20 November 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Is imposing tariffs on Chinese imports a good idea?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
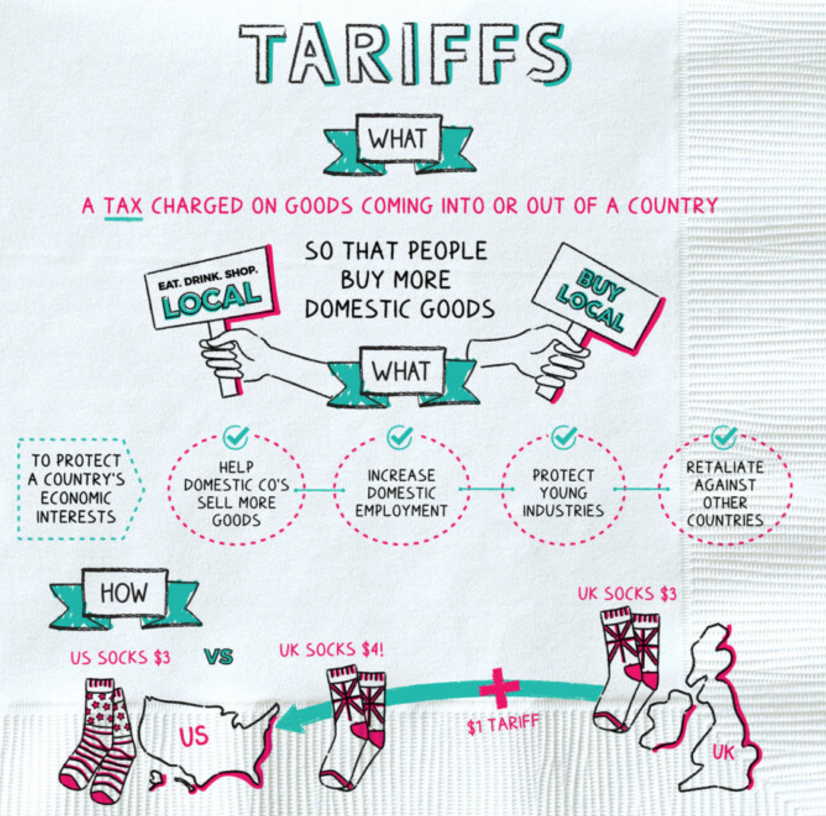
Proposed Tariffs and India’s Position
- India’s exports to global markets face potential tariff hikes, especially in sectors like textiles, steel, and electronics.
- Protectionist policies by nations like the U.S. and EU aim to correct trade imbalances but create challenges for Indian exporters.
- Indian manufacturers face stiff competition from heavily subsidised foreign goods, making local products less competitive.
Impact of Tariffs on India
- Inflationary Pressures: Increased import tariffs on Indian goods could make exported items more expensive, reducing demand.
- Trade Balance Issues: Tariffs imposed on Indian exports may widen the trade deficit, especially with large trading partners like the U.S. or EU.
- Domestic Boost: Shifts in global trade due to tariffs could encourage India to strengthen domestic manufacturing and reduce reliance on imports.
- Global Trade Wars: Retaliatory tariffs from India and other affected nations could escalate trade conflicts, destabilising global markets and impacting commodity prices.
Material Impact: A Hypothetical Example
- If a textile product from India costs ₹7,000 and is sold abroad for $100 (₹8,000), a 10% tariff raises the cost to $110.
- The price hike makes Indian goods less competitive, giving an advantage to domestic producers in the importing country.
India’s Potential Responses
- Incentivizing Exporters: Subsidies or tax rebates could offset the tariff burden on Indian exporters.
- Currency Adjustments: India could consider a controlled depreciation of the rupee to make exports cheaper and more attractive.
- Policy Reforms: Strengthening “Make in India” initiatives and improving ease of doing business can bolster India’s global competitiveness.
Conclusion
- India must adopt targeted strategies to mitigate tariff impacts while leveraging global challenges to enhance domestic production and trade resilience.
| PYQ: ‘China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia’, In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Rising protectionism in global trade is impacting India’s export potential and trade balance. Suggest policy measures to mitigate these challenges while enhancing India’s global competitiveness. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. The dangers of high-altitude sickness
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice-Health |
| Context |
|
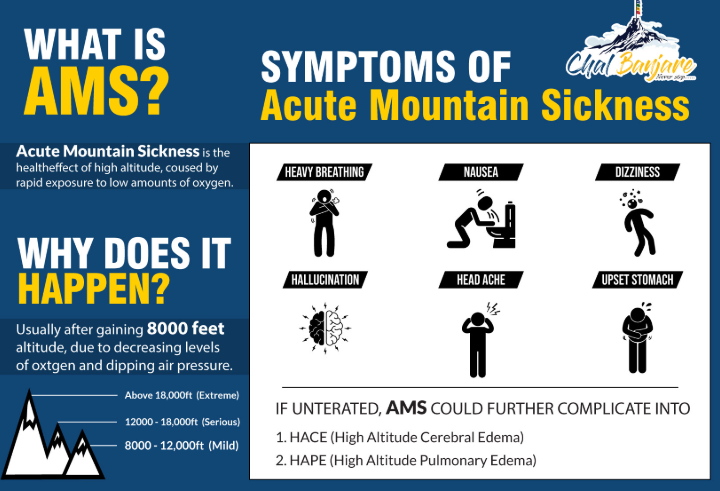
Infrastructural Challenges
- Healthcare Facilities: Many Himalayan regions lack adequate healthcare facilities to manage AMS cases, particularly beyond major towns.
- While some areas like Leh have specialised facilities, most regions lack basic preventive health screenings at entry points for tourists.
- Health Screening Proposal: Implementing health screenings, similar to the old “Inner Line Permit” system, could help save lives by identifying at-risk tourists before they venture into high-altitude areas.
| High-Altitude Sickness (AMS) |
|
Definition: High-altitude sickness, or Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS), occurs when the body cannot acclimatise to high elevations, usually above 8,000 feet (2,400 metres). Symptoms: Early symptoms include headache, nausea, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Without treatment, AMS can escalate into high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) or high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE), both of which are life-threatening conditions requiring immediate medical attention. Causes: At high altitudes, the body struggles to get enough oxygen, which can lead to hypoxia. The body increases breathing and red blood cell production, which can strain the heart. |
Registration System
- Mandatory Registration: A mandatory registration system for tourists would help authorities track tourist movement, respond quickly to emergencies, and support research on high-altitude illnesses.
Prevention and Treatment
- Gradual Ascent: Gradual ascent is crucial to acclimatise the body to reduced oxygen levels.
- Medications: Acetazolamide and Dexamethasone may help with acclimatisation and symptom relief, but descent remains the primary treatment.
- Immediate Descent: Descending to lower altitudes is the most effective treatment for AMS, HAPE, and HACE.
Policy Proposals
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Establish state-of-the-art medical facilities in high-altitude regions and create research centres for AMS.
- Air Ambulance Services: Equip regions with air-ambulance services for rapid evacuations.
- Information Dissemination: Provide health and safety information at check-in points and on government websites.
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges of managing high-altitude sickness in India’s Himalayan regions. Suggest measures to improve healthcare infrastructure to mitigate risks associated with Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS). (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Act fast to mitigate a disaster in Teesta Valley, groups urge PM, CMs
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS1 – Geography, GS3 – Disaster Management |
| Context |
|
Warning for the Teesta Valley
- The Teesta Valley has only six months to prepare before the 2025 monsoon exacerbates the damage caused by the 2023 Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) and the subsequent dam breach by NHPC Ltd.
- The 2023 disaster claimed over 100 lives, disrupted livelihoods, destroyed assets and critical military installations, and caused significant ecological damage across Sikkim and West Bengal.
| Teesta River: |
|
Lack of Coordinated Response
- The governments of Sikkim and West Bengal have been working in isolation, focusing only on their respective areas instead of addressing the issue at a broader landscape level.
- The two states need to implement both structural and non-structural mitigation measures across the Teesta Valley before the next monsoon to reduce the future flood impacts.
Call for Central Assistance and Joint Committee
- Central assistance is necessary due to the scale and complexity of the problem, which cannot be handled at the state level.
- A joint Sikkim-West Bengal committee is recommended to address common issues and develop coordinated disaster management strategies for both states.
Urgent Rehabilitation and Infrastructure Repair
- The disaster has displaced numerous families, worsening their economic stability and mental distress.
- The NH10 road, crucial for transport, remains unstable, further burdening infrastructure and the local economy.
- Urgent repairs to roads and bridges, along with reinforcement of evacuation centres with backup solar power, are necessary.
Sustainable Mitigation Measures
- Sustainable engineering solutions like re-channeling the Teesta River and strengthening land-use planning are vital to prevent future damage.
- Non-structural measures such as early warning systems, afforestation programs, and awareness campaigns are essential for long-term disaster resilience.
|
PYQ: Q.1 How will the melting of Himalayan glaciers have a far-reaching impact on the water resources of India? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2020) Q.2 “The Himalayas are highly prone to landslides.” Discuss the causes and suggest suitable measures of mitigation. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
| Practice Question: Examine the environmental, economic, and social impacts of the 2023 Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) in the Teesta Valley. Discuss the measures required to mitigate future flood risks. (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Labour Shortages Drive Mechanisation in Agriculture: The Sugarcane Harvesting Revolution in Maharashtra
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context: |
| The article discusses the growing mechanisation in sugarcane harvesting in Maharashtra as a solution to labour shortages in agriculture, highlighting its benefits, challenges, and future potential. |
Analysis of News:
About Farm Mechanisation in India
- Farm mechanisation refers to the adoption of machinery and technology in various agricultural operations. It plays a pivotal role in enhancing productivity, reducing manual labour, and ensuring timely and efficient farm practices.
- In India, where agriculture remains a backbone of the economy, mechanisation becomes even more critical.
Labour Shortages in Agriculture
- Labour shortages in agriculture are driven by the physically demanding nature of tasks like transplanting, spraying, and harvesting, coupled with alternative employment opportunities in sectors like construction and manufacturing.
- Government welfare schemes such as MGNREGA and direct cash transfers have further increased the opportunity cost of agricultural work, prompting rural labourers to seek less taxing livelihoods.
Impact on Mechanisation and Herbicide Use
- The decline in manual labour availability has accelerated the adoption of mechanisation in Indian agriculture.
- For example, mechanised solutions, such as sugarcane harvesters, have started replacing traditional manual practices in states like Maharashtra.
- Additionally, the use of herbicides has risen to address labour shortages in manual weeding.
Sugarcane Harvesting in Maharashtra: Traditional System
- In Maharashtra, sugar mills, rather than farmers, manage sugarcane harvesting through muqaddams (middlemen) who organize labour gangs (tolis).
- These gangs, largely composed of migrant workers, are supervised by the muqaddams, who also coordinate with mills to ensure consistent cane supply.
- However, this system faces challenges due to labour shortages, aging workforce, and instances of workers not reporting for duty after receiving advances.
Rise of Mechanical Harvesters
- The deployment of mechanical harvesters, pioneered by mills like the Manjara Farmers’ Cooperative in Latur, is transforming sugarcane harvesting.
- With increased efficiency and reduced dependence on labour, mills like Manjara now aim for 100% mechanisation.
- Mechanical harvesters also enable better cane recovery by cutting the stalk closer to the ground, enhancing sugar extraction efficiency.
Economic Viability of Mechanisation
- Farmers in Maharashtra have invested significantly in mechanisation, supported by cooperative bank loans.
- While the initial investment is high, the operating costs—including labour, maintenance, and diesel—are offset by the efficiency and profitability of mechanical harvesting.
- Entrepreneurs in this space report substantial returns, showcasing the financial feasibility of this shift.
Challenges of Mechanical Harvesting
- Despite its advantages, mechanical harvesting has drawbacks.
- Machines chop cane tops into fine pieces, making them unsuitable for fodder—a key source of animal feed in states like Uttar Pradesh.
- However, proponents argue that the chopped tops enhance soil health by acting as organic mulch, improving water retention and nutrient cycling.
Future Prospects
- The mechanisation of sugarcane harvesting is expected to grow, with mills increasingly adopting advanced technologies.
- Scaling up mechanisation across multiple mills, coupled with innovations to address fodder challenges, can further enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability in India.
| Global Comparisons |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of labour shortages on agricultural practices in India, with a focus on the increasing adoption of mechanisation in sugarcane harvesting. What are its benefits and challenges? (250 words/15 m) |
5. India and Italy Unveil Strategic Action Plan 2025-29 to Strengthen Bilateral Ties Across Key Sectors
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 08)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Defence Cooperation
The action plan emphasizes:
- Joint Engagements: Annual Defence Consultative Meetings and Staff Talks to foster coordination in training and information exchange.
- Indo-Pacific Synergy: Cooperation to enhance interoperability, particularly in light of Italy’s increasing focus on the Indo-Pacific region.
- Technology Partnerships: Collaboration between public and private stakeholders to advance defence technologies.
Economic Cooperation
- Industrial Partnerships: Promotion of technological centers and investments in key industries, including semiconductors, automotive, and infrastructure.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Strengthening mutual ties in cutting-edge production and industrial development.
Connectivity Initiatives
- Maritime and Land Infrastructure: Joint efforts in developing connectivity under frameworks like the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor.
Science and Innovation
- Technological Advancements: Focus on critical technologies such as artificial intelligence, telecom, and service digitization.
- Value Chain Partnerships: Collaboration in emerging technology sectors to bolster innovation in both countries.
Space Exploration
- Collaborative Projects: Expanded partnership between ISRO and the Italian Space Agency in Earth observation, heliophysics, and lunar exploration.
Migration and Mobility
- Labour and Skill Development: Initiatives to promote legal migration, including a pilot program for training Indian health professionals for employment in Italy.
Energy Transition
- Global Alliances: Strengthened roles in the Global Biofuels Alliance and International Solar Alliance to enhance sustainable energy practices.
Conclusion
- The India-Italy Joint Strategic Action Plan 2025-29 reflects a shared vision for deepened bilateral ties, with a focus on leveraging technology, sustainability, and cultural cooperation.
- This collaboration has the potential to contribute significantly to global peace, security, and prosperity.
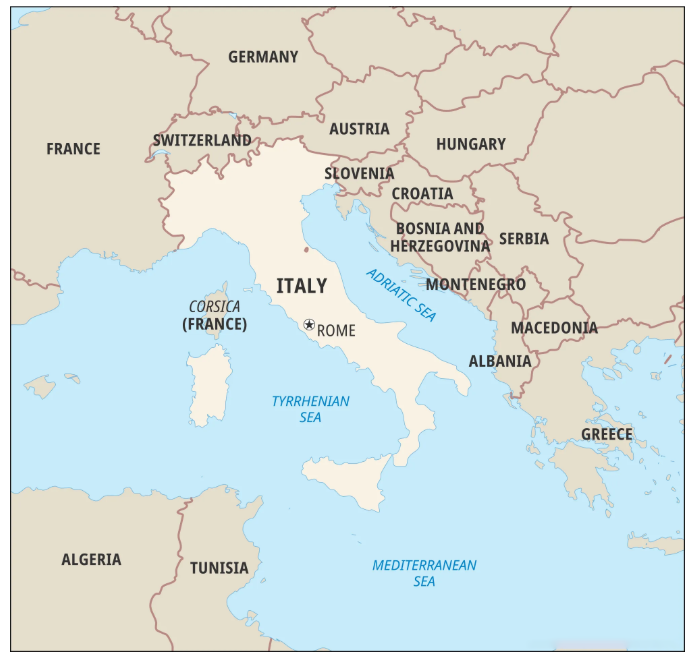
| Key Facts About Italy |
|
Bordering Countries: Italy has international borders with Austria, France, the Holy See (Vatican City), San Marino, Slovenia, and Switzerland. Italy also shares maritime borders with Albania, Algeria, Croatia, Greece, Libya, Malta, Montenegro, Spain, and Tunisia. Form of Government: Republic Capital: Rome Money: Euro Major Mountains: Alps, Apennines Major Rivers: Po, Adige, Arno, Tiber |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the India-Italy Strategic Action Plan 2025-29 in enhancing bilateral relations. How can this collaboration contribute to global peace, security, and sustainable development? (250 words/15 m) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Ukraine Deploys U.S.-Made ATACMS Missiles, Strikes Deep into Russian Territory
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 16)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Overview of ATACMS Missiles

Variants and Capabilities:
- M39A1 Block IA: Guided via GPS, these missiles have a range of 70 to 300 km and carry up to 300 cluster bomblets. Used earlier in Operation Iraqi Freedom, they entered service in 1997.
- M57 ATACMS: Equipped with a single 230-kg high-explosive warhead, these missiles also have a range of 70 to 300 km. First used in 2004, they have been deployed in multiple conflicts.
Reasons for U.S. Authorization
Geopolitical Dynamics:
- The U.S. decision followed Russia’s deployment of North Korean ground troops to bolster its forces, raising concerns in Washington and Kyiv.
- Ukraine’s persistent appeals for long-range weapons to target Russian military infrastructure far from the frontlines influenced the decision.
Timing:
- The move precedes a major U.S. political transition, with President-elect Donald Trump set to assume office in January 2024.
Impact on the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
Enhanced Strike Capability:
- ATACMS enable Ukraine to target deep within Russia, including regions like Kursk, where Russian and North Korean forces are concentrated.
- Hundreds of Russian military assets now fall within Ukraine’s operational range, increasing Kyiv’s ability to disrupt logistics and supply chains.
Russian Countermeasures: Anticipating such strikes, some Russian military assets have reportedly been relocated deeper into its territory to mitigate vulnerabilities.
2. Coal India Ltd under the Aegis of Ministry of Coal receives Green World Awards 2024 in London
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2074651®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|

Green World Environment Award :
- Purpose: Recognizes organisations globally for excellence in environmental sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
- Administered by: The Green Organization, an independent, non-political, non-profit environmental group founded in 1994.
- Categories: Awards are given for achievements in areas like CSR, waste management, energy efficiency, water conservation, and sustainable practices.
- Global Reach: Open to organisations, governments, and individuals worldwide.
- Criteria: Based on innovative environmental efforts, sustainability projects, and long-term contributions to the environment.
- Impact: Encourages best practices in environmental management, promoting global sustainability and inspiring others to adopt eco-friendly initiatives.
3. INDIAN ARMY SUCCESSFULLY CONCLUDES MULTI AGENCY DISASTER RELIEF EXERCISE ‘SANYUKT VIMOCHAN 2024’
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2074664®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
Exercise Sanyukt Vimochan 2024:
- Date And Location: Held on 18-19 November 2024 at Ahmedabad and Porbandar, Gujarat.
- Organiser: Conducted by the Konark Corps of Southern Command, Indian Army.
- Theme: Focused on disaster response to a ‘Cyclone in Coastal Region of Gujarat’.
- Participants: Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, Coast Guard, NDRF, SDRF, NDMA, and senior officials from nine foreign countries.
- Activities: Tabletop exercise and Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration, showcasing coordinated disaster management strategies.
- Objective: Strengthened national and international disaster response capabilities, aligned with Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Key Highlight: Display of indigenous disaster response technologies by Indian industries.

 About
About
