2 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Record Surge in Undocumented Indian Crossings from Canada to the US Raises Concerns Over Visa Policies and Border Security
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Migrant
- The International Organization for Migration defines a migrant as any person who is moving or has moved across an international border or within a state away from his/her habitual place of residence.
- Migration is the movement of people from one place to another, either permanently or temporarily.
Surge in Undocumented Indian Crossings from Canada to the US
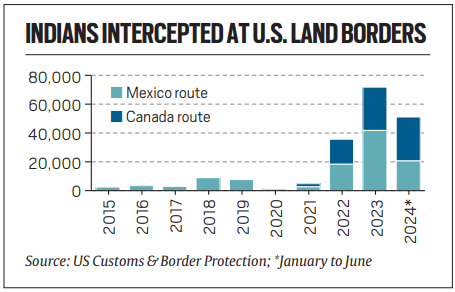
- The number of undocumented Indians crossing from Canada into the United States on foot has reached a record high, surpassing those entering via the Mexico route.
- In June alone, 5,152 Indians entered the US from Canada, a sharp rise attributed to the accessible Canadian visa process and the relatively soft border compared to the US-Mexico border.
Canada’s Visa Process Under Scrutiny
- This surge has drawn attention to Canada’s visa screening process, especially as Indian nationals bound for Canada have also been seeking asylum in the UK during stopovers.
- Both the US and the UK have raised concerns with Canada, urging for more stringent visa checks and the introduction of transit visas for Indian passengers stopping in the UK.
Increase in Asylum Claims
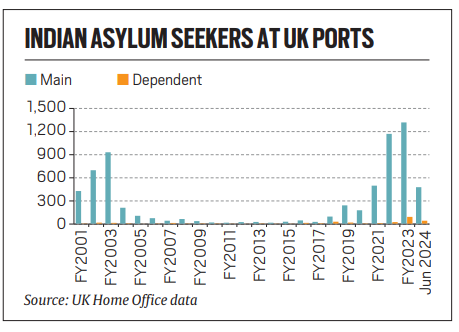
- Parallelly, there has been a significant increase in asylum claims from Indian nationals in both Canada and the UK.
- In Canada, claims rose dramatically following a relaxation in visa policies aimed at attracting foreign students.
- This trend is echoed in the UK, where a loophole allowing Canada-bound Indians to transit without a visa has led to a spike in asylum applications.
Asylum Statistics
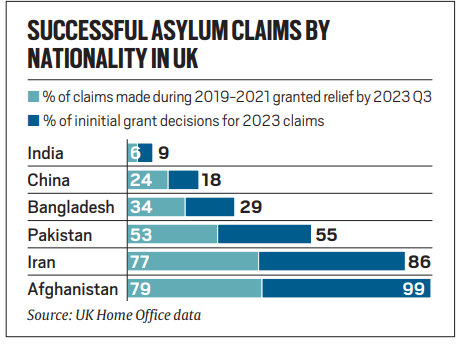
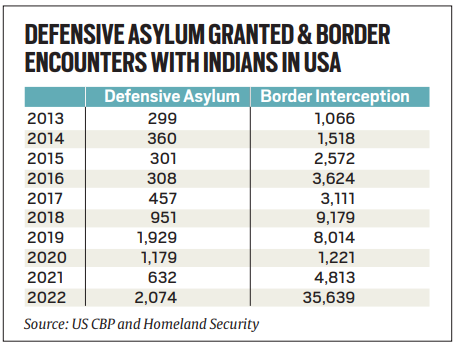
- UK: Indians have a very low chance of receiving asylum, with only 6-9% success, compared to higher rates for nationals from countries like China, Pakistan, and Iran. Between 2019-2023, fewer than 300 Indians were granted asylum or leave to remain. Despite efforts to reduce the backlog, over 95,000 applications were still pending at the end of 2023.
- US: The success rate for Indian asylum seekers remains below 15%, despite an increase in defensive asylum grants since 2018. The number of pending cases involving Indian nationals has surged, reaching 53,457 in 2023. The overall backlog in immigration courts is substantial, with nearly 8 lakh defensive asylum seekers awaiting hearings by the end of 2022.
Policy and Security Implications
- The rise in undocumented crossings and asylum claims has prompted calls for enhanced border security and more rigorous immigration controls in both the US and Canada.
- The situation highlights the complexities of immigration policies and the unintended consequences of visa leniencies, which can lead to increased illegal migration and strain on border enforcement.
| Contributing Factors |
|
The rise in unauthorized Indian migrants is attributed to various factors, including:
|
| PYQ: “Refugees should not be turned back to the country where they would face persecution or human right violation”. Examine the statement with reference to the ethical dimension being violated by the nation claiming to be democratic with open society. (2021) |
| Practice Question: Analyze the factors contributing to the rising number of Indian asylum seekers in the US and the UK. Discuss the challenges these countries face in processing these applications and the implications for their immigration systems. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Diverging Paths: Wheat Faces Production Woes While Rice Battles Surplus in India’s Cereal Landscape
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context: |
| The article highlights the contrasting challenges of surplus in rice and production constraints in wheat, emphasizing the need for distinct policy approaches for each cereal. |
Analysis of News:
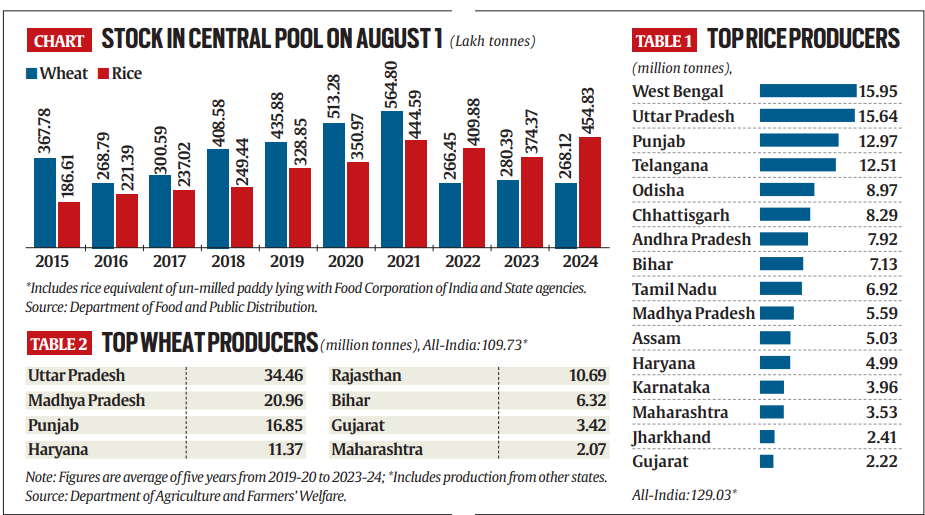
Economists and policymakers often group wheat and rice together as part of a “cereal surplus” and “mono-cropping/lack of diversification” issue. However, the situations of these two cereals have diverged significantly, necessitating a nuanced approach to each.
Rice: A Surplus Problem
- Export Trends: India has seen a consistent increase in rice exports, with 21.21 million tonnes (mt) in 2021-22, 22.35 mt in 2022-23, and 16.36 mt in 2023-24.
- Stock Levels: Despite these exports, rice stocks in government godowns reached an all-time high of 45.48 mt on August 1, indicating a surplus issue.
- Policy Recommendations: There is a need to lift the ban on exports of white non-basmati rice, reduce the 20% duty on parboiled non-basmati rice, and remove the $950/tonne floor price on basmati shipments to manage excess stock.
Wheat: A Production Challenge
- Export Decline: Wheat exports have significantly decreased from 7.24 mt in 2021-22 to just 0.19 mt in 2023-24.
- Stock Levels: Central pool wheat stocks on August 1 were 26.81 mt, the lowest for this date in recent times, signaling production challenges.
- Geographical and Temporal Constraints: Wheat is more geographically and temporally constrained than rice, with production concentrated in fewer states and affected by climate change, leading to greater volatility.
Consumption Divergence
- Wheat: Consumption of wheat is rising, driven by processed foods like bread, biscuits, and other products made from refined flour (maida). This trend is fueled by increasing incomes and urbanization.
- Rice: Rice consumption has not seen similar growth in processed forms, and its consumption patterns remain more traditional.
Policy Implications
- Wheat: Given the production challenges and rising consumption, India may need to import wheat in the short term. Long-term strategies should focus on boosting yields and developing climate-smart varieties.
- Rice: The surplus in rice production requires policy adjustments to manage excess stock through exports.
Conclusion
- Rice and wheat, though often treated together, face distinct challenges and require separate strategies.
- Wheat’s production volatility contrasts with rice’s surplus, necessitating targeted policies for each to address their unique issues.
| PYQ: What are the major factors responsible for making rice-wheat system a success? In spite of this success how has this system become bane in India? (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the distinct challenges faced by wheat and rice production in India. How should policymakers address the divergent issues of wheat production volatility and rice surplus to ensure food security and economic stability? (250 words/15 m) |
3. Ensure LGBTQIA+ couples get ration cards, says Centre
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Vulnerable sections. |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Ration Cards: LGBTQIA+ couples will now be recognized as part of the same household for ration card purposes. States and Union Territories have been directed to ensure non-discrimination in issuing these cards.
- Health Ministry Directives:
- Body Claim: Partners in LGBTQIA+ relationships can claim each other’s body if no next of kin is available.
- Intersex Guidelines: New guidelines for medical interventions for intersex children and those with sexual differentiation disorders aim to ensure normal health without complications.
- Mental Health: Guidelines are being developed to address mental health and well-being issues for the LGBTQIA+ community.
- Social Justice Measures: These actions are interim measures taken following the Supreme Court’s directions in the marriage equality case of October 2023.
- Committee Formation: Following the Supreme Court’s directive, a committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary was formed in April, with a sub-committee under the Home Secretary discussing discrimination and welfare issues.
- Additional Measures:
- Prison Visitation: Advisories issued for LGBTQIA+ rights in prisons.
- Financial Services: LGBTQIA+ couples can open joint bank accounts and nominate each other as beneficiaries.
- Healthcare:
- Rights: Advisories ensure rights concerning healthcare, including awareness activities and prohibition of conversion therapy.
- Access: The Directorate General of Health Services is working to reduce discrimination and improve healthcare access for the LGBTQIA+ community.
| Practice Question: Discuss the recent measures taken by the Indian government to address the needs and rights of LGBTQIA+ individuals, including their access to ration cards, healthcare, and financial services. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Cities in Asia are growing upwards more than outwards
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Vertical vs. Horizontal Growth:
- A recent study published in Nature Cities highlights that cities, particularly in Asia, are expanding upwards faster than outwards.
- This shift is driven by the need to accommodate a global urban population increase of about two billion people from 1990 to 2020.
Study Methodology:
- The research analysed over 1,500 cities worldwide using remote-sensing satellite data to measure both vertical (building volume) and horizontal (ground area covered) growth.
- Data from scatterometers, which measure the volume of buildings, indicated that while horizontal expansion has slowed, vertical growth has accelerated.
Findings:
- The study shows a global trend of increased vertical growth in urban areas, with notable examples in East Asian cities, particularly China.
- Cities with populations exceeding 10 million have shown more prominent vertical expansion, especially in the 2010s.
International Context:
- The study is recognized for its extensive analysis of long-term upward growth across a broad sample of cities.
- Urban growth patterns differ globally, with some countries experiencing more vertical development due to fewer regulations.
- For example, Indian cities face more stringent height regulations compared to East Asian cities.
Regulations and Variations in India:
- In India, the growth pattern varies, with large cities showing significant vertical expansion, while others exhibit more horizontal growth.
- For instance, Delhi has primarily seen outward expansion, with some vertical growth in recent years.
- Urban growth is influenced by a combination of policies, regulations, historical patterns, and geographical factors.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Vertical growth can increase population density but also poses challenges related to infrastructure, climate resilience, and sustainability.
- It requires improved public transport, job opportunities, and essential infrastructure like sewage and water systems.
- Tall buildings contribute to the urban heat island effect, affecting local climate conditions such as wind speeds and rainfall.
Policy Implications:
- The study underscores the need for updated master planning in cities to address contemporary challenges.
- Existing planning laws are often outdated and do not adequately address modern issues like transportation and climate change.
- There is a call for locally tailored planning decisions and updated regulations to ensure sustainable and livable urban environments.
Conclusion:
- While vertical growth offers solutions for accommodating larger populations, it also requires a balanced approach considering sustainability, infrastructure needs, and climate impacts.
- Revising planning strategies and policies is essential for effective future urbanisation management.
| PYQ: With a brief background of quality of urban life in India, introduce the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme’ (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
| Practice Question: Analyse the implications of increasing vertical urban growth on infrastructure, climate, and sustainability in rapidly urbanising cities. How should urban planning adapt to these changes? (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Supreme Court Rebukes AYUSH Ministry for Weakening Rule 170 on Misleading Ads
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is Rule 170?
- Purpose: Introduced in 2018, Rule 170 governs the manufacture, storage, and sale of Ayurvedic, Siddha, and Unani medicines to control inappropriate advertisements.
- Requirements: AYUSH drug manufacturers must obtain approval and a unique identification number from state licensing authorities before advertising their products. Applications must include textual references, safety evidence, and quality assurance. The rule also prohibits advertisements that are misleading, obscene, or make exaggerated claims.
- Background: The rule was introduced following concerns from a parliamentary standing committee about misleading claims in AYUSH product advertisements.
Challenges in Regulating AYUSH Drugs
- Licensing Requirements: Like allopathic drugs, AYUSH drug manufacturers need a license from the drug controller. However, unlike allopathic drugs, AYUSH drugs do not require Phase I, II, and III clinical trials for approval.
- Safety Trials: Only formulations containing specific ingredients, such as snake venom and heavy metals, require safety trials. Most AYUSH drugs can be approved based on rationale from authoritative texts.
AYUSH Ministry’s Directive to Ignore Rule 170
- ASUDTAB Recommendation: The Ayurvedic, Siddha, and Unani Drugs Technical Advisory Board (ASUDTAB) suggested omitting Rule 170 during a meeting in May 2023. The reasoning was that amendments to the Drugs and Magic Remedies Act, which also addresses misleading advertisements, were being considered by the health and AYUSH ministries.
- Ministry’s Notification: In this context, the AYUSH Ministry issued a notification advising state licensing authorities to ignore Rule 170, leading to the Supreme Court’s criticism.
2. Namibia to Cull Hundreds of Wild Animals Amid Worst Drought in a Century
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
About Namibia
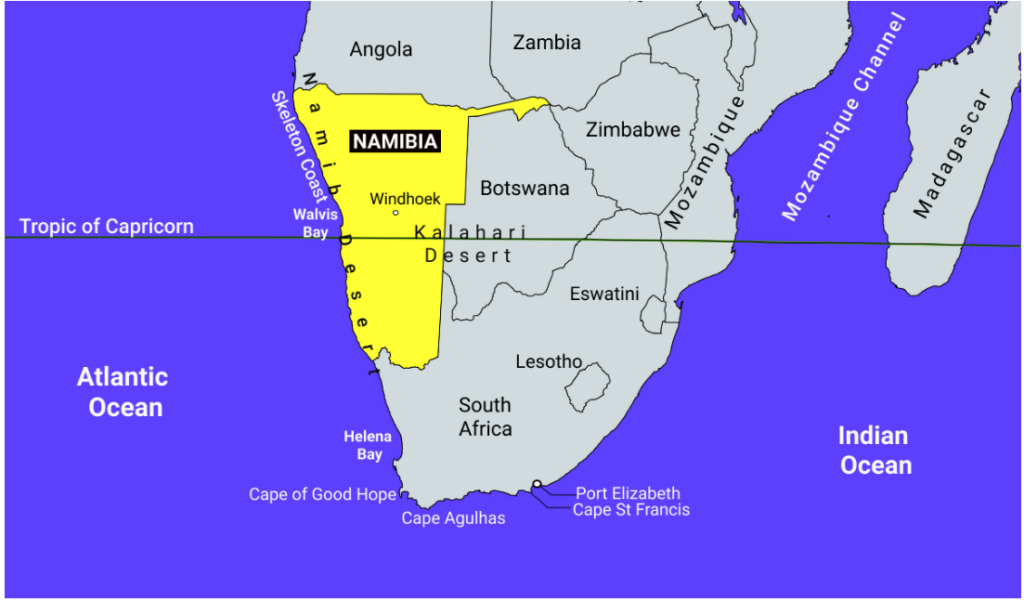
- Namibia is the second least densely populated, located along the Southern African coast.
- Namibia shares a border with the surrounding countries of South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Zambia, and Angola.
- It has a diverse environment that is home to deserts, marshlands, savannas, mountains, and river valleys.
Scope of the Culling
- The culling plan includes 723 animals, with over 150 already killed, yielding around 63 tonnes of meat.
- The animals targeted include 83 elephants, 30 hippos, and various species of antelopes, zebras, and buffaloes.
Drought’s Impact on Namibia
- The ongoing drought, exacerbated by the El Niño weather pattern and climate change, has severely affected Namibia.
- Crop failures, livestock deaths, and a depletion of food reserves have led to a significant food crisis, with over a million people facing acute food insecurity.
Government’s Rationale
- Namibia’s Ministry of Environment, Forestry, and Tourism justifies the culling as a necessary measure to manage the country’s natural resources for the benefit of its citizens.
- The culling also aims to reduce grazing pressure and water scarcity in wildlife habitats.
Ethical Considerations
- While the culling of wild animals for meat is not unusual in southern Africa, it has raised ethical questions.
- Experts argue that if done sustainably and in accordance with both domestic and international regulations, it should not be a cause for concern.
3. ASI copying old stone inscriptions on temple walls in Tiruchi district
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 2)
| Context |
| The ASI is copying inscriptions from two temples in Srirangam and Manachanallur taluks, Tiruchi district. |
Inscriptions on temple walls in Tiruchi district:
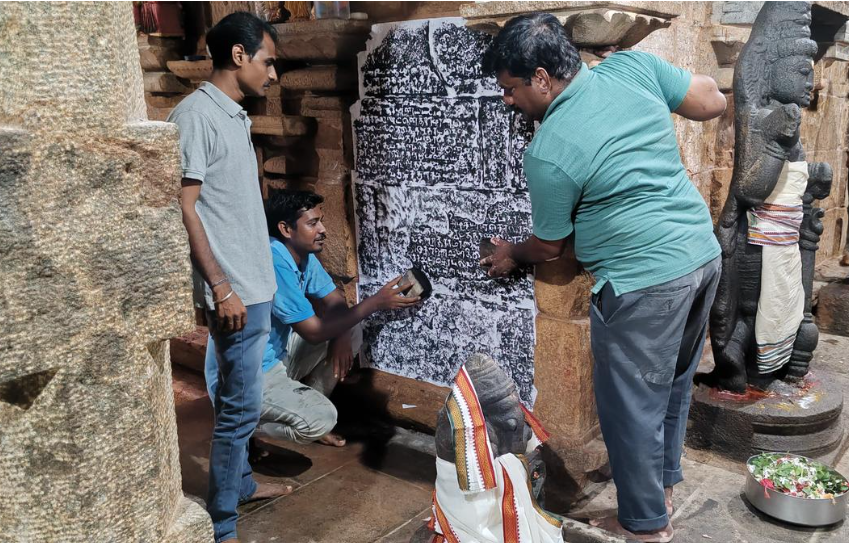

- The inscriptions at Mattrurai Varadeswarar Temple, Thiruvasi, are believed to be from the Kulothunga Chola period, a significant era in South Indian history marked by Chola rule and temple construction.
- The Chola dynasty, particularly under Kulothunga, was known for its contributions to art, architecture, and temple endowments, reflecting the importance of religion and temple patronage during that time.
- Inscriptions at Agneeswarar Temple in Periya Karuppur village, dating back to the Vijayanagara Kingdom of the 14th century, highlight the continued tradition of temple donations and patronage by rulers.
- These Vijayanagara inscriptions often recorded grants of land or resources to temples, showcasing the strong connection between political power and religious institutions.
- Such inscriptions offer valuable insights into the socio-political and economic systems of mediaeval South India, especially the role temples played as cultural, religious, and economic hubs.
- The inscriptions also reflect the evolving temple architecture and religious practices across different dynasties.
4. Japan bets on heat-resistant rice against climate change
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Heat-Resistant Rice:
- Heat-resistant rice varieties are being developed in Japan to address shortages caused by extreme weather conditions.
- High temperatures and dry conditions last summer led to reduced rice yields and poor grain quality, contributing to the lowest inventories in 25 years.
- Saitama Agricultural Technology Centre is working on new varieties, such as ’emihokoro,’ to withstand higher temperatures and maintain quality.
- High heat disrupts starch accumulation in rice grains, causing them to become opaque and mottled, reducing market value.
- The initiative involves cultivating and cross-pollinating seeds to create more resilient rice strains.
- Climate change is expected to further impact rice yields, with projections indicating a 20% decline by 2100.
5. Paris seeks UNESCO heritage status for its zinc roofers
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
| Paris is nominating its iconic zinc roofs for UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage status, highlighting their historical and aesthetic value.The bid reflects efforts to preserve this traditional craft while addressing the challenges posed by climate change. The decision will be made in December. |
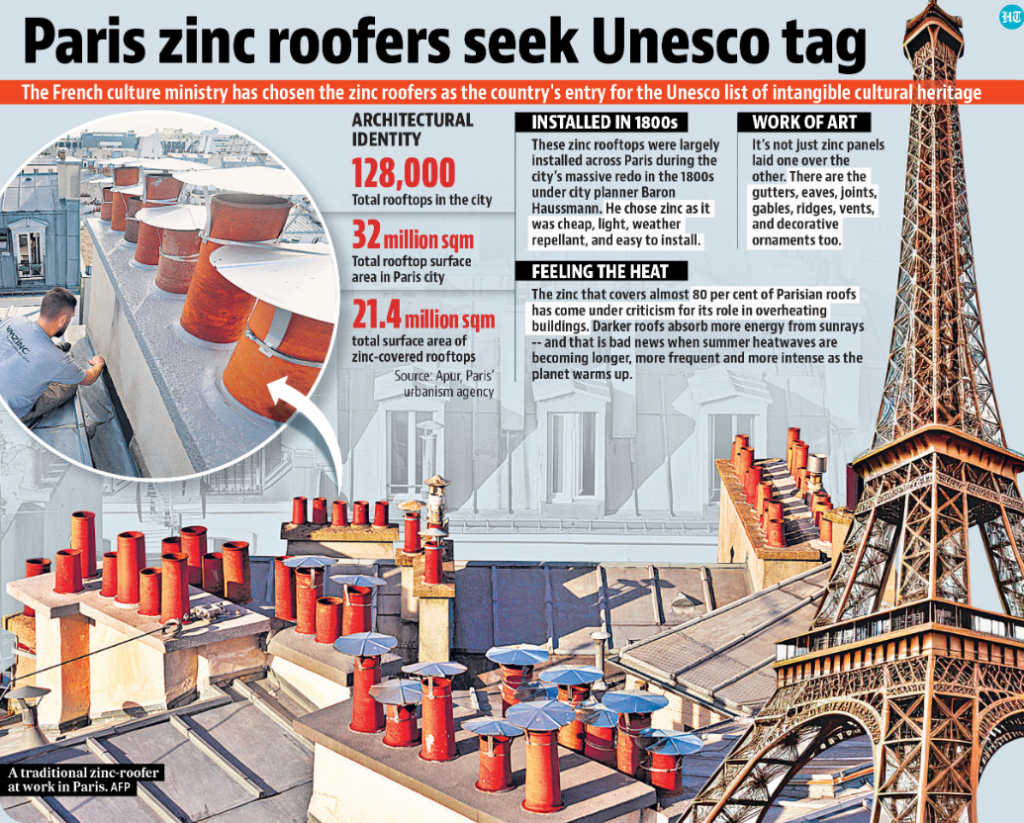
Zinc Roofers of Paris:
- Zinc roofers have been a significant part of Paris’s skyline for nearly two centuries, contributing to the city’s distinctive grey appearance.
- Paris features approximately 128,000 roofs, with 21.4 million square metres covered in traditional zinc.
- Zinc roofs are known for their durability and distinctive appearance, contributing to the city’s unique character.
- The craftsmanship involved includes both functional roofing and ornamental work.
- The profession is adapting to challenges posed by climate change, including the need for more resilient materials and techniques.
- Efforts are underway to ensure the continuation and preservation of this traditional craft in the face of modern challenges.
6. Shri Satish Kumar takes charge as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Railway Board
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050631 )
| Context |
|
Railway Board:
- Overview: The Railway Board is the apex body responsible for the administration and oversight of Indian Railways, operating under the Ministry of Railways.
- Structure: Comprises a Chairman, who is the Chief Executive Officer (CEO), and several Members, each in charge of different domains like Traffic, Engineering, and Mechanical.
- Functions:
- Policy Formulation: Develops and implements policies for the overall management and development of Indian Railways.
- Planning and Coordination: Oversees planning of railway projects, including infrastructure development, modernization, and expansion.
- Financial Management: Prepares and monitors the railway budget, ensuring efficient allocation and utilisation of resources.
- Operational Oversight: Ensures smooth and safe operation of train services, including scheduling, maintenance, and safety measures.
- Regulatory Role: Establishes standards for railway operations and infrastructure, and ensures compliance with safety and quality regulations.
- Human Resource Management: Oversees recruitment, training, and management of railway personnel.
7. NHPC and SJVNL Conferred ‘Navratna’ Status
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2050604 )
| Context |
|
National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC)
- Established in 1975, NHPC is a major Indian public sector undertaking (PSU) focused on hydroelectric power generation.
- Headquartered in Faridabad, Haryana.
- Operates and maintains several hydro power projects across India.
- Currently has an installed capacity of 7,144 MW.
- Engaged in constructing projects totaling 10,443 MW.
- Plays a key role in generating clean, renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Satluj Jal Vidyut Nigam Limited (SJVNL)
- Established in 1988, SJVNL is a joint venture between the Government of India and the Government of Himachal Pradesh.
- Headquartered in Shimla, Himachal Pradesh.
- Focuses on hydro power generation with an installed capacity of 2,467 MW.
- Involved in constructing projects with a total capacity of 4,836 MW.
- Contributes significantly to renewable energy and sustainable development.



