relations
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Ajit Doval, India’s National Security Adviser, emphasised the need for India and the U.S. to lead in technology to safeguard their values and strategic interests at the iCET CEO roundtable.
- Jake Sullivan, his U.S. counterpart, joined the discussion where both assured industry leaders of addressing barriers hindering deeper India-U.S. ties, particularly in defence and emerging technologies.
- The roundtable, organised by CII, focused on enhancing bilateral collaboration, including defence innovation and semiconductor industries.
- Issues discussed included India’s export controls, ease of doing business, and advancing deals for MQ-9B drones and GE-414 jet engines, pending clearance by India’s Cabinet Committee on Security.
- India sought liberalisation of licensing for high-tech sectors and increased R&D funding.
- Both sides welcomed industry inputs and committed to resolving specific issues to foster closer ties.
| India – US Defence Cooperation |
|
| PYQ: ‘Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad)’ is transforming itself into a trade bloc from a military alliance, in present times – Discuss. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of India-U.S. defence cooperation in the context of enhancing regional stability and advancing technological capabilities. How do foundational agreements and defence deals contribute to this strategic partnership? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Russia ready to ship turbine hall valves for Kudankulam
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Topic: GS2 – International relations – Bilateral relations, GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context:- |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Russia’s Rosatom is set to deliver 26 turbine hall pipeline valves weighing 27.5 tonnes for Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project’s reactors 5 and 6.
- These valves, designed to withstand temperatures up to 350 degrees Celsius, ensure tight fluid or gas flow control crucial for system reliability.
- Each valve underwent rigorous factory tests including pneumatic, hydraulic, and tightness tests to ensure operational readiness.
- Manufactured by Rosatom’s Petrozavodskmash, these valves are also deployed in Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant and Belarusian Nuclear Power Plant.
- Rosatom will also supply fuel for Kudankulam reactors throughout their operational lifespan.
| Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project (KKNPP) |
|
| PYQ: With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project (KKNPP) in India’s energy security and its strategic collaboration with Russia. Highlight the key features of the project and its future expansion plans. (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. First Session of the 18th Lok Sabha: Speaker Election and Pro Tem Procedures
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
Role and Appointment of the Pro Tem Speaker:
Who is a Pro Tem Speaker?
- A pro tem Speaker, derived from the Latin term meaning “for the time being,” is a temporary appointee who fulfills the duties of the Speaker until the permanent Speaker is elected by the Lok Sabha.
- This role is not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution but is detailed in the official “Handbook on the Working of Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs.”
How is the Pro Tem Speaker Chosen?
- The pro tem Speaker is typically the senior-most MP in the Lok Sabha. The process begins with the Legislative I Section of the Legislative Department preparing a list of the most senior MPs, which is then reviewed by the Minister for Parliamentary Affairs or the Prime Minister.
- The final appointment is made by the President of India, who also appoints three additional senior MPs to assist the pro tem Speaker. This selection is based on seniority and is aimed at ensuring experienced leadership during the initial proceedings of the new Lok Sabha session.
How are Oaths Administered?
- Once the Prime Minister approves the list of senior MPs, the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs seeks their consent and submits a note to the President for final approval. Upon the President’s consent, the appointed members are informed of their roles.
- The President then administers the oath to the Speaker pro tem at Rashtrapati Bhavan. The Speaker pro tem, with the assistance of the three senior MPs, subsequently administers the oath or affirmation to the newly elected MPs in the Lok Sabha.
- This process ensures that the new members can officially assume their parliamentary duties.
2. Researchers Witness Supermassive Black Hole Awakening in Galaxy SDSS1335+07
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
Findings on the Supermassive Black Hole:
The Nature of Black Holes
- Black holes are known for their extreme density and gravitational pull so strong that even light cannot escape. This powerful gravity creates a chaotic environment around the black hole, especially when it starts to draw in and consume nearby matter.
Formation of an Accretion Disk
- In galaxy SDSS1335+0728, located about 360 million light-years from Earth, researchers observed the formation of a spinning disk of diffuse material around its supermassive black hole.
- This disk, known as an accretion disk, radiates energy at extremely high temperatures, often outshining the entire galaxy. Such a bright and compact region powered by a supermassive black hole is termed an “active galactic nucleus.”
- Experts from the European Southern Observatory in Germany explained that these nuclei emit large amounts of energy across various wavelengths.
- Studying these active galactic nuclei is essential for understanding both galaxy evolution and the physics of supermassive black holes.
Potential Triggers of the Awakening
Uncertain Activation Causes
- The exact cause of the black hole’s sudden activation remains unknown. Experts admitted that the current understanding does not provide a clear reason for this awakening.
Theories and Speculations
- One researcher suggested that this could be a natural phase in the life cycle of galaxies, which may oscillate between periods of activity and dormancy.
- If these observations do not signify the onset of an active galactic nucleus, they might represent an entirely new and previously unseen astrophysical phenomenon.
This discovery not only highlights the dynamic nature of galaxies but also opens new avenues for research into the behavior and life cycles of supermassive black holes.
3. China has 500 nuclear warheads, says SIPRI
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context:- |
|
Analysis of the news:
- SIPRI (Stockholm International Peace Research Institute) is a renowned global think tank specialising in research on conflict, armaments, arms control, and disarmament.
- Founded in 1966, SIPRI is based in Stockholm, Sweden, and operates as an independent international institute.
- It conducts research on global security issues, including military expenditure, arms transfers, and nuclear weapons.
- SIPRI provides data and analysis to policymakers, researchers, media, and the public to promote transparency and informed decision-making in international security.
- The institute publishes the annual SIPRI Yearbook, a comprehensive resource on global security developments, including trends in military spending, arms production, and nuclear weapons.
- SIPRI’s research covers a wide range of topics, including arms control treaties, regional conflicts, and the impact of military technology advancements.
- It collaborates with governments, international organisations, and civil society to foster dialogue and promote efforts towards disarmament and conflict resolution.
4.Scientists from India, China, U.K. develop catalyst to produce cheaper biodiesel
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context:- |
|
Analysis of the news:
- A team of scientists from India (NIT Silchar and NIT Rourkela), China, and the UK has developed a water-repellent catalyst to enhance biodiesel production cost-effectively.
- Published in Advanced Functional Materials, their research introduces a “spherical superhydrophobic activated carbon catalyst” designed to resist water, a common byproduct in biodiesel production.
- This catalyst prevents water from poisoning active sites crucial for the biodiesel conversion process, ensuring high efficiency and reusability.
- Derived from biomass (cellulose), the catalyst is environmentally friendly, abundant, and affordable.
- Current biodiesel costs approximately ₹100 or $1.2 per litre in India; implementing this catalyst could potentially reduce costs to about 37 cents per litre, making biodiesel more competitive against conventional diesel priced at ₹87 per litre.
- Scientists highlighted the catalyst’s role in advancing sustainable energy solutions, aiming to increase biodiesel adoption for a greener future.


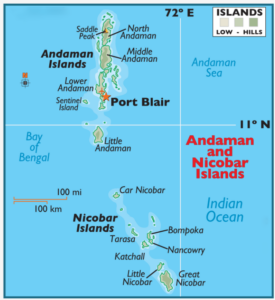 Great Nicobar is the southernmost island of the Nicobar Islands Archipelago.
Great Nicobar is the southernmost island of the Nicobar Islands Archipelago.


