20 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. US Federal Reserve Cuts Interest Rates: Global Implications and Impact on India
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 15)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is US Fed Rate Cut?
- A Fed rate cut is essentially a reduction in the interest rate that the Federal Reserve charges banks to borrow money. This rate, known as the federal funds rate, serves as a benchmark for other interest rates in the economy.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) decides whether to cut or raise this rate based on economic conditions such as inflation, employment, and overall economic growth.
- When the Fed lowers this rate, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow money, which, in turn, can lead to lower interest rates on loans for consumers and businesses.
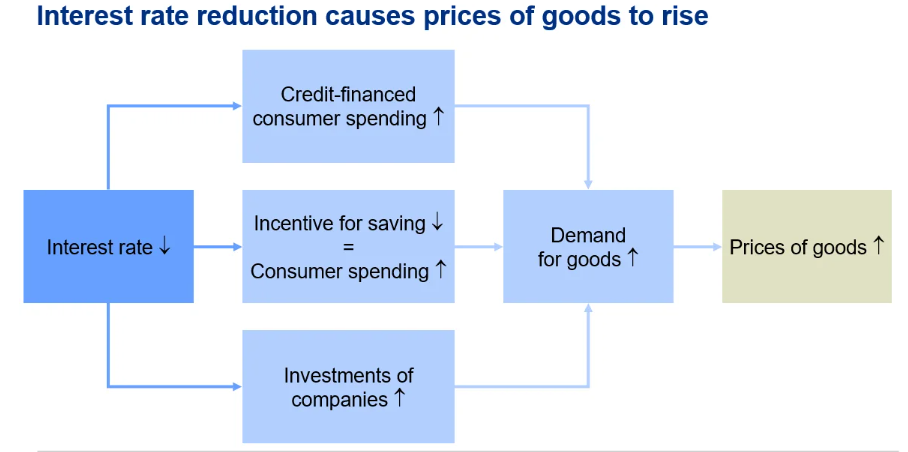
Global Impact of US Monetary Policy
- As the US dollar is the most widely traded and trusted currency, changes in US monetary policy have widespread global implications, especially for emerging economies like India.
- This makes the Fed’s actions important not only domestically but also globally, influencing capital flows and economic decisions elsewhere.
Reasons for the Rate Cut
- The Fed initially slashed rates to near-zero during the COVID-19 pandemic to support the economy.
- As inflation soared due to supply chain disruptions and the Russia-Ukraine war, the Fed raised rates aggressively, reaching 5.5%.
- Now, with inflation moderating and concerns over unemployment growing, the Fed has shifted towards rate cuts to balance inflation control with economic stability.
Impact on India
- India, being a capital-scarce economy, stands to benefit from lower US interest rates as global investors may channel funds into Indian stocks, debt, or FDI.
- A weaker US dollar could also strengthen the Indian rupee, benefiting importers but potentially harming exporters.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), while facing pressure to lower rates, is likely to maintain its distinct policy approach, given the country’s unique inflationary challenges and economic conditions.
| Impact of a Fed Rate Cut on the Common Man |
|
The impact of a Fed Rate Cut will influence mortgages, credit cards and saving rates for millions of people in the US – and even around the world. A Fed rate cut can have a direct impact on the common man in several ways: Lower Mortgage Rates: One of the most immediate effects of a rate cut is a decline in mortgage interest rates. This makes it cheaper for people to buy homes or refinance existing mortgages, which can boost homeownership rates and stimulate the housing market. Reduced Credit Card Interest and Personal Loans Interest: For individuals with credit card debt or personal loans, a rate cut can ease the burden by reducing the interest on these debts. This can help consumers manage their debt more effectively and increase their disposable income. Increased Consumer Spending: When people have more money in their pockets due to lower interest rates, they are more likely to spend. This increased consumer spending can drive economic growth and create jobs. Potential for Job Growth: As businesses invest and expand due to lower borrowing costs, they may need to hire more workers. This can lead to increased employment opportunities and a stronger labour market. Savings: On the flip side, a Fed rate cut can have a negative impact on savings accounts and other interest-bearing accounts like certificates of deposit (CDs). As interest rates fall, the returns on savings also decrease, meaning that people earn less interest on their stored funds. |
|
PYQ: Consider the following statements: (2022) Tight monetary policy of US Federal Reserve could lead to capital flight.Capital flight may increase cost of firms with existing External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)Devaluation of domestic currency decreases the currency risk associated with ECBs Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Analyze the implications of the recent interest rate cut by the US Federal Reserve on the global economy, particularly focusing on emerging economies like India. How might this decision influence foreign investment, currency exchange rates, and India’s monetary policy? (250 words/15 m) |
2. Escalating Tensions in West Asia: Hezbollah Blames Israel for Attacks Amid Fears of Wider Conflict
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 15)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
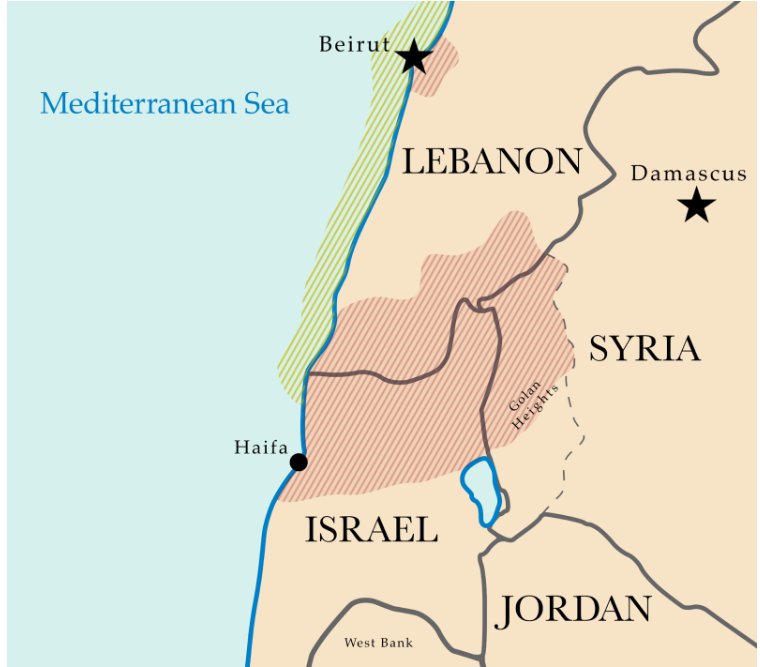
Context of the Ongoing Gaza Conflict
- The current tensions follow the Gaza conflict that began after Hamas attacked Israel on October 7, leading to massive Israeli retaliation.
- Hezbollah has been intermittently engaging Israel along its northern border, displacing both Lebanese and Israelis, further straining the situation.
Signals of Escalation from Israel
- Israel’s actions signal a potential escalation. Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant indicated that military action might be necessary to secure the return of displaced Israelis from Hezbollah-controlled areas. Israel has diverted military resources to the north and has been targeting Hezbollah’s leadership and communication infrastructure.
Hezbollah and Iran’s Possible Response
- Hezbollah is expected to retaliate, but the timing remains uncertain. Iran, Hezbollah’s primary backer, might also respond, potentially involving other allies like Hamas and the Houthis. However, Iran may take a calculated approach, as seen in previous limited strikes.
Impact on India
For India, the situation poses several challenges:
- Energy Security: Two-thirds of India’s crude oil comes from West Asia, making any disruption critical to India’s energy supplies.
- Safety of Indian Nationals: The region hosts 9 million Indians, whose safety could be at risk in case of further escalation.
- Diplomatic Balancing: India has so far maintained a balanced stance between Israel and the Palestinians, but a larger conflict involving Iran and the U.S. could present complex diplomatic challenges.
India’s past calls for de-escalation may need to be reinforced if tensions continue to rise.
Conclusion
- As the conflict evolves, the possibility of a wider war in the region looms, with serious geopolitical implications for West Asia and beyond, including India’s diplomatic, economic, and security interests.
| How escalation can be avoided on the Global Stage? |
|
Diplomatic Engagement: The United States and other international actors must continue to engage in diplomatic efforts aimed at de-escalating tensions. This includes facilitating dialogue between Israel and Hezbollah, as well as addressing the underlying issues related to the Gaza conflict. A ceasefire in Gaza could help reduce hostilities in Lebanon. Regional Agreements: Need to make efforts to establish regional agreements that address territorial disputes and security concerns that can mitigate the risk of conflict. Monitoring and Mediation:
|
| PYQ: ‘India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the recent escalation in tensions between Hezbollah and Israel for regional stability in West Asia, and analyze how this situation may affect India’s diplomatic and security interests. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Protecting Forest Habitats in MP and Rajasthan Key to Long-Term Cheetah Conservation: Project Cheetah Report
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 10)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservation |
| Context: |
| The government’s 2023-24 annual progress report of Project Cheetah emphasizes the need to protect contiguous forested habitats across Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan to establish a long-term metapopulation of 60-70 cheetahs. |
Analysis of News:

What is Project Cheetah?
- Project Cheetah is the reintroduction of Cheetah to India’s forest ecosystem to conserve threatened species and restore ecosystem functions.
- As part of the project, 50 cheetahs will be introduced to various National parks including Kuno national Park, Madhya Pradesh.
- The first batch of eight Cheetahs arrived in 2022 from Namibia and the second batch of 12 cheetahs arrived in 2023 from South Africa.
- Under this project, India plans to assist the Government of Iran, and the international conservation community with conserving the Asiatic cheetah and increasing its distribution range to include protected landscapes in India.
Kuno-Gandhi Sagar Landscape
- The report identifies the Kuno-Gandhi Sagar landscape, located along the MP-Rajasthan border, as crucial for cheetah conservation.
- This area, which includes protected areas and forest divisions, covers a total of over 6,800 sq km, with 3,200 sq km in MP and 2,500 sq km in Rajasthan having high potential for cheetah occupancy.
Metapopulation Management
- A metapopulation refers to a species spread over a large but connected landscape.
- The report envisions that within the next 25 years, the Kuno-Gandhi Sagar region can support 60-70 cheetahs through integrated interstate conservation efforts under Project Cheetah.
Cheetah’s Habitat Requirements
- Cheetahs require expansive areas to thrive due to their natural behavior of exploring large landscapes.
- However, once they settle, they tend to use smaller areas. The conservation plan aims to achieve its goals over the next 10 years, according to experts from the Wildlife Institute of India.
Broader Landscape Inclusion
- Additional districts from MP, Rajasthan, and UP, such as Bhind, Datia, Dholpur, Lalitpur, and Jhansi, may be incorporated into the cheetah landscape depending on their utility for cheetah movement and habitat use.
Challenges with Prey Population
- Leopards in Kuno pose competition to cheetahs by vying for the same prey, leading to a deficit in the chital population, which is a main component of the cheetah’s diet.
- This imbalance presents a challenge for sustaining cheetah numbers.
| Success criteria of this project |
|
The project outlines short-term and long-term success criteria for introducing cheetahs in India. Short term The goals include a 50% survival rate for the first year. Cheetahs establishing home ranges. Successful reproduction in the wild. Generating revenue for local communities through eco-tourism. Long-term Long-term success is measured by cheetahs becoming a stable part of the ecosystem with natural survival rates. Establishing a viable metapopulation. Improving habitat quality and prey diversity. Benefiting local economies through sustainable conservation efforts. |
|
PYQ: Consider the following: (2012) Black-necked craneCheetahFlying squirrelSnow leopard Which of the above are naturally found in India? (a) 1, 2 and 3 only Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the importance of protecting contiguous forested habitats for the successful establishment of a metapopulation of cheetahs under Project Cheetah. What are the key challenges in managing such a landscape, and how can these be addressed for long-term conservation? (250 words/15 m) |
4. The true cost of hospital-acquired infections
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the News:
| Hospital-Acquired Infections (HAIs) |
|
Concerns with HAIs
- Increased Morbidity and Mortality: HAIs contribute significantly to complications, prolonged hospital stays, and increased mortality rates.
- Financial Burden: Patients face substantial medical expenses, including prolonged treatment and rehabilitation, leading to economic strain.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Questions arise regarding hospital accountability for infection prevention and the ethical implications of billing patients for HAIs.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): HAIs often involve drug-resistant organisms, complicating treatment and increasing public health concerns.
Comparison: Developed Countries vs. India
- In developed countries, stringent regulations and accountability measures significantly reduce hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), with mandatory reporting and non-reimbursement policies incentivizing prevention.
- In contrast, India faces diverse healthcare standards and inadequate HAI reporting, leading to higher infection rates and financial burdens on patients, highlighting the need for improved infection control measures.
Way Forward
- Mandatory Disclosure: Require National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) and accredited hospitals to publicly disclose HAI rates, fostering transparency and accountability.
- Benchmarking Standards: Establish Indian benchmarks for HAIs based on local data, aiding hospitals in improving infection control practices.
- Insurance Collaboration: Encourage insurance companies to direct funds towards enhancing hospital infection control rather than solely covering costs of HAIs.
- Patient Education: Raise awareness among patients and families regarding the nature of HAIs, promoting understanding of the complexities involved in hospital care.
- No Charge Policy: Implement policies in accredited hospitals to not charge patients for treatment of HAIs, ensuring equitable healthcare access.
| Practice Question: Define hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) and discuss the major challenges they pose to the healthcare system in India. How can these challenges be addressed to improve patient safety and care quality? (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. AI development cannot be left to market whim, UN warns
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Global Cooperation on AI
- UN experts emphasise that artificial intelligence development should not be driven solely by market forces.
- The call is for tools to enhance global cooperation and governance around AI technology.
Current Governance Deficit
- A report highlights a significant global governance deficit regarding AI, particularly affecting developing countries.
- Of the 193 UN member states, only seven participate in major AI initiatives, while 118 are absent, mostly from the global south.
Proposed Solutions
- Experts advocate for the establishment of a scientific expert group on AI, akin to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
- This group would assess emerging risks and identify research needs to use AI for alleviating issues like hunger and inequality.
Recommendations for UN Structure
- A light-touch coordination structure within the UN secretariat is proposed, though a robust international governance body is not suggested at this time.
- Experts acknowledge that if AI risks escalate, a more comprehensive international institution with monitoring and enforcement powers may become necessary.
Identified Risks
- Key concerns include disinformation, realistic deepfakes, autonomous weapons, and potential misuse by criminal entities.
- Experts warn that the rapid evolution of AI could render responses to threats too late if proactive measures are not taken.
| PYQ: Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does AI help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of Al in healthcare? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the global governance deficit in artificial intelligence as highlighted by UN experts. What measures can be taken to enhance international cooperation and mitigate potential risks associated with AI technology? (250 Words /15 marks) |
6. Shri Piyush Goyal chairs inter-ministerial meeting to address rising freight cost and shipping delays
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2056726 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure – Ports |
| Context |
|
Rising Freight Costs
- Geopolitical Factors: Recent global tensions, such as the Red Sea Crisis, Houthi operations, and ongoing wars, have led to a significant increase in shipping costs. Disruptions in international trade have resulted in price hikes for freight services.
- Increased Operational Costs: Shipping companies have increased their fees due to higher fuel costs, longer turnaround times, and limited availability of containers.
- Impact on Exporters: Exporters are facing increased costs of transporting goods, leading to reduced profit margins and making Indian goods less competitive in the global market.
Shipping Delays
- Port Congestion: Major Indian ports, including Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA), are experiencing congestion due to an increase in cargo volume and limited handling capacity.
- Turnaround Time: Delays in clearing and processing cargo have further led to extended shipping timelines. In some cases, cargo is stuck for weeks, causing delays in international deliveries.
- Simultaneous Container Scanning: To address delays, simultaneous scanning of containers has been introduced at JNPA, aiming to speed up the customs clearance process.
Shortage & Non-Availability of Containers
- Global Supply Chain Disruption: The pandemic, coupled with geopolitical tensions, has disrupted the global supply of shipping containers. India, like other countries, is facing a shortage of empty containers.
- Container Storage Initiatives: To ease this problem, the Container Corporation of India (CONCOR) has allowed storage of empty containers for 90 days free of cost at JNPA, helping to ease supply issues and reduce congestion at ports.
Congestion at Ports
- Increased Cargo Volumes: Indian ports are handling a higher volume of cargo due to increased demand for exports, leading to bottlenecks and congestion.
- Port Capacity Enhancement: The Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways has increased port capacities by 2.3 million Twenty-foot Equivalent Units (TEUs), and steps are being taken to minimise traffic delays around key ports like JNPA.
- Additional Measures: The Shipping Corporation of India is acquiring five new container ships and enhancing cargo handling capacity to address congestion and shortages.
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of rising freight costs, container shortages, and port congestion on India’s export sector. Evaluate the steps taken by the Indian government to address these challenges and their potential effectiveness. (250 Words /15 marks) |
7. FATF lauds India’s efforts to implement measures to tackle illicit finance including money laundering and terror funding
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2056773 )
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security – Role of external state and non-state actors. |
| Context |
|
Observations by FATF:
- AML/CFT Framework: India has implemented a robust Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) framework that is effective and compliant with FATF Recommendations.
- Financial Intelligence Usage: Indian authorities make efficient use of financial intelligence, both domestically and internationally, to combat illicit financial flows.
- Financial Inclusion: Significant strides in financial inclusion, more than doubling bank account holders, promote financial transparency and enhance AML/CFT efforts.
- International Cooperation: India has shown positive results in international cooperation, particularly in asset recovery and applying targeted financial sanctions for proliferation financing.
- Risk Understanding: There is a comprehensive understanding of money laundering, terrorism, and proliferation financing risks by Indian authorities, particularly in the financial sector, but further coordination across stakeholders is needed.
- Complex Financial Investigations: India has demonstrated the ability to conduct intricate financial investigations linked to terrorist financing, though it needs to focus on concluding prosecutions and sanctioning terrorist financiers.
- Outreach to Non-Profit Sector: India needs to strengthen its outreach to non-profit organisations to mitigate the risk of terrorist financing in line with a risk-based approach.
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs): Financial institutions have enhanced measures to monitor PEPs, though coverage of domestic PEPs and supervision of the non-financial sector need improvement.
- Sector-Specific Improvements: India is urged to improve restrictions on cash transactions in the precious metals and stones sector, considering its significance.
| Financial Action Task Force (FATF) |
|
Established: 1989, by G7 countries to combat money laundering, expanded later to include terrorist financing and other illicit financial activities. Headquarters: Paris, France. Objective: To set global standards for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) and monitor compliance. Members: 40 members, including countries and regional organisations like the EU. FATF Recommendations: 40 recommendations that serve as a framework for countries to strengthen financial systems against money laundering and terror financing. Black & Grey Lists: FATF issues blacklists and grey lists for countries with insufficient AML/CFT measures. |
| PYQ: Analyse the complexity and intensity of terrorism, its causes, linkages and obnoxious nexus. Also suggest measures required to be taken to eradicate the menace of terrorism. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the impact of India’s efforts in combating money laundering and terrorist financing as recognized by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). What are the challenges India still faces, and what measures can be adopted to address them? (250 Words /15 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Tamenglong District in Manipur Enforces Ban on Hunting as Amur Falcons Arrive for Migration
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 10)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
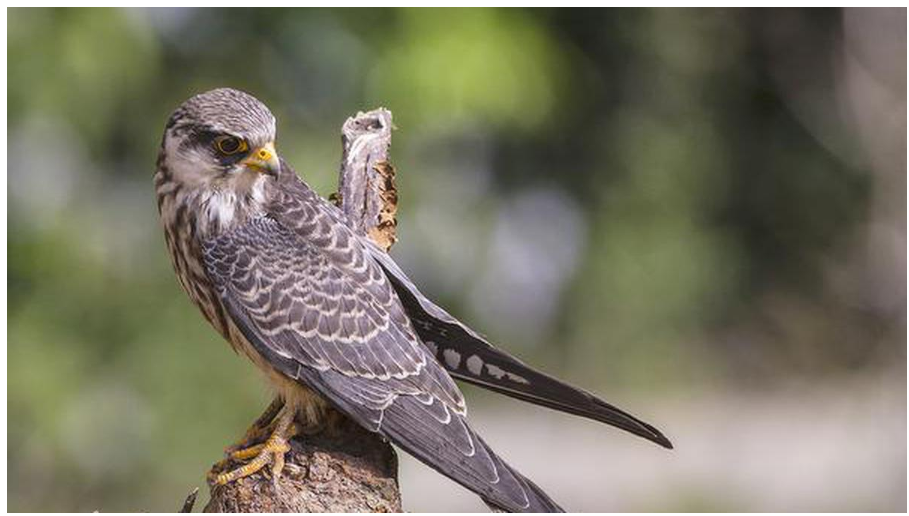

About Amur falcon:
- It is a small raptor of the falcon family.
- Locally known as Akhuipuina, the bird arrives mainly in Manipur and Nagaland.
- They breed in south-eastern Siberia and Northern China and migrate long distances in large flocks to winter in Southern and East Africa.
- The one-way journey via India is about 20,000 km long and the birds do this twice a year.
- Conservation efforts:
- It is protected under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and included under its Schedule IV.
- Hunting of the birds or possessing its meat is punishable with imprisonment up to three years or a fine upto 25,000 or with bonds.
- In 2018, the forest department started a conservation programme by radio-tagging the birds to study their migratory route.
- IUCN: Least Concern.
- Threats: Illegal trapping and killing during migration, habitat loss from agricultural practices and land reclamation.
Ban on Hunting and Poaching
- The district administration has imposed an immediate ban on hunting, catching, killing, and selling Amur falcons, locally known as ‘Kahuaipuina’.
- This measure is in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 (sections 50 and 51), making violations punishable offenses.
Conservation Efforts
- Conservation efforts in Tamenglong have been ongoing since 2016, including the tagging of two falcons with radio transmitters to track their migration routes.
- The district also holds an annual “Amur Falcon Festival” and is planning to tag two more birds to enhance migration studies.
2. Amit Shah Launches ‘White Revolution 2.0’ to Boost Dairy Sector and Empower Women Farmers
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 07)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Focus Areas
The key objectives of White Revolution 2.0 are:
- Empowering women farmers
- Enhancing local milk production
- Strengthening dairy infrastructure
- Boosting dairy exports
Women Empowerment and Malnutrition Fight
- Shah emphasized that the program will enhance women’s self-reliance and empowerment, while also contributing to the fight against malnutrition through increased dairy output.
Budgetary Support Assured
- Addressing concerns over budget allocation, Shah assured full financial support for White Revolution 2.0, stating that it is a high-priority area for the government, particularly the Department of Animal Husbandry.
3. India’s GDP Set to Double to $7 Trillion by FY31, Becoming World’s Third-Largest Economy: S&P Global
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Impressive GDP Growth
- India achieved an 8.2% GDP growth in FY24, surpassing the government’s initial estimate of 7.3%. S&P forecasts a moderated real GDP growth of 6.8% for the current fiscal year (FY25), driven by structural reforms and enhanced private sector investment.
Key Economic Drivers
- Continued reforms in business transactions and logistics will reduce dependence on public capital expenditure, bolstering private sector investments.
- India’s equity markets are expected to remain dynamic, attracting foreign inflows into government bonds due to India’s inclusion in major emerging market indices.
Inflation and Climate Risks
- S&P warns that high food price inflation, exacerbated by climate change, could tighten monetary policy, making investments costlier.
- The report stresses the importance of climate adaptation and mitigation policies, particularly in agriculture, to maintain stable economic growth.
GST Collection and Infrastructure Needs
- FY25 saw strong GST collections, with April hitting an all-time high of Rs 2.1 trillion.
- To sustain trade growth, India must enhance its port infrastructure, as 90% of the country’s trade is seaborne.
- Strong manufacturing activity, as indicated by the HSBC India Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), is a key driver of GST collections.
4. India abstains from voting on UNGA resolution against Israel’s ‘occupation’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
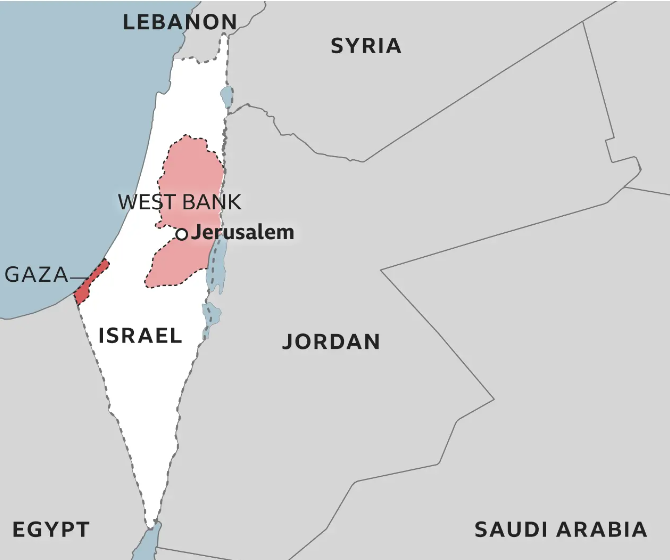
Analysis of the news:
- This decision emphasises the necessity of dialogue and diplomacy in addressing the complexities of the Israel-Palestine conflict.
- The resolution was passed by 124 of 181 countries, while India was among 43 nations that abstained.
- India’s Permanent Representative to the UN, P. Harish, emphasised the need to “build bridges” between Israel and Palestine rather than further divide them.
- India reiterated support for a two-state solution, condemned both the Hamas attacks and Israel’s retaliatory bombardment, and called for an immediate ceasefire.
- Differences in resolution wording and its call for sanctions and arms export bans were cited as reasons for India’s abstention.
| ‘Arms To Kyiv’ Report |
|
5. Harappan civilisation: enigma remains even after 100 years of exploration
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Context |
|
Indus Valley Civilisation:
- On September 20, 1924, The Illustrated London News published an article by John Marshall, Director-General of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), announcing the discovery of the Indus Valley Civilisation.
- This Bronze Age civilisation, later called the Harappan Civilisation, was named after Harappa, one of the first sites excavated, now located in Pakistan.
- The Harappan civilisation has fascinated scholars in various fields for the past century, with its advanced town planning, water management, bronze and copper artefacts creation, and intricate seal carvings.
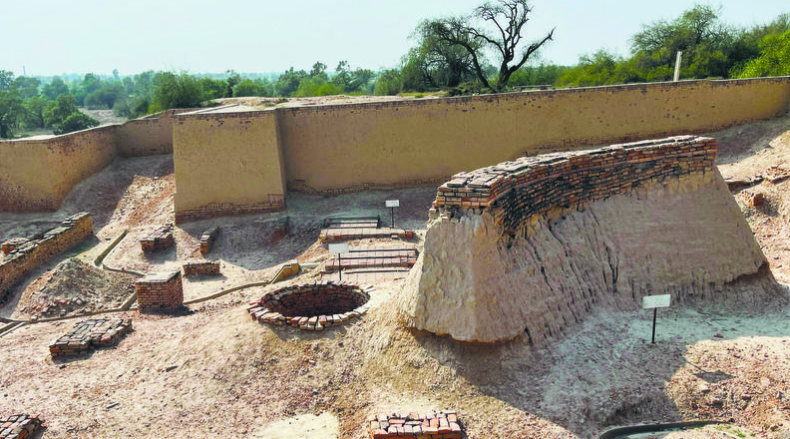

- Daya Ram Sahni and Rakhal Das Banerji, two ASI archaeologists, were instrumental in the discovery, excavating Harappa (1921-22) and Mohenjo-daro (1922), respectively.
- Marshall noticed the similarity of artefacts found at Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, located 640 km apart, leading him to conclude that they were part of the same civilization.
- The Harappan civilisation is divided into three phases:early (3200-2600 BC), mature (2600-1900 BC), and late (1900-1500 BC).
- Major sites include Mohenjo-daro, Harappa, Ganweriwala, Rakhigarhi, and Dholavira, spanning across Pakistan and India.
- The civilisation thrived on the banks of the Indus and Saraswati rivers, with over 1,500 sites in India and around 500 in Pakistan.
- Indus scholar Asko Parpola highlighted key features such as the Indus script, burnt brick construction, and carnelian bead production.
- The discovery pushed back the timeline of settled life in South Asia by over 3,000 years, filling a gap in historical understanding.
6. How Kerala reduced mortality from amoebic meningoencephalitis
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
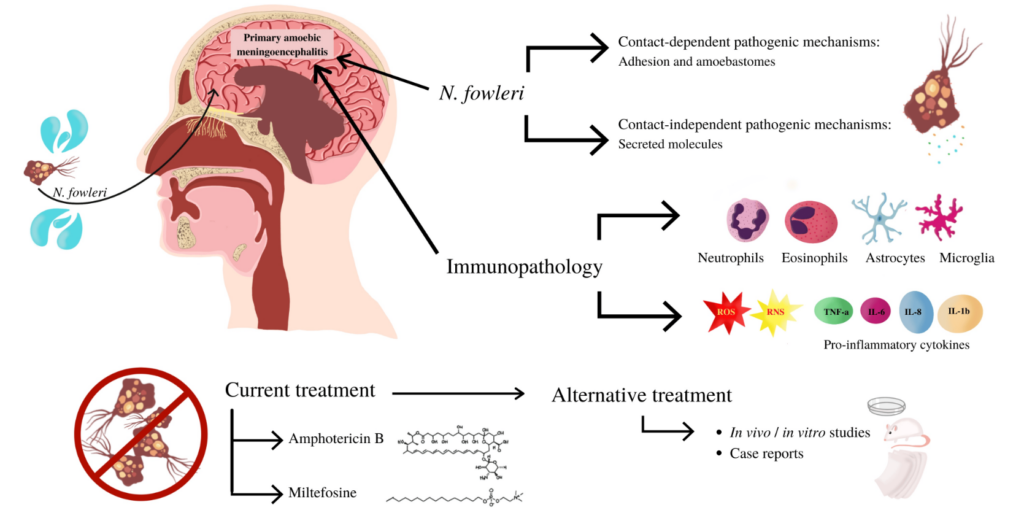
Analysis of the news:
- Kerala faced an unusually high number of amoebic meningoencephalitis cases, reporting 19 cases in five months.
- Despite the infection’s 97% global fatality rate, Kerala saved 14 out of 19 patients, reducing the mortality rate to 26%.
- Early identification and intervention played a crucial role in saving lives.
- The State adopted the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention treatment protocol for effective management.
- A cocktail of antibiotics, including Miltefosine, was used as part of the treatment.
- Proactive case-finding involved testing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples for amoebic infections in all encephalitis cases.
- The high degree of clinical suspicion and early diagnosis helped clinicians act quickly and save patients.
| Amoebic Meningoencephalitis |
|
7. India’s First Fashion Forecasting Initiative ‘VisioNxt’
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2056619 )
| Context |
|
VisioNxt – Key Information:
- Initiative: Fashion forecasting project developed by the National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) and supported by the Ministry of Textiles.
- Objective: To enhance India’s global fashion presence by providing AI and Emotional Intelligence-based trend insights, reducing reliance on international forecasting agencies.
- Features:
- Cultural Insight: Focuses on India’s diverse cultural, linguistic, and socio-economic landscape.
- Technology: Uses the “DeepVision” model for AI-driven trend forecasting.
- Data Collection: Gathers data through over 800 trained spotters across 16 cities.
- Benefits: Supports weavers, manufacturers, retailers, and designers by offering localised trend insights and fostering industry growth.
- Operational Hubs: Chennai (Insights Lab) and Delhi (Creative Lab).
- Trend Book: “Paridhi” provides an in-depth view of Indian fashion trends, integrating cultural and regional insights.



